Ventricular Dilation on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cardiomegaly (sometimes megacardia or megalocardia) is a medical condition in which the
 * Chest X-ray:
* Chest X-ray: 
 *
*
American Heart Association
{{portal bar, Medicine
heart
The heart is a muscular Organ (biology), organ found in humans and other animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels. The heart and blood vessels together make the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrie ...
becomes enlarged. It is more commonly referred to simply as "having an enlarged heart". It is usually the result of underlying conditions that make the heart work harder, such as obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, considered by multiple organizations to be a disease, in which excess Adipose tissue, body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it can potentially have negative effects on health. People are classifi ...
, heart valve disease, high blood pressure (hypertension
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a Chronic condition, long-term Disease, medical condition in which the blood pressure in the artery, arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms i ...
), and coronary artery disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also called coronary heart disease (CHD), or ischemic heart disease (IHD), is a type of cardiovascular disease, heart disease involving Ischemia, the reduction of blood flow to the cardiac muscle due to a build-up ...
. Cardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathy is a group of primary diseases of the heart muscle. Early on there may be few or no symptoms. As the disease worsens, shortness of breath, feeling tired, and swelling of the legs may occur, due to the onset of heart failure. A ...
is also associated with cardiomegaly.
Cardiomegaly can be serious and can result in congestive heart failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome caused by an impairment in the heart's ability to fill with and pump blood.
Although symptoms vary based on which side of the heart is affected, HF typically pr ...
. Recent studies suggest that cardiomegaly is associated with a higher risk of sudden cardiac death
Cardiac arrest (also known as sudden cardiac arrest ''SCA is when the heart suddenly and unexpectedly stops beating. When the heart stops beating, blood cannot properly circulate around the body and the blood flow to the brain and other org ...
.
Cardiomegaly may diminish over time, but many people with an enlarged heart (dilated cardiomyopathy) need lifelong medication. Having a family history of cardiomegaly may indicate an increased risk for this condition.
Lifestyle factors that can help prevent cardiomegaly include eating a healthy diet, controlling blood pressure, exercise, medications, and not abusing anabolic-androgenic steroids, alcohol and cocaine
Cocaine is a tropane alkaloid and central nervous system stimulant, derived primarily from the leaves of two South American coca plants, ''Erythroxylum coca'' and ''Erythroxylum novogranatense, E. novogranatense'', which are cultivated a ...
.
Signs and symptoms
For many people, cardiomegaly isasymptomatic
Asymptomatic (or clinically silent) is an adjective categorising the medical conditions (i.e., injuries or diseases) that patients carry but without experiencing their symptoms, despite an explicit diagnosis (e.g., a positive medical test).
P ...
. For others, if the enlarged heart begins to affect the body's ability to pump blood, then symptoms associated with congestive heart failure may arise, including:
* Heart palpitations
Palpitations occur when a person becomes aware of their heartbeat. The heartbeat may feel hard, fast, or uneven in their chest.
Symptoms include a very fast or irregular heartbeat. Palpitations are a sensory symptom. They are often described as ...
– the irregular beating of the heart, usually associated with a valve
* Severe shortness of breath (especially when physically active)
* Chest pain
* Coughing, when lying down
* Fatigue
* Leg swelling
* Increased abdominal girth
* Weight gain
* Edema
Edema (American English), also spelled oedema (British English), and also known as fluid retention, swelling, dropsy and hydropsy, is the build-up of fluid in the body's tissue (biology), tissue. Most commonly, the legs or arms are affected. S ...
– swelling
* Fainting
Causes
The causes of cardiomegaly are not well understood and many cases have no known cause. Lifestyle-related risk factors includetobacco use
Tobacco is the common name of several plants in the genus ''Nicotiana'' of the family Solanaceae, and the general term for any product prepared from the cured leaves of these plants. More than 70 species of tobacco are known, but the chi ...
and high cholesterol
Cholesterol is the principal sterol of all higher animals, distributed in body Tissue (biology), tissues, especially the brain and spinal cord, and in Animal fat, animal fats and oils.
Cholesterol is biosynthesis, biosynthesized by all anima ...
