Verisign Identity Protection on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A security token is a
A security token is a
 All tokens contain some secret information used to prove identity. There are four different ways in which this information can be used:
; Static password token: The device contains a password that is physically hidden (not visible to the possessor), but is transmitted for each authentication. This type is vulnerable to
All tokens contain some secret information used to prove identity. There are four different ways in which this information can be used:
; Static password token: The device contains a password that is physically hidden (not visible to the possessor), but is transmitted for each authentication. This type is vulnerable to
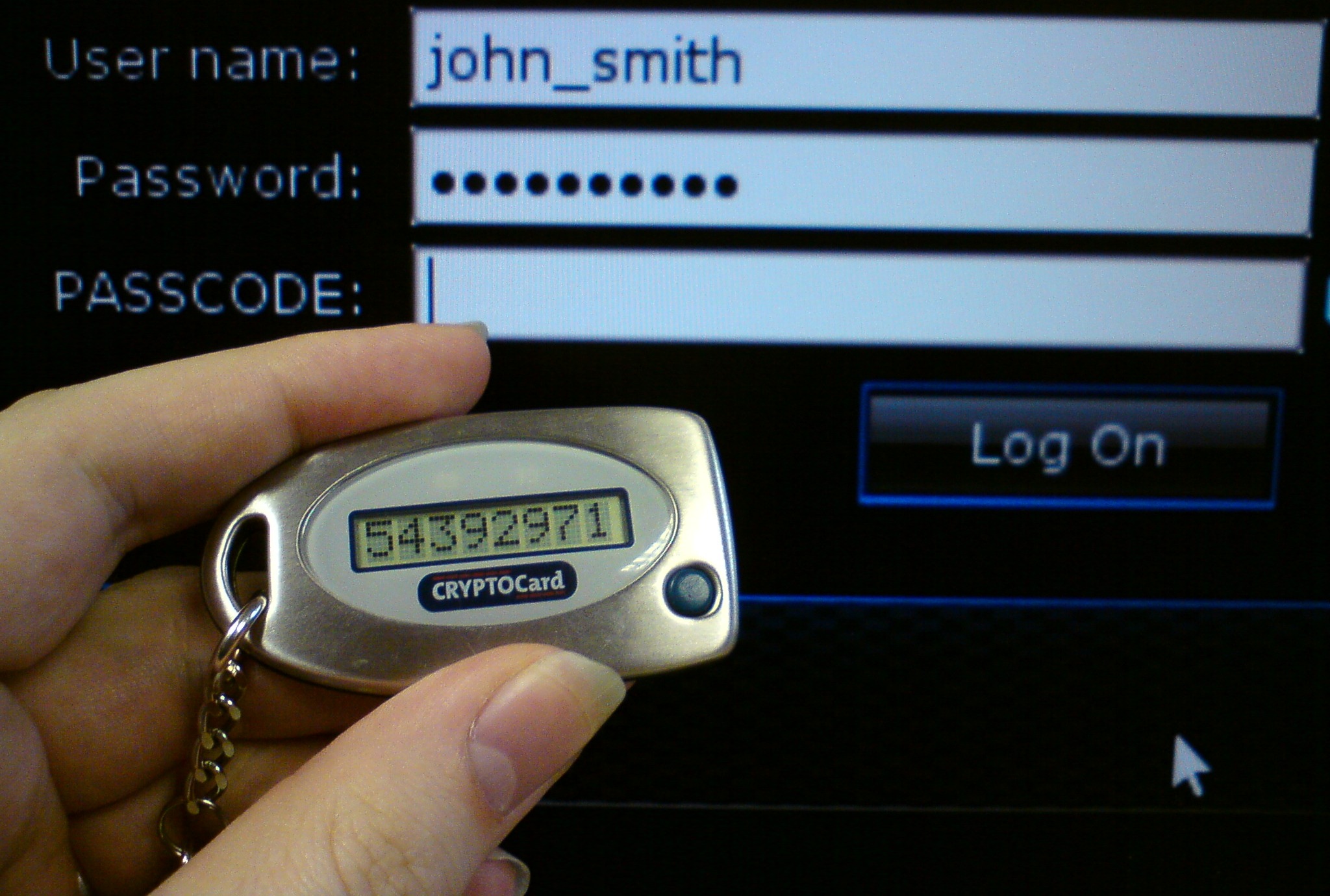 Disconnected tokens have neither a physical nor logical connection to the client computer. They typically do not require a special input device, and instead use a built-in screen to display the generated authentication data, which the user enters manually themselves via a
Disconnected tokens have neither a physical nor logical connection to the client computer. They typically do not require a special input device, and instead use a built-in screen to display the generated authentication data, which the user enters manually themselves via a
, usb.org
US Personal Identity Verification (PIV)
OATH Initiative for open authentication
{{DEFAULTSORT:Security Token Computer access control Authentication methods
 A security token is a
A security token is a peripheral device
A peripheral device, or simply peripheral, is an auxiliary hardware device that a computer uses to transfer information externally. A peripheral is a hardware component that is accessible to and controlled by a computer but is not a core compo ...
used to gain access to an electronically restricted resource. The token is used in addition to, or in place of, a password
A password, sometimes called a passcode, is secret data, typically a string of characters, usually used to confirm a user's identity. Traditionally, passwords were expected to be memorized, but the large number of password-protected services t ...
. Examples of security tokens include wireless key cards used to open locked doors, a banking token used as a digital authenticator for signing in to online banking
Online banking, also known as internet banking, virtual banking, web banking or home banking, is a system that enables customers of a bank or other financial institution to conduct a range of financial transactions through the financial institut ...
, or signing transactions such as wire transfers.
Security tokens can be used to store information such as passwords
