Victorian Railways N Class on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The N class is a
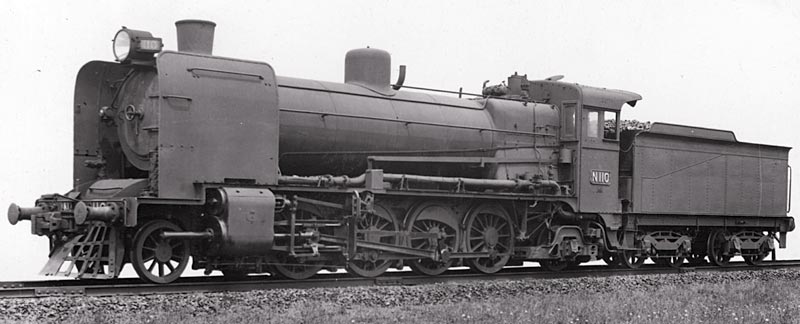 In 1927, class leader N 110 was equipped with a two-cylinder Franklin
In 1927, class leader N 110 was equipped with a two-cylinder Franklin
 Despite the relatively large number of N class locomotives built, all but one of the 73 locomotives remaining on the VR after 1951 were scrapped.
N 432, the last of the group of three N locomotives built by Newport Workshops in 1951, was withdrawn from service in 1966 after a service life of just . It is preserved at the
Despite the relatively large number of N class locomotives built, all but one of the 73 locomotives remaining on the VR after 1951 were scrapped.
N 432, the last of the group of three N locomotives built by Newport Workshops in 1951, was withdrawn from service in 1966 after a service life of just . It is preserved at the
victorianrailways.net N class locomotive page
Details and further photographs of N class locomotives
A photographic essay of the ARHS "Farewell N class" special hauled by N 468 and N 475 in October 1966 {{DEFAULTSORT:Victorian Railways N Class 1925 2-8-2 locomotives 1′D1′ steam locomotives Railway locomotives introduced in 1925 Preserved steam locomotives of Australia Broad gauge locomotives in Australia N class 1925 Newport Workshops locomotives NBL locomotives Freight locomotives
branch line
A branch line is a secondary railway line which branches off a more important through route, usually a main line. A very short branch line may be called a spur line. Branch lines may serve one or more industries, or a city or town not located ...
steam locomotive
A steam locomotive is a locomotive that provides the force to move itself and other vehicles by means of the expansion of steam. It is fuelled by burning combustible material (usually coal, Fuel oil, oil or, rarely, Wood fuel, wood) to heat ...
that ran on the Victorian Railways
The Victorian Railways (VR), trading from 1974 as VicRail, was the state-owned operator of most rail transport in the Australian state of Victoria from 1859 to 1983. The first railways in Victoria were private companies, but when these companie ...
(VR) from 1925 to 1966. A development of the successful K class 2-8-0
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle, usually in a leading truck, eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles, and no trailing wheels. ...
, it was the first VR locomotive class designed for possible conversion
Conversion or convert may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
* ''The Convert'', a 2023 film produced by Jump Film & Television and Brouhaha Entertainment
* "Conversion" (''Doctor Who'' audio), an episode of the audio drama ''Cyberman''
* ...
from to .
History
In 1923, in response to the recommendations made by the 1921 Royal Commission on the matter of uniform railway gauge, the VR announced a policy that all new locomotive designs were to be capable ofconversion
Conversion or convert may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
* ''The Convert'', a 2023 film produced by Jump Film & Television and Brouhaha Entertainment
* "Conversion" (''Doctor Who'' audio), an episode of the audio drama ''Cyberman''
* ...
from broad to standard gauge.Pearce et al., p. 12 The rationale was that the task of converting VR from broad to standard gauge at a future date would be far easier if existing locomotives and rolling stock could be easily modified for standard gauge operation, rather than requiring expensive re-engineering or replacement.
The K class 2-8-0, built by the VR in 1922-23, was a success, but it was engineered for broad gauge operation only, having a firebox mounted between frames, so it was not readily gauge convertible. So when additional branch line locomotives were required, the VR produced a 2-8-2
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle, usually in a leading truck, eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles and two trailing wh ...
