Vascular Diseases on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Vascular disease is a class of diseases of the vessels of the
 *
*
 Vascular disease is a pathological state of large and medium muscular arteries and is triggered by
Vascular disease is a pathological state of large and medium muscular arteries and is triggered by
 Treatment varies based on the type of vascular disease being treated. In treating renal artery disease, a 2014 study indicates that balloon angioplasty can improve diastolic blood pressure and potentially reduce antihypertensive drug requirements. In the case of peripheral artery disease, treatment to prevent complications is important; without treatment, sores or
Treatment varies based on the type of vascular disease being treated. In treating renal artery disease, a 2014 study indicates that balloon angioplasty can improve diastolic blood pressure and potentially reduce antihypertensive drug requirements. In the case of peripheral artery disease, treatment to prevent complications is important; without treatment, sores or
circulatory system
In vertebrates, the circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the body. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of the heart ...
in the body
Body may refer to:
In science
* Physical body, an object in physics that represents a large amount, has mass or takes up space
* Body (biology), the physical material of an organism
* Body plan, the physical features shared by a group of anim ...
, including blood vessel
Blood vessels are the tubular structures of a circulatory system that transport blood throughout many Animal, animals’ bodies. Blood vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to most of the Tissue (biology), tissues of a Body (bi ...
s – the arteries
An artery () is a blood vessel in humans and most other animals that takes oxygenated blood away from the heart in the systemic circulation to one or more parts of the body. Exceptions that carry deoxygenated blood are the pulmonary arteries in ...
and veins
Veins () are blood vessels in the circulatory system of humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are those of the pulmonary and fetal c ...
, and the lymphatic vessel
The lymphatic vessels (or lymph vessels or lymphatics) are thin-walled vessels (tubes), structured like blood vessels, that carry lymph. As part of the lymphatic system, lymph vessels are complementary to the cardiovascular system. Lymph vessel ...
s. Vascular disease is a subgroup of cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is any disease involving the heart or blood vessels. CVDs constitute a class of diseases that includes: coronary artery diseases (e.g. angina, heart attack), heart failure, hypertensive heart disease, rheumati ...
. Disorders in this vast network of blood and lymph vessels can cause a range of health problems that can sometimes become severe, and fatal. Coronary heart disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also called coronary heart disease (CHD), or ischemic heart disease (IHD), is a type of cardiovascular disease, heart disease involving Ischemia, the reduction of blood flow to the cardiac muscle due to a build-up ...
for example, is the leading cause of death for men and women in the United States.
Types
There are several types of vascular disease, including venous diseases, and arterial diseases, and signs and symptoms vary depending on the disease. Those of the arterial system are associated with blood supply to tissues and its obstruction due to blockages or narrowing. In thevenous system
Veins () are blood vessels in the circulatory system of humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are those of the pulmonary and fetal c ...
disorders are often caused by a slow return of blood due to insufficient valves, or to a blood clot
A thrombus ( thrombi) is a solid or semisolid aggregate from constituents of the blood (platelets, fibrin, red blood cells, white blood cells) within the circulatory system during life. A blood clot is the final product of the blood coagulatio ...
.
Venous disease
Most disorders of the veins involve obstruction such as athrombus
A thrombus ( thrombi) is a solid or semisolid aggregate from constituents of the blood (platelets, fibrin, red blood cells, white blood cells) within the circulatory system during life. A blood clot is the final product of the blood coagulatio ...
or insufficiency of the valves
A valve is a device or natural object that regulates, directs or controls the flow of a fluid (gases, liquids, fluidized solids, or slurries) by opening, closing, or partially obstructing various passageways. Valves are technically fittings, ...
, or both of these. Other conditions may be due to inflammation
Inflammation (from ) is part of the biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function (Latin ''calor'', '' ...
.Phlebitis
Phlebitis
Phlebitis (or venitis) is inflammation of a vein, usually in the legs. It most commonly occurs in superficial veins. Phlebitis often occurs in conjunction with thrombosis (clotting inside blood vessels) and is then called thrombophlebitis or ...
is the inflammation
Inflammation (from ) is part of the biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function (Latin ''calor'', '' ...
of a vein. It is usually accompanied by a blood clot
A thrombus ( thrombi) is a solid or semisolid aggregate from constituents of the blood (platelets, fibrin, red blood cells, white blood cells) within the circulatory system during life. A blood clot is the final product of the blood coagulatio ...
when it is known as thrombophlebitis
Thrombophlebitis is a phlebitis (inflammation of a vein) related to a thrombus (blood clot). When it occurs repeatedly in different locations, it is known as thrombophlebitis migrans (migratory thrombophlebitis).