A password, sometimes called a passcode, is secret data, typically a string of characters, usually used to confirm a user's identity. Traditionally, passwords were expected to be memorized, but the large number of password-protected services ...
, cryptographic key
A key in cryptography is a piece of information, usually a string of numbers or letters that are stored in a file, which, when processed through a cryptographic algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm () is a finite sequenc ...
s used to generate digital signatures, or biometric
Biometrics are body measurements and calculations related to human characteristics and features. Biometric authentication (or realistic authentication) is used in computer science as a form of identification and access control. It is also used t ...
data (such as fingerprints
A fingerprint is an impression left by the friction ridges of a human finger. The recovery of partial fingerprints from a crime scene is an important method of forensic science. Moisture and grease on a finger result in fingerprints on surf ...
). Some designs incorporate tamper resistant packaging, while others may include small keypad
A keypad is a block or pad of buttons set with an arrangement of digits, symbols, or alphabetical letters. Pads mostly containing numbers and used with computers are numeric keypads. Keypads are found on devices which require mainly numeric in ...
s to allow entry of a PIN or a simple button to start a generation routine with some display capability to show a generated key number. Connected tokens utilize a variety of interfaces including USB
Universal Serial Bus (USB) is an industry standard, developed by USB Implementers Forum (USB-IF), for digital data transmission and power delivery between many types of electronics. It specifies the architecture, in particular the physical ...
, near-field communication
Near-field communication (NFC) is a set of communication protocols that enables communication between two electronic devices over a distance of or less. NFC offers a low-speed connection through a simple setup that can be used for the boots ...
(NFC), radio-frequency identification
Radio-frequency identification (RFID) uses electromagnetic fields to automatically Automatic identification system, identify and Tracking system, track tags attached to objects. An RFID system consists of a tiny radio transponder called a tag, ...
(RFID), or Bluetooth
Bluetooth is a short-range wireless technology standard that is used for exchanging data between fixed and mobile devices over short distances and building personal area networks (PANs). In the most widely used mode, transmission power is li ...
. Some tokens have audio capabilities designed for those who are vision-impaired.