, high blood pressure, and diabetes
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin, or the cells of th ...
. Non-lifestyle risk factors include a family history of cardiomegaly, coronary artery disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also called coronary heart disease (CHD), or ischemic heart disease (IHD), is a type of cardiovascular disease, heart disease involving Ischemia, the reduction of blood flow to the cardiac muscle due to a build-up ...
(CAD), congenital heart failure, atherosclerotic
Atherosclerosis is a pattern of the disease arteriosclerosis, characterized by development of abnormalities called lesions in walls of arteries. This is a chronic inflammatory disease involving many different cell types and is driven by elev ...
disease, valvular heart disease
Valvular heart disease is any cardiovascular disease process involving one or more of the four valves of the heart (the aortic and mitral valves on the left side of heart and the pulmonic and tricuspid valves on the right side of heart). The ...
, exposure to cardiac toxins, sleep-disordered breathing (such as sleep apnea
Sleep apnea (sleep apnoea or sleep apnœa in British English) is a sleep-related breathing disorder in which repetitive Apnea, pauses in breathing, periods of shallow breathing, or collapse of the upper airway during sleep results in poor vent ...
), sustained cardiac arrhythmias
Arrhythmias, also known as cardiac arrhythmias, are irregularities in the heartbeat, including when it is too fast or too slow. Essentially, this is anything but normal sinus rhythm. A resting heart rate that is too fast – above 100 beats ...
, abnormal electrocardiograms
Electrocardiography is the process of producing an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG), a recording of the heart's electrical activity through repeated cardiac cycles.
It is an electrogram of the heart which is a graph of voltage versus time of ...
, and cardiomegaly on chest X-ray.
Research and the evidence of previous cases link the following (below) as possible causes of cardiomegaly.
The most common causes of cardiomegaly are congenital
A birth defect is an abnormal condition that is present at childbirth, birth, regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disability, disabilities that may be physical disability, physical, intellectual disability, intellectual, or dev ...
(patients are born with the condition based on a genetic inheritance), high blood pressure (which can enlarge the left ventricle causing the heart muscle to weaken over time), and coronary artery disease. In the latter case, the disease creates blockages in the heart's blood supply, leading to tissue death which causes other areas of the heart to work harder, causing the heart to expand in size.
Other possible causes include:
* Heart valve disease
* Cardiomyopathy (disease of the heart muscle)
* Pulmonary
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in many animals, including humans. In mammals and most other tetrapods, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of the heart. Their function in the respiratory syste ...
hypertension
* Pericardial effusion
In physics and chemistry, effusion is the process in which a gas escapes from a container through a hole of diameter considerably smaller than the mean free path of the molecules. Such a hole is often described as a ''pinhole'' and the escape ...
(fluid around the heart)
* Thyroid
The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans, it is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck below the Adam's apple. It consists of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by ...
Disorders
* Hemochromatosis
Iron overload is the abnormal and increased accumulation of total iron in the body, leading to organ damage. The primary mechanism of organ damage is oxidative stress, as elevated intracellular iron levels increase free radical formation via the ...
(excessive iron in the blood)
* Amyloidosis
Amyloidosis is a group of diseases in which abnormal proteins, known as amyloid fibrils, build up in tissue. There are several non-specific and vague signs and symptoms associated with amyloidosis. These include fatigue, peripheral edema, weigh ...
* Chagas disease
Chagas disease, also known as American trypanosomiasis, is a tropical parasitic disease caused by ''Trypanosoma cruzi''. It is spread mostly by insects in the subfamily Triatominae, known as "kissing bugs". The symptoms change throughout the ...
, an important cause of cardiomegaly in Latin America
Latin America is the cultural region of the Americas where Romance languages are predominantly spoken, primarily Spanish language, Spanish and Portuguese language, Portuguese. Latin America is defined according to cultural identity, not geogr ...