Signs and symptoms
The following ...
. When the affected vein is a superficial vein in the leg, it is known as superficial thrombophlebitis
Superficial thrombophlebitis is a thrombosis and inflammation of superficial veins presenting as a painful induration (thickening) with erythema, often in a linear or branching configuration with a cordlike appearance.
Superficial thrombophlebi ...
, and unlike deep vein thrombosis there is little risk of the clot breaking off as an embolus
An embolus (; : emboli; from the Greek ἔμβολος "wedge", "plug") is an unattached mass that travels through the circulatory system, bloodstream and is capable of creating blockages. When an embolus Vascular occlusion, occludes a blood vess ...
.
Venous insufficiency
Venous insufficiency is the most common disorder of the venous system, and is usually manifested as eitherspider veins
Telangiectasias (), also known as spider veins, are small dilated blood vessels that can occur near the surface of the skin or mucous membranes, measuring between 0.5 and 1 millimeter in diameter. These dilated blood vessels can develop anywhere ...
or varicose veins
Varicose veins, also known as varicoses, are a medical condition in which superficial veins become enlarged and twisted. Although usually just a cosmetic ailment, in some cases they cause fatigue, pain, itch, itching, and cramp, nighttime leg cram ...
. Several treatments are available including endovenous thermal ablation
Varicose veins, also known as varicoses, are a medical condition in which superficial veins become enlarged and twisted. Although usually just a cosmetic ailment, in some cases they cause fatigue, pain, itch, itching, and cramp, nighttime leg cram ...
(using radiofrequency or laser energy), vein stripping
A phlebectomy, or vein stripping, is a surgical procedure done under general or local anaesthetic to aid in the treatment of varicose veins and other manifestations of chronic venous disease. The vein "stripped" (pulled out from under the skin ...
, ambulatory phlebectomy
An ambulatory phlebectomy is a surgical phlebectomy treatment for superficial varicose veins and tributaries.
Indications
General accepted indications for this technique are side branch varicose veins (semicirculatory varicose veins), varicose ...
, foam sclerotherapy
Sclerotherapy (the word reflects the Greek ''skleros'', meaning ''hard'')
is a procedure used to treat blood vessel malformations ( vascular malformations) and also malformations of the lymphatic system. A medication is injected into the vessels ...
, laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word ''laser'' originated as an acronym for light amplification by stimulated emission of radi ...
, or compression.
Postphlebitic syndrome
Post-thrombotic syndrome (PTS), also called postphlebitic syndrome and venous stress disorder is a medical condition that may occur as a long-term complication of deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
Signs and symptoms
Signs and symptoms of PTS in the le ...
is venous insufficiency that develops following deep vein thrombosis
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a type of venous thrombosis involving the formation of a blood clot in a deep vein, most commonly in the legs or pelvis. A minority of DVTs occur in the arms. Symptoms can include pain, swelling, redness, and enl ...
.
Venous thrombosis
Venous thrombosis
Venous thrombosis is the blockage of a vein caused by a thrombus (blood clot). A common form of venous thrombosis is deep vein thrombosis (DVT), when a blood clot forms in the deep veins. If a thrombus breaks off ( embolizes) and flows to the lu ...
is the formation of a thrombus
A thrombus ( thrombi) is a solid or semisolid aggregate from constituents of the blood (platelets, fibrin, red blood cells, white blood cells) within the circulatory system during life. A blood clot is the final product of the blood coagulatio ...
(blood clot) in a vein. This most commonly affects a deep vein
A deep vein is a vein that is deep in the body. This contrasts with superficial veins that are close to the body's surface.
Deep veins are almost always beside an artery with the same name (e.g. the femoral vein is beside the femoral artery). ...
known as deep vein thrombosis
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a type of venous thrombosis involving the formation of a blood clot in a deep vein, most commonly in the legs or pelvis. A minority of DVTs occur in the arms. Symptoms can include pain, swelling, redness, and enl ...