Password types
 All tokens contain some secret information used to prove identity. There are four different ways in which this information can be used:
; Static password token: The device contains a password that is physically hidden (not visible to the possessor), but is transmitted for each authentication. This type is vulnerable to
All tokens contain some secret information used to prove identity. There are four different ways in which this information can be used:
; Static password token: The device contains a password that is physically hidden (not visible to the possessor), but is transmitted for each authentication. This type is vulnerable to replay attack
A replay attack (also known as a repeat attack or playback attack) is a form of network attack in which valid data transmission is maliciously or fraudulently repeated or delayed. This is carried out either by the originator or by an adversary w ...
s.
; Synchronous dynamic password token: A timer is used to rotate through various combinations produced by a cryptographic algorithm
In cryptography, encryption (more specifically, encoding) is the process of transforming information in a way that, ideally, only authorized parties can decode. This process converts the original representation of the information, known as pla ...
. The token and the authentication server must have synchronized clocks.
; Asynchronous password token: A one-time password
A one-time password (OTP), also known as a one-time PIN, one-time passcode, one-time authorization code (OTAC) or dynamic password, is a password that is valid for only one login session or transaction, on a computer system or other digital dev ...
is generated without the use of a clock, either from a one-time pad
The one-time pad (OTP) is an encryption technique that cannot be Cryptanalysis, cracked in cryptography. It requires the use of a single-use pre-shared key that is larger than or equal to the size of the message being sent. In this technique, ...
or cryptographic algorithm.
; Challenge–response token: Using public key cryptography
Public-key cryptography, or asymmetric cryptography, is the field of cryptographic systems that use pairs of related keys. Each key pair consists of a public key and a corresponding private key. Key pairs are generated with cryptographic al ...
, it is possible to prove possession of a private key without revealing that key. The authentication server encrypts a challenge (typically a random number, or at least data with some random parts) with a public key; the device proves it possesses a copy of the matching private key by providing the decrypted challenge.
Time-synchronized, one-time passwords change constantly at a set time interval; e.g., once per minute. To do this, some sort of synchronization must exist between the client
Client(s) or The Client may refer to:
* Client (business)
* Client (computing), hardware or software that accesses a remote service on another computer
* Customer or client, a recipient of goods or services in return for monetary or other valuable ...
's token and the authentication server
Server may refer to:
Computing
*Server (computing), a computer program or a device that provides requested information for other programs or devices, called clients.
Role
* Waiting staff, those who work at a restaurant or a bar attending custome ...
. For disconnected tokens, this time-synchronization is done before the token is distributed to the client
Client(s) or The Client may refer to:
* Client (business)
* Client (computing), hardware or software that accesses a remote service on another computer
* Customer or client, a recipient of goods or services in return for monetary or other valuable ...
. Other token types do the synchronization when the token is inserted into an input device
In computing, an input device is a piece of equipment used to provide data and control signals to an information processing system, such as a computer or information appliance. Examples of input devices include keyboards, computer mice, scanne ...
. The main problem with time-synchronized tokens is that they can, over time, become unsynchronized. However, some such systems, such as RSA's SecurID, allow the user to re-synchronize the server with the token, sometimes by entering several consecutive passcodes. Most also cannot have replaceable batteries and only last up to 5 years before having to be replaced – so there is an additional cost.
Another type of one-time password uses a complex mathematical algorithm, such as a hash chain
A hash chain is the successive application of a cryptographic hash function to a piece of data. In computer security, a hash chain is a method used to produce many one-time keys from a single key or password. For non-repudiation, a hash functi ...
, to generate a series of one-time passwords from a secret shared key. Each password is unique, even when previous passwords are known. The open-source OATH
Traditionally, an oath (from Old English, Anglo-Saxon ', also a plight) is a utterance, statement of fact or a promise taken by a Sacred, sacrality as a sign of Truth, verity. A common legal substitute for those who object to making sacred oaths ...
algorithm is standardized; other algorithms are covered by US patent
A patent is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the legal right to exclude others from making, using, or selling an invention for a limited period of time in exchange for publishing an sufficiency of disclosure, enabling discl ...
s. Each password is observably unpredictable and independent of previous ones, whereby an adversary would be unable to guess what the next password may be, even with knowledge of all previous passwords.
