Voivodina on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Vojvodina ( ; sr-Cyrl, Војводина, ), officially the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina, is an autonomous province that occupies the northernmost part of
 During the 1848–49 revolutions, Vojvodina was a site of a war between Serbs and Hungarians, due to the opposite national conceptions of the two peoples. At the
During the 1848–49 revolutions, Vojvodina was a site of a war between Serbs and Hungarians, due to the opposite national conceptions of the two peoples. At the
 Vojvodina remained Austrian Crown land until 1860, when Emperor
Vojvodina remained Austrian Crown land until 1860, when Emperor
 At the end of
At the end of  Between 1929 and 1941, the region was part of the Danube Banovina, a province of the
Between 1929 and 1941, the region was part of the Danube Banovina, a province of the
Dragoljub Živković
some 47,000 ethnic Serbs were murdered in Vojvodina between 1941 and 1948. About half were killed by occupational Axis forces and the other half by the post-war Communist authorities. The region was politically restored in 1944 (incorporating Syrmia, Banat, Bačka and Baranja) and became an autonomous province of Serbia in 1945. Instead of the previous name (Danube Banovina), the region regained its historical name of Vojvodina, while its capital city remained Novi Sad. When the final borders of Vojvodina were defined, Baranja was assigned to Croatia, while the northern part of the Mačva region was assigned to Vojvodina.
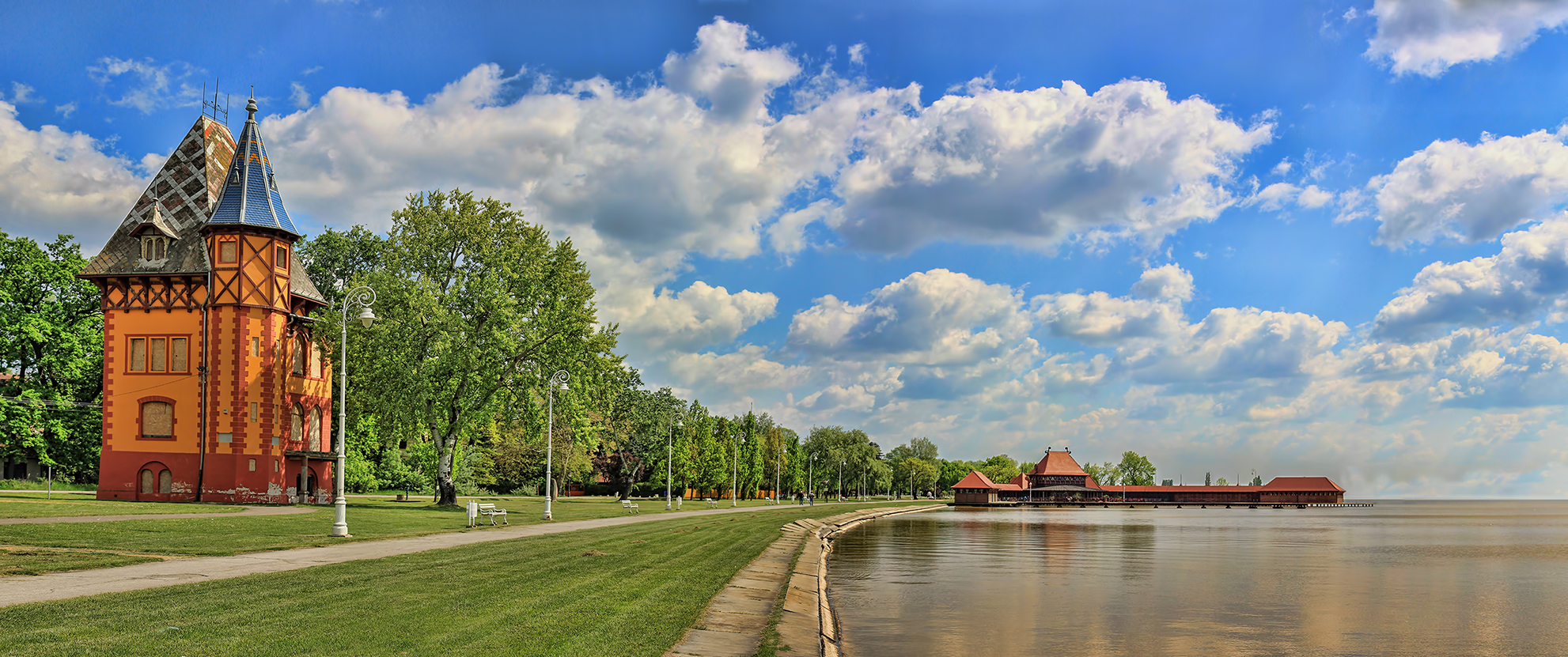 Vojvodina is situated in the northern quarter of
Vojvodina is situated in the northern quarter of
Serbia
, image_flag = Flag of Serbia.svg
, national_motto =
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Serbia.svg
, national_anthem = ()
, image_map =
, map_caption = Location of Serbia (gree ...
, located in Central Europe. It lies within the Pannonian Basin
The Pannonian Basin, with the term Carpathian Basin being sometimes preferred in Hungarian literature, is a large sedimentary basin situated in southeastern Central Europe. After the Treaty of Trianon following World War I, the geomorpholog ...
, bordered to the south by the national capital Belgrade
Belgrade is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Serbia, largest city of Serbia. It is located at the confluence of the Sava and Danube rivers and at the crossroads of the Pannonian Basin, Pannonian Plain and the Balkan Peninsula. T ...
and the Sava
The Sava, is a river in Central Europe, Central and Southeast Europe, a right-bank and the longest tributary of the Danube. From its source in Slovenia it flows through Croatia and along its border with Bosnia and Herzegovina, and finally reac ...
and Danube
The Danube ( ; see also #Names and etymology, other names) is the List of rivers of Europe#Longest rivers, second-longest river in Europe, after the Volga in Russia. It flows through Central and Southeastern Europe, from the Black Forest sou ...
Rivers. The administrative centre, Novi Sad
Novi Sad ( sr-Cyrl, Нови Сад, ; #Name, see below for other names) is the List of cities in Serbia, second largest city in Serbia and the capital of the autonomous province of Vojvodina. It is located in the southern portion of the Pannoni ...
, is the second-largest city in Serbia.
The historic regions of Banat
Banat ( , ; ; ; ) is a geographical and Historical regions of Central Europe, historical region located in the Pannonian Basin that straddles Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe. It is divided among three countries: the eastern part lie ...
, Bačka
Bačka ( sr-Cyrl, Бачка, ) or Bácska (), is a geographical and historical area within the Pannonian Plain bordered by the river Danube to the west and south, and by the river Tisza to the east. It is divided between Serbia and Hungary. ...
, Syrmia
Syrmia (Ekavian sh-Latn-Cyrl, Srem, Срем, separator=" / " or Ijekavian sh-Latn-Cyrl, Srijem, Сријем, label=none, separator=" / ") is a region of the southern Pannonian Plain, which lies between the Danube and Sava rivers. It is div ...
and northernmost part of Mačva
Mačva ( sr-Cyrl, Мачва, ; ) is a geographical and historical region in the northwest of Central Serbia, on a fertile plain between the Sava (river), Sava and Drina rivers. The chief town is Šabac. The modern Mačva District of Serbia is nam ...
overlap the province. Modern Vojvodina is multi-ethnic and multi-cultural, with some 26 ethnic groups and six official languages. Fewer than two million people, nearly 27% of Serbia's population, live in the province.
Name
''Vojvodina'' is also the Serbian word forvoivodeship
A voivodeship ( ) or voivodate is the area administered by a voivode (governor) in several countries of central and eastern Europe. Voivodeships have existed since medieval times and the area of extent of voivodeship resembles that of a duchy in ...
, a type of duchy overseen by a voivode
Voivode ( ), also spelled voivod, voievod or voevod and also known as vaivode ( ), voivoda, vojvoda, vaivada or wojewoda, is a title denoting a military leader or warlord in Central, Southeastern and Eastern Europe in use since the Early Mid ...
. The Serbian Voivodeship, a precursor to modern Vojvodina, was an Austrian province from 1849 to 1860.
Its official name is the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina. Its name in the province's six official languages is:
* Serbian: / ()
* Hungarian:
* Croatian:
* Pannonian Rusyn
Pannonian Rusyn (, ), also historically referred to as Yugoslav Rusyn, is a linguistic variety, variety of the Slovak language, spoken by the Pannonian Rusyns, primarily in the regions of Vojvodina (northern part of modern Serbia) and Slavonia ...
: ()
* Slovak:
* Romanian:
History
Pre-Roman times and Roman rule
In the Neolithic period, two important archaeological cultures flourished in this area: the Starčevo culture and theVinča culture
The Vinča culture , also known as Turdaș culture, Turdaș–Vinča culture or Vinča-Turdaș culture, is a Neolithic archaeological culture of Southeast Europe, dated to the period 5400–4500 BC. It is named for its type site, Vinča-Belo B ...
