Wheel Base on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
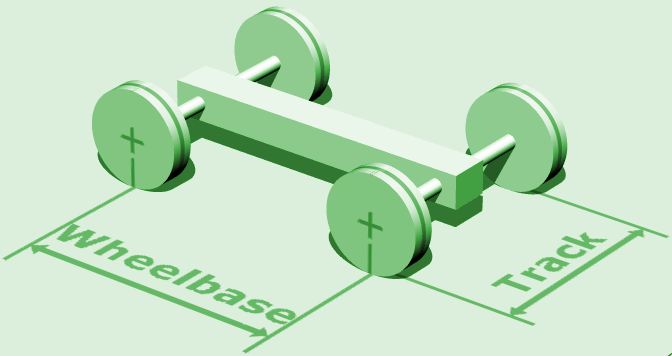
 In both road and rail
In both road and rail

vehicle
A vehicle (from la, vehiculum) is a machine that transports people or cargo. Vehicles include wagons, bicycles, motor vehicles ( motorcycles, cars, trucks, buses, mobility scooters for disabled people), railed vehicles ( trains, trams ...
s, the wheelbase is the horizontal distance between the centers of the front and rear wheels. For road vehicles with more than two axles (e.g. some trucks), the wheelbase is the distance between the steering (front) axle and the centerpoint of the driving axle group. In the case of a tri-axle truck, the wheelbase would be the distance between the steering axle and a point midway between the two rear axles.
Vehicles
The wheelbase of avehicle
A vehicle (from la, vehiculum) is a machine that transports people or cargo. Vehicles include wagons, bicycles, motor vehicles ( motorcycles, cars, trucks, buses, mobility scooters for disabled people), railed vehicles ( trains, trams ...
equals the distance between its front and rear wheels. At equilibrium, the total torque
In physics and mechanics, torque is the rotational equivalent of linear force. It is also referred to as the moment of force (also abbreviated to moment). It represents the capability of a force to produce change in the rotational motion of t ...
of the forces acting on a vehicle is zero. Therefore, the wheelbase is related to the force
In physics, a force is an influence that can change the motion of an object. A force can cause an object with mass to change its velocity (e.g. moving from a state of rest), i.e., to accelerate. Force can also be described intuitively as a ...
on each pair of tires by the following formula:
:
:
where is the force on the front tires, is the force on the rear tires, is the wheelbase, is the distance from the center of mass (CM) to the rear wheels, is the distance from the center of mass to the front wheels ( + = ), is the mass
Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a physical body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different element ...
of the vehicle, and is the gravity constant. So, for example, when a truck is loaded, its center of gravity shifts rearward and the force on the rear tires increases. The vehicle will then ride lower. The amount the vehicle sinks will depend on counter acting forces, like the size of the tires, tire pressure, and the spring rate
A spring is an elastic object that stores mechanical energy. In everyday use the term often refers to coil springs, but there are many different spring designs. Modern springs are typically manufactured from spring steel, although some n ...
of the suspension
Suspension or suspended may refer to:
Science and engineering
* Suspension (topology), in mathematics
* Suspension (dynamical systems), in mathematics
* Suspension of a ring, in mathematics
* Suspension (chemistry), small solid particles suspen ...
.
If the vehicle is accelerating or decelerating, extra torque is placed on the rear or front tire
A tire (American English) or tyre (British English) is a ring-shaped component that surrounds a wheel's rim to transfer a vehicle's load from the axle through the wheel to the ground and to provide traction on the surface over which t ...
respectively. The equation relating the wheelbase, height above the ground of the CM, and the force on each pair of tires becomes:
:
:
where is the force on the front tires, is the force on the rear tires, is the distance from the CM to the rear wheels, is the distance from the CM to the front wheels, is the wheelbase, is the mass of the vehicle, is the acceleration of gravity (approx. 9.8 m/s2), is the height of the CM above the ground, is the acceleration (or deceleration if the value is negative). So, as is common experience, when the vehicle accelerates, the rear usually sinks and the front rises depending on the suspension. Likewise, when braking the front noses down and the rear rises.:
Because of the effect the wheelbase has on the weight distribution of the vehicle, wheelbase dimensions are crucial to the balance and steering. For example, a car
A car or automobile is a motor vehicle with wheels. Most definitions of ''cars'' say that they run primarily on roads, seat one to eight people, have four wheels, and mainly transport people instead of goods.
