Web annotation on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Web annotation can refer to online
 The body can be a literal value or structured content (a URI). The target can be identified by an URI (e.g., fragment identifiers) and/or a selector that defines a domain-, resource- or application-specific access protocol, e.g., offset-based, XPath-based, etc.
Web Annotation was standardized on February 23, 2017 with the release of three official Recommendations by the W3C Web Annotation Working Group:
* Web Annotation Data Model
* Web Annotation Vocabulary
* Web Annotation Protocol
These recommendations were accompanied by additional working group notes that describe their application:
* Embedding Web Annotations in HTML
* Selectors and States
The Web Annotation data model is also provided in machine-readable form as the Web Annotation ontology.
Note that this ontology defines the Web Annotation namespace (
The body can be a literal value or structured content (a URI). The target can be identified by an URI (e.g., fragment identifiers) and/or a selector that defines a domain-, resource- or application-specific access protocol, e.g., offset-based, XPath-based, etc.
Web Annotation was standardized on February 23, 2017 with the release of three official Recommendations by the W3C Web Annotation Working Group:
* Web Annotation Data Model
* Web Annotation Vocabulary
* Web Annotation Protocol
These recommendations were accompanied by additional working group notes that describe their application:
* Embedding Web Annotations in HTML
* Selectors and States
The Web Annotation data model is also provided in machine-readable form as the Web Annotation ontology.
Note that this ontology defines the Web Annotation namespace (
"An Architecture for Open Cross-Media Annotation Services"
Proceedings of WISE 2009, 10th International Conference on Web Information Systems Engineering, Poznan, Poland, October 2009
On Web Annotations: Promises and Pitfalls of Current Web Infrastructure. Venu Vasudevan and Mark Palmer, Proceedings of the 32nd Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences - 1999
* ttp://www9.org/final-posters/poster46.html New ways of using Web annotations. Laurent Denoue, Laurence Vignollet.* Ricardo Kawase, George Papadakis, Eelco Herder, Wolfgang Nejdl
The impact of bookmarks and annotations on refinding information. ACM Hypertext Conference 2010: 29-34
* Ricardo Kawase, Eelco Herder, George Papadakis, Wolfgang Nejdl
In-Context Annotations for Refinding and Sharing
'' Webist'' (Selected Papers) 2010: 85-100
W3C Web Annotation Working Group
Recommendations (as of February 23, 2017):
Web Annotation Data Model
Web Annotation Vocabulary
Web Annotation Protocol
Web Annotation Architecture
W3C's interactive illustration
annotation
An annotation is extra information associated with a particular point in a document or other piece of information. It can be a note that includes a comment or explanation. Annotations are sometimes presented Marginalia, in the margin of book page ...
s of web resources such as web page
A web page (or webpage) is a World Wide Web, Web document that is accessed in a web browser. A website typically consists of many web pages hyperlink, linked together under a common domain name. The term "web page" is therefore a metaphor of pap ...
s or parts of them, or a set of W3C
The World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) is the main international standards organization for the World Wide Web. Founded in 1994 by Tim Berners-Lee, the consortium is made up of member organizations that maintain full-time staff working together in ...
standards developed for this purpose. The term can also refer to the creations of annotations on the World Wide Web
The World Wide Web (WWW or simply the Web) is an information system that enables Content (media), content sharing over the Internet through user-friendly ways meant to appeal to users beyond Information technology, IT specialists and hobbyis ...
and it has been used in this sense for the annotation tool INCEpTION, formerly WebAnno. This is a general feature of several tools for annotation in natural language processing or in the philologies.
Annotation of web resources
With a web annotation system, a user can add, modify or remove information from a Web resource without modifying the resource itself. The annotations can be thought of as a layer on top of the existing resource, and this annotation layer is usually visible to other users who share the same annotation system. In such cases, the web annotation tool is a type ofsocial software
Social software, also known as social apps or social platform includes communications and interactive tools that are often based on the Internet. Communication tools typically handle capturing, storing and presenting communication, usually writt ...
tool. For Web-based text annotation systems, see Text annotation
Text annotation is the practice and the result of adding a note or gloss to a text, which may include highlights or underlining, comments, footnotes, tags, and links. Text annotations can include notes written for a reader's private purposes, as ...