. Indo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the northern Indian subcontinent, most of Europe, and the Iranian plateau with additional native branches found in regions such as Sri Lanka, the Maldives, parts of Central Asia (e. ...
peoples first settled in the territory of present-day Vojvodina in 3200 BC. During the Eneolithic
The asterisk ( ), from Late Latin , from Ancient Greek , , "little star", is a typographical symbol. It is so called because it resembles a conventional image of a heraldic star.
Computer scientists and mathematicians often vocalize it as st ...
period, the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
and the Iron Age
The Iron Age () is the final epoch of the three historical Metal Ages, after the Chalcolithic and Bronze Age. It has also been considered as the final age of the three-age division starting with prehistory (before recorded history) and progre ...
, several Indo-European archaeological cultures were centered in or around Vojvodina, including the Vučedol culture, the Vatin culture, and the Bosut culture, among others.
Before the Roman conquest in the 1st century BC, Indo-European peoples of Illyrian, Thracian
The Thracians (; ; ) were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Southeast Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied the area that today is shared between north-eastern Greece, ...
and Celtic
Celtic, Celtics or Keltic may refer to:
Language and ethnicity
*pertaining to Celts, a collection of Indo-European peoples in Europe and Anatolia
**Celts (modern)
*Celtic languages
**Proto-Celtic language
*Celtic music
*Celtic nations
Sports Foot ...
origin inhabited this area. The first states organized in this area were the Celtic State of the Scordisci (3rd century BC-1st century AD) with capital in Singidunum
Singidunum ( sr-Cyrl-Latn, Сингидунум, Singidunum) was an ancient city which later evolved into modern Belgrade, the capital of Serbia. The name is of Celtic origin, going back to the time when the Celtic tribe Scordisci settled the a ...
(Belgrade
Belgrade is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Serbia, largest city of Serbia. It is located at the confluence of the Sava and Danube rivers and at the crossroads of the Pannonian Basin, Pannonian Plain and the Balkan Peninsula. T ...
), and the Dacian Kingdom
Dacia (, ; ) was the land inhabited by the Dacians, its core in Transylvania, stretching to the Danube in the south, the Black Sea in the east, and the Tisza in the west. The Carpathian Mountains were located in the middle of Dacia. It thus r ...
of Burebista
Burebista () was the king of the Getae and Dacian tribes from 82/61BC to 45/44BC. He was the first king who successfully unified the tribes of the Dacian kingdom, which comprised the area located between the Danube, Tisza, and Dniester rivers, ...
(1st century BC).
During Roman rule, Sirmium
Sirmium was a city in the Roman province of Pannonia, located on the Sava river, on the site of modern Sremska Mitrovica in the Vojvodina autonomous province of Serbia. First mentioned in the 4th century BC and originally inhabited by Illyrians ...
(modern Sremska Mitrovica
Sremska Mitrovica (; sr-Cyrl, Сремска Митровица, ) is a List of cities in Serbia, city in Serbia. It is situated on the left bank of the Sava, Sava river. , the city has a total population of 36,764 inhabitants, while its adminis ...
) was one of the four capital cities of the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
, and six Roman Emperors were born in this city or in its surroundings. The city was also the capital of several Roman administrative units, including Pannonia Inferior
Pannonia Inferior, lit. Lower Pannonia, was a province of the Roman Empire. Its capital was Sirmium. It was one of the border provinces on the Danube. It was formed in the year 103 AD by Emperor Trajan who divided the former province of Pannonia ...
, Pannonia Secunda
Pannonia Secunda was one of the provinces of the Roman Empire. It was formed in 296 AD, during the reign of Emperor Diocletian. The capital of the province was Sirmium (today Sremska Mitrovica). Pannonia Secunda comprised parts of present-day Serb ...
, the Diocese of Pannonia
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associate ...
, and the Praetorian prefecture of Illyricum
The praetorian prefecture of Illyricum (; , also termed simply the prefecture of Illyricum) was one of four praetorian prefectures into which the Later Roman Empire, Late Roman Empire was divided.
The administrative centre of the prefecture wa ...
.
Roman rule lasted until the 5th century, after which the region came into the possession of various peoples and states. While Banat
Banat ( , ; ; ; ) is a geographical and Historical regions of Central Europe, historical region located in the Pannonian Basin that straddles Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe. It is divided among three countries: the eastern part lie ...
was a part of the Roman province of Dacia
Dacia (, ; ) was the land inhabited by the Dacians, its core in Transylvania, stretching to the Danube in the south, the Black Sea in the east, and the Tisza in the west. The Carpathian Mountains were located in the middle of Dacia. It thus ro ...
, Syrmia
Syrmia (Ekavian sh-Latn-Cyrl, Srem, Срем, separator=" / " or Ijekavian sh-Latn-Cyrl, Srijem, Сријем, label=none, separator=" / ") is a region of the southern Pannonian Plain, which lies between the Danube and Sava rivers. It is div ...
belonged to the Roman province of Pannonia
Pannonia (, ) was a Roman province, province of the Roman Empire bounded on the north and east by the Danube, on the west by Noricum and upper Roman Italy, Italy, and on the southward by Dalmatia (Roman province), Dalmatia and upper Moesia. It ...
. Bačka
Bačka ( sr-Cyrl, Бачка, ) or Bácska (), is a geographical and historical area within the Pannonian Plain bordered by the river Danube to the west and south, and by the river Tisza to the east. It is divided between Serbia and Hungary. ...
was not part of the Roman Empire and was populated and ruled by Sarmatian Iazyges
The Iazyges () were an ancient Sarmatians, Sarmatian tribe that traveled westward in 200BC from Central Asia to the steppes of modern Ukraine. In , they moved into modern-day Hungary and Serbia near the Pannonian steppe between the Danube ...
.
Early Middle Ages and Slavic settlement
After the Romans were driven away from this region, various Indo-European and Turkic peoples and states ruled in the area. These peoples included Goths, Sarmatians, Huns, Gepids and Avars. For regional history, the largest in importance was a Gepid state, which had its capital in Sirmium. According to the 7th-century ''Miracles of Saint Demetrius
The ''Miracles of Saint Demetrius'' () is a 7th-century collection of homilies, written in Greek, accounting the miracles performed by the patron saint of Thessalonica, Saint Demetrius. It is a unique work for the history of the city and the Balka ...
'', Avars gave the region of Syrmia to a Bulgar leader named Kuber circa 680. The Bulgars of Kuber moved south with Maurus to Macedonia where they co-operated with Tervel in the 8th century.
Slavs
The Slavs or Slavic people are groups of people who speak Slavic languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout the northern parts of Eurasia; they predominantly inhabit Central Europe, Eastern Europe, Southeastern Europe, and ...
settled today's Vojvodina in the 6th and 7th centuries, before some of them crossed the rivers Sava and Danube and settled in the Balkans. Slavic tribes that lived in the territory of present-day Vojvodina included Abodrites, Severans, Braničevci and Timočani.
In the 9th century, after the fall of the Avar state, the first forms of Slavic statehood emerged in this area. The first Slavic states that ruled over this region included the Bulgarian Empire, Great Moravia
Great Moravia (; , ''Meghálī Moravía''; ; ; , ), or simply Moravia, was the first major state that was predominantly West Slavic to emerge in the area of Central Europe, possibly including territories which are today part of the Czech Repub ...
and Ljudevit's Pannonian Duchy. During the Bulgarian administration (9th century), local Bulgarian dukes, Salan and Glad, ruled over the region. Salan's residence was Titel, while that of Glad was possibly in the rumoured rampart of Galad or perhaps in the Kladovo (Gladovo) in eastern Serbia. Glad's descendant was the duke Ahtum, another local ruler from the 11th century who opposed the establishment of Hungarian rule over the region.
In the village of Čelarevo
Čelarevo ( sr-Cyrl, Челарево; ) is a village located in the Bačka Palanka municipality, in the South Bačka District of Serbia. It is situated in the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina. The village has a Serb ethnic majority and its popul ...
archaeologists have also found traces of people who practised the Judaic religion. Bunardžić dated Avar-Bulgar graves excavated in Čelarevo, containing skulls with Mongolian features and Judaic symbols, to the late 8th and 9th centuries. Erdely and Vilkhnovich consider the graves to belong to the Kabars
The Kabars (), also known as Qavars (Qabars) or Khavars, were Khazar rebels who joined Magyar tribes and the Rus' Khaganate confederations in the 9th century CE.
Sources
The Byzantine Emperor Constantine VII is the principal source of the Kaba ...
who eventually broke ties with the Khazar Empire between the 830s and 862. (Three other Khazar
The Khazars ; 突厥可薩 ''Tūjué Kěsà'', () were a nomadic Turkic people who, in the late 6th century CE, established a major commercial empire covering the southeastern section of modern European Russia, southern Ukraine, Crimea, an ...
tribes joined the Magyars
Hungarians, also known as Magyars, are an ethnic group native to Hungary (), who share a common culture, language and history. They also have a notable presence in former parts of the Kingdom of Hungary. The Hungarian language belongs to the ...
and took part in the Magyar conquest of the Carpathian basin including what is now Vojvodina in 895–907.)
