Water Resources on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Water resources are natural resources of
 Surface water is water in a river,
Surface water is water in a river,
Image:Sinclair Wetlands.jpg, ''Panorama of a natural wetland ( Sinclair Wetlands, New Zealand)''

 The total quantity of water available at any given time is an important consideration. Some human water users have an intermittent need for water. For example, many farms require large quantities of water in the spring, and no water at all in the winter. Other users have a continuous need for water, such as a power plant that requires water for cooling. Over the long term the average rate of precipitation within a watershed is the upper bound for average consumption of natural surface water from that watershed.
The total quantity of water available at any given time is an important consideration. Some human water users have an intermittent need for water. For example, many farms require large quantities of water in the spring, and no water at all in the winter. Other users have a continuous need for water, such as a power plant that requires water for cooling. Over the long term the average rate of precipitation within a watershed is the upper bound for average consumption of natural surface water from that watershed.
 It is estimated that 8% of worldwide water use is for domestic purposes. These include drinking water, bathing,
It is estimated that 8% of worldwide water use is for domestic purposes. These include drinking water, bathing,

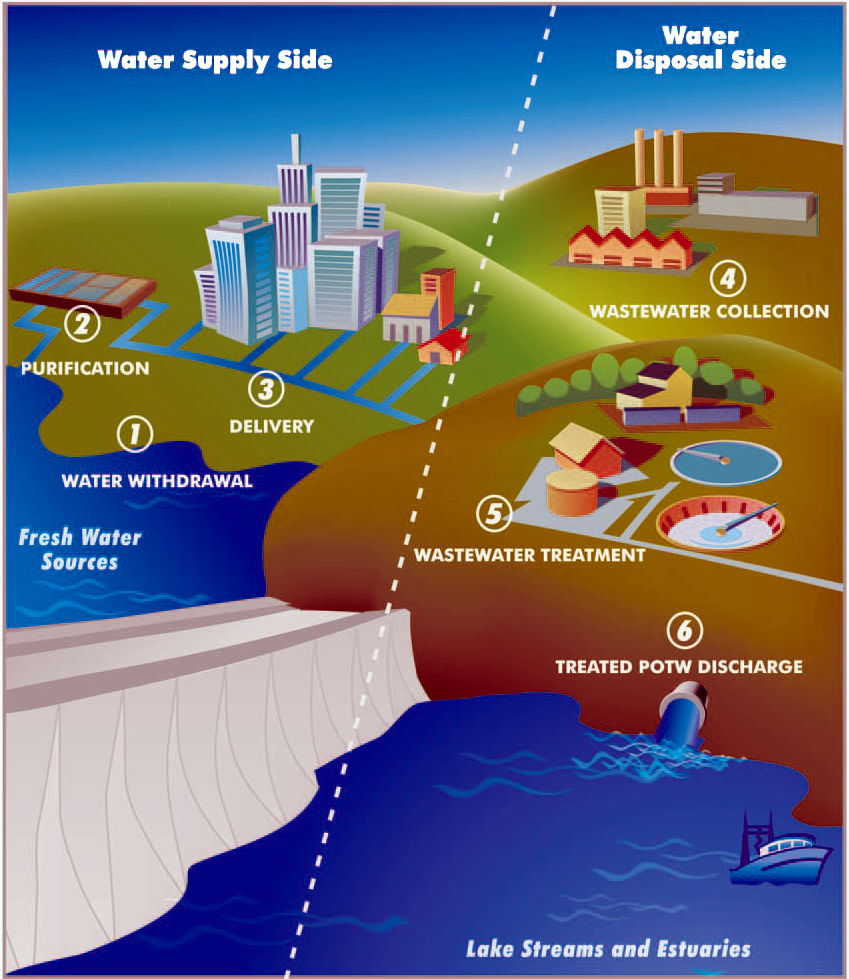
 Water resource management is the activity of planning, developing, distributing and managing the optimum use of water resources. It is an aspect of water cycle management. The field of water resources management will have to continue to adapt to the current and future issues facing the allocation of water. With the growing uncertainties of global
Water resource management is the activity of planning, developing, distributing and managing the optimum use of water resources. It is an aspect of water cycle management. The field of water resources management will have to continue to adapt to the current and future issues facing the allocation of water. With the growing uncertainties of global
"Measuring progress towards the Sustainable Development Goals." (SDG 6)
''SDG-Tracker.org, website''United Nations (2017) Resolution adopted by the General Assembly on 6 July 2017, Work of the Statistical Commission pertaining to the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development
A/RES/71/313
Renewable water resources in the world by country
Portal to international hydrology and water resources
Sustainable Sanitation and Water Management Toolbox
{{DEFAULTSORT:Water Resources Aquatic ecology Hydrology Irrigation Natural resources Water and the environment Water management
water
Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance. It is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known liv ...