(DVT). DVT usually occurs in the veins of the legs, although it can also occur in the veins of the arms. Immobility, active cancer, obesity, traumatic damage and congenital disorders that make clots more likely are all risk factors for deep vein thrombosis. It can cause the affected limb to swell, and cause pain and an overlying skin rash. In the worst case, a deep vein thrombosis can extend, or a part of a clot can break off as an embolus
An embolus (; : emboli; from the Greek ἔμβολος "wedge", "plug") is an unattached mass that travels through the circulatory system, bloodstream and is capable of creating blockages. When an embolus Vascular occlusion, occludes a blood vess ...
and lodge in a pulmonary artery
A pulmonary artery is an artery in the pulmonary circulation that carries deoxygenated blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs. The largest pulmonary artery is the ''main pulmonary artery'' or ''pulmonary trunk'' from the heart, and ...
in the lungs, known as a pulmonary embolism
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a blockage of an pulmonary artery, artery in the lungs by a substance that has moved from elsewhere in the body through the bloodstream (embolism). Symptoms of a PE may include dyspnea, shortness of breath, chest pain ...
.The decision to treat deep vein thrombosis depends on its size, a person's symptoms, and their risk factors. It generally involves anticoagulation
An anticoagulant, commonly known as a blood thinner, is a chemical substance that prevents or reduces the coagulation of blood, prolonging the clotting time. Some occur naturally in blood-eating animals, such as leeches and mosquitoes, which h ...
to prevents clots or to reduce the size of the clot. Intermittent pneumatic compression Intermittent pneumatic compression is a therapeutic technique used in medical devices that include an air pump and inflatable auxiliary sleeves, gloves or boots in a system designed to improve venous circulation in the limbs of patients who have ede ...
is a method used to improve venous circulation in cases of edema or in those at risk from a deep vein thrombosis.
A clot can also form in a superficial vein
Superficial veins are veins that are close to the surface of the body, as opposed to deep veins, which are far from the surface.
Superficial veins are not paired with an artery, unlike the deep veins, which are typically associated with an art ...
( superficial venous thrombosis) which is normally not clinically significant, but the thrombus can migrate into the deep venous system where it can also give rise to a pulmonary embolism.
Portal hypertension
Theportal vein
The portal vein or hepatic portal vein (HPV) is a blood vessel that carries blood from the gastrointestinal tract, gallbladder, pancreas and spleen to the liver. This blood contains nutrients and toxins extracted from digested contents. Approxima ...
also known as the ''hepatic portal vein'' carries blood drained from most of the gastrointestinal tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the Digestion, digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The tract is the largest of the body's systems, after the cardiovascula ...
to the liver
The liver is a major metabolic organ (anatomy), organ exclusively found in vertebrates, which performs many essential biological Function (biology), functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of var ...
. Portal hypertension
Portal hypertension is defined as increased portal venous pressure, with a hepatic venous pressure gradient greater than 5 mmHg. Normal portal pressure is 1–4 mmHg; clinically insignificant portal hypertension is present at portal pressures 5� ...
is mainly caused by cirrhosis
Cirrhosis, also known as liver cirrhosis or hepatic cirrhosis, chronic liver failure or chronic hepatic failure and end-stage liver disease, is a chronic condition of the liver in which the normal functioning tissue, or parenchyma, is replaced ...
of the liver. Other causes can include an obstructing clot in a hepatic vein
In human anatomy, the hepatic veins are the veins that drain venous blood from the liver into the inferior vena cava (as opposed to the hepatic portal vein which conveys blood from the gastrointestinal organs to the liver). There are usually thre ...
( Budd Chiari syndrome) or compression from tumors or tuberculosis lesions. When the pressure increases in the portal vein, a collateral circulation
Collateral circulation is the alternate Circulatory system, circulation around a blocked blood vessel, artery or vein via another path, such as nearby minor vessels. It may occur via preexisting vascular redundancy (analogous to redundancy (engi ...
develops, causing visible veins such as esophageal varices
Esophageal varices are extremely Vasodilation, dilated sub-mucosal veins in the lower third of the esophagus. They are most often a consequence of portal hypertension, commonly due to cirrhosis. People with esophageal varices have a strong tendenc ...
.
Vascular anomalies
A vascular anomaly can be either avascular tumor
A vascular tumor is a vascular anomaly where a tumor forms from cells that make blood or lymph vessels; a soft tissue growth that can be either benign or malignant. Examples of vascular tumors include hemangiomas, hemangioendotheliomas, Kapo ...
or a birthmark
A birthmark is a congenital, benign irregularity on the skin which is present at birth or appears shortly after birth—usually in the first month. Birthmarks can occur anywhere on the skin. They are caused by overgrowth of blood vessels, melanocy ...
