Vertebral Artery Dissection on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Vertebral artery dissection (VAD) is a flap-like tear of the inner lining of the
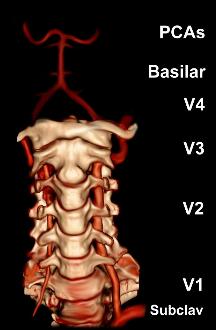 The vertebral arteries arise from the subclavian artery, and run through the transverse foramen of the upper six vertebrae of the neck. After exiting at the level of the first cervical vertebra, its course changes from vertical to horizontal, and then enters the
The vertebral arteries arise from the subclavian artery, and run through the transverse foramen of the upper six vertebrae of the neck. After exiting at the level of the first cervical vertebra, its course changes from vertical to horizontal, and then enters the
 Various diagnostic modalities exist to demonstrate blood flow or absence thereof in the vertebral arteries. The
Various diagnostic modalities exist to demonstrate blood flow or absence thereof in the vertebral arteries. The
 From analysis of the existing small treatment trials of cervical artery dissection (carotid and vertebral) it appears that
From analysis of the existing small treatment trials of cervical artery dissection (carotid and vertebral) it appears that
Cervical Artery Dissections and Ischemic Stroke Patients
international research collaboration into cervical artery dissection
vertebral artery
The vertebral arteries are major artery, arteries of the neck. Typically, the vertebral arteries originate from the subclavian arteries. Each vessel courses superiorly along each side of the neck, merging within the skull to form the single, m ...
, which is located in the neck and supplies blood to the brain
The brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head (cephalization), usually near organs for ...
. After the tear, blood enters the arterial wall and forms a blood clot
A thrombus ( thrombi) is a solid or semisolid aggregate from constituents of the blood (platelets, fibrin, red blood cells, white blood cells) within the circulatory system during life. A blood clot is the final product of the blood coagulatio ...
, thickening the artery wall and often impeding blood flow. The symptoms of vertebral artery dissection include head and neck pain and intermittent or permanent stroke symptoms such as difficulty speaking, impaired coordination, and visual loss. It is usually diagnosed with a contrast-enhanced CT or MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and rad ...
scan.
Vertebral dissection may occur after physical trauma
Injury is physiology, physiological damage to the living tissue of any organism, whether Injury in humans, in humans, Injury in animals, in other animals, or Injury in plants, in plants.
Injuries can be caused in many ways, including mechanic ...
to the neck, such as a blunt injury (e.g. traffic collision
A traffic collision, also known as a motor vehicle collision, or car crash, occurs when a vehicle collides with another vehicle, pedestrian, animal, road debris, or other moving or stationary obstruction, such as a tree, pole or building. Tr ...
) or strangulation
Strangling or strangulation is compression of the neck that may lead to unconsciousness or death by causing an increasingly hypoxic state in the brain by restricting the flow of oxygen through the trachea. Fatal strangulation typically occurs ...
, or after sudden neck movements (e.g. coughing), but may also happen spontaneously. 1–4% of spontaneous cases have a clear underlying connective tissue disorder affecting the blood vessels. Treatment is usually with either antiplatelet drug
An antiplatelet drug (antiaggregant), also known as a platelet agglutination inhibitor or platelet aggregation inhibitor, is a member of a class of pharmaceuticals that decrease platelet aggregation and inhibit thrombus formation. They are effectiv ...
s such as aspirin
Aspirin () is the genericized trademark for acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to reduce pain, fever, and inflammation, and as an antithrombotic. Specific inflammatory conditions that aspirin is ...
or with anticoagulant
An anticoagulant, commonly known as a blood thinner, is a chemical substance that prevents or reduces the coagulation of blood, prolonging the clotting time. Some occur naturally in blood-eating animals, such as leeches and mosquitoes, which ...
s such as heparin
Heparin, also known as unfractionated heparin (UFH), is a medication and naturally occurring glycosaminoglycan. Heparin is a blood anticoagulant that increases the activity of antithrombin. It is used in the treatment of myocardial infarction, ...
or warfarin
Warfarin, sold under the brand name Coumadin among others. It is used as an anticoagulant, anticoagulant medication. It is commonly used to prevent deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism, and to protect against stroke in people who ha ...
.