that are potentially useful for humans, for example as a source of drinking water supply or irrigation water. These resources can be either freshwater from natural sources, or water produced artificially from other sources, such as from reclaimed water ( wastewater) or desalinated water ( seawater). 97% of the water on Earth is salt water and only three percent is fresh water
Fresh water or freshwater is any naturally occurring liquid or frozen water containing low concentrations of dissolved salt (chemistry), salts and other total dissolved solids. The term excludes seawater and brackish water, but it does include ...
; slightly over two-thirds of this is frozen in glacier
A glacier (; or ) is a persistent body of dense ice, a form of rock, that is constantly moving downhill under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires ...
s and polar ice caps. The remaining unfrozen freshwater is found mainly as groundwater, with only a small fraction present above ground or in the air. Natural sources of fresh water
Fresh water or freshwater is any naturally occurring liquid or frozen water containing low concentrations of dissolved salt (chemistry), salts and other total dissolved solids. The term excludes seawater and brackish water, but it does include ...
include surface water, under river flow, groundwater
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and Pore space in soil, soil pore spaces and in the fractures of stratum, rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available fresh water in the world is groundwater. A unit ...
and frozen water. People use water resources for agricultural, industrial and household activities.
Water resources are under threat from multiple issues. There is water scarcity, water pollution
Water pollution (or aquatic pollution) is the contamination of Body of water, water bodies, with a negative impact on their uses. It is usually a result of human activities. Water bodies include lakes, rivers, oceans, aquifers, reservoirs and ...
, water conflict and climate change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in ...
. Fresh water is in principle a renewable resource
A renewable resource (also known as a flow resource) is a natural resource which will replenish to replace the portion depleted by usage and consumption, either through natural reproduction or other recurring processes in a finite amount of t ...
. However, the world's supply of groundwater
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and Pore space in soil, soil pore spaces and in the fractures of stratum, rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available fresh water in the world is groundwater. A unit ...
is steadily decreasing. Groundwater depletion (or overdrafting) is occurring for example in Asia, South America and North America.
Natural sources of fresh water
Natural sources offresh water
Fresh water or freshwater is any naturally occurring liquid or frozen water containing low concentrations of dissolved salt (chemistry), salts and other total dissolved solids. The term excludes seawater and brackish water, but it does include ...
include surface water, under river flow, groundwater
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and Pore space in soil, soil pore spaces and in the fractures of stratum, rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available fresh water in the world is groundwater. A unit ...
and frozen water.
Surface water
 Surface water is water in a river,
Surface water is water in a river, lake
A lake is often a naturally occurring, relatively large and fixed body of water on or near the Earth's surface. It is localized in a basin or interconnected basins surrounded by dry land. Lakes lie completely on land and are separate from ...
or fresh water wetland. Surface water is naturally replenished by precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls from clouds due to gravitational pull. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, rain and snow mixed ("sleet" in Commonwe ...
and naturally lost through discharge to the oceans, evaporation, evapotranspiration and groundwater recharge. The only natural input to any surface water system is precipitation within its watershed. The total quantity of water in that system at any given time is also dependent on many other factors. These factors include storage capacity in lakes, wetlands and artificial reservoirs, the permeability of the soil
Soil, also commonly referred to as earth, is a mixture of organic matter, minerals, gases, water, and organisms that together support the life of plants and soil organisms. Some scientific definitions distinguish dirt from ''soil'' by re ...
beneath these storage bodies, the runoff characteristics of the land in the watershed, the timing of the precipitation and local evaporation rates. All of these factors also affect the proportions of water loss.
Humans often increase storage capacity by constructing reservoirs and decrease it by draining wetlands. Humans often increase runoff quantities and velocities by paving areas and channelizing the stream flow.
Natural surface water can be augmented by importing surface water from another watershed through a canal
Canals or artificial waterways are waterways or engineered channels built for drainage management (e.g. flood control and irrigation) or for conveyancing water transport vehicles (e.g. water taxi). They carry free, calm surface ...
or pipeline.
Brazil
Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil, is the largest country in South America. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, fifth-largest country by area and the List of countries and dependencies by population ...
is estimated to have the largest supply of fresh water in the world, followed by Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
and Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
.