"Mikado" variant of the K, the first 2-8-2
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle, usually in a leading truck, eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles and two trailing wh ...
tender engine in Australia. It retained the same wheels, cylinders, motion, and much of the frame of the K, but featured a longer boiler with a wider, larger grate, mounted above the frames and supported by a trailing truck. That enabled possible gauge conversion without radical re-engineering of the frames and grate.
Despite those design features, no N class locomotive ever ran on standard gauge. By the time the standard gauge Albury
Albury (; ) is a major regional city that is located in the Murray River, Murray region of New South Wales, Australia. It is part of the twin city of Albury–Wodonga, Albury-Wodonga and is located on the Hume Highway and the northern side of ...
to Melbourne
Melbourne ( , ; Boonwurrung language, Boonwurrung/ or ) is the List of Australian capital cities, capital and List of cities in Australia by population, most populous city of the States and territories of Australia, Australian state of Victori ...
mainline opened in 1962, alongside the existing broad gauge line, steam locomotives were rapidly being withdrawn from service. Large-scale standardisation of Australia's broad gauge rail network did not get under way until 1995, nearly thirty years after the withdrawal of the N class.
Production
Twenty N class locomotives were built byNewport Workshops
The Newport Railway Workshops is a facility in the Melbourne suburb of Newport, Victoria, Newport, Australia, that builds, maintains and refurbishes Rolling stock, railway rollingstock. It is located between the Williamstown railway line, Willia ...
between 1925 and 1928. A second batch of ten locomotives followed in 1930 and 1931. They went into service with road numbers N 110–139.
A third batch of fifty locomotives was built in 1949-1950 by North British Locomotive Company
The North British Locomotive Company (NBL, NB Loco or North British) was created in 1903 through the merger of three Glasgow locomotive manufacturing companies; Sharp, Stewart and Company (Atlas Works), Neilson, Reid and Company (Hyde Park W ...
, as part of Operation Phoenix, the post-war rebuilding of Victorian Railways. A fourth batch of twenty N class, of a modified design, was also ordered from Newport Workshops. At that time, the class was renumbered, with numbers 400-429 assigned to the pre-war Newport locomotives, 450-499 assigned to the North British locomotives, and 430-449 reserved for the post-war Newport locomotives. However, production of the fourth batch ceased in 1951, after only three had been built, because the VR opted to order more of a new design of 2-8-0 branch line locomotive, the J class.
The VR sold ten of the North British-built N class locomotives (461, 465, 471, 474, 477, 485, 490, 491, 494 and 495) to the South Australian Railways
South Australian Railways (SAR) was the organisation through which the Government of South Australia built and operated railways in South Australia from 1854 until March 1978, when its non-urban railways were incorporated into Australian Natio ...
, which was experiencing a severe motive power shortage. They became that system's 750 class. Many of those locomotives had only run a few days in VR service before being transferred to the SAR.
Thus although a total of 83 N class locomotives were built, only 73 were in VR service for a substantial period of time.
Regular service
The N class had anaxle load
The axle load of a wheeled vehicle is the total weight bearing on the roadway for all wheels connected to a given axle. Axle load is an important design consideration in the engineering of roadways and railways, as both are designed to tolerate a m ...
almost as light as that of the K and so were able to travel on much of VR light-lines network, which was built with rail
Rail or rails may refer to:
Rail transport
*Rail transport and related matters
*Railway track or railway lines, the running surface of a railway
Arts and media Film
* ''Rails'' (film), a 1929 Italian film by Mario Camerini
* ''Rail'' (1967 fil ...
. However, the N class was more limited in area of operation than the K, because its wheelbase
In both road and rail vehicles, the wheelbase is the horizontal distance between the centers of the front and rear wheels. For road vehicles with more than two axles (e.g. some trucks), the wheelbase is the distance between the steering (front ...
was too long for the turntables
A phonograph, later called a gramophone, and since the 1940s a record player, or more recently a turntable, is a device for the mechanical and analogue reproduction of sound. The sound vibration Waveform, waveforms are recorded as correspond ...
used on many branch lines.