Vertebral artery dissection is less common than carotid artery dissection (dissection of the large arteries in the front of the neck). The two conditions together account for 10–25% of non-hemorrhagic strokes in young and middle-aged people. Over 75% recover completely or with minimal impact on functioning, with the remainder having more severe disability and a very small proportion (about 2%) dying from complications. It was first described in the 1970s by the Canadian neurologist C. Miller Fisher.
Classification
Vertebral artery dissection is one of the two types of cervical artery dissection. The other type, carotid artery dissection, involves the carotid arteries. Vertebral artery dissection is further classified as being either traumatic (caused by mechanical trauma to the neck) or spontaneous, and it may also be classified by the part of the artery involved: extracranial (the part outside the skull) and intracranial (the part inside the skull).Signs and symptoms
Head pain occurs in 50–75% of all cases of vertebral artery dissection. It tends to be located at the back of the head, either on the affected side or in the middle, and develops gradually. It is either dull or pressure-like in character or throbbing. About half of those with VAD consider the headache distinct, while the remainder have had a similar headache before. It is suspected that VAD with headache as the only symptom is fairly common; 8% of all cases of vertebral and carotid dissection are diagnosed on the basis of pain alone. Obstruction of blood flow through the affected vessel may lead to dysfunction of part of the brain supplied by the artery. This happens in 77–96% of cases. This may be temporary (" transient ischemic attack") in 10–16% of cases, but many (67–85% of cases) end up with a permanent deficit or a stroke. The vertebral artery supplies the part of the brain that lies in the posterior fossa of the skull, and this type of stroke is therefore called a posterior circulation infarct. Problems may include difficulty speaking or swallowing ( lateral medullary syndrome); this occurs in less than a fifth of cases and occurs due to dysfunction of thebrainstem
The brainstem (or brain stem) is the posterior stalk-like part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. In the human brain the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is conti ...
. Others may experience unsteadiness or lack of coordination due to involvement of the cerebellum
The cerebellum (: cerebella or cerebellums; Latin for 'little brain') is a major feature of the hindbrain of all vertebrates. Although usually smaller than the cerebrum, in some animals such as the mormyrid fishes it may be as large as it or eve ...
, and still others may develop visual loss ( on one side of the visual field) due to involvement of the visual cortex
The visual cortex of the brain is the area of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information. It is located in the occipital lobe. Sensory input originating from the eyes travels through the lateral geniculate nucleus in the thalam ...
in the occipital lobe
The occipital lobe is one of the four Lobes of the brain, major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The name derives from its position at the back of the head, from the Latin , 'behind', and , 'head'.
The occipital lobe is the ...
. In the event of involvement of the sympathetic tracts in the brainstem, a partial Horner's syndrome may develop; this is the combination of a drooping eyelid, constricted pupil, and an apparently sunken eye on one side of the face.
If the dissection of the artery extends to the part of the artery that lies inside the skull, subarachnoid hemorrhage
Subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) is bleeding into the subarachnoid space—the area between the arachnoid (brain), arachnoid membrane and the pia mater surrounding the human brain, brain. Symptoms may include a thunderclap headache, severe heada ...
may occur (1% of cases). This arises due to rupture of the artery and accumulation of blood in the subarachnoid space. It may be characterized by a different, usually severe headache; it may also cause a range of additional neurological symptoms.
13–16% of all people with vertebral or carotid dissection have dissection in another cervical artery. It is therefore possible for the symptoms to occur on both sides, or for symptoms of carotid artery dissection to occur at the same time as those of vertebral artery dissection. Some give a figure of multiple vessel dissection as high as 30%.
Causes
The causes of vertebral artery dissection can be grouped under two main categories, spontaneous and traumatic.Spontaneous
Spontaneous cases are considered to be caused by intrinsic factors that weaken the arterial wall. Only a very small proportion (1–4%) have a clear underlying connective tissue disorder, such as Ehlers–Danlos syndrome type 4 and, more rarely,Marfan syndrome
Marfan syndrome (MFS) is a multi-systemic genetic disorder that affects the connective tissue. Those with the condition tend to be tall and thin, with dolichostenomelia, long arms, legs, Arachnodactyly, fingers, and toes. They also typically ha ...
. However, ultrastructural abnormalities of the dermal connective tissue components are discernible in two out of three patients with spontaneous dissection. Ehlers–Danlos syndrome type 4, caused by mutations of the ''COL3A'' gene, leads to defective production of the collagen, type III, alpha 1 protein and causes skin fragility as well as weakness of the walls of arteries and internal organs. Marfan syndrome results from mutations in the '' FBN1'' gene, defective production of the protein fibrillin-1, and a number of physical abnormalities including aneurysm of the aortic root.