* Viral infection of the heart
* Pregnancy, with enlarged heart developing around the time of delivery (peripartum cardiomyopathy)
* Kidney disease requiring dialysis
* Alcohol
Alcohol may refer to:
Common uses
* Alcohol (chemistry), a class of compounds
* Ethanol, one of several alcohols, commonly known as alcohol in everyday life
** Alcohol (drug), intoxicant found in alcoholic beverages
** Alcoholic beverage, an alco ...
or cocaine abuse
* HIV infection
* Diabetes
Cardiomegaly can also occur non-pathologically as part of athletic heart syndrome (AHS) in individuals who frequently engage in high-intensity physical exercise
Exercise or workout is physical activity that enhances or maintains fitness and overall health. It is performed for various reasons, including weight loss or maintenance, to aid growth and improve strength, develop muscles and the cardio ...
, for instance endurance
Endurance (also related to sufferance, forbearance, resilience, constitution, fortitude, persistence, tenacity, steadfastness, perseverance, stamina, and hardiness) is the ability of an organism to exert itself and remain active for a ...
athletes and other individuals who exercise for more than 1 hour daily. AHS is a result of physiological cardiac remodeling, which is a natural adaptation to frequent physical exercise and a high level of physical fitness
Physical fitness is a state of health and well-being and, more specifically, the ability to perform aspects of Outline of sports, sports, occupations, and daily activities. Physical fitness is generally achieved through proper nutrition, modera ...
. Cardiomegaly due to AHS is usually benign and reversible, but it is important that athletes with suspected AHS undergo screening to rule out potentially life-threatening underlying heart problems
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is any disease involving the heart or blood vessels. CVDs constitute a class of diseases that includes: coronary artery diseases (e.g. angina pectoris, angina, myocardial infarction, heart attack), heart failure, ...
.
In recent years, after the deaths of several rock
Rock most often refers to:
* Rock (geology), a naturally occurring solid aggregate of minerals or mineraloids
* Rock music, a genre of popular music
Rock or Rocks may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* Rock, Caerphilly, a location in Wale ...
and metal
A metal () is a material that, when polished or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electrical resistivity and conductivity, electricity and thermal conductivity, heat relatively well. These properties are all associated wit ...
drummers from drug overdoses, autopsies
An autopsy (also referred to as post-mortem examination, obduction, necropsy, or autopsia cadaverum) is a surgical procedure that consists of a thorough examination of a corpse by dissection to determine the cause, mode, and manner of death; ...
have revealed that they were suffering from cardiomegaly, which may have been worsened by a mix of drug use and the cardiovascular effects of the exertion
Exertion is the Action (physics), physical or perceived use of energy.Newton's Third Law, Elert, Glenn. “Forces.” ''Viscosity – The Physics Hypertextbook'', physics.info/newton-first/. Exertion traditionally connotes a strenuous or costly ''e ...
involved in rock drumming. Examples of such cases include Jimmy 'The Rev' Sullivan (Avenged Sevenfold
Avenged Sevenfold (abbreviated as A7X) is an American Heavy metal music, heavy metal band from Huntington Beach, California, formed in 1999. The band's current lineup consists of vocalist M. Shadows, rhythm guitarist Zacky Vengeance, lead gui ...
) and Taylor Hawkins
Oliver Taylor Hawkins (February 17, 1972 – March 25, 2022) was an American musician who was the drummer and a vocalist of the rock band Foo Fighters, sharing vocals with Dave Grohl. He joined the band in 1997, and remained the band's drummer ...
(Foo Fighters
The Foo Fighters are an American Rock music, rock band formed in Seattle in 1994. Initially founded as a one-man project by former Nirvana (band), Nirvana drummer Dave Grohl, the band comprises vocalist/guitarist Grohl, bassist Nate Mendel, gu ...
).