Notwithstanding the limitation of their longer wheelbase, the locomotives were widely used on both branch line and main line goods services. Later in their life, N class locomotives were a common sight assisting other locomotives on heavy wheat trains heading for the ports of Geelong
Geelong ( ) (Wathawurrung language, Wathawurrung: ''Djilang''/''Djalang'') is a port city in Victoria, Australia, located at the eastern end of Corio Bay (the smaller western portion of Port Phillip Bay) and the left bank of Barwon River (Victo ...
or Portland
Portland most commonly refers to:
*Portland, Oregon, the most populous city in the U.S. state of Oregon
*Portland, Maine, the most populous city in the U.S. state of Maine
*Isle of Portland, a tied island in the English Channel
Portland may also r ...
, or shunting in yards such as at Ararat.
A later highlight in the operating life of the class was the assignment of Newport-built N 430 to haul the special ''Centenary-Jubilee Train'' in 1951, marking the centenary of the establishment of the Colony of Victoria and the jubilee of the establishment of the Commonwealth of Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and numerous smaller islands. It has a total area of , making it the sixth-largest country in ...
. That special train, containing valuable artworks and manuscripts from the National Gallery of Victoria
The National Gallery of Victoria, popularly known as the NGV, is an art museum in Melbourne, Victoria (state), Victoria, Australia. Founded in 1861, it is Australia's oldest and list of most visited art museums in the world, most visited art mu ...
, as well as Commonwealth and Victorian Government displays, consisted of N 430 plus eleven coaches and a van, painted in a special green and gold livery. It travelled throughout Victoria from 1 February to 30 June 1951, visiting 168 stations and attracting 548,000 people to inspect its onboard exhibits.
The ten N class locomotives sold to the South Australian Railways saw service on lightly built lines branching from Tailem Bend
Tailem Bend (locally, "Tailem") is a rural town in South Australia, south-east of the state capital of Adelaide. It is located on the lower reaches of the River Murray, near where the river flows into Lake Alexandrina (South Australia), Lake Al ...
into the Murray Mallee
The Murray Mallee is a cereal, grain-growing and sheep-farming area in the east of the Australian state of South Australia. The name is not formally designated but is widely used to refer to an area of approximately bounded by the Murray Rive ...
. They were unpopular with crews owing to their cabs being more cramped than other SAR locomotives.
Design improvements
 In 1927, class leader N 110 was equipped with a two-cylinder Franklin
In 1927, class leader N 110 was equipped with a two-cylinder Franklin booster engine
A locomotive booster for steam locomotives is a small supplementary two-cylinder steam engine back-gear-connected to the trailing truck axle on the locomotive or one of the trucks on the tender. It was invented in 1918 by Howard L. Ingersoll, ...
which drove the trailing truck axle. Based on the success of that device, the VR built all but two of the much larger X class 2-8-2
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle, usually in a leading truck, eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles and two trailing wh ...
s with booster engines. The VR also modified the design of the Delta trailing truck on the second (1930-31 built) batch of N class locomotives to enable easy retrofitting of booster engines. Despite that, no further boosters were fitted and, in 1945, the booster from N 110 was removed and fitted to one of the two non-booster-equipped X class locomotives.
In 1936, class leader N 110 was again selected to test new features, this time a series of design changes for improved drafting and reduced cylinder back pressure, referred to as "modified front end", which had already been successfully applied to the C class locomotive. The performance of N 110 was dramatically improved, and all the original thirty N class locomotives were similarly equipped. The most visible change resulting from those enhancements was that their original cast iron funnels were replaced by a less ornate "flowerpot" funnel. They also received other improvements during that period, such as the fitting of cross-compound air compressors and smoke deflectors
Smoke deflectors, sometimes called "blinkers" in the UK because of their strong resemblance to the Blinkers (horse tack), blinkers used on horses, and "elephant ears" in US railway slang, are vertical plates attached to each side of the smok ...
.
The post-war N class locomotives had a revised boiler design featuring a combustion chamber
A combustion chamber is part of an internal combustion engine in which the air–fuel ratio, fuel/air mix is burned. For steam engines, the term has also been used for an extension of the Firebox (steam engine), firebox which is used to allow a mo ...
firebox and thermic syphon
Thermic siphons (alt. thermic syphons) are Heat-exchanger, heat-exchanging elements in the Firebox (steam engine), firebox or Combustion chamber#Steam engine, combustion chamber of some steam boiler and steam locomotive designs. As they are dire ...
s. The final batch of three Newport-built locomotives had a further evolution of the design, with German "Witte"-style smoke deflectors, and boxpok
A Boxpok is a steam locomotive wheel that gains its strength through being made of a number of box sections rather than having traditional solid spokes (the name is a variation on "box-spoke"). Being hollow, they allow better counterbalancing a ...
wheels.