Hungarian rule
Following territorial disputes with Byzantine and Bulgarian states, most of Vojvodina became part of theKingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from 1000 to 1946 and was a key part of the Habsburg monarchy from 1526-1918. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the Coro ...
between the 10th and 12th century and remained under Hungarian administration until the 16th century (Following periods of Ottoman and Habsburg administrations, Hungarian political dominance over most of the region was established again in 1867 and over entire region in 1882, after abolition of the Habsburg Military Frontier).
The regional demographic balance started changing in the 11th century when Magyars began to replace the local Slavic population. But from the 14th century, the balance changed again in favour of the Slavs when Serbian refugees fleeing from territories conquered by the Ottoman army settled in the area. Most of the Hungarians left the region during the Ottoman conquest and early period of Ottoman administration, so the population of Vojvodina in Ottoman times was predominantly Serbs (who comprised an absolute majority of Vojvodina at the time), with significant presence of Muslims of various ethnic backgrounds.
Ottoman rule
After the defeat of theKingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from 1000 to 1946 and was a key part of the Habsburg monarchy from 1526-1918. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the Coro ...
at Mohács
Mohács (; Croatian: ''Mohač''; ; ; ; ) is a town in Baranya County, Hungary, on the right bank of the Danube.
Etymology
The name probably comes from the Slavic ''*Mъchačь'',''*Mocháč'': ''mъchъ'' (moss, Hungarian ''moha'' is a loanword ...
by the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
, the region fell into a period of anarchy and civil wars. In 1526 Jovan Nenad
Jovan Nenad ( sr-Cyrl, Јован Ненад; or ; c. 1492 – 26 July 1527), known as "the Black", was a Serb military commander in the service of the Kingdom of Hungary who took advantage of a Hungarian military defeat at Mohács and subseque ...
, a leader of Serb mercenaries, established his rule in Bačka
Bačka ( sr-Cyrl, Бачка, ) or Bácska (), is a geographical and historical area within the Pannonian Plain bordered by the river Danube to the west and south, and by the river Tisza to the east. It is divided between Serbia and Hungary. ...
, northern Banat
Banat ( , ; ; ; ) is a geographical and Historical regions of Central Europe, historical region located in the Pannonian Basin that straddles Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe. It is divided among three countries: the eastern part lie ...
and a small part of Syrmia
Syrmia (Ekavian sh-Latn-Cyrl, Srem, Срем, separator=" / " or Ijekavian sh-Latn-Cyrl, Srijem, Сријем, label=none, separator=" / ") is a region of the southern Pannonian Plain, which lies between the Danube and Sava rivers. It is div ...
. He created an ephemeral independent state, with Subotica
Subotica (, ; , , ) is a List of cities in Serbia, city in Central Europe and the administrative center of the North Bačka District in the autonomous province of Vojvodina, Serbia. Formerly the largest city of Vojvodina region, contemporary Sub ...
as its capital.
At the peak of his power, Jovan Nenad proclaimed himself Serbian Emperor in Subotica. Taking advantage of the extremely confused military and political situation, the Hungarian noblemen from the region joined forces against him and defeated the Serbian troops in the summer of 1527. Emperor Jovan Nenad was assassinated and his state collapsed. After the fall of emperor's state, the supreme military commander of Jovan Nenad's army, Radoslav Čelnik, established his own temporary state in the region of Syrmia, where he ruled as Ottoman vassal.
A few decades later, the whole region was added to the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
, which ruled over it until the end of the 17th and the first half of the 18th century, when it was incorporated into the Habsburg monarchy
The Habsburg monarchy, also known as Habsburg Empire, or Habsburg Realm (), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities (composite monarchy) that were ruled by the House of Habsburg. From the 18th century it is ...
. The Treaty of Karlowitz
The Treaty of Karlowitz, concluding the Great Turkish War of 1683–1699, in which the Ottoman Empire was defeated by the Holy League at the Battle of Zenta, was signed in Karlowitz, in the Military Frontier of the Habsburg Monarchy (present-day ...
of 1699, between Holy League and Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
, marked the withdrawal of the Ottoman forces from Central Europe
Central Europe is a geographical region of Europe between Eastern Europe, Eastern, Southern Europe, Southern, Western Europe, Western and Northern Europe, Northern Europe. Central Europe is known for its cultural diversity; however, countries in ...
, and the supremacy of the Habsburg monarchy
The Habsburg monarchy, also known as Habsburg Empire, or Habsburg Realm (), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities (composite monarchy) that were ruled by the House of Habsburg. From the 18th century it is ...
in that part of the continent. According to the treaty, the western part of Vojvodina passed to Habsburgs. The eastern part (eastern Syrmia and Province of Tamışvar) remained in Ottoman hands until Austrian conquest in 1716. This new border change was ratified by the Treaty of Passarowitz
The Treaty of Passarowitz, or Treaty of Požarevac, was the peace treaty signed in Požarevac ( sr-cyr, Пожаревац, , ), a town that was in the Ottoman Empire but is now in Serbia, on 21 July 1718 between the Ottoman Empire and its ad ...
in 1718.
Habsburg rule
Hungarian Crown land (1699–1849)
During theGreat Serb Migration
The Great Migrations of the Serbs (), also known as the Great Exoduses of the Serbs, were two migrations of Serbs from various territories under the rule of the Ottoman Empire to the Kingdom of Hungary under the Habsburg monarchy.
The First ...
, Serbs from Ottoman territories settled in the Habsburg monarchy at the end of the 17th century (in 1690). Most settled in what is now Hungary, with the lesser part settling in western Vojvodina. All Serbs in the Habsburg monarchy gained the status of a recognized nation with extensive rights, in exchange for providing a border militia (in the Military Frontier
The Military Frontier (; sh-Cyrl-Latn, Војна крајина, Vojna krajina, sh-Cyrl-Latn, Војна граница, Vojna granica, label=none; ; ) was a borderland of the Habsburg monarchy and later the Austrian and Austro-Hungari ...
) that could be mobilized against invaders from the south (such as the Ottomans), as well as in case of civil unrest in the Habsburg Kingdom of Hungary. Wallachian Right became the point of reference in the 18th century for military settlement in lowland region. The Vlachs who settled there were actually mainly Serbs, although there were also Romanians while Aromanians
The Aromanians () are an Ethnic groups in Europe, ethnic group native to the southern Balkans who speak Aromanian language, Aromanian, an Eastern Romance language. They traditionally live in central and southern Albania, south-western Bulgari ...
lived in the urban areas.
At the beginning of Habsburg rule, most of the region was integrated into the Military Frontier, while western parts of Bačka were put under civil administration within the County of Bač. Later, the civil administration was expanded to other (mostly northern) parts of the region, while southern parts remained under military administration. The eastern part of this area was held again by the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
between 1787 and 1788, during the Russo-Turkish War
The Russo-Turkish wars ( ), or the Russo-Ottoman wars (), began in 1568 and continued intermittently until 1918. They consisted of twelve conflicts in total, making them one of the longest series of wars in the history of Europe. All but four of ...
. In 1716, Vienna
Vienna ( ; ; ) is the capital city, capital, List of largest cities in Austria, most populous city, and one of Federal states of Austria, nine federal states of Austria. It is Austria's primate city, with just over two million inhabitants. ...
temporarily forbade settlement by Hungarians and Jews in the area, while large numbers of German speakers were settled in the region from Bavaria and southern areas, in order to repopulate it and develop agriculture. From 1782, Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
Hungarians and ethnic Germans
Germans (, ) are the natives or inhabitants of Germany, or sometimes more broadly any people who are of German descent or native speakers of the German language. The constitution of Germany, implemented in 1949 following the end of World War ...
settled in larger numbers.
 During the 1848–49 revolutions, Vojvodina was a site of a war between Serbs and Hungarians, due to the opposite national conceptions of the two peoples. At the
During the 1848–49 revolutions, Vojvodina was a site of a war between Serbs and Hungarians, due to the opposite national conceptions of the two peoples. At the May Assembly
May Assembly ( sr-Cyrl-Latn, Мајска скупштина, Majska skupština, separator=" / ") was the national assembly of the Serbs in Austrian Empire, held on 1 and 3 (O.S.) 3 and 15 (N.S.)May 1848 in Sremski Karlovci, during which the S ...
in Sremski Karlovci
Sremski Karlovci ( sr-Cyrl, Сремски Карловци, ) is a town and municipality located in the South Bačka Districtautonomous province of Vojvodina, Serbia. It is situated on the banks of the Danube, from Novi Sad. According to the 202 ...
(13–15 May 1848), Serbs declared the constitution of the '' Serbian Voivodship'' (''Serbian Duchy''), a Serbian autonomous region within the Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire, officially known as the Empire of Austria, was a Multinational state, multinational European Great Powers, great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the Habsburg monarchy, realms of the Habsburgs. Duri ...