Mechanism
Within the heart, the working fibers of the myocardial tissue increase in size. As the heart works harder theactin
Actin is a family of globular multi-functional proteins that form microfilaments in the cytoskeleton, and the thin filaments in muscle fibrils. It is found in essentially all eukaryotic cells, where it may be present at a concentration of ...
and myosin
Myosins () are a Protein family, family of motor proteins (though most often protein complexes) best known for their roles in muscle contraction and in a wide range of other motility processes in eukaryotes. They are adenosine triphosphate, ATP- ...
filaments experience less overlap which increases the size of the myocardial fibers. If there is less overlap of the protein filaments within the sarcomeres of the muscle fibers, they will not be able to effectively pull on one another. If the heart tissue gets too big and stretches too far, then those filaments cannot effectively pull on one another to shorten the muscle fibers, impacting the heart's sliding filament mechanism. If fibers cannot shorten properly and the heart cannot contract properly, then blood cannot be effectively pumped to the lungs to be re-oxygenated or to the body to deliver oxygen to the working tissues of the body.
An enlarged heart is more susceptible to forming blood clots in the heart lining. These clots can form elsewhere in the body, potentially disrupting blood supply to other organs.
Diagnosis
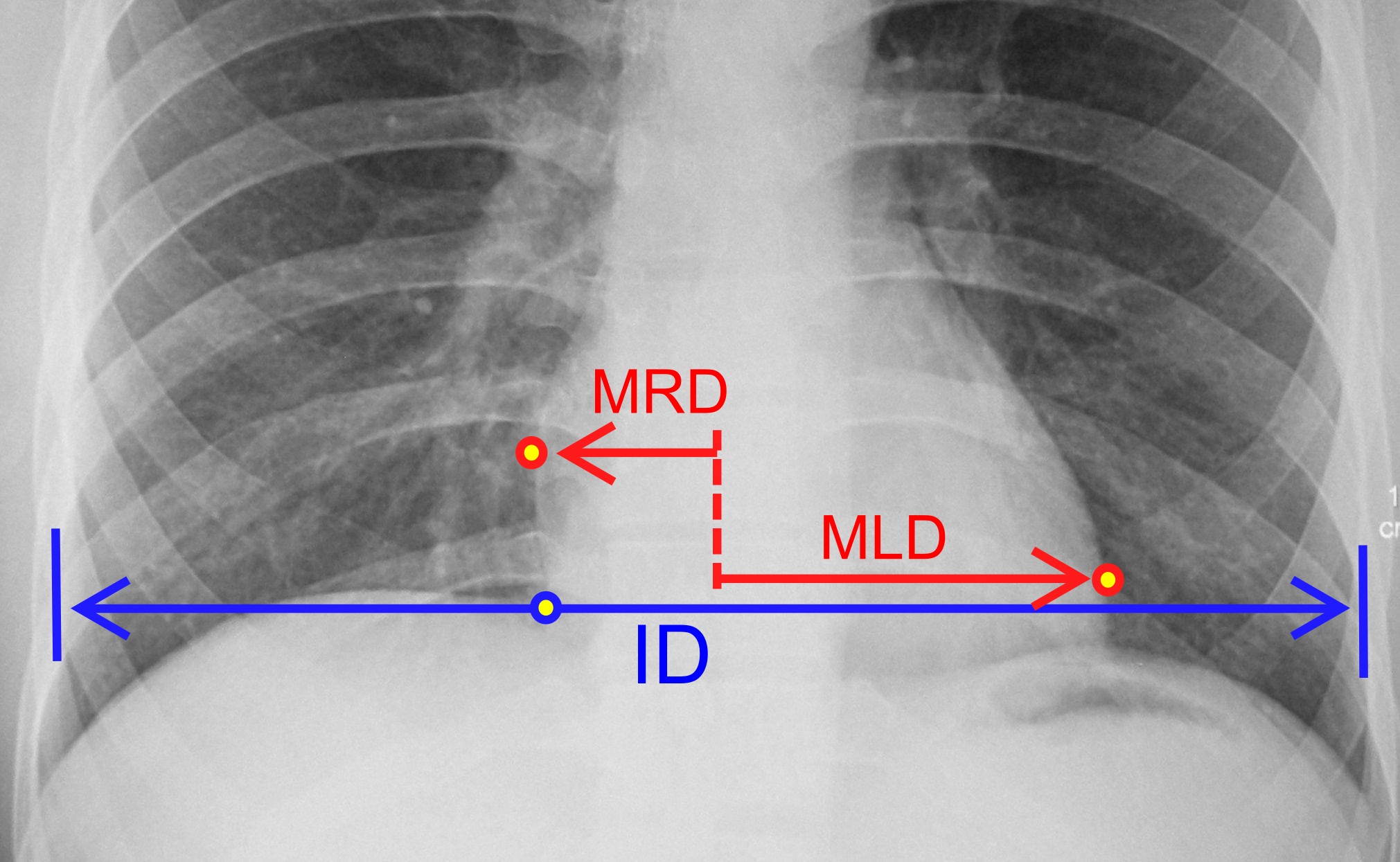
Many techniques and tests are used to diagnose an enlarged heart. These tests can be used to see how efficiently the heart is pumping, determine which chambers of the heart are enlarged, look for evidence of prior heart attacks and determine if a person has congenital heart disease. * Chest X-ray:
* Chest X-ray: X-ray
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ran ...