Physical types
Tokens can containchips
''CHiPs'' is an American crime drama television series created by Rick Rosner and originally aired on NBC from September 15, 1977, to May 1, 1983. After the final first-run telecast on NBC in May 1983, the series went into reruns on Sundays fr ...
with functions varying from very simple to very complex, including multiple authentication methods.
The simplest security tokens do not need any connection to a computer
A computer is a machine that can be Computer programming, programmed to automatically Execution (computing), carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (''computation''). Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic set ...
. The tokens have a physical display; the authenticating user simply enters the displayed number to log in. Other tokens connect to the computer using wireless techniques, such as Bluetooth
Bluetooth is a short-range wireless technology standard that is used for exchanging data between fixed and mobile devices over short distances and building personal area networks (PANs). In the most widely used mode, transmission power is li ...
. These tokens transfer a key sequence to the local client or to a nearby access point.
Alternatively, another form of token that has been widely available for many years is a mobile device which communicates using an out-of-band channel (like voice, SMS
Short Message Service, commonly abbreviated as SMS, is a text messaging service component of most telephone, Internet and mobile device systems. It uses standardized communication protocols that let mobile phones exchange short text messages, t ...
, or USSD
Unstructured Supplementary Service Data (USSD), sometimes referred to as "quick codes" or "feature codes", is a communications protocol used by GSM cellular telephones to communicate with the mobile network operator's computers. USSD can be used ...
).
Still other tokens plug into the computer and may require a PIN. Depending on the type of the token, the computer
A computer is a machine that can be Computer programming, programmed to automatically Execution (computing), carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (''computation''). Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic set ...
OS will then either read the key from the token and perform a cryptographic operation on it, or ask the token's firmware to perform this operation.
A related application is the hardware dongle
A dongle is a small piece of computer hardware that connects to a port on another device to provide it with additional functionality, or enable a pass-through to such a device that adds functionality.
In computing, the term was initially synony ...
required by some computer programs to prove ownership of the software
Software consists of computer programs that instruct the Execution (computing), execution of a computer. Software also includes design documents and specifications.
The history of software is closely tied to the development of digital comput ...
. The dongle is placed in an input device
In computing, an input device is a piece of equipment used to provide data and control signals to an information processing system, such as a computer or information appliance. Examples of input devices include keyboards, computer mice, scanne ...
and the software
Software consists of computer programs that instruct the Execution (computing), execution of a computer. Software also includes design documents and specifications.
The history of software is closely tied to the development of digital comput ...
accesses the I/O device in question to authorize
Authorization or authorisation (see spelling differences), in information security, computer security and IAM (Identity and Access Management), is the function of specifying rights/privileges for accessing resources, in most cases through an a ...
the use of the software
Software consists of computer programs that instruct the Execution (computing), execution of a computer. Software also includes design documents and specifications.
The history of software is closely tied to the development of digital comput ...
in question.
Commercial solutions are provided by a variety of vendors, each with their own proprietary (and often patented) implementation of variously used security features. Token designs meeting certain security standards are certified in the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
as compliant with FIPS 140
The 140 series of Federal Information Processing Standards ( FIPS) are U.S. government computer security standards that specify requirements for cryptographic modules.
, FIPS 140-2 and FIPS 140-3 are both accepted as current and active. FIPS 1 ...
, a federal security standard. Tokens without any kind of certification are sometimes viewed as suspect, as they often do not meet accepted government or industry security standards, have not been put through rigorous testing, and likely cannot provide the same level of cryptographic security as token solutions which have had their designs independently audited by third-party agencies.