. The Serbian Voivodship consisted of Srem, Bačka, Banat, and Baranja.
The head of the metropolitanate of Sremski Karlovci, Josif Rajačić
Josif Rajačić ( sr-Cyrl, Јосиф Рајачић; 20 July 1785 – 1 December 1861), also known as Josif Rajačić-Brinski, was the Serbian Orthodox Church, Serbian Orthodox Archbishop and Metropolitanate of Karlovci, metropolitan of Sremski ...
, was elected patriarch
The highest-ranking bishops in Eastern Orthodoxy, Oriental Orthodoxy, the Roman Catholic Church (above major archbishop and primate), the Hussite Church, Church of the East, and some Independent Catholic Churches are termed patriarchs (and ...
, while Stevan Šupljikac was chosen as first voivod (duke). The ethnic war erupted violently in the area, with both sides committing atrocities against the civilian populations.
Austrian Crown land (1849–1860)
Following the Habsburg-Russian and Serb victory over the Hungarians in 1849, a new administrative territory was created in the region in November 1849, in accordance with a decision made by the Austrian emperor. By this decision, the Serbian autonomous region created in 1848 was transformed into the new Austriancrown land
Crown land, also known as royal domain, is a territorial area belonging to the monarch, who personifies the Crown. It is the equivalent of an entailed estate and passes with the monarchy, being inseparable from it. Today, in Commonwealth realm ...
known as Voivodeship of Serbia and Banat of Temeschwar
The Voivodeship of Serbia and Banat of Temeschwar, or Voivodeship of Serbia and Temes Banat (, , , ), was a crownland of the Austrian Empire that existed between 1849 and 1861, centered in Temeschwar. It was created by reorganization of admini ...
. It consisted of Banat, Bačka and Srem, excluding the southern parts of these regions which were part of the Military Frontier with significant Serbian populations. An Austrian governor seated in Temeschwar ruled the area, while the title of Voivod belonged to the emperor
The word ''emperor'' (from , via ) can mean the male ruler of an empire. ''Empress'', the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife (empress consort), mother/grandmother (empress dowager/grand empress dowager), or a woman who rules ...
himself. The full title of the emperor
The word ''emperor'' (from , via ) can mean the male ruler of an empire. ''Empress'', the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife (empress consort), mother/grandmother (empress dowager/grand empress dowager), or a woman who rules ...
was " Grand Voivod of the Voivodship of Serbia" (German: ''Großwoiwode der Woiwodschaft Serbien''). German and Serbian were the official languages of the crown land. In 1860, the new province was abolished and most of it (with exception of Syrmia) was again integrated into the Habsburg Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from 1000 to 1946 and was a key part of the Habsburg monarchy from 1526-1918. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the Coro ...
.
Hungarian rule
Hungarian Crown land (1860–1867)
 Vojvodina remained Austrian Crown land until 1860, when Emperor
Vojvodina remained Austrian Crown land until 1860, when Emperor Franz Joseph
Franz Joseph I or Francis Joseph I ( ; ; 18 August 1830 – 21 November 1916) was Emperor of Austria, King of Hungary, and the ruler of the Grand title of the emperor of Austria, other states of the Habsburg monarchy from 1848 until his death ...
decided that it would be Hungarian Crown land again. After 1867, the Kingdom of Hungary became one of two self-governing parts of Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, also referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire, the Dual Monarchy or the Habsburg Monarchy, was a multi-national constitutional monarchy in Central Europe#Before World War I, Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. A military ...
, and the territory was returned again to Hungarian administration.
Counties in the Kingdom of Hungary (1867–1920)
In 1867, a new county system was introduced. This territory was organized among Bács-Bodrog, Torontál and Temes counties. The era following the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867 was a period of economic flourishing. The Kingdom of Hungary had the second-fastest growing economy in Europe between 1867 and 1913, but ethnic relations were strained. According to the 1910 census, the last census conducted in Austria-Hungary, the population of Vojvodina included 510,754 (33.8%) Serbs; 425,672 (28.1%) Hungarians; and 324,017 (21.4%) Germans.Kingdom of Yugoslavia
 At the end of
At the end of World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, the Austro-Hungarian Empire collapsed. On 29 October 1918, Syrmia became a part of the State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs
The State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs ( / ; ) was a political entity that was constituted in October 1918, at the end of World War I, by Slovenes, Croats and Serbs (Prečani (Serbs), Prečani) residing in what were the southernmost parts of th ...
. On 31 October 1918, the Banat Republic
The Banat Republic (, or ''Bánsági Köztársaság'', or ''Republica Banatului'', sr-Cyrl-Latn, Банатска република, Banatska republika, separator=" / ") was a short-lived state proclaimed in Timișoara 31 October 1918, dur ...
was proclaimed in Timișoara
Timișoara (, , ; , also or ; ; ; see #Etymology, other names) is the capital city of Timiș County, Banat, and the main economic, social and cultural center in Western Romania. Located on the Bega (Tisza), Bega River, Timișoara is consider ...
. The government of Hungary recognized its independence, but it was short-lived.
On 25 November 1918, the Great People's Assembly of Serbs, Bunjevci and other Slavs in Banat, Bačka and Baranja
The Great People's Assembly of Serbs, Bunjevci and other Slavs in Banat, Bačka and Baranja () or Novi Sad Assembly () was a political assembly held in Novi Sad on 25 November 1918, which proclaimed the secession of Banat, Bačka and Baranya (regi ...
in Novi Sad proclaimed the unification of Vojvodina (Banat, Bačka and Baranja
Banat, Bačka and Baranya ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Banat, Bačka i Baranja, Банат, Бачка и Барања) was a province of the Kingdom of Serbia and the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes between November 1918 and 1922. It ...
) with the Kingdom of Serbia
The Kingdom of Serbia was a country located in the Balkans which was created when the ruler of the Principality of Serbia, Milan I of Serbia, Milan I, was proclaimed king in 1882. Since 1817, the Principality was ruled by the Obrenović dynast ...
(The assembly numbered 757 deputies, of which 578 were Serbs
The Serbs ( sr-Cyr, Срби, Srbi, ) are a South Slavs, South Slavic ethnic group native to Southeastern Europe who share a common Serbian Cultural heritage, ancestry, Culture of Serbia, culture, History of Serbia, history, and Serbian lan ...
, 84 Bunjevci
Bunjevci ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Bunjevci, Буњевци, ; sh-Latn-Cyrl, label=, separator=" / ", Bunjevac, Буњевац, sh-Latn-Cyrl, label=, separator=" / ", Bunjevka, Буњевка) are a South Slavs, South Slavic sub-ethnic ...
, 62 Slovaks
The Slovaks ( (historical Sloveni ), singular: ''Slovák'' (historical: ''Sloven'' ), feminine: ''Slovenka'' , plural: ''Slovenky'') are a West Slavic ethnic group and nation native to Slovakia who share a common ancestry, culture, history ...
, 21 Rusyns
Rusyns, also known as Carpatho-Rusyns, Carpatho-Russians, Ruthenians, or Rusnaks, are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group from the Carpathian Rus', Eastern Carpathians in Central Europe. They speak Rusyn language, Rusyn, an East Slavic lan ...
, 6 Germans
Germans (, ) are the natives or inhabitants of Germany, or sometimes more broadly any people who are of German descent or native speakers of the German language. The Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany, constitution of Germany, imple ...
, 3 Šokci
Šokci ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Šokci, Шокци, , ; sh-Latn-Cyrl, label=, separator=" / ", Šokac, Шокац, sh-Latn-Cyrl, label=, separator=" / ", Šokica, Шокица; ) are a South Slavs, South Slavic ethnic group native t ...
, 2 Croats
The Croats (; , ) are a South Slavs, South Slavic ethnic group native to Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina and other neighboring countries in Central Europe, Central and Southeastern Europe who share a common Croatian Cultural heritage, ancest ...
and 1 Hungarian). One day before this, on 24 November, the Assembly of Syrmia also proclaimed the unification of Syrmia with Serbia. On 1 December 1918, Vojvodina (as part of the Kingdom of Serbia) officially became part of the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes
The Kingdom of Yugoslavia was a country in Southeast and Central Europe that existed from 1918 until 1941. From 1918 to 1929, it was officially called the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes, but the term "Yugoslavia" () has been its colloq ...
.
 Between 1929 and 1941, the region was part of the Danube Banovina, a province of the
Between 1929 and 1941, the region was part of the Danube Banovina, a province of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia
The Kingdom of Yugoslavia was a country in Southeast Europe, Southeast and Central Europe that existed from 1918 until 1941. From 1918 to 1929, it was officially called the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes, but the term "Yugoslavia" () h ...
. Its capital city was Novi Sad. Apart from the core territories of Vojvodina and Baranja, it included significant parts of Šumadija
Šumadija ( sr-Cyrl, Шумадија, ) is a geographical region in the central part of Serbia. The area used to be heavily covered with forests, hence the name (from ''šuma'' 'forest'). The city of Kragujevac is the administrative center of t ...
and Braničevo regions south of the Danube (but not the capital city of Belgrade).