There have also been reports in other genetic conditions, such as osteogenesis imperfecta type 1, autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) is one of the most common, life-threatening Genetic disorder, inherited human disorders and the most common hereditary kidney disease. It is associated with large interfamilial and intrafamilia ...
and pseudoxanthoma elasticum, α1 antitrypsin deficiency and hereditary hemochromatosis, but evidence for these associations is weaker. Genetic studies in other connective tissue-related genes have mostly yielded negative results. Other abnormalities to the blood vessels, such as fibromuscular dysplasia, have been reported in a proportion of cases. Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is a pattern of the disease arteriosclerosis, characterized by development of abnormalities called lesions in walls of arteries. This is a chronic inflammatory disease involving many different cell types and is driven by eleva ...
does not appear to increase the risk.
There have been numerous reports of associated risk factors for vertebral artery dissection; many of these reports suffer from methodological
In its most common sense, methodology is the study of research methods. However, the term can also refer to the methods themselves or to the philosophical discussion of associated background assumptions. A method is a structured procedure for bri ...
weaknesses, such as selection bias
Selection bias is the bias introduced by the selection of individuals, groups, or data for analysis in such a way that proper randomization is not achieved, thereby failing to ensure that the sample obtained is representative of the population inte ...
. Elevated homocysteine levels, often due to mutations in the '' MTHFR'' gene, appear to increase the risk of vertebral artery dissection. People with an aneurysm
An aneurysm is an outward :wikt:bulge, bulging, likened to a bubble or balloon, caused by a localized, abnormal, weak spot on a blood vessel wall. Aneurysms may be a result of a hereditary condition or an acquired disease. Aneurysms can also b ...
of the aortic root and people with a history of migraine
Migraine (, ) is a complex neurological disorder characterized by episodes of moderate-to-severe headache, most often unilateral and generally associated with nausea, and light and sound sensitivity. Other characterizing symptoms may includ ...
may be predisposed to vertebral artery dissection. Vascular tortuosity or redundancy in young patients is associated with an increased risk of spontaneous dissection.
Traumatic
Traumatic vertebral dissection may follow blunt trauma to the neck, such as in atraffic collision
A traffic collision, also known as a motor vehicle collision, or car crash, occurs when a vehicle collides with another vehicle, pedestrian, animal, road debris, or other moving or stationary obstruction, such as a tree, pole or building. Tr ...
, direct blow to the neck, strangulation
Strangling or strangulation is compression of the neck that may lead to unconsciousness or death by causing an increasingly hypoxic state in the brain by restricting the flow of oxygen through the trachea. Fatal strangulation typically occurs ...
, or whiplash injury. 1–2% of those with major trauma may have an injury to the carotid or vertebral arteries. In many cases of vertebral dissection, people report recent very mild trauma to the neck or sudden neck movements, e.g. in the context of playing sports. Others report a recent infection, particularly respiratory tract infections associated with cough
A cough is a sudden expulsion of air through the large breathing passages which can help clear them of fluids, irritants, foreign particles and Microorganism, microbes. As a protective reflex, coughing can be repetitive with the cough reflex fol ...
ing. Trauma has been reported to have occurred within a month of dissection in 40% with nearly 90% of the traumas being minor. It has been difficult to prove the association of vertebral artery dissection with mild trauma and infections statistically. It is likely that many "spontaneous" cases may in fact have been caused by such relatively minor insults in someone predisposed by other structural problems to the vessels. A more likely theory, also as yet unproven, is that the low-energy traumatic dissections are actually spontaneous dissections brought to medical attention by the onset of neurological symptoms. These neurological events represent embolic phenomena due to loosening or breakdown of the clot at the site of the dissection, which can be triggered by low energy trauma or even occur spontaneously. The fragments travel within the arterial system downstream to the brain to cause stroke or stroke-like symptoms.
Vertebral artery dissection has also been reported in association with some forms of neck manipulation. There is significant controversy about the level of risk of stroke from neck manipulation. It may be that manipulation can cause dissection, or it may be that the dissection is already present in some people who seek manipulative treatment. At this time, conclusive evidence does not exist to support either a strong association between neck manipulation and stroke, or no association. However, the two most authoritative articles on the subject, recent literature reviews and analyses, conclude that although there exists an association between ''stroke'' from vertebral artery dissection and chiropractic adjustment, there is insufficient evidence to indicate that the adjustment ''caused'' the dissection. A recent meta-analysis of the published data on the topic also looked to apply Hill's criteria for assigning causation in biological systems to the relationship between chiropractic adjustment and cervical artery dissection, finding that the relationship did not fulfill the required criteria for causality.