Disconnected tokens
 Disconnected tokens have neither a physical nor logical connection to the client computer. They typically do not require a special input device, and instead use a built-in screen to display the generated authentication data, which the user enters manually themselves via a
Disconnected tokens have neither a physical nor logical connection to the client computer. They typically do not require a special input device, and instead use a built-in screen to display the generated authentication data, which the user enters manually themselves via a keyboard
Keyboard may refer to:
Text input
* Keyboard, part of a typewriter
* Computer keyboard
** Keyboard layout, the software control of computer keyboards and their mapping
** Keyboard technology, computer keyboard hardware and firmware
Music
* Mus ...
or keypad
A keypad is a block or pad of buttons set with an arrangement of digits, symbols, or alphabetical letters. Pads mostly containing numbers and used with computers are numeric keypads. Keypads are found on devices which require mainly numeric in ...
. Disconnected tokens are the most common type of security token used (usually in combination with a password) in two-factor authentication for online identification.
Connected tokens
Connected tokens are tokens that must be physically connected to the computer with which the user is authenticating. Tokens in this category automatically transmit the authentication information to the client computer once a physical connection is made, eliminating the need for the user to manually enter the authentication information. However, in order to use a connected token, the appropriate input device must be installed. The most common types of physical tokens aresmart card
A smart card (SC), chip card, or integrated circuit card (ICC or IC card), is a card used to control access to a resource. It is typically a plastic credit card-sized card with an Embedded system, embedded integrated circuit (IC) chip. Many smart ...
s and USB tokens (also called ''security keys''), which require a smart card reader and a USB port respectively. Increasingly, FIDO2 tokens, supported by the open specification group FIDO Alliance
The FIDO ("Fast IDentity Online") Alliance is an open industry association launched in February 2013 whose stated mission is to develop and promote authentication standards that "help reduce the world’s over-reliance on passwords". FIDO addres ...
have become popular for consumers with mainstream browser support beginning in 2015 and supported by popular websites and social media sites.
Older PC card
PC Card is a technical standard specifying an expansion card interface for laptops and personal digital assistants, PDAs. The PCMCIA originally introduced the 16-bit Industry Standard Architecture, ISA-based PCMCIA Card in 1990, but renamed it to ...
tokens are made to work primarily with laptop
A laptop computer or notebook computer, also known as a laptop or notebook, is a small, portable personal computer (PC). Laptops typically have a Clamshell design, clamshell form factor (design), form factor with a flat-panel computer scree ...
s. Type II PC Cards are preferred as a token as they are half as thick as Type III.
The audio jack port is a relatively practical method to establish connection between mobile devices, such as iPhone
The iPhone is a line of smartphones developed and marketed by Apple that run iOS, the company's own mobile operating system. The first-generation iPhone was announced by then–Apple CEO and co-founder Steve Jobs on January 9, 2007, at ...
, iPad
The iPad is a brand of tablet computers developed and marketed by Apple Inc., Apple that run the company's mobile operating systems iOS and later iPadOS. The IPad (1st generation), first-generation iPad was introduced on January 27, 2010. ...
and Android, and other accessories. The most well known device is called Square
In geometry, a square is a regular polygon, regular quadrilateral. It has four straight sides of equal length and four equal angles. Squares are special cases of rectangles, which have four equal angles, and of rhombuses, which have four equal si ...
, a credit card reader for iOS
Ios, Io or Nio (, ; ; locally Nios, Νιός) is a Greek island in the Cyclades group in the Aegean Sea. Ios is a hilly island with cliffs down to the sea on most sides. It is situated halfway between Naxos and Santorini. It is about long an ...
and Android devices.
Some use a special purpose interface (e.g. the crypto ignition key deployed by the United States National Security Agency
The National Security Agency (NSA) is an intelligence agency of the United States Department of Defense, under the authority of the director of national intelligence (DNI). The NSA is responsible for global monitoring, collection, and proces ...