.
Web annotation can be used for the following purposes:
* to rate a Web resource, such as by its usefulness, user-friendliness, suitability for viewing by minors.
* to improve or adapt its contents by adding/removing material (like wiki
A wiki ( ) is a form of hypertext publication on the internet which is collaboratively edited and managed by its audience directly through a web browser. A typical wiki contains multiple pages that can either be edited by the public or l ...
).
* as a collaborative
Collaboration (from Latin ''com-'' "with" + ''laborare'' "to labor", "to work") is the process of two or more people, entities or organizations working together to complete a task or achieve a goal. Collaboration is similar to cooperation. The f ...
tool, e.g. to discuss the contents of a certain resource.
* as a medium of artistic or social criticism, by allowing Web users to reinterpret, enrich or protest against institution or ideas that appear on the Web.
* to quantify transient relationships between information fragments.
*to save, retain and synthesize selected information.
Annotations can be considered an additional layer with respect to comments. Comments are published by the same publisher who hosts the original document. Annotations are added on top of that, but may eventually become comments which, in turn, may be integrated in a further version of the document itself.
Web Annotation standard
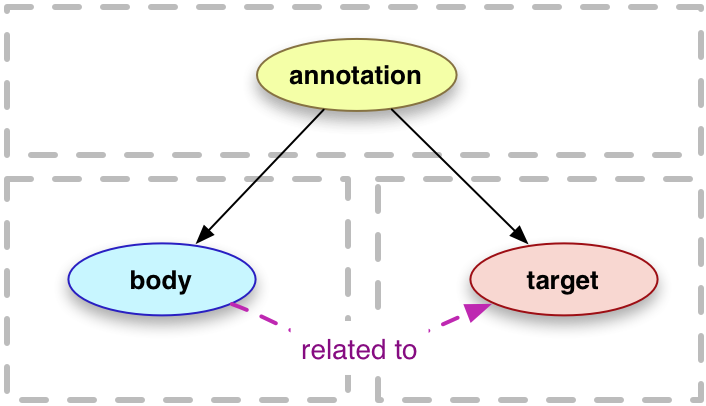
In the Web Annotation standard, The basic data structures of Web Annotation (Fig. 1) are * target (the element being annotated, e.g., a web document or a part of it), * body (the content of the annotation, e.g., a string value), and * annotation (the element that serves to relate body and target of an annotation) The body can be a literal value or structured content (a URI). The target can be identified by an URI (e.g., fragment identifiers) and/or a selector that defines a domain-, resource- or application-specific access protocol, e.g., offset-based, XPath-based, etc.
Web Annotation was standardized on February 23, 2017 with the release of three official Recommendations by the W3C Web Annotation Working Group:
* Web Annotation Data Model
* Web Annotation Vocabulary
* Web Annotation Protocol
These recommendations were accompanied by additional working group notes that describe their application:
* Embedding Web Annotations in HTML
* Selectors and States
The Web Annotation data model is also provided in machine-readable form as the Web Annotation ontology.
Note that this ontology defines the Web Annotation namespace (
The body can be a literal value or structured content (a URI). The target can be identified by an URI (e.g., fragment identifiers) and/or a selector that defines a domain-, resource- or application-specific access protocol, e.g., offset-based, XPath-based, etc.
Web Annotation was standardized on February 23, 2017 with the release of three official Recommendations by the W3C Web Annotation Working Group:
* Web Annotation Data Model
* Web Annotation Vocabulary
* Web Annotation Protocol
These recommendations were accompanied by additional working group notes that describe their application:
* Embedding Web Annotations in HTML
* Selectors and States
The Web Annotation data model is also provided in machine-readable form as the Web Annotation ontology.
Note that this ontology defines the Web Annotation namespace (https://www.w3.org/ns/oa#), and that this namespace is conventionally abbreviated as oa. This is the abbreviation for ''Open Annotation'', a W3C Community Group whose specifications formed the basis for the Web Annotation standard.
Web Annotation supersedes other standardization initiatives for annotations on the web within the W3C, e.g., the earlier Annotea project discontinued after 2003.