With industrial action in the late 1940s threatening black coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other Chemical element, elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal i ...
supplies, the VR began to convert the class to burn fuel oil
Fuel oil is any of various fractions obtained from the distillation of petroleum (crude oil). Such oils include distillates (the lighter fractions) and residues (the heavier fractions). Fuel oils include heavy fuel oil (bunker fuel), marine f ...
, commencing with N 460 in September 1951. However, only 36 conversions were completed before the program was cancelled in 1956, following the arrival of large numbers of diesel electric locomotive
A diesel locomotive is a type of railway locomotive in which the power source is a diesel engine. Several types of diesel locomotives have been developed, differing mainly in the means by which mechanical power is conveyed to the driving whee ...
s.
Demise
The introduction of the T classdiesel electric locomotive
A diesel locomotive is a type of railway locomotive in which the power source is a diesel engine. Several types of diesel locomotives have been developed, differing mainly in the means by which mechanical power is conveyed to the driving whee ...
on VR's branch lines from 1955 onwards, led to progressive retirement of the N class. Many were put into storage, to be used only for seasonal grain traffic. Wholesale withdrawals occurred during 1965 and 1966. The final run of the class was in October 1966, when N 468 and N 475 hauled an Australian Railway Historical Society
The Australian Railway Historical Society (ARHS) has been a railway organisation concerned with history and preservation of railway heritage at a national level.
It has had divisions in every state and the Australian Capital Territory, althou ...
special passenger train.
In South Australia, the new 830 class diesel electrics began to displace branch line steam power. Most of the 750 class had been withdrawn by 1962, and locomotive 752 steamed for the last time in November 1964.
Accidents and incidents
* At around midnight on January 15, 1966, N class #N476 was at the Ararat Locomotive Depot when J-class #J503 had become a runaway and rear-ended the N476 causing the locomotive to crash through the shed wall of the depot. N476 was damaged beyond repair and was scrapped after the wreck.Preservation
Newport Railway Museum
The Newport Railway Museum is located on Champion Road, Newport, Victoria, near the North Williamstown railway station, North Williamstown station.
History
The museum opened on 10 November 1962, after the Australian Railway Historical Society (A ...
. As well as its historical value as the only remaining N class locomotive, N 432 is also notable for being the last steam locomotive built by the VR Newport Workshops.
In addition to N 432, one of the ten locomotives built by the North British Locomotive Co. and sold to the SAR also remains. No. 752 (originally VR N 477), withdrawn after a service life of , is preserved at the National Railway Museum, Port Adelaide
The National Railway Museum, Port Adelaide, South Australia is the largest under-cover railway museum in Australia. More than 100 major exhibits, mainly from the South Australian Railways (SAR) and Commonwealth Railways and their successor, ...
.
A preservation group is engaged in a project to construct a Victorian Railways N class. A feasibility study was conducted for the N441 Steam Locomotive Project to investigate the viability of converting a K class frame into that of a first-series Victorian Railways N class, using the frames and wheels of locomotive K 154, together with one of the remaining spare N class boilers, and constructing a trailing axle
On a steam locomotive, a trailing wheel or trailing axle is generally an unpowered wheel or axle ( wheelset) located behind the driving wheels. The axle of the trailing wheels is usually located in a trailing truck. On some large locomotives, ...
with components acquired from a number of state heritage assets.
References
Further reading
* Dee et al., ''Power Parade'', VicRail Public Relations Division, Melbourne, 1981, * Pearce et al., ''North Williamstown Railway Museum'', ARHS, Melbourne, 1980,External links
victorianrailways.net N class locomotive page
Details and further photographs of N class locomotives
A photographic essay of the ARHS "Farewell N class" special hauled by N 468 and N 475 in October 1966 {{DEFAULTSORT:Victorian Railways N Class 1925 2-8-2 locomotives 1′D1′ steam locomotives Railway locomotives introduced in 1925 Preserved steam locomotives of Australia Broad gauge locomotives in Australia N class 1925 Newport Workshops locomotives NBL locomotives Freight locomotives