). Tokens can also be used as a photo ID card. Cell phones
A mobile phone or cell phone is a portable telephone that allows users to make and receive Telephone call, calls over a radio frequency link while moving within a designated telephone service area, unlike fixed-location phones (landline phone ...
and PDAs can also serve as security tokens with proper programming.
Smart cards
Many connected tokens use smart card technology. Smart cards can be very cheap (around ten cents) and contain proven security mechanisms (as used by financial institutions, like cash cards). However, computational performance of smart cards is often rather limited because of extreme low power consumption and ultra-thin form-factor requirements. Smart-card-basedUSB
Universal Serial Bus (USB) is an industry standard, developed by USB Implementers Forum (USB-IF), for digital data transmission and power delivery between many types of electronics. It specifies the architecture, in particular the physical ...
tokens which contain a smart card
A smart card (SC), chip card, or integrated circuit card (ICC or IC card), is a card used to control access to a resource. It is typically a plastic credit card-sized card with an Embedded system, embedded integrated circuit (IC) chip. Many smart ...
chip inside provide the functionality of both USB tokens and smart cards. They enable a broad range of security solutions and provide the abilities and security of a traditional smart card without requiring a unique input device. From the computer operating system
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common services for computer programs.
Time-sharing operating systems schedule tasks for efficient use of the system and may also ...
's point of view such a token is a USB-connected smart card reader with one non-removable smart card present.Specification for Integrated Circuit(s) Cards Interface Devices, usb.org
Contactless tokens
Unlike connected tokens, contactless tokens form a logical connection to the client computer but do not require a physical connection. The absence of the need for physical contact makes them more convenient than both connected and disconnected tokens. As a result, contactless tokens are a popular choice forkeyless entry
A remote keyless system (RKS), also known as remote keyless entry (RKE) or remote central locking, is an electronic lock that controls access to a building or vehicle by using an electronic remote control (activated by a handheld device or aut ...
systems and electronic payment solutions such as Mobil
Mobil Oil Corporation, now known as just Mobil, is a petroleum brand owned and operated by American oil and gas corporation ExxonMobil, formerly known as Exxon, which took its current name after history of ExxonMobil#merger, it and Mobil merge ...
Speedpass
Speedpass was a keychain radio-frequency identification (RFID) device introduced in 1997 by Mobil (which merged with Exxon to become ExxonMobil in 1999) for electronic payment. It was originally developed by Verifone. By 2004, more than seven mil ...
, which uses RFID
Radio-frequency identification (RFID) uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. An RFID system consists of a tiny radio transponder called a tag, a radio receiver, and a transmitter. When tri ...
to transmit authentication info from a keychain token. However, there have been various security concerns raised about RFID tokens after researchers at Johns Hopkins University
The Johns Hopkins University (often abbreviated as Johns Hopkins, Hopkins, or JHU) is a private university, private research university in Baltimore, Maryland, United States. Founded in 1876 based on the European research institution model, J ...
and RSA Laboratories
RSA Security LLC, formerly RSA Security, Inc. and trade name RSA, is an American computer and network security company with a focus on encryption and decryption standards. RSA was named after the initials of its co-founders, Ron Rivest, Adi Sh ...
discovered that RFID tags could be easily cracked and cloned.
Another downside is that contactless tokens have relatively short battery lives; usually only 5–6 years, which is low compared to USB
Universal Serial Bus (USB) is an industry standard, developed by USB Implementers Forum (USB-IF), for digital data transmission and power delivery between many types of electronics. It specifies the architecture, in particular the physical ...
tokens which may last more than 10 years. Some tokens however do allow the batteries to be changed, thus reducing costs.
Bluetooth tokens
TheBluetooth Low Energy
Bluetooth Low Energy (Bluetooth LE, colloquially BLE, formerly marketed as Bluetooth Smart) is a wireless personal area network technology designed and marketed by the Bluetooth Special Interest Group (Bluetooth SIG) aimed at novel applications ...
protocols provide long lasting battery lifecycle of wireless transmission.