images help to visualize the condition of the lungs and heart. If the heart is enlarged on an X-ray, other tests will usually be needed to find the cause. A useful measurement on X-ray is the cardio-thoracic ratio, which is the transverse diameter of the heart, compared with that of the thoracic cage. These diameters are taken from PA chest x-rays using the widest point of the chest and measuring as far as the lung pleura
The pleurae (: pleura) are the two flattened closed sacs filled with pleural fluid, each ensheathing each lung and lining their surrounding tissues, locally appearing as two opposing layers of serous membrane separating the lungs from the med ...
, rather than lateral skin margins. If the ratio is greater than 50%, pathology is suspected. The measurement was first proposed in 1919 to screen military recruits. A newer approach to using these x-rays for evaluating heart health takes the ratio of heart area to chest area and has been called the two-dimensional cardiothoracic ratio.
* Electrocardiogram: This test records the electrical activity of the heart through electrodes attached to the skin. Impulses are recorded as waves and displayed on a monitor or printed on paper. This test helps diagnose heart rhythm problems and assess the damage to a person's heart from a heart attack.
* Echocardiogram
Echocardiography, also known as cardiac ultrasound, is the use of ultrasound to examine the heart. It is a type of medical imaging, using standard ultrasound or Doppler ultrasound. The visual image formed using this technique is called an echo ...
: This test uses sound waves to produce a video image of the heart. With this test, the four chambers of the heart can be evaluated.
* Stress test
Stress testing is a form of deliberately intense or thorough testing, used to determine the stability of a given system, critical infrastructure or entity. It involves testing beyond normal operational capacity, often to a breaking point, in orde ...
: A stress test, also called an exercise stress test, provides information about how well the heart works during physical activity. It usually involves walking on a treadmill or riding a stationary bike while heart rhythm, blood pressure, and breathing are monitored.
* Cardiac computerized tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and ...
(MRI). These techniques create images of the heart for inspection.
* Blood tests: Blood tests may be ordered to check the levels of substances in the blood that may show a heart problem. Blood tests can also help rule out other conditions.

 *
* Cardiac catheterization
Cardiac catheterization (heart cath) is the insertion of a catheter into a heart chamber, chamber or Blood vessel, vessel of the heart. This is done both for diagnostic and interventional purposes.
A common example of cardiac catheterization is c ...
and biopsy: In this procedure, a catheter is inserted into the groin and threaded through the blood vessels to the heart, where a biopsy of the heart can be extracted for laboratory analysis.
* Autopsy
An autopsy (also referred to as post-mortem examination, obduction, necropsy, or autopsia cadaverum) is a surgical procedure that consists of a thorough examination of a corpse by dissection to determine the cause, mode, and manner of deat ...
: Cardiomegaly is indicated if the heart weighs more than >399 grams in women and >449 grams in men.