World War II and immediate aftermath
Between 1941 and 1944, duringWorld War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German Reich, German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a Totalit ...
and its allies, Hungary
Hungary is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning much of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and ...
and the Independent State of Croatia
The Independent State of Croatia (, NDH) was a World War II–era puppet state of Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy (1922–1943), Fascist Italy. It was established in parts of Axis occupation of Yugoslavia, occupied Yugoslavia on 10 April 1941, ...
, occupied Vojvodina and divided it. Bačka and Baranja were annexed by Hungary and Syrmia was included in the Independent State of Croatia. A smaller Danube Banovina (including Banat, Šumadija, and Braničevo) was designated as part of the area governed by the Military Administration in Serbia. The administrative center of this smaller province was Smederevo
Smederevo ( sr-Cyrl, Смедерево, ) is a list of cities in Serbia, city and the administrative center of the Podunavlje District in eastern Serbia. It is situated on the right bank of the Danube, about downstream of the Serbian capital, ...
. But, Banat was a separate autonomous region ruled by its ethnic German minority.
The occupying powers committed numerous crimes against the civilian population, especially against Serbs, Jews and Roma; the Jewish population of Vojvodina was almost completely killed or deported. In total, Axis
An axis (: axes) may refer to:
Mathematics
*A specific line (often a directed line) that plays an important role in some contexts. In particular:
** Coordinate axis of a coordinate system
*** ''x''-axis, ''y''-axis, ''z''-axis, common names ...
occupational authorities killed about 50,000 citizens of Vojvodina (mostly Serbs, Jews and Roma) while more than 280,000 people were interned, arrested, violated or tortured. Such crimes in varying regions of Vojvodina were carried out by Nazi Germans, Ustaše and Hungarian Axis forces. Many historians and authors describe the Ustashe regime's mass killings as genocide of the Serbs, including Raphael Lemkin
Raphael Lemkin (; 24 June 1900 – 28 August 1959) was a Polish lawyer who is known for coining the term "genocide" and for campaigning to establish the Genocide Convention, which legally defines the act. Following the German invasion of Poland ...
. In 1942, in the Novi Sad Raid, a military operation carried out by the Királyi Honvédség, the armed forces of Hungary
Hungary is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning much of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and ...
, during World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, after occupation and annexation of former Yugoslav territories. It resulted in the deaths of 3,000–4,000 civilians in the southern Bačka
Bačka ( sr-Cyrl, Бачка, ) or Bácska (), is a geographical and historical area within the Pannonian Plain bordered by the river Danube to the west and south, and by the river Tisza to the east. It is divided between Serbia and Hungary. ...
(Bácska) region. Under the Hungarian authority, 19,573 people were killed in Bačka, of which the majority of victims were of Serb, Jewish and Romani origin.
When Axis occupation ended in 1944, the region was temporarily placed under a military administration (1944–45) run by the new communist authorities. During and after the military administration, several thousands of citizens were killed. Victims were mostly ethnic Germans, but Hungarian and Serb populations were also killed. Both the war-time Axis occupational authorities and the post-war communist authorities ran concentration/prison camps in the territory of Vojvodina (see List of concentration and internment camps
This is a list of Internment, internment and concentration camps, organized by country. In general, a camp or group of camps is designated to the country whose government was responsible for the establishment and/or operation of the camp regardle ...
). While war-time prisoners in these camps were mostly Jews, Serbs and communists, post-war camps were formed for ethnic Germans (historically known as Danube Swabians
The Danube Swabians ( ) is a collective term for the ethnic German-speaking population who lived in the Kingdom of Hungary in east-central Europe, especially in the Danube River valley, first in the 12th century, and in greater numbers in the 17 ...
).
Most Vojvodina ethnic Germans (about 200,000) fled the region in 1944, together with the defeated German army. Most of those who remained in the region (about 150,000) were sent to some of the villages cordoned off as prisons. It is estimated that some 48,447 Germans died in the camps from disease, hunger, malnutrition, mistreatment, and cold. Some 8,049 Germans were killed by partisans during military administration in Vojvodina after October 1944.
It has also been estimated that post-war communist authorities killed some 15,000–20,000 Hungarians and some 23,000–24,000 Serbs during Communist purges in Serbia in 1944–45. According tDragoljub Živković
some 47,000 ethnic Serbs were murdered in Vojvodina between 1941 and 1948. About half were killed by occupational Axis forces and the other half by the post-war Communist authorities. The region was politically restored in 1944 (incorporating Syrmia, Banat, Bačka and Baranja) and became an autonomous province of Serbia in 1945. Instead of the previous name (Danube Banovina), the region regained its historical name of Vojvodina, while its capital city remained Novi Sad. When the final borders of Vojvodina were defined, Baranja was assigned to Croatia, while the northern part of the Mačva region was assigned to Vojvodina.
Socialist Yugoslavia
For decades, the province enjoyed only a small level of autonomy within Serbia. Under the 1974 Yugoslav constitution, it gained extensive rights of self-rule, as both Kosovo and Vojvodina were given ''de facto'' veto power in the Serbian and Yugoslav parliaments. Changes to their status could not be made without the consent of the two Provincial Assemblies. The 1974 Serbian constitution, adopted at the same time, reiterated that "the Socialist Republic of Serbia comprises the Socialist Autonomous Province of Vojvodina and theSocialist Autonomous Province of Kosovo
The Socialist Autonomous Province of Kosovo, sh-Latn-Cyrl, Socijalistička Autonomna Pokrajina Kosovo, Социјалистичка Аутономна Покрајина Косово, separator=" / "; ; . Also abbreviated as SAP Kosovo. referre ...
, which originated in the common struggle of nations and nationalities of Yugoslavia in the National Liberation War (the Second World War) and socialist revolution".
In 1990s, during the war in Croatia
The Croatian War of Independence) and (rarely) "War in Krajina" ( sr-Cyrl-Latn, Рат у Крајини, Rat u Krajini) are used. was an armed conflict fought in Croatia from 1991 to 1995 between Croats, Croat forces loyal to the Governmen ...
in persecution of Croats in Serbia during Yugoslav Wars was organized and participated in the expulsion of the Croats in some places in Vojvodina. Based on an investigation by the ''Humanitarian Law Fund'' from Belgrade in the course of June, July, and August 1992, more than 10,000 Croats from Vojvodina exchanged their property for the property of Serbs from Croatia, and altogether about 20,000 Croats left Serbia. According to other estimations, the number of Croats which have left Serbia under political pressure of Milošević's regime might be between 20,000 and 40,000. According to Petar Kuntić of Democratic Alliance of Croats in Vojvodina, 50,000 Croats were pressured to move out from Serbia during the Yugoslav wars.
Under the rule of Serbian president Slobodan Milošević
Slobodan Milošević ( sr-Cyrl, Слободан Милошевић, ; 20 August 1941 – 11 March 2006) was a Yugoslav and Serbian politician who was the President of Serbia between 1989 and 1997 and President of the Federal Republic of Yugos ...
, a series of protests against Vojvodina's party leadership took place during the summer and autumn of 1988, which forced it to resign. Eventually Vojvodina and Kosovo had to accept Serbia's constitutional amendments that practically dismissed the autonomy of the provinces in Serbia. Vojvodina and Kosovo lost elements of statehood in September 1990 when the new constitution of the Republic of Serbia was adopted.
Vojvodina was still referred to as an autonomous province of Serbia, but most of its autonomous powers – including, crucially, its vote on the Yugoslav collective presidency – were transferred to the control of Belgrade, the capital. The province still had its own parliament and government, and some other autonomous functions as well. According to Đorđe Tomić, this is an example of a phantom border.
Contemporary period
The fall of Milošević in 2000 created a new political climate in Vojvodina. Following talks between the political parties, the level of the province's autonomy was somewhat increased by the omnibus law in 2002. The Vojvodina provincial assembly adopted a new statute on 15 October 2008, which, after being partially amended, was approved by the Parliament of Serbia. On 28 January 2013, as an answer to the proposal of the Third Serbia political organization from Novi Sad to abolish the autonomy of Vojvodina, the pro-autonomist Vojvodina's Party performed a campaign that involved the posting of "Republic of Vojvodina" posters inNovi Sad
Novi Sad ( sr-Cyrl, Нови Сад, ; #Name, see below for other names) is the List of cities in Serbia, second largest city in Serbia and the capital of the autonomous province of Vojvodina. It is located in the southern portion of the Pannoni ...
.
Geography
 Vojvodina is situated in the northern quarter of
Vojvodina is situated in the northern quarter of Serbia
, image_flag = Flag of Serbia.svg
, national_motto =
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Serbia.svg
, national_anthem = ()
, image_map =
, map_caption = Location of Serbia (gree ...