* The transmission of inherent Bluetooth identity data is the lowest quality for supporting authentication.
* A bidirectional connection for transactional data interchange serves for the most sophisticated authentication procedures.
Although, the automatic transmission power control attempts for radial distance estimates. The escape is available apart from the standardised Bluetooth power control algorithm to provide a calibration on minimally required transmission power.
Bluetooth tokens are often combined with a USB token, thus working in both a connected and a disconnected state. Bluetooth authentication works when closer than . When the Bluetooth link is not properly operable, the token may be inserted into a USB
Universal Serial Bus (USB) is an industry standard, developed by USB Implementers Forum (USB-IF), for digital data transmission and power delivery between many types of electronics. It specifies the architecture, in particular the physical ...
input device
In computing, an input device is a piece of equipment used to provide data and control signals to an information processing system, such as a computer or information appliance. Examples of input devices include keyboards, computer mice, scanne ...
to function.
Another combination is with a smart card
A smart card (SC), chip card, or integrated circuit card (ICC or IC card), is a card used to control access to a resource. It is typically a plastic credit card-sized card with an Embedded system, embedded integrated circuit (IC) chip. Many smart ...
to store locally larger amounts of identity data and process information as well. Another is a contactless BLE token that combines secure storage and tokenized release of fingerprint credentials.
In the USB mode of operation sign-off requires care for the token while mechanically coupled to the USB plug. The advantage with the Bluetooth mode of operation is the option of combining sign-off with distance metrics. Respective products are in preparation, following the concepts of electronic leash.
NFC tokens
Near-field communication
Near-field communication (NFC) is a set of communication protocols that enables communication between two electronic devices over a distance of or less. NFC offers a low-speed connection through a simple setup that can be used for the boots ...
(NFC) tokens combined with a Bluetooth token may operate in several modes, thus working in both a connected and a disconnected state. NFC authentication works when closer than . The NFC protocol bridges short distances to the reader while the Bluetooth connection serves for data provision with the token to enable authentication. Also when the Bluetooth link is not connected, the token may serve the locally stored authentication information in coarse positioning to the NFC reader and relieves from exact positioning to a connector.
Single sign-on software tokens
Some types of single sign-on (SSO) solutions, like enterprise single sign-on, use the token to store software that allows for seamless authentication and password filling. As the passwords are stored on the token, users need not remember their passwords and therefore can select more secure passwords, or have more secure passwords assigned. Usually most tokens store a cryptographic hash of the password so that if the token is compromised, the password is still protected.Programmable tokens
Programmable tokens are marketed as "drop-in" replacement of mobile applications such as Google Authenticator (miniOTP). They can be used as mobile app replacement, as well as in parallel as a backup.Vulnerabilities
Loss and theft
The simplest vulnerability with any password container is theft or loss of the device. The chances of this happening, or happening unaware, can be reduced with physical security measures such as locks, electronic leash, or body sensor and alarm. Stolen tokens can be made useless by usingtwo factor authentication
Multi-factor authentication (MFA; two-factor authentication, or 2FA) is an electronic authentication method in which a user is granted access to a website or application only after successfully presenting two or more distinct types of evidence ...
. Commonly, in order to authenticate, a personal identification number
A personal identification number (PIN; sometimes RAS syndrome, redundantly a PIN code or PIN number) is a numeric (sometimes alpha-numeric) passcode used in the process of authenticating a user accessing a system.
The PIN has been the key to faci ...
(PIN) must be entered along with the information provided by the token the same time as the output of the token.
Attacking
Any system which allows users to authenticate via an untrusted network (such asthe Internet
The Internet (or internet) is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a network of networks that consists of private, publ ...