Water from glaciers
Glacier
A glacier (; or ) is a persistent body of dense ice, a form of rock, that is constantly moving downhill under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires ...
runoff is considered to be surface water. The Himalayas, which are often called "The Roof of the World", contain some of the most extensive and rough high altitude areas on Earth as well as the greatest area of glaciers and permafrost outside of the poles. Ten of Asia's largest rivers flow from there, and more than a billion people's livelihoods depend on them. To complicate matters, temperatures there are rising more rapidly than the global average. In Nepal, the temperature has risen by 0.6 degrees Celsius over the last decade, whereas globally, the Earth has warmed approximately 0.7 degrees Celsius over the last hundred years.
Groundwater
Under river flow
Throughout the course of a river, the total volume of water transported downstream will often be a combination of the visible free water flow together with a substantial contribution flowing through rocks and sediments that underlie the river and its floodplain called the hyporheic zone. For many rivers in large valleys, this unseen component of flow may greatly exceed the visible flow. The hyporheic zone often forms a dynamic interface between surface water and groundwater from aquifers, exchanging flow between rivers and aquifers that may be fully charged or depleted. This is especially significant in karst areas where pot-holes and underground rivers are common.Artificial sources of usable water
There are several artificial sources of fresh water. One is treated wastewater ( reclaimed water). Another is atmospheric water generators. Desalinated seawater is another important source. It is important to consider the economic and environmental side effects of these technologies.Wastewater reuse
Desalinated water
Research into other options
Researchers proposed air capture over oceans which would "significantly increasing freshwater through the capture of humid air over oceans" to address present and, especially, future water scarcity/insecurity. A 2021 study proposed hypothetical portable solar-powered atmospheric water harvesting devices. However, such off-the-grid generation may sometimes "undermine efforts to develop permanent piped infrastructure" among other problems.Water uses
 The total quantity of water available at any given time is an important consideration. Some human water users have an intermittent need for water. For example, many farms require large quantities of water in the spring, and no water at all in the winter. Other users have a continuous need for water, such as a power plant that requires water for cooling. Over the long term the average rate of precipitation within a watershed is the upper bound for average consumption of natural surface water from that watershed.
The total quantity of water available at any given time is an important consideration. Some human water users have an intermittent need for water. For example, many farms require large quantities of water in the spring, and no water at all in the winter. Other users have a continuous need for water, such as a power plant that requires water for cooling. Over the long term the average rate of precipitation within a watershed is the upper bound for average consumption of natural surface water from that watershed.
Agriculture and other irrigation
Industries
It is estimated that 22% of worldwide water is used in industry. Major industrial users includehydroelectric
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is Electricity generation, electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies 15% of the world's electricity, almost 4,210 TWh in 2023, which is more than all other Renewable energ ...
dams, thermoelectric power plants, which use water for cooling, ore and oil refineries, which use water in chemical processes, and manufacturing plants, which use water as a solvent. Water withdrawal can be very high for certain industries, but consumption is generally much lower than that of agriculture.
Water is used in renewable power generation. Hydroelectric power derives energy from the force of water flowing downhill, driving a turbine connected to a generator. This hydroelectricity
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is Electricity generation, electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies 15% of the world's electricity, almost 4,210 TWh in 2023, which is more than all other Renewable energ ...
is a low-cost, non-polluting, renewable energy source. Significantly, hydroelectric power can also be used for load following unlike most renewable energy sources which are intermittent. Ultimately, the energy in a hydroelectric power plant is supplied by the sun. Heat from the sun evaporates water, which condenses as rain in higher altitudes and flows downhill. Pumped-storage hydroelectric plants also exist, which use grid electricity to pump water uphill when demand is low, and use the stored water to produce electricity when demand is high.
Thermoelectric power plants using cooling towers have high consumption, nearly equal to their withdrawal, as most of the withdrawn water is evaporated as part of the cooling process. The withdrawal, however, is lower than in once-through cooling systems.
Water is also used in many large scale industrial processes, such as thermoelectric power production, oil refining, fertilizer production and other chemical plant use, and natural gas extraction from shale rock. Discharge of untreated water from industrial uses is pollution. Pollution includes discharged solutes and increased water temperature ( thermal pollution).
Drinking water and domestic use (households)
 It is estimated that 8% of worldwide water use is for domestic purposes. These include drinking water, bathing,
It is estimated that 8% of worldwide water use is for domestic purposes. These include drinking water, bathing, cooking
Cooking, also known as cookery or professionally as the culinary arts, is the art, science and craft of using heat to make food more palatable, digestible, nutritious, or Food safety, safe. Cooking techniques and ingredients vary widely, from ...