, in Central Europe. In the southeast part of the Pannonian Plain
The Pannonian Basin, with the term Carpathian Basin being sometimes preferred in Hungarian literature, is a large sedimentary basin situated in southeastern Central Europe. After the Treaty of Trianon following World War I, the geomorphologic ...
, the plain
In geography, a plain, commonly known as flatland, is a flat expanse of land that generally does not change much in elevation, and is primarily treeless. Plains occur as lowlands along valleys or at the base of mountains, as coastal plains, and ...
that remained when the Pliocene
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch (geology), epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.33 to 2.58Pannonian Sea'' dried out. As a consequence of this, Vojvodina is rich in fertile

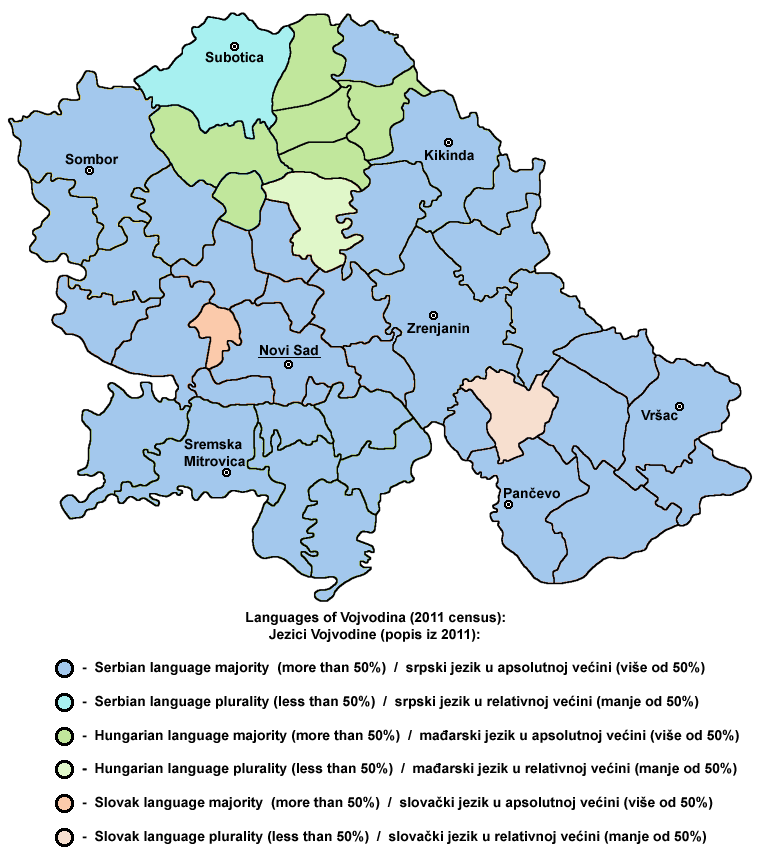
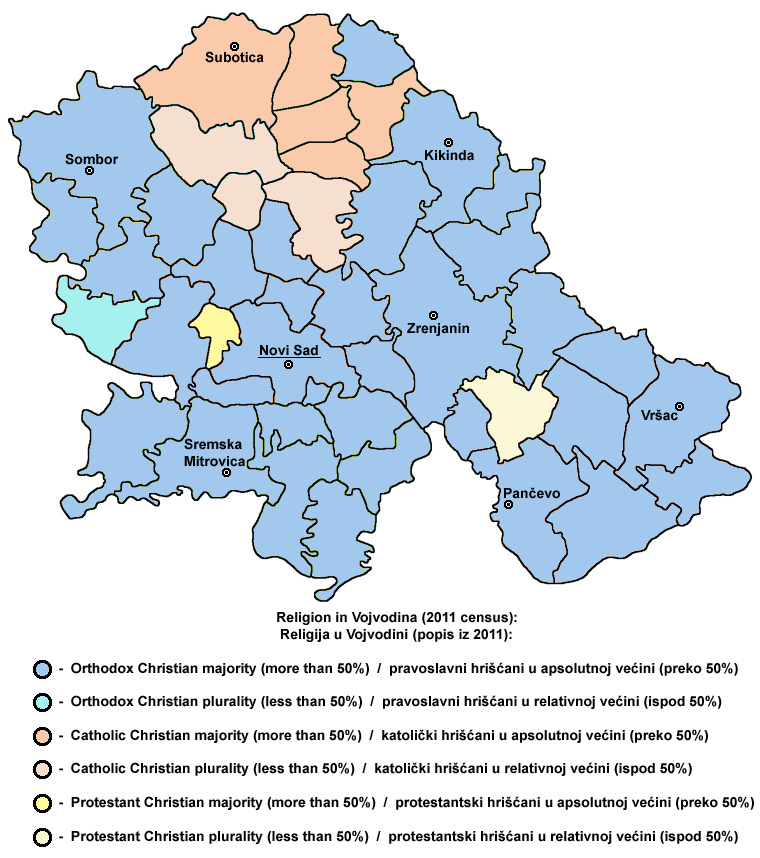 Vojvodina is more diverse than the rest of Serbia with more than 25 ethnic groups and six languages which are in official use by the provincial administration.
Population by ethnicity:
Population by mother tongue:
Population by religion:
Vojvodina is more diverse than the rest of Serbia with more than 25 ethnic groups and six languages which are in official use by the provincial administration.
Population by ethnicity:
Population by mother tongue:
Population by religion:
 There are two daily newspapers published in Vojvodina, '' Dnevnik'' in Serbian and '' Magyar Szó'' in Hungarian. Monthly and weekly publications in minority languages include '' Hrvatska riječ'' ("Croatian Word") in Croatian, '' Hlas Ľudu'' ("The Voice of the People") in Slovak, ''
There are two daily newspapers published in Vojvodina, '' Dnevnik'' in Serbian and '' Magyar Szó'' in Hungarian. Monthly and weekly publications in minority languages include '' Hrvatska riječ'' ("Croatian Word") in Croatian, '' Hlas Ľudu'' ("The Voice of the People") in Slovak, ''
 The economy of Vojvodina is largely based on developed food industry and fertile agricultural soil. Agriculture is a priority sector in Vojvodina. Traditionally, it has always been a significant part of the local economy and a generator of positive results, due to the abundance of fertile agricultural land which makes up 84% of its territory. The share of agribusiness in the total industrial production is 40%, that is 30% in the total exports of Vojvodina.
The metal industry of Vojvodina has a long tradition and consists of smaller metal processing companies for components manufacturing and, to a lesser extent, of original equipment manufacturers (OEM) with their own brand name products. Vojvodina Metal Cluster gathers 116 companies with 6,300 employees. Other branches of industry are also developed such as the chemical industry, electrical industry, oil industry and construction industry. In the past decade, ICT sector has been growing rapidly and has taken significant role in Vojvodina's economic development.
High- tech sector is a fast-growing sector in Vojvodina. Software development represents the main source of revenue, particularly development of ERP solutions, Java applications and mobile applications. IT sector companies mainly deal with software outsourcing, based on demands of international clients or with development of their own software products for purposes of domestic and international market.
Vojvodina pays particular attention to interregional and cross-border economic cooperation, as well as to implementation of priorities defined within the EU Strategy for the Danube Region.
Some of the companies from Vojvodina:
*
The economy of Vojvodina is largely based on developed food industry and fertile agricultural soil. Agriculture is a priority sector in Vojvodina. Traditionally, it has always been a significant part of the local economy and a generator of positive results, due to the abundance of fertile agricultural land which makes up 84% of its territory. The share of agribusiness in the total industrial production is 40%, that is 30% in the total exports of Vojvodina.
The metal industry of Vojvodina has a long tradition and consists of smaller metal processing companies for components manufacturing and, to a lesser extent, of original equipment manufacturers (OEM) with their own brand name products. Vojvodina Metal Cluster gathers 116 companies with 6,300 employees. Other branches of industry are also developed such as the chemical industry, electrical industry, oil industry and construction industry. In the past decade, ICT sector has been growing rapidly and has taken significant role in Vojvodina's economic development.
High- tech sector is a fast-growing sector in Vojvodina. Software development represents the main source of revenue, particularly development of ERP solutions, Java applications and mobile applications. IT sector companies mainly deal with software outsourcing, based on demands of international clients or with development of their own software products for purposes of domestic and international market.
Vojvodina pays particular attention to interregional and cross-border economic cooperation, as well as to implementation of priorities defined within the EU Strategy for the Danube Region.