The year 1886 is regarded as t ...
with a much greater weight load on the rear tends to understeer
Understeer and oversteer are vehicle dynamics terms used to describe the sensitivity of a vehicle to steering. Oversteer is what occurs when a car turns (steers) by more than the amount commanded by the driver. Conversely, understeer is what occ ...
due to the lack of the load (force) on the front tires and therefore the grip (friction
Friction is the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and material elements sliding (motion), sliding against each other. There are several types of friction:
*Dry friction is a force that opposes the relative la ...
) from them. This is why it is crucial, when towing a single-axle caravan, to distribute the caravan's weight so that down-thrust on the tow-hook is about 100 pounds force (400 N). Likewise, a car may oversteer
Understeer and oversteer are vehicle dynamics terms used to describe the sensitivity of a vehicle to steering. Oversteer is what occurs when a car turns (steers) by more than the amount commanded by the driver. Conversely, understeer is what occu ...
or even "spin out" if there is too much force on the front tires and not enough on the rear tires. Also, when turning there is lateral torque placed upon the tires which imparts a turning force that depends upon the length of the tire distances from the CM. Thus, in a car with a short wheelbase ("SWB"), the short lever arm from the CM to the rear wheel will result in a greater lateral force
In physics, a force is an influence that can change the motion of an object. A force can cause an object with mass to change its velocity (e.g. moving from a state of rest), i.e., to accelerate. Force can also be described intuitively as a ...
on the rear tire which means greater acceleration and less time for the driver to adjust and prevent a spin out or worse.
Wheelbases provide the basis for one of the most common vehicle size class
Vehicle size classes are series of ratings assigned to different segments of automotive vehicles for the purposes of vehicle emissions control and fuel economy calculation. Various methods are used to classify vehicles; in North America, pass ...
systems.
Varying wheelbases within nameplate
Someluxury vehicle
A luxury car is a car that provides increased levels of comfort, equipment, amenities, quality, performance, and associated status compared to moderately priced cars.
The term is subjective and reflects both the qualities of the car and th ...
s are offered with long-wheelbase variants to increase the spaciousness and therefore the luxury of the vehicle. This practice can often be found on full-size car
Full-size car—also known as large car—is a vehicle size class which originated in the United States and is used for cars larger than mid-size cars, it is the largest size class for cars. In Europe, it is known as E-segment or F-segment. ...
s like the Mercedes-Benz S-Class
The Mercedes-Benz S-Class, formerly known as ''Sonderklasse'' (German for "special class", abbreviated as "S-Klasse"), is a series of full-sized luxury sedans, limousines and armored sedans produced by the German automaker Mercedes-Benz, a di ...
, but ultra-luxury vehicles such as the Rolls-Royce Phantom and even large family cars like the Rover 75
The Rover 75 is an executive car manufactured initially by the Rover Group and later by MG Rover, under the Rover marque and available over a single generation with front-wheel drive in either saloon/sedan or station wagon/estate configur ...
came with 'limousine' versions. Prime Minister of the United Kingdom Tony Blair
Sir Anthony Charles Lynton Blair (born 6 May 1953) is a British former politician who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1997 to 2007 and Leader of the Labour Party from 1994 to 2007. He previously served as Leader of the ...
was given a long-wheelbase version of the Rover 75 for official use.
and even some SUVs like the VW Tiguan
The Volkswagen Tiguan () is a car produced by German manufacturer Volkswagen since 2007, sitting between the smaller T-Roc and the larger Touareg in the company's crossover SUV range. The first generation is based on the PQ46 platform, whil ...
and Jeep Wrangler
The Jeep Wrangler is a series of compact and mid-size four-wheel drive off-road SUVs manufactured by Jeep since 1986 and is currently in its fourth generation. The Wrangler JL, the most recent generation, was revealed in late 2017 and is produ ...
come in LWB models
In contrast, coupé
A coupe or coupé (, ) is a passenger car with a sloping or truncated rear roofline and two doors.
The term ''coupé'' was first applied to horse-drawn carriages for two passengers without rear-facing seats. It comes from the French past parti ...
varieties of some vehicles such as the Honda Accord
The , also known as the in Japan and China for certain generations, is a series of cars manufactured by Honda since 1976, best known for its four-door sedan variant, which has been one of the best-selling cars in the United States since 1989. ...
are usually built on shorter wheelbases than the sedans they are derived from.