, toilet flushing, cleaning, laundry and gardening. Basic domestic water requirements have been estimated by Peter Gleick at around 50 liters per person per day, excluding water for gardens.
Drinking water is water that is of sufficiently high quality so that it can be consumed or used without risk of immediate or long term harm. Such water is commonly called potable water. In most developed countries, the water supplied to domestic, commerce and industry is all of drinking water standard even though only a very small proportion is actually consumed or used in food preparation.
844 million people still lacked even a basic drinking water service in 2017. Of those, 159 million people worldwide drink water directly from surface water sources, such as lakes and streams. One in eight people in the world do not have access to safe water. Unsafe drinking water leads to 1.2 million deaths per year according to the World Bank.
Challenges and threats
Water scarcity
Water pollution

Water conflict
Climate change
Groundwater overdrafting
The world's supply ofgroundwater
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and Pore space in soil, soil pore spaces and in the fractures of stratum, rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available fresh water in the world is groundwater. A unit ...
is steadily decreasing. Groundwater depletion (or overdrafting) is occurring for example in Asia, South America and North America. It is still unclear how much natural renewal balances this usage, and whether ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) is a system formed by Organism, organisms in interaction with their Biophysical environment, environment. The Biotic material, biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and en ...
s are threatened.
Water resource management
 Water resource management is the activity of planning, developing, distributing and managing the optimum use of water resources. It is an aspect of water cycle management. The field of water resources management will have to continue to adapt to the current and future issues facing the allocation of water. With the growing uncertainties of global
Water resource management is the activity of planning, developing, distributing and managing the optimum use of water resources. It is an aspect of water cycle management. The field of water resources management will have to continue to adapt to the current and future issues facing the allocation of water. With the growing uncertainties of global climate change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in ...
and the long-term impacts of past management actions, this decision-making will be even more difficult. It is likely that ongoing climate change will lead to situations that have not been encountered. As a result, alternative management strategies, including participatory approaches and adaptive capacity are increasingly being used to strengthen water decision-making.
Ideally, water resource management planning has regard to all the competing demands for water and seeks to allocate water on an equitable basis to satisfy all uses and demands. As with other resource management, this is rarely possible in practice so decision-makers must prioritise issues of sustainability, equity and factor optimisation (in that order!) to achieve acceptable outcomes. One of the biggest concerns for water-based resources in the future is the sustainability
Sustainability is a social goal for people to co-exist on Earth over a long period of time. Definitions of this term are disputed and have varied with literature, context, and time. Sustainability usually has three dimensions (or pillars): env ...
of the current and future water resource allocation.
Sustainable Development Goal 6 has a target related to water resources management: "Target 6.5: By 2030, implement integrated water resources management at all levels, including through transboundary cooperation as appropriate."Ritchie, Roser, Mispy, Ortiz-Ospina (2018"Measuring progress towards the Sustainable Development Goals." (SDG 6)
''SDG-Tracker.org, website''United Nations (2017) Resolution adopted by the General Assembly on 6 July 2017, Work of the Statistical Commission pertaining to the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development
A/RES/71/313
Sustainable water management
At present, only about 0.08 percent of all the world's fresh water is accessible. And there is ever-increasing demand for drinking,manufacturing
Manufacturing is the creation or production of goods with the help of equipment, labor, machines, tools, and chemical or biological processing or formulation. It is the essence of the
secondary sector of the economy. The term may refer ...
, leisure and agriculture. Due to the small percentage of water available, optimizing the fresh water we have left from natural resources has been a growing challenge around the world.
Much effort in water resource management is directed at optimizing the use of water and in minimizing the environmental impact of water use on the natural environment. The observation of water as an integral part of the ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) is a system formed by Organism, organisms in interaction with their Biophysical environment, environment. The Biotic material, biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and en ...
is based on integrated water resources management, based on the 1992 Dublin Principles (see below).
Sustainable water management requires a holistic approach based on the principles of Integrated Water Resource Management, originally articulated in 1992 at the Dublin (January) and Rio (July) conferences. The four Dublin Principles, promulgated in the Dublin Statement are:
# Fresh water is a finite and vulnerable resource, essential to sustain life, development and the environment;
# Water development and management should be based on a participatory approach, involving users, planners and policy-makers at all levels;
# Women play a central part in the provision, management and safeguarding of water;
# Water has an economic value in all its competing uses and should be recognized as an economic good.
Implementation of these principles has guided reform of national water management law around the world since 1992.
Further challenges to sustainable and equitable water resources management include the fact that many water bodies are shared across boundaries which may be international (see water conflict) or intra-national (see Murray-Darling basin).