Some of the companies from Vojvodina:
*

Government of the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina
Assembly of the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina
Provincial Secretariat for Regional and International Cooperation
Tourism organization of VojvodinaUseful information about Vojvodina, Parks of Nature, River Expedition, Wine Trails, Cities, Etno, Adventure and moreInteractive map of Novi Sad
* Atlas of Vojvodina (Wikimedia Commons)
Statistical information about municipalities of VojvodinaList of largest cities of Vojvodina
''The encyclopedia of Vojvodina''Official symbols of AP Vojvodina
{{Authority control Autonomous provinces of Serbia Statistical regions of Serbia States and territories established in 1944 Autonomous provinces Historical regions in Serbia Autonomous regions Countries and territories where Serbian is an official language Countries and territories where Romanian is an official language Countries and territories where Hungarian is an official language Countries and territories where Croatian is an official language Regions of Europe with multiple official languages 1944 establishments in Yugoslavia Rusyn communities
loam
Loam (in geology and soil science) is soil composed mostly of sand (particle size > ), silt (particle size > ), and a smaller amount of clay (particle size < ). By weight, its mineral composition is about 40–40–20% concentration of sand–si ...
y loess
A loess (, ; from ) is a clastic rock, clastic, predominantly silt-sized sediment that is formed by the accumulation of wind-blown dust. Ten percent of Earth's land area is covered by loesses or similar deposition (geology), deposits.
A loess ...
soil
Soil, also commonly referred to as earth, is a mixture of organic matter, minerals, gases, water, and organisms that together support the life of plants and soil organisms. Some scientific definitions distinguish dirt from ''soil'' by re ...
, covered with a layer of chernozem
Chernozem ( ),; also called black soil, regur soil or black cotton soil, is a black-colored soil containing a high percentage of humus (4% to 16%) and high percentages of phosphorus and ammonia compounds. Chernozem is very fertile soil and can ...
. The region is divided by the Danube
The Danube ( ; see also #Names and etymology, other names) is the List of rivers of Europe#Longest rivers, second-longest river in Europe, after the Volga in Russia. It flows through Central and Southeastern Europe, from the Black Forest sou ...
and Tisa rivers into: Bačka
Bačka ( sr-Cyrl, Бачка, ) or Bácska (), is a geographical and historical area within the Pannonian Plain bordered by the river Danube to the west and south, and by the river Tisza to the east. It is divided between Serbia and Hungary. ...
in the northwest, Banat
Banat ( , ; ; ; ) is a geographical and Historical regions of Central Europe, historical region located in the Pannonian Basin that straddles Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe. It is divided among three countries: the eastern part lie ...
in the east and Syrmia
Syrmia (Ekavian sh-Latn-Cyrl, Srem, Срем, separator=" / " or Ijekavian sh-Latn-Cyrl, Srijem, Сријем, label=none, separator=" / ") is a region of the southern Pannonian Plain, which lies between the Danube and Sava rivers. It is div ...
(Srem) in the southwest. A small part of the Mačva
Mačva ( sr-Cyrl, Мачва, ; ) is a geographical and historical region in the northwest of Central Serbia, on a fertile plain between the Sava (river), Sava and Drina rivers. The chief town is Šabac. The modern Mačva District of Serbia is nam ...
region is also located in Vojvodina south of the Sava
The Sava, is a river in Central Europe, Central and Southeast Europe, a right-bank and the longest tributary of the Danube. From its source in Slovenia it flows through Croatia and along its border with Bosnia and Herzegovina, and finally reac ...
river, in the Srem District
The Srem District (, ) is one of administrative districts of Serbia. It lies in the geographical regions of Syrmia and Mačva. According to the 2022 census, the Srem District has a population of 282,547 inhabitants. The administrative center is ...
.
Today, the western part of Syrmia
Syrmia (Ekavian sh-Latn-Cyrl, Srem, Срем, separator=" / " or Ijekavian sh-Latn-Cyrl, Srijem, Сријем, label=none, separator=" / ") is a region of the southern Pannonian Plain, which lies between the Danube and Sava rivers. It is div ...
is in Croatia
Croatia, officially the Republic of Croatia, is a country in Central Europe, Central and Southeast Europe, on the coast of the Adriatic Sea. It borders Slovenia to the northwest, Hungary to the northeast, Serbia to the east, Bosnia and Herze ...
, the northern part of Bačka is in Hungary
Hungary is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning much of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and ...
, the eastern part of Banat is in Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe. It borders Ukraine to the north and east, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Bulgaria to the south, Moldova to ...
(with a small piece in Hungary), while Baranja (which is between the Danube and the Drava
The Drava or Drave (, ; ; ; ; ), historically known as the Dravis or Dravus, is a river in southern Central Europe.
) is in Hungary and Croatia. Vojvodina has a total surface area of . Vojvodina is also part of the Danube-Kris-Mures-Tisa euroregion. The Gudurica peak (Gudurički vrh) on the Vršac Mountains, is the highest peak in Vojvodina, at an altitude of 641 m above sea level.
The climate of the area is moderate continental, including cold winters and hot and humid summers. The Vojvodina climate is characterized by a vast range of extreme temperatures and very irregular rainfall distribution per month.
Politics
TheAssembly of Vojvodina
The Assembly of Vojvodina ( sr-cyrl, Скупштина Војводине, Skupština Vojvodine), officially known as the Assembly of the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina (; ; ; ; Pannonian Rusyn: Скупштина Автономней Покр� ...
is the provincial legislature
A legislature (, ) is a deliberative assembly with the legal authority to make laws for a political entity such as a country, nation or city on behalf of the people therein. They are often contrasted with the executive and judicial power ...
composed of 120 proportionally elected members. The current members were elected in the 2020 provincial elections. The Government of Vojvodina is the executive
Executive ( exe., exec., execu.) may refer to:
Role or title
* Executive, a senior management role in an organization
** Chief executive officer (CEO), one of the highest-ranking corporate officers (executives) or administrators
** Executive dir ...
administrative body composed of a president
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
* President (education), a leader of a college or university
*President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment Film and television
*'' Præsident ...
and cabinet ministers.
The current ruling coalition in the Vojvodina parliament is composed of the following political parties: Serbian Progressive Party
The Serbian Progressive Party (, SNS) is a major populist, catch-all party, catch-all List of political parties in Serbia, political party in Serbia. It has been the Ruling party, ruling party since 2012. Miloš Vučević, the former prime mi ...
, Socialist Party of Serbia
The Socialist Party of Serbia (, abbr. SPS) is a populist political party in Serbia. Ivica Dačić has led SPS as its president since 2006.
SPS was founded in 1990 as a merger of the League of Communists of Serbia and Socialist Alliance ...
and Alliance of Vojvodina Hungarians
The Alliance of Vojvodina Hungarians (, abbr. VMSZ; , abbr. SVM) is a regionalist political party in Serbia, representing the Hungarian minority.
History Foundation and early history
The party was founded in 1994 in Senta by József Kas ...
. The current president of Vojvodinian government is Igor Mirović (Serbian Progressive Party
The Serbian Progressive Party (, SNS) is a major populist, catch-all party, catch-all List of political parties in Serbia, political party in Serbia. It has been the Ruling party, ruling party since 2012. Miloš Vučević, the former prime mi ...
), while the president of the provincial Assembly is Bálint Juhász (Alliance of Vojvodina Hungarians
The Alliance of Vojvodina Hungarians (, abbr. VMSZ; , abbr. SVM) is a regionalist political party in Serbia, representing the Hungarian minority.
History Foundation and early history
The party was founded in 1994 in Senta by József Kas ...
).
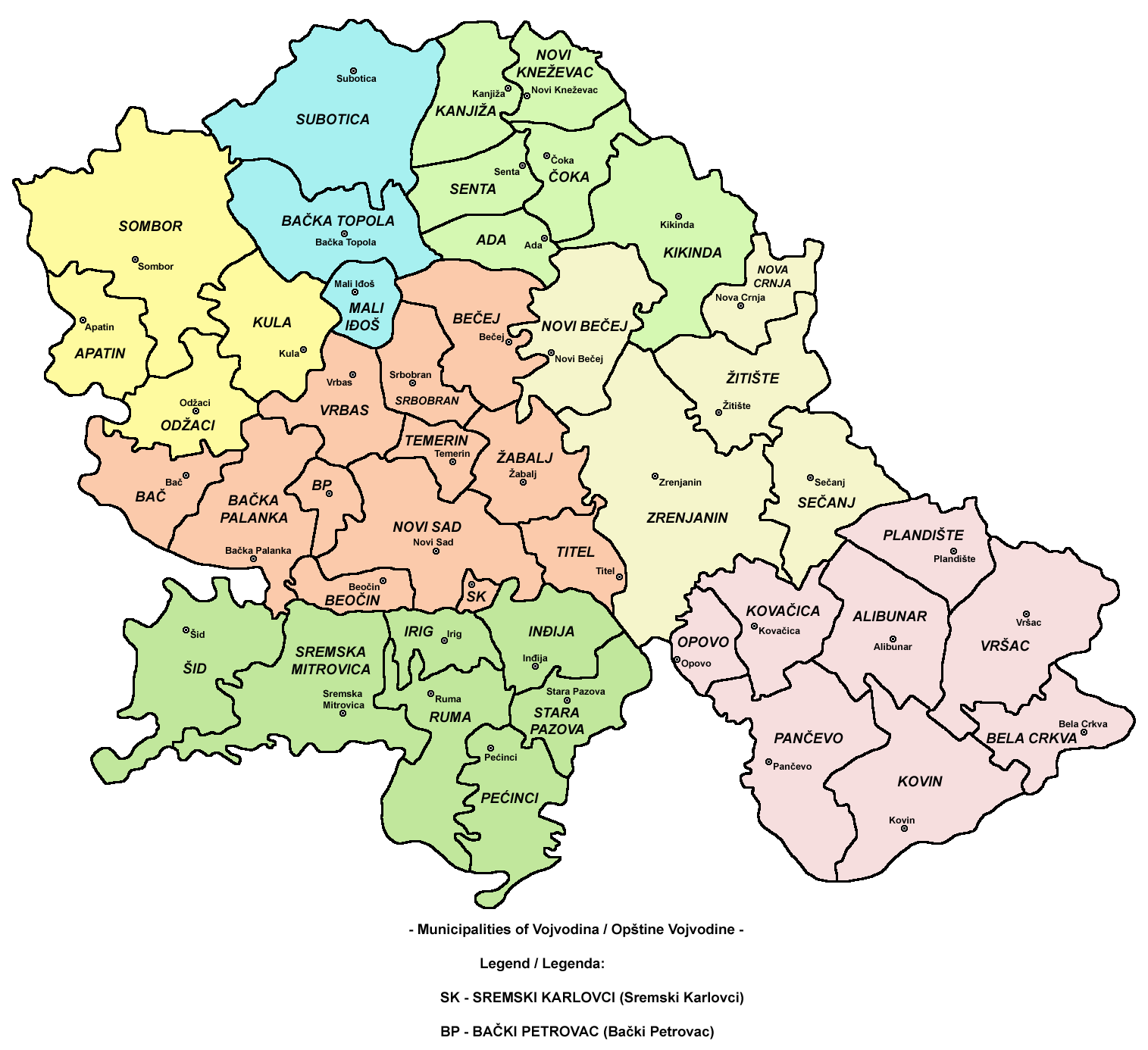
Administrative divisions
Vojvodina is divided into sevendistricts
A district is a type of administrative division that in some countries is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or counties, several municipalities, subdivisions ...