Related specifications
Web Annotation can be used in conjunction with (or as an alternative to) fragment identifiers that describe how to address elements within a web document by means of URIs. These include * RFC 5147 (URI fragment identifiers for the text/plain media type) * RFC 7111 (URI fragment identifiers for the text/csv media type) * RFC 8118 (URI fragment identifiers for the application/pdf media type) * SVG fragment identifiers * XPointer (for addressing components of XML documents) * Media Fragments (for addressing components of media files) Other, non-standardized fragment identifiers are in use, as well, e.g., within the NLP Interchange Format. Independently from Web Annotation, more specialized data models for representing annotations on the web have been developed, e.g., the NLP Interchange Format (NIF) for applications in language technology. In early 2020, theW3C
The World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) is the main international standards organization for the World Wide Web. Founded in 1994 by Tim Berners-Lee, the consortium is made up of member organizations that maintain full-time staff working together in ...
Community Group "Linked Data for Language Technology" launched an initiative to harmonize these vocabularies and to develop a consolidated RDF vocabulary for linguistic annotations on the web.
Web Annotation Systems
Comparison of web annotation systems
Many of these systems require software to be installed to enable some or all of the features below. This fact is only noted in footnotes if the software that is required is additional software provided by a third party.Discontinued web annotation systems
See also
* Comparison of notetaking software *Social bookmarking
Social bookmarking is an online service which allows users to add, annotate, edit, and share Internet bookmark, bookmarks of web documents. Many online bookmark management services have launched since 1996; Delicious (website), Delicious, founded i ...
* Some reference management software packages also support web annotations
* Backlinks
* Online deliberation
* Perusall
* Folksonomy
Folksonomy is a classification system in which end users apply public tags to online items, typically to make those items easier for themselves or others to find later. Over time, this can give rise to a classification system based on those tag ...
* Metadata
Metadata (or metainformation) is "data that provides information about other data", but not the content of the data itself, such as the text of a message or the image itself. There are many distinct types of metadata, including:
* Descriptive ...
* Threaded discussion
* Virtual graffiti
* Comparison of software saving Web pages for offline use
References
Further reading
* {{cite conference , doi=10.1145/1816123.1816125 , chapter=Making Web Annotations Persistent over Time , last1=Sanderson , first1=Robert , last2=Van de Sompel , first2=Herbert , title=Proceedings of the 10th annual joint conference on Digital libraries - JCDL '10 , author-link2=Herbert Van de Sompel , year=2010 , publisher=Association for Computing Machinery
The Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) is a US-based international learned society for computing. It was founded in 1947 and is the world's largest scientific and educational computing society. The ACM is a non-profit professional membe ...
, book-title=Proceedings of JCDL '10, Joint Conference on Digital Libraries , pages=1–10 , arxiv=1003.2643 , isbn=9781450300858
* Signer, Beat"An Architecture for Open Cross-Media Annotation Services"
Proceedings of WISE 2009, 10th International Conference on Web Information Systems Engineering, Poznan, Poland, October 2009
On Web Annotations: Promises and Pitfalls of Current Web Infrastructure. Venu Vasudevan and Mark Palmer, Proceedings of the 32nd Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences - 1999
* ttp://www9.org/final-posters/poster46.html New ways of using Web annotations. Laurent Denoue, Laurence Vignollet.* Ricardo Kawase, George Papadakis, Eelco Herder, Wolfgang Nejdl
The impact of bookmarks and annotations on refinding information. ACM Hypertext Conference 2010: 29-34
* Ricardo Kawase, Eelco Herder, George Papadakis, Wolfgang Nejdl
In-Context Annotations for Refinding and Sharing
'' Webist'' (Selected Papers) 2010: 85-100
External links
W3C Web Annotation Working Group
Recommendations (as of February 23, 2017):
Web Annotation Data Model
Web Annotation Vocabulary
Web Annotation Protocol
Web Annotation Architecture
W3C's interactive illustration
Web annotation
Web annotation can refer to online annotations of web resources such as web pages or parts of them, or a set of World Wide Web Consortium, W3C W3C recommendation, standards developed for this purpose. The term can also refer to the creations of an ...
Web software