Mechanism
 The vertebral arteries arise from the subclavian artery, and run through the transverse foramen of the upper six vertebrae of the neck. After exiting at the level of the first cervical vertebra, its course changes from vertical to horizontal, and then enters the
The vertebral arteries arise from the subclavian artery, and run through the transverse foramen of the upper six vertebrae of the neck. After exiting at the level of the first cervical vertebra, its course changes from vertical to horizontal, and then enters the skull
The skull, or cranium, is typically a bony enclosure around the brain of a vertebrate. In some fish, and amphibians, the skull is of cartilage. The skull is at the head end of the vertebrate.
In the human, the skull comprises two prominent ...
through the foramen magnum
The foramen magnum () is a large, oval-shaped opening in the occipital bone of the skull. It is one of the several oval or circular openings (foramina) in the base of the skull. The spinal cord, an extension of the medulla oblongata, passes thro ...
. Inside the skull, the arteries merge to form the basilar artery
The basilar artery (U.K.: ; U.S.: ) is one of the arteries that supplies the brain with oxygen-rich blood.
The two vertebral arteries and the basilar artery are known as the vertebral basilar system, which supplies blood to the posterior part o ...
, which joins the circle of Willis
The circle of Willis (also called Willis' circle, loop of Willis, cerebral arterial circle, and Willis polygon) is a circulatory anastomosis that supplies blood to the brain and surrounding structures in reptiles, birds and mammals, including huma ...
. In total, three quarters of the artery are outside the skull; it has a high mobility in this area due to rotational movement in the neck and is therefore vulnerable to trauma. Most dissections happen at the level of the first and second vertebrae. The vertebral artery supplies a number of vital structures in the posterior cranial fossa
The posterior cranial fossa is the part of the cranial cavity located between the foramen magnum, and tentorium cerebelli. It is formed by the sphenoid bones, temporal bones, and occipital bone. It lodges the cerebellum, and parts of the brai ...
, such as the brainstem
The brainstem (or brain stem) is the posterior stalk-like part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. In the human brain the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is conti ...
, the cerebellum
The cerebellum (: cerebella or cerebellums; Latin for 'little brain') is a major feature of the hindbrain of all vertebrates. Although usually smaller than the cerebrum, in some animals such as the mormyrid fishes it may be as large as it or eve ...
and the occipital lobe
The occipital lobe is one of the four Lobes of the brain, major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The name derives from its position at the back of the head, from the Latin , 'behind', and , 'head'.
The occipital lobe is the ...
s. The brainstem harbors a number of vital functions (such as respiration) and controls the nerves of the face and neck. The cerebellum is part of the diffuse system that coordinates movement. Finally, the occipital lobes participate in the sense of vision.
Dissection occurs when blood accumulates in the wall of the blood vessel. This is most likely due to a tear in the tunica intima
The tunica intima (Neo-Latin "inner coat"), or intima for short, is the innermost tunica (biology), tunica (layer) of an artery or vein. It is made up of one layer of endothelium, endothelial cells (and macrophages in areas of disturbed blood flo ...
(the inner layer), allowing blood to enter the tunica media
The tunica media (Neo-Latin "middle coat"), or media for short, is the middle tunica (layer) of an artery or vein. It lies between the internal elastic lamina of the tunica intima on the inside and the tunica externa on the outside.
Artery
The ...
, although other lines of evidence have suggested that the blood may instead arise from the vasa vasorum
Vasa vasorum are networks of small blood vessels that supply the walls of large blood vessels, such as elastic arteries (e.g., the aorta) and large veins (e.g., the venae cavae).
The name derives . Occasionally, two different singular forms ar ...