. They are regional centers of state authority, but have no powers of their own; they present purely administrative divisions. The seven districts are further subdivided into 37 municipalities
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having municipal corporation, corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate.
The term ''municipality' ...
and the 8 cities of Kikinda
Kikinda ( sr-Cyrl, Кикинда, ; ) is a List of cities in Serbia, city and the administrative center of the North Banat District in Serbia. The city's urban area has 32,084 inhabitants, while the city administrative area has 49,326 inhabit ...
, Novi Sad
Novi Sad ( sr-Cyrl, Нови Сад, ; #Name, see below for other names) is the List of cities in Serbia, second largest city in Serbia and the capital of the autonomous province of Vojvodina. It is located in the southern portion of the Pannoni ...
, Subotica
Subotica (, ; , , ) is a List of cities in Serbia, city in Central Europe and the administrative center of the North Bačka District in the autonomous province of Vojvodina, Serbia. Formerly the largest city of Vojvodina region, contemporary Sub ...
, Zrenjanin
Zrenjanin ( sr-Cyrl, Зрењанин, ; ; ; ; ) is a List of cities in Serbia, city and the administrative center of the Central Banat District in the autonomous province of Vojvodina, Serbia. The city urban area has a population of 67,129 inh ...
, Pančevo
Pančevo (Serbian Cyrillic: Панчево, ; ; ; ; ) is a list of cities in Serbia, city and the administrative center of the South Banat District in the autonomous province of Vojvodina, Serbia. It is located on the shores of rivers Timiș (ri ...
, Sombor
Sombor ( sr-Cyrl, Сомбор, ; ; ) is a List of cities in Serbia, city and the administrative center of the West Bačka District in the autonomous province of Vojvodina, Serbia. The city has a total population of 41,814 (), while its adminis ...
, Sremska Mitrovica
Sremska Mitrovica (; sr-Cyrl, Сремска Митровица, ) is a List of cities in Serbia, city in Serbia. It is situated on the left bank of the Sava, Sava river. , the city has a total population of 36,764 inhabitants, while its adminis ...
, and Vršac
Vršac ( sr-Cyrl, Вршац, ) is a city in the autonomous province of Vojvodina, Serbia. As of 2022, the city urban area had a population of 31,946, while the city administrative area had 45,462 inhabitants. It is located in the geographical ...
.

Demographics

 Vojvodina is more diverse than the rest of Serbia with more than 25 ethnic groups and six languages which are in official use by the provincial administration.
Population by ethnicity:
Population by mother tongue:
Population by religion:
Vojvodina is more diverse than the rest of Serbia with more than 25 ethnic groups and six languages which are in official use by the provincial administration.
Population by ethnicity:
Population by mother tongue:
Population by religion:
Largest cities
Culture
Libertatea
(; "Freedom") is a Romanian daily newspaper and online news website covering current affairs, entertainment, sports and lifestyle. It was founded on December 22, 1989 (12:45 p.m.), by Octavian Andronic, as "the first independent newspaper ...
'' ("Freedom") in Romanian, and '' Руске слово'' ("Rusyn Word") in Rusyn. There is also '' Bunjevačke novine'' ("The Bunjevac newspaper") in Bunjevac.
The public broadcaster Radio Television of Vojvodina
Radio Television of Vojvodina, sr-Lat, Radio-televizija Vojvodine, , , , Rusyn: Радіо Телебачення Воєводини; abbr. РТВ/RTV (RTV) is the regional public broadcaster in the Serbian province of Vojvodina, headquartered ...
was founded in 1974 as Radio Television of Novi Sad, as an equal member of the association of JRT, Yugoslav Radio Television. Radio Novi Sad's first broadcast was on 29 November 1949. During the NATO bombing in the spring of 1999, the RT Novi Sad building of 20 thousand square meters was completely destroyed along with its basic production and technical premises . The Venac terrestrial broadcasting site was heavily damaged.
The Radio-Television of Vojvodina produces and broadcasts regional programming on two channels, RTV1 (Serbian language) and RTV2 (minority languages), and three radio frequencies: Radio Novi Sad 1 (Serbian), Radio Novi Sad 2 (Hungarian), Radio Novi Sad 3 (other minority communities).
Economy
Naftna Industrija Srbije
Naftna Industrija Srbije ( sr-Cyrl, Нафтна Индустрија Србије, lit=Petroleum Industry of Serbia; abbr. NIS / НИС) is a Serbian multinational oil and gas company with headquarters in NIS building, Novi Sad, Serbia. NIS ...
* Srbijagas
* HIP Petrohemija
* Apatin Brewery
* Novosadski sajam
Vojvodina promotes its investment potentials through the Vojvodina Investment Promotion (VIP) agency, which was founded by the Parliament of the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina.
Transport
There are many important roads which pass through Vojvodina. First of all, the motorway A1 motorway which goes from Central Europe and the Horgos border crossing to Hungary, via Novi Sad to Belgrade and further to the southeast toward Niš, where it branches: one way leads east to the border with Bulgaria; the other to the south, towards Greece. Motorway A3 in Srem separates the west, towards the neighboring Croatia and further to Western Europe. There is also a network of regional and local roads and railway lines. The three largest rivers in Vojvodina are navigable stream. Danube River with a length of 588 kilometers and its tributaries Tisa (168 km), Sava (206 km) and Bega (75 km). Among them was dug extensive network of irrigation canals, drainage and transport, with a total length of , of which navigable.
Tourism
Tourist destinations in Vojvodina include well known Orthodox monasteries onFruška Gora
Fruška gora ( sr-Cyrl, Фрушка гора) is a mountain in Syrmia, with most of the mountain being part of Serbia and its westernmost edge extending into eastern Croatia. The Serbian part of the mountain forms the country's oldest National p ...
mountain, numerous hunting grounds, cultural-historical monuments, different folklores, interesting galleries and museums, plain landscapes with a lot of greenery, big rivers, canals and lakes, sandy terrain Deliblatska Peščara ("the European Sahara"), etc.
In the last few years, Exit
Exit(s) may refer to:
Architecture and engineering
* Door
* Portal (architecture), an opening in the walls of a structure
* Emergency exit
* Overwing exit, a type of emergency exit on an airplane
* Exit ramp, a feature of a road interchange
A ...
has been a popular music festival.
See also
* Vojvodina Autonomist Movement * RinflajšReferences
External links
Government of the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina
Assembly of the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina
Provincial Secretariat for Regional and International Cooperation
Tourism organization of Vojvodina
* Atlas of Vojvodina (Wikimedia Commons)
Statistical information about municipalities of Vojvodina
''The encyclopedia of Vojvodina''
{{Authority control Autonomous provinces of Serbia Statistical regions of Serbia States and territories established in 1944 Autonomous provinces Historical regions in Serbia Autonomous regions Countries and territories where Serbian is an official language Countries and territories where Romanian is an official language Countries and territories where Hungarian is an official language Countries and territories where Croatian is an official language Regions of Europe with multiple official languages 1944 establishments in Yugoslavia Rusyn communities