Integrated water resources management
Integrated water resources management (IWRM) has been defined by the Global Water Partnership (GWP) as "a process which promotes the coordinated development and management of water, land and related resources, in order to maximize the resultanteconomic
An economy is an area of the Production (economics), production, Distribution (economics), distribution and trade, as well as Consumption (economics), consumption of Goods (economics), goods and Service (economics), services. In general, it is ...
and social welfare in an equitable manner without compromising the sustainability
Sustainability is a social goal for people to co-exist on Earth over a long period of time. Definitions of this term are disputed and have varied with literature, context, and time. Sustainability usually has three dimensions (or pillars): env ...
of vital ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) is a system formed by Organism, organisms in interaction with their Biophysical environment, environment. The Biotic material, biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and en ...
s".
Some scholars say that IWRM is complementary to water security because water security is a goal or destination, whilst IWRM is the process necessary to achieve that goal.
IWRM is a paradigm that emerged at international conferences in the late 1900s and early 2000s, although participatory water management institutions have existed for centuries. Discussions on a holistic way of managing water resources began already in the 1950s leading up to the 1977 United Nations Water Conference. The development of IWRM was particularly recommended in the final statement of the ministers at the International Conference on Water and the Environment in 1992, known as the Dublin Statement. This concept aims to promote changes in practices which are considered fundamental to improved water resource management. IWRM was a topic of the second World Water Forum, which was attended by a more varied group of stakeholders than the preceding conferences and contributed to the creation of the GWP.
In the International Water Association definition, IWRM rests upon three principles that together act as the overall framework:
# Social equity: ensuring equal access for all users (particularly marginalized and poorer user groups) to an adequate quantity and quality of water necessary to sustain human well-being
Well-being is what is Intrinsic value (ethics), ultimately good for a person. Also called "welfare" and "quality of life", it is a measure of how well life is going for someone. It is a central goal of many individual and societal endeavors.
...
.
# Economic efficiency: bringing the greatest benefit to the greatest number of users possible with the available financial and water resources.
# Ecological sustainability: requiring that aquatic ecosystems are acknowledged as users and that adequate allocation is made to sustain their natural functioning.
In 2002, the development of IWRM was discussed at the World Summit on Sustainable Development held in Johannesburg, which aimed to encourage the implementation of IWRM at a global level. The third World Water Forum recommended IWRM and discussed information sharing, stakeholder participation, and gender and class dynamics.
Operationally, IWRM approaches involve applying knowledge from various disciplines as well as the insights from diverse stakeholders to devise and implement efficient, equitable and sustainable solutions to water and development problems. As such, IWRM is a comprehensive, participatory planning and implementation tool for managing and developing water resources in a way that balances social and economic needs, and that ensures the protection of ecosystems for future generations. In addition, in light of contributing the achievement of Sustainable Development goals (SDGs), IWRM has been evolving into more sustainable approach as it considers the Nexus approach, which is a cross-sectoral water resource management. The Nexus approach is based on the recognition that "water, energy and food are closely linked through global and local water, carbon and energy cycles or chains."
An IWRM approach aims at avoiding a fragmented approach of water resources management by considering the following aspects: Enabling environment, roles of Institutions, management Instruments. Some of the cross-cutting conditions that are also important to consider when implementing IWRM are: Political will and commitment, capacity development, adequate investment, financial stability and sustainable cost recovery, monitoring and evaluation. There is not one correct administrative model. The art of IWRM lies in selecting, adjusting and applying the right mix of these tools for a given situation. IWRM practices depend on context; at the operational level, the challenge is to translate the agreed principles into concrete action.
Managing water in urban settings

By country
Water resource management and governance is handled differently by different countries. For example, in theUnited States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
, the United States Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), founded as the Geological Survey, is an agency of the U.S. Department of the Interior whose work spans the disciplines of biology, geography, geology, and hydrology. The agency was founded on Mar ...
(USGS) and its partners monitor water resources, conduct research and inform the public about groundwater quality. Water resources in specific countries are described below:
See also
* List of sovereign states by freshwater withdrawal * List of countries by total renewable water resources * * * * *References
External links
Renewable water resources in the world by country
Portal to international hydrology and water resources
Sustainable Sanitation and Water Management Toolbox
{{DEFAULTSORT:Water Resources Aquatic ecology Hydrology Irrigation Natural resources Water and the environment Water management
Resources
''Resource'' refers to all the materials available in our environment which are Technology, technologically accessible, Economics, economically feasible and Culture, culturally Sustainability, sustainable and help us to satisfy our needs and want ...
Water resources management
Water industry
Sanitation