Classification
Cardiomegaly can be classified by the main enlarged location of the heart, and/or by the structure of the enlargement. Specific subtypes include athletic heart syndrome, which is a non-pathological
Pathology is the study of disease. The word ''pathology'' also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in the context of modern medical treatme ...
condition commonly seen in sports medicine
Sports medicine is a branch of medicine that deals with physical fitness and the treatment and prevention of injuries related to sports and exercise. Although most sports teams have employed team physicians for many years, it is only since the ...
in which the heart is enlarged, and the resting heart rate
Heart rate is the frequency of the cardiac cycle, heartbeat measured by the number of contractions of the heart per minute (''beats per minute'', or bpm). The heart rate varies according to the body's Human body, physical needs, including the nee ...
is lower
Lower may refer to:
* ''Lower'' (album), 2025 album by Benjamin Booker
*Lower (surname)
*Lower Township, New Jersey
*Lower Receiver (firearms)
*Lower Wick
Lower Wick is a small hamlet located in the county of Gloucestershire, England. It is sit ...
than normal.
By enlarged location
*Ventricular hypertrophy
Ventricular hypertrophy (VH) is thickening of the walls of a ventricle (lower chamber) of the heart. Although left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) is more common, right ventricular hypertrophy (RVH), as well as concurrent hypertrophy of both vent ...
** Left
Left may refer to:
Music
* ''Left'' (Hope of the States album), 2006
* ''Left'' (Monkey House album), 2016
* ''Left'' (Helmet album), 2023
* "Left", a song by Nickelback from the album ''Curb'', 1996
Direction
* Left (direction), the relativ ...
** Right
Rights are law, legal, social, or ethics, ethical principles of freedom or Entitlement (fair division), entitlement; that is, rights are the fundamental normative rules about what is allowed of people or owed to people according to some legal sy ...
/ Cor pulmonale
* Atrial enlargement
** Left
Left may refer to:
Music
* ''Left'' (Hope of the States album), 2006
* ''Left'' (Monkey House album), 2016
* ''Left'' (Helmet album), 2023
* "Left", a song by Nickelback from the album ''Curb'', 1996
Direction
* Left (direction), the relativ ...
** Right
Rights are law, legal, social, or ethics, ethical principles of freedom or Entitlement (fair division), entitlement; that is, rights are the fundamental normative rules about what is allowed of people or owed to people according to some legal sy ...
Structure of enlargement
Dilated cardiomyopathy
Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) is a condition in which the heart becomes enlarged and cannot pump blood effectively. Symptoms vary from none to feeling tired, leg swelling, and shortness of breath. It may also result in chest pain or fainting. C ...
is the most common type of cardiomegaly. In this condition, the walls of the left and/or right ventricles of the heart become thin and stretched.
In the other types, the heart's left ventricle becomes abnormally thick. Hypertrophy is usually what causes left ventricular enlargement. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM, or HOCM when obstructive) is a condition in which muscle tissues of the heart become thickened without an obvious cause. The parts of the heart most commonly affected are the interventricular septum and the ...
is typically an inherited condition.
Treatment
Treatments include a combination of medications and medical/surgical procedures. Below are some of the treatment options:Medications
*Diuretics
A diuretic () is any substance that promotes diuresis, the increased production of urine. This includes forced diuresis. A diuretic tablet is sometimes colloquially called a water tablet. There are several categories of diuretics. All diuretics in ...
: to lower the amount of sodium and water in the body, which can help lower the pressure in the arteries and heart.
* Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors: to lower blood pressure and improve pumping ability.
* Angiotensin receptor blockers
Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs), formally angiotensin II receptor type 1 (AT1) antagonists, also known as angiotensin receptor blockers, angiotensin II receptor antagonists, or AT1 receptor antagonists, are a group of pharmaceuticals tha ...
(ARBs): to provide the benefits of ACE inhibitors for patients with ACE inhibitor issues.
* Beta blockers
Beta blockers, also spelled β-blockers, are a class of medications that are predominantly used to manage abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmia), and to protect the heart from a second heart attack after a first heart attack (secondary prevention). ...
: to lower blood pressure and improve heart function.
* Digoxin
Digoxin (better known as digitalis), sold under the brand name Lanoxin among others, is a medication used to treat various heart disease, heart conditions. Most frequently it is used for atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, and heart failure. ...
: to help improve heart pumping function and lessen the need for hospitalization for heart failure.
* Anticoagulants
An anticoagulant, commonly known as a blood thinner, is a chemical substance that prevents or reduces the coagulation of blood, prolonging the clotting time. Some occur naturally in blood-eating animals, such as leeches and mosquitoes, which h ...