, the small blood vessels that supply the outer layer of larger blood vessels. Various theories exist as to whether people who sustain carotid and vertebral artery dissection, even if they do not have a connective tissue disorder, have an underlying vulnerability. Biopsy samples of skin and other arteries has indicated that this might be a possibility, but no genetic defect in collagen
Collagen () is the main structural protein in the extracellular matrix of the connective tissues of many animals. It is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up 25% to 35% of protein content. Amino acids are bound together to form a trip ...
or elastin
Elastin is a protein encoded by the ''ELN'' gene in humans and several other animals. Elastin is a key component in the extracellular matrix of gnathostomes (jawed vertebrates). It is highly Elasticity (physics), elastic and present in connective ...
genes has been convincingly proven. Other studies have indicated inflammation
Inflammation (from ) is part of the biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function (Latin ''calor'', '' ...
of the blood vessels, as measured by highly sensitive C-reactive protein (hsCRP, a marker of inflammation) in the blood.
Once dissection has occurred, two mechanisms contribute to the development of stroke symptoms. Firstly, the flow through the blood vessel may be disrupted due to the accumulation of blood under the vessel wall, leading to ischemia
Ischemia or ischaemia is a restriction in blood supply to any tissue, muscle group, or organ of the body, causing a shortage of oxygen that is needed for cellular metabolism (to keep tissue alive). Ischemia is generally caused by problems ...
(insufficient blood supply). Secondly, irregularities in the vessel wall and turbulence increase the risk of thrombosis
Thrombosis () is the formation of a Thrombus, blood clot inside a blood vessel, obstructing the flow of blood through the circulatory system. When a blood vessel (a vein or an artery) is injured, the body uses platelets (thrombocytes) and fib ...
(the formation of blood clots) and embolism
An embolism is the lodging of an embolus, a blockage-causing piece of material, inside a blood vessel. The embolus may be a blood clot (thrombus), a fat globule (fat embolism), a bubble of air or other gas (air embolism, gas embolism), amniotic ...
(migration) of these clots of the brain. From various lines of evidence, it appears that thrombosis and embolism is the predominant problem.
Subarachnoid hemorrhage due to arterial rupture typically occurs if the dissection extends into the V4 section of the artery. This may be explained by the fact that the arterial wall is thinner and lacks a number of structural supports in this section.
Diagnosis
 Various diagnostic modalities exist to demonstrate blood flow or absence thereof in the vertebral arteries. The
Various diagnostic modalities exist to demonstrate blood flow or absence thereof in the vertebral arteries. The gold standard
A gold standard is a backed currency, monetary system in which the standard economics, economic unit of account is based on a fixed quantity of gold. The gold standard was the basis for the international monetary system from the 1870s to the ...
is cerebral angiography
Cerebral angiography is a form of angiography which provides images of blood vessels in and around the brain, thereby allowing detection of abnormalities such as arteriovenous malformations and aneurysms.
It was pioneered in 1927 by the Portugues ...
(with or without digital subtraction angiography). This involves puncture of a large artery (usually the femoral artery
The femoral artery is a large artery in the thigh and the main arterial supply to the thigh and leg. The femoral artery gives off the deep femoral artery and descends along the anteromedial part of the thigh in the femoral triangle. It enters ...
) and advancing an intravascular catheter through the aorta
The aorta ( ; : aortas or aortae) is the main and largest artery in the human body, originating from the Ventricle (heart), left ventricle of the heart, branching upwards immediately after, and extending down to the abdomen, where it splits at ...
towards the vertebral arteries. At that point, radiocontrast
Radiocontrast agents are substances used to enhance the visibility of internal structures in X-ray-based imaging techniques such as computed tomography (contrast CT), projectional radiography, and fluoroscopy. Radiocontrast agents are typically iod ...
is injected and its downstream flow captured on fluoroscopy
Fluoroscopy (), informally referred to as "fluoro", is an imaging technique that uses X-rays to obtain real-time moving images of the interior of an object. In its primary application of medical imaging, a fluoroscope () allows a surgeon to see t ...
(continuous X-ray imaging). The vessel may appear stenotic (narrowed, 41–75%), occluded (blocked, 18–49%), or as an aneurysm
An aneurysm is an outward :wikt:bulge, bulging, likened to a bubble or balloon, caused by a localized, abnormal, weak spot on a blood vessel wall. Aneurysms may be a result of a hereditary condition or an acquired disease. Aneurysms can also b ...
(area of dilation, 5–13%). The narrowing may be described as "rat's tail" or "string sign". Cerebral angiography is an invasive procedure, and it requires large volumes of radiocontrast that can cause complications such as kidney damage. Angiography also does not directly demonstrate the blood in the vessel wall, as opposed to more modern modalities. The only remaining use of angiography is when endovascular treatment is contemplated (see below).
More modern methods involve computed tomography
A computed tomography scan (CT scan), formerly called computed axial tomography scan (CAT scan), is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or ...