Bikes
Thewheelbase
In both road and rail vehicles, the wheelbase is the horizontal distance between the centers of the front and rear wheels. For road vehicles with more than two axles (e.g. some trucks), the wheelbase is the distance between the steering (front ...
on many commercially available bicycles and motorcycle
A motorcycle (motorbike, bike, or trike (if three-wheeled)) is a two or three-wheeled motor vehicle steered by a handlebar. Motorcycle design varies greatly to suit a range of different purposes: long-distance travel, commuting, cruisin ...
s is so short, relative to the height of their centers of mass
In physics, the center of mass of a distribution of mass in space (sometimes referred to as the balance point) is the unique point where the weighted relative position of the distributed mass sums to zero. This is the point to which a force may ...
, that they are able to perform stoppies and wheelie
In vehicle acrobatics, a wheelie, or wheelstand, is a vehicle maneuver in which the front wheel or wheels come off the ground due to sufficient torque being applied to the rear wheel or wheels, or rider motion relative to the vehicle. Whee ...
s.
Skateboards
In skateboarding the word 'wheelbase' is used for the distance between the two inner pairs of mounting holes on the deck. This is different from the distance between the rotational centers of the two wheel pairs. A reason for this alternative use is that decks are sold with prefabricated holes, but usually without trucks and wheels. It is therefore easier to use the prefabricated holes for measuring and describing this characteristic of the deck. A common misconception is that the choice of wheelbase is influenced by the height of the skateboarder. However, the length of the deck would then be a better candidate, because the wheelbase affects characteristics useful in different speeds or terrains regardless of the height of the skateboarder. For example, a deck with a long wheelbase, say , will respond slowly to turns, which is often desirable in high speeds. A deck with a short wheelbase, say , will respond quickly to turns, which is often desirable when skating backyard pools or other terrains requiring quick or intense turns.Rail
In rail vehicles, the wheelbase follows a similar concept. However, since the wheels may be of different sizes (for example, on asteam locomotive
A steam locomotive is a locomotive that provides the force to move itself and other vehicles by means of the expansion of steam. It is fuelled by burning combustible material (usually coal, oil or, rarely, wood) to heat water in the loco ...
), the measurement is taken between the points where the wheels contact the rail, and not between the centers of the wheels.
On vehicles where the wheelsets (axles) are mounted inside the vehicle frame (mostly in steam locomotives), the wheelbase is the distance between the front-most and rear-most wheelsets.
On vehicles where the wheelsets are mounted on bogies (American: trucks), three wheelbase measurements can be distinguished:
* the distance between the pivot points of the front-most and rear-most bogie;
* the distance between the front-most and rear-most wheelsets of the vehicle;
* the distance between the front-most and rear-most wheelsets of each bogie.
The wheelbase affects the rail vehicle's capability to negotiate curves. Short-wheelbased vehicles can negotiate sharper curves. On some larger wheelbase locomotives, inner wheels may lack flange
A flange is a protruded ridge, lip or rim (wheel), rim, either external or internal, that serves to increase shear strength, strength (as the flange of an iron beam (structure), beam such as an I-beam or a T-beam); for easy attachment/transfer of ...
s in order to pass curves.
The wheelbase also affects the load the vehicle poses to the track, track infrastructure and bridges. All other conditions being equal, a shorter wheelbase vehicle represents a more concentrated load to the track than a longer wheelbase vehicle. As railway lines are designed to take a pre-determined maximum load per unit of length (tonnes per meter, or pounds per foot), the rail vehicles' wheelbase is designed according to their intended gross weight. The higher the gross weight, the longer the wheelbase must be.
See also
*Axle track
In automobiles (and other wheeled vehicles which have two wheels on an axle), the axle track is the distance between the hub flanges on an axle. Wheel track, track width or simply track refers to the distance between the centerline of two wheels ...
*Bicycle and motorcycle geometry
Bicycle and motorcycle geometry is the collection of key measurements (lengths and angles) that define a particular bike configuration. Primary among these are wheelbase, steering axis angle, fork offset, and trail. These parameters have a majo ...
*Force
In physics, a force is an influence that can change the motion of an object. A force can cause an object with mass to change its velocity (e.g. moving from a state of rest), i.e., to accelerate. Force can also be described intuitively as a ...
* Overhang (vehicles)
* Static equilibrium
*Weight
In science and engineering, the weight of an object is the force acting on the object due to gravity.
Some standard textbooks define weight as a vector quantity, the gravitational force acting on the object. Others define weight as a scalar q ...
* Wheel gauge
* Wheelset
References
{{Powertrain Vehicle technology Automotive engineering Physical quantities Vehicle dynamics