) is vulnerable to man-in-the-middle attack
In cryptography and computer security, a man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack, or on-path attack, is a cyberattack where the attacker secretly relays and possibly alters the communications between two parties who believe that they are directly communi ...
s. In this type of attack, an attacker acts as the "go-between" of the user and the legitimate system, soliciting the token output from the legitimate user and then supplying it to the authentication system themselves. Since the token value is mathematically correct, the authentication succeeds and the fraudster is granted access. In 2006, Citibank
Citibank, N.A. ("N. A." stands for "National bank (United States), National Association"; stylized as citibank) is the primary U.S. banking subsidiary of Citigroup, a financial services multinational corporation, multinational corporation. Ci ...
was the victim of an attack when its hardware-token-equipped business users became the victims of a large Ukrainian-based man-in-the-middle phishing
Phishing is a form of social engineering and a scam where attackers deceive people into revealing sensitive information or installing malware such as viruses, worms, adware, or ransomware. Phishing attacks have become increasingly sophisticate ...
operation.
Breach of codes
In 2012, the Prosecco research team at INRIA Paris-Rocquencourt developed an efficient method of extracting the secret key from several PKCS #11 cryptographic devices. These findings were documented in INRIA Technical Report RR-7944, ID hal-00691958, and published at CRYPTO 2012.Digital signature
Trusted as a regular hand-written signature, the digital signature must be made with a private key known only to the person authorized to make the signature. Tokens that allow secure on-board generation and storage of private keys enable secure digital signatures, and can also be used for user authentication, as the private key also serves as a proof of the user's identity. For tokens to identify the user, all tokens must have some kind of number that is unique. Not all approaches fully qualify as digital signatures according to some national laws. Tokens with no on-board keyboard or anotheruser interface
In the industrial design field of human–computer interaction, a user interface (UI) is the space where interactions between humans and machines occur. The goal of this interaction is to allow effective operation and control of the machine fro ...
cannot be used in some signing scenarios, such as confirming a bank transaction based on the bank account number that the funds are to be transferred to.
See also
*Authentication
Authentication (from ''authentikos'', "real, genuine", from αὐθέντης ''authentes'', "author") is the act of proving an Logical assertion, assertion, such as the Digital identity, identity of a computer system user. In contrast with iden ...
* Authenticator
An authenticator is a means used to confirm a user's identity, that is, to perform digital authentication. A person authenticates to a computer system or application by demonstrating that he or she has possession and control of an authenticator. I ...
* Hardware security module
A hardware security module (HSM) is a physical computing device that safeguards and manages secrets (most importantly digital keys), and performs encryption and decryption functions for digital signatures, strong authentication and other crypt ...
* Identity management
Identity and access management (IAM or IdAM) or Identity management (IdM), is a framework of policies and technologies to ensure that the right users (that are part of the ecosystem connected to or within an enterprise) have the appropriate acce ...
* Initiative for Open Authentication
* Mobile signature
A mobile signature is a digital signature generated either on a mobile phone or on a SIM card on a mobile phone.
Origins of the term
mSign
The term first appeared in articles introducing mSign (short for Mobile Electronic Signature Consortium ...
* Multi-factor authentication
Multi-factor authentication (MFA; two-factor authentication, or 2FA) is an electronic authentication method in which a user is granted access to a website or application only after successfully presenting two or more distinct types of evidence ...
* Mutual authentication
Mutual authentication or two-way authentication (not to be confused with two-factor authentication) refers to two parties authenticating each other at the same time in an authentication protocol. It is a default mode of authentication in some prot ...
* One-time pad
The one-time pad (OTP) is an encryption technique that cannot be Cryptanalysis, cracked in cryptography. It requires the use of a single-use pre-shared key that is larger than or equal to the size of the message being sent. In this technique, ...
* Single sign-on
* Software token
A software token (a.k.a. ''soft token'') is a piece of a two-factor authentication security device that may be used to authorize the use of computer services. Software tokens are stored on a general-purpose electronic device such as a desktop comp ...
References
;General referencesUS Personal Identity Verification (PIV)
External links
*OATH Initiative for open authentication
{{DEFAULTSORT:Security Token Computer access control Authentication methods