( CT angiography) and magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and ...
(MR angiography
Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) is a group of techniques based on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to image blood vessels. Magnetic resonance angiography is used to generate images of arteries (and less commonly veins) in order to evaluate ...
). They use smaller amounts of contrast and are not invasive. CT angiography and MR angiography are more or less equivalent when used to diagnose or exclude vertebral artery dissection. CTA has the advantage of showing certain abnormalities earlier, tends to be available outside office hours, and can be performed rapidly. When MR angiography is used, the best results are achieved in the '' T1'' setting using a protocol known as "fat suppression". Doppler ultrasound
Doppler ultrasonography is medical ultrasonography that employs the Doppler effect to perform imaging of the movement of tissues and body fluids (usually blood), and their relative velocity to the probe. By calculating the frequency shift of a ...
is less useful as it provides little information about the part of the artery close to the skull base and in the vertebral foramina, and any abnormality detected on ultrasound would still require confirmation with CT or MRI.
Treatment
Treatment is focused on reducing stroke episodes and damage from a distending artery. Four treatment modalities have been reported in the treatment of vertebral artery dissection. The two main treatments involve medication:anticoagulation
An anticoagulant, commonly known as a blood thinner, is a chemical substance that prevents or reduces the coagulation of blood, prolonging the clotting time. Some occur naturally in blood-eating animals, such as leeches and mosquitoes, which h ...
(using heparin
Heparin, also known as unfractionated heparin (UFH), is a medication and naturally occurring glycosaminoglycan. Heparin is a blood anticoagulant that increases the activity of antithrombin. It is used in the treatment of myocardial infarction, ...
and warfarin
Warfarin, sold under the brand name Coumadin among others. It is used as an anticoagulant, anticoagulant medication. It is commonly used to prevent deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism, and to protect against stroke in people who ha ...
) and antiplatelet drug
An antiplatelet drug (antiaggregant), also known as a platelet agglutination inhibitor or platelet aggregation inhibitor, is a member of a class of pharmaceuticals that decrease platelet aggregation and inhibit thrombus formation. They are effectiv ...
s (usually aspirin
Aspirin () is the genericized trademark for acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to reduce pain, fever, and inflammation, and as an antithrombotic. Specific inflammatory conditions that aspirin is ...
). More rarely, thrombolysis
Thrombolysis, also called fibrinolytic therapy, is the breakdown (lysis) of thrombus, blood clots formed in blood vessels, using medication. It is used in ST elevation myocardial infarction, stroke, and in cases of severe venous thromboembolism ( ...
(medication that dissolves blood clots) may be administered, and occasionally obstruction may be treated with angioplasty
Angioplasty, also known as balloon angioplasty and percutaneous transluminal angioplasty, is a minimally invasive procedure, minimally invasive endovascular surgery, endovascular Medical procedure, procedure used to widen narrowed or obstructe ...
and stent
In medicine, a stent is a tube usually constructed of a metallic alloy or a polymer. It is inserted into the Lumen (anatomy), lumen (hollow space) of an anatomic vessel or duct to keep the passageway open.
Stenting refers to the placement of ...
ing. No randomized controlled trial
A randomized controlled trial (or randomized control trial; RCT) is a form of scientific experiment used to control factors not under direct experimental control. Examples of RCTs are clinical trials that compare the effects of drugs, surgical ...
s have been performed to compare the different treatment modalities. Surgery
Surgery is a medical specialty that uses manual and instrumental techniques to diagnose or treat pathological conditions (e.g., trauma, disease, injury, malignancy), to alter bodily functions (e.g., malabsorption created by bariatric surgery s ...
is only used in exceptional cases.
Anticoagulation and aspirin
 From analysis of the existing small treatment trials of cervical artery dissection (carotid and vertebral) it appears that
From analysis of the existing small treatment trials of cervical artery dissection (carotid and vertebral) it appears that aspirin
Aspirin () is the genericized trademark for acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to reduce pain, fever, and inflammation, and as an antithrombotic. Specific inflammatory conditions that aspirin is ...
and anticoagulation (heparin
Heparin, also known as unfractionated heparin (UFH), is a medication and naturally occurring glycosaminoglycan. Heparin is a blood anticoagulant that increases the activity of antithrombin. It is used in the treatment of myocardial infarction, ...
followed by warfarin
Warfarin, sold under the brand name Coumadin among others. It is used as an anticoagulant, anticoagulant medication. It is commonly used to prevent deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism, and to protect against stroke in people who ha ...