: to reduce blood clot risk.
* Anti-arrhythmics: to maintain normal heart rhythm.
Devices to regulate heartbeat
*Pacemaker
A pacemaker, also known as an artificial cardiac pacemaker, is an implanted medical device that generates electrical pulses delivered by electrodes to one or more of the chambers of the heart. Each pulse causes the targeted chamber(s) to co ...
: Coordinates contractions between ventricles. In people at risk of arrhythmia
Arrhythmias, also known as cardiac arrhythmias, are irregularities in the cardiac cycle, heartbeat, including when it is too fast or too slow. Essentially, this is anything but normal sinus rhythm. A resting heart rate that is too fast – ab ...
s, drug therapy or an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator
An implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) or automated implantable cardioverter defibrillator (AICD) is a device implantable inside the body, able to perform defibrillation, and depending on the type, cardioversion and pacing of the h ...
(ICD).
* ICDs: Small devices implanted in the chest to monitor heart rhythm and deliver electrical shocks to control abnormal heartbeats. The devices can also work as pacemakers.
Surgical procedures
* Valve surgery: If an enlarged heart is caused by a problem with a heart valve, surgery can remove the valve and replace it with either an artificial valve or a tissue valve from a pig, cow or deceased human donor. If blood leaks backward through a valve (valve regurgitation), the leaky valve may be surgically repaired or replaced. * Coronary bypass surgery: to address coronary artery disease, which can lead to an enlarged heart. * Left ventricular assist device: (LVAD): to help a weak heart pump, potentially while waiting for a heart transplant or as a long-term treatment for heart failure. *Heart transplant
A heart transplant, or a cardiac transplant, is a surgical transplant procedure performed on patients with end-stage heart failure when other medical or surgical treatments have failed. , the most common procedure is to take a functioning heart ...
: to provide a final option after other treatments fail.
Consequences
The exact mortality rate for people with cardiomegaly is unknown. However, many people live for a long time with an enlarged heart and, if detected early, treatment can help improve the condition and prolong their lives. * Heart failure: One of the most serious types of enlarged heart, an enlarged left ventricle, increases the risk of heart failure. In heart failure, the heart muscle weakens, and the ventricles stretch (dilate) to the point that the heart can't pump blood efficiently throughout the body. * Blood clots: If clots enter the bloodstream, they can block blood flow to vital organs, possibly causing a heart attack or stroke. Clots that develop on the right side of the heart may travel to the lungs, a dangerous condition called apulmonary embolism
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a blockage of an pulmonary artery, artery in the lungs by a substance that has moved from elsewhere in the body through the bloodstream (embolism). Symptoms of a PE may include dyspnea, shortness of breath, chest pain ...
.
* Heart murmur
Heart murmurs are unique heart sounds produced when blood flows across a heart valve or blood vessel. This occurs when turbulent blood flow creates a sound loud enough to hear with a stethoscope. The sound differs from normal heart sounds by th ...
: Two of the heart's four valves – the mitral
The mitral valve ( ), also known as the bicuspid valve or left atrioventricular valve, is one of the four heart valves. It has two Cusps of heart valves, cusps or flaps and lies between the atrium (heart), left atrium and the ventricle (heart), ...
and tricuspid valves – may become dilated and not close properly, leading to a backflow of blood. This flow creates sounds called heart murmurs
Heart murmurs are unique heart sounds produced when blood flows across a heart valve or blood vessel. This occurs when turbulent blood flow creates a sound loud enough to hear with a stethoscope. The sound differs from normal heart sounds by t ...
.
* Cardiomegaly may be a temporary condition that can resolve on its own.
Recommended lifestyle changes
The following recommendations are: * Smoking cessation * Limiting alcohol and caffeine intake * Maintaining a healthy weight * Increasing fruits and vegetables in a daily diet * Limiting consumption of high-fat and/or high-sugar foods * Getting adequate restful sleepReferences
Further reading
* * * *External links
American Heart Association
{{portal bar, Medicine