) are equally effective in reducing the risk of further stroke or death. Anticoagulation is regarded as more powerful than antiplatelet therapy, but anticoagulants may increase the size of the hematoma and worsen obstruction of the affected artery. Anticoagulation may be relatively unsafe if a large stroke has already occurred, as hemorrhagic transformation is relatively common, and if the dissection extends into V4 (carrying a risk of subarachnoid hemorrhage). Anticoagulation may be appropriate if there is rapid blood flow (through a severely narrowed vessel) on transcranial doppler despite the use of aspirin, if there is a completely occluded vessel, if there are recurrent stroke-like episodes, or if free-floating blood clot is visible on scans. Warfarin is typically continued for 3–6 months, as during this time the flow through the artery usually improves, and most strokes happen within the first 6 months after the development of the dissection. Some regard 3 months as sufficient.
Professional guidelines in the UK recommend that patients with VA dissection should be enrolled in a clinical trial
Clinical trials are prospective biomedical or behavioral research studies on human subject research, human participants designed to answer specific questions about biomedical or behavioral interventions, including new treatments (such as novel v ...
comparing aspirin and anticoagulation if possible. American guidelines state that the benefit of anticoagulation is not currently established.
Thrombolysis, stenting and surgery
Thrombolysis, stenting and surgery are not used as widely as anticoagulation or antiplatelet drugs. These treatments are invasive, and are typically reserved for situations where symptoms worsen despite medical treatment, or where medical treatment may be unsafe (e.g. an unacceptable bleeding tendency). Thrombolysis is enzymatic destruction of blood clots. This is achieved by the administration of a drug (such asurokinase
Urokinase, also known as urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA), is a serine protease present in humans and other animals. The human urokinase protein was discovered, but not named, by McFarlane and Pilling in 1947. Urokinase was originally ...
or alteplase
Alteplase, sold under the brand name Activase among others, is a biosynthetic form of human tissue-type plasminogen activator (t-PA). It is a thrombolytic medication used to treat acute ischemic stroke, acute ST-elevation myocardial infarct ...
) that activates plasmin
Plasmin is an important enzyme () present in blood that degrades many blood plasma proteins, including fibrin thrombus, clots. The degradation of fibrin is termed fibrinolysis. In humans, the plasmin protein (in the zymogen form of plasminogen) i ...
, an enzyme that occurs naturally in the body and digests clots when activated. Thrombolysis is an accepted treatment for heart attacks
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow decreases or stops in one of the coronary arteries of the heart, causing infarction (tissue death) to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is retr ...
and stroke unrelated to dissection. In cervical artery dissection, only small case series are available. The thrombolytic drug is administered either intravenously
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutr ...
or during cerebral angiography through a catheter directly into the affected artery. The data indicates that thrombolysis is safe, but its place in the treatment of VAD is uncertain.
Stenting involves the catheterization of the affected artery during angiography, and the insertion of a mesh-like tube; this is known as " endovascular therapy" (inside the blood vessel). This may be performed to allow the blood to flow through a severely narrowed vessel, or to seal off an aneurysm. However, it is unclear whether the technical success of the procedure translates into improved outcomes, as in both cases the problem often resolves spontaneously over time. Stenting, as well as the insertion of coils by means of angiography, may be performed if there is an aneurysm and/or extension of the dissection into the V4 section of the artery.
Surgery carries a high risk of complications, and is typically only offered in case of inexorable deterioration or contraindications to any of the other treatments. Various arterial repair procedures have been described.
Prognosis
Prognosis of spontaneous cervical arterial dissection involves neurological and arterial results. The overall functional prognosis of individuals with stroke due to cervical artery dissection does not appear to vary from that of young people with stroke due to other causes. The rate of survival with good outcome (a modified Rankin score of 0–2) is generally about 75%, or possibly slightly better (85.7%) if antiplatelet drugs are used. In studies of anticoagulants and aspirin, the combined mortality with either treatment is 1.8–2.1%. After the initial episode, 2% may experience a further episode within the first month. After this, there is a 1% annual risk of recurrence. Those with highblood pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of Circulatory system, circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term ...
and dissections in multiple arteries may have a higher risk of recurrence. Further episodes of cervical artery dissection are more common in those who are younger, have a family history of cervical artery dissection, or have a diagnosis of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome or fibromuscular dysplasia.
Epidemiology
The annual incidence is about 1.1 per 100,000 annually in population studies from theUnited States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
and France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
. From 1994 to 2003, the incidence increased threefold; this has been attributed to the more widespread use of modern imaging modalities rather than a true increase. Similarly, those living in urban areas are more likely to receive appropriate investigations, accounting for increased rates of diagnosis in those dwelling in cities. It is suspected that a proportion of cases in people with mild symptoms remains undiagnosed.
There is controversy as to whether VAD is more common in men or in women; an aggregate of all studies shows that it is slightly higher incidence in men (56% versus 44%). Men are on average 37–44 years old at diagnosis, and women 34–44. While dissection of the carotid and vertebral arteries accounts for only 2% of strokes (which are usually caused by high blood pressure
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms itself. It is, however, a major ri ...
and other risk factors, and tend to occur in the elderly), they cause 10–25% of strokes in young and middle-aged people.
Dissecting aneurysms of the vertebral artery constitute 4% of all cerebral aneurysm
An intracranial aneurysm, also known as a cerebral aneurysm, is a Cerebrovascular disease, cerebrovascular disorder characterized by a localized dilation or ballooning of a blood vessel in the brain due to a weakness in the vessel wall. These a ...
s, and are hence a relatively rare but important cause of subarachnoid hemorrhage.
History
Spontaneous vertebral artery dissection was described in the 1970s. Prior to this, there had been isolated case reports about carotid dissection. In 1971, C. Miller Fisher, aCanadian
Canadians () are people identified with the country of Canada. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultural. For most Canadians, many (or all) of these connections exist and are collectively the source of their being ''C ...
neurologist
Neurology (from , "string, nerve" and the suffix -logia, "study of") is the branch of medicine dealing with the diagnosis and treatment of all categories of conditions and disease involving the nervous system, which comprises the brain, the ...
and stroke physician working at Massachusetts General Hospital
Massachusetts General Hospital (Mass General or MGH) is a teaching hospital located in the West End neighborhood of Boston, Massachusetts. It is the original and largest clinical education and research facility of Harvard Medical School/Harvar ...
, first noted the "string sign" abnormality in carotid arteries on cerebral angiograms of stroke patients, and subsequently discovered that the same abnormality could occur in the vertebral arteries. He reported the discovery in a paper in 1978.
Notable cases
Australian cricketerPhillip Hughes
Phillip Joel Hughes (30 November 1988 – 27 November 2014) was an Australian Test cricket, Test and One Day International (ODI) cricketer who played domestic cricket for South Australia cricket team, South Australia and Worcestershire County C ...
died on 27 November 2014 after developing a vertebral artery dissection as a result of being struck on the side of the neck by a cricket ball, while representing South Australia
South Australia (commonly abbreviated as SA) is a States and territories of Australia, state in the southern central part of Australia. With a total land area of , it is the fourth-largest of Australia's states and territories by area, which in ...
in a Sheffield Shield
The Sheffield Shield is the domestic first-class cricket competition of Australia. The tournament is contested between teams representing the six states of Australia. The Sheffield Shield is named after Henry Holroyd, 3rd Earl of Sheffield, Lor ...
match on 25 November 2014 at the Sydney Cricket Ground
The Sydney Cricket Ground (SCG) is a sports stadium in the Moore Park, New South Wales, Moore Park suburb of Sydney, New South Wales, Australia. It is used for Test cricket, Test, One Day International and Twenty20 cricket, as well as, Australi ...
. The short-pitched delivery bowled by NSW player Sean Abbott
Sean Anthony Abbott (born 29 February 1992) is an Australian international cricketer who represents the Australia national cricket team in ODI and T20I cricket as a bowling all-rounder who bats right-handed. He was a part of the Australian squa ...
struck Hughes on the base of the skull, just behind his left ear which caused a vertebral artery dissection complicated by subarachnoid hemorrhage
Subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) is bleeding into the subarachnoid space—the area between the arachnoid (brain), arachnoid membrane and the pia mater surrounding the human brain, brain. Symptoms may include a thunderclap headache, severe heada ...
.
References
External links
Cervical Artery Dissections and Ischemic Stroke Patients
international research collaboration into cervical artery dissection
See also
* Aortic dissection * Carotid artery dissection {{DEFAULTSORT:Vertebral Artery Dissection Vascular diseases Neurological disorders