, or a vascular malformation
A vascular malformation is a type of vascular anomaly. They may cause aesthetic problems as they have a growth cycle, and can continue to grow throughout life.
Vascular malformations of the brain include those involving capillaries, and those in ...
.
In a tumor such as infantile hemangioma the mass is soft, and easily compressed, and their coloring is due to the dilated anomalous involved veins. They are most commonly found in the head and neck. Venous malformations are the type of vascular malformation that involves the veins. They can often extend deeper from their surface appearance, reaching underlying muscle or bone. In the neck they may extend into the lining of the mouth cavity or into the salivary gland
The salivary glands in many vertebrates including mammals are exocrine glands that produce saliva through a system of ducts. Humans have three paired major salivary glands ( parotid, submandibular, and sublingual), as well as hundreds of min ...
s. They are the most common of the vascular malformations. A severe venous malformation can involve the lymph vessels as a ''lymphaticovenous malformation''.
Arterial disease
 *
* Coronary artery disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also called coronary heart disease (CHD), or ischemic heart disease (IHD), is a type of cardiovascular disease, heart disease involving Ischemia, the reduction of blood flow to the cardiac muscle due to a build-up ...
– the most common of the cardiovascular diseases
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is any disease involving the heart or blood vessels. CVDs constitute a class of diseases that includes: coronary artery diseases (e.g. angina, heart attack), heart failure, hypertensive heart disease, rheuma ...
, types include angina
Angina, also known as angina pectoris, is chest pain or pressure, usually caused by insufficient blood flow to the heart muscle (myocardium). It is most commonly a symptom of coronary artery disease.
Angina is typically the result of parti ...
, and myocardial infarction
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when Ischemia, blood flow decreases or stops in one of the coronary arteries of the heart, causing infarction (tissue death) to the heart muscle. The most common symptom ...
* Carotid artery stenosis
Carotid artery stenosis is a narrowing or constriction of any part of the carotid artery, carotid arteries, usually caused by atherosclerosis.
Signs and symptoms
The common carotid artery is the large artery whose Common carotid artery#Clinical ...
– any narrowing of the carotid arteries
In anatomy, the left and right common carotid arteries (carotids) () are arteries that supply the head and neck with oxygenated blood; they divide in the neck to form the external and internal carotid arteries.
Structure
The common carotid ...
* Peripheral artery disease
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is a vascular disorder that causes abnormal narrowing of arteries other than those that supply the heart or brain. PAD can happen in any blood vessel, but it is more common in the legs than the arms.
When narr ...
– occurs when atheromatous plaques build up in the arteries that supply blood to the arms and legs, causing the arteries to narrow or become blocked.
* Erythromelalgia
Erythromelalgia, or Mitchell's disease (after Silas Weir Mitchell (physician), Silas Weir Mitchell), is a rare vascular peripheral pain disorder in which blood vessels, usually in the Human leg, lower extremities or hands, are episodically blocke ...
- a rare peripheral vascular disease with symptoms that include burning pain, increased temperature, erythema and swelling that generally affect the hands and feet.
* Renal artery stenosis
Renal artery stenosis (RAS) is the narrowing of one or both of the renal arteries, most often caused by atherosclerosis or fibromuscular dysplasia. This narrowing of the renal artery can impede blood flow to the target kidney, resulting in r ...
- the narrowing of renal arteries
The renal arteries are paired arteries that supply the kidneys with blood. Each is directed across the crus of the diaphragm, so as to form nearly a right angle.
The renal arteries carry a large portion of total blood flow to the kidneys. Up to a ...
that carry blood to the kidney
In humans, the kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped blood-filtering organ (anatomy), organs that are a multilobar, multipapillary form of mammalian kidneys, usually without signs of external lobulation. They are located on the left and rig ...
s from the aorta
The aorta ( ; : aortas or aortae) is the main and largest artery in the human body, originating from the Ventricle (heart), left ventricle of the heart, branching upwards immediately after, and extending down to the abdomen, where it splits at ...
.
* Buerger's disease
Thromboangiitis obliterans, also known as Buerger disease (English ; ) or Winiwarter-Buerger disease, is a recurring progressive inflammation and thrombosis (clotting) of small and medium arteries and veins of the hands and feet. It is strongly ...
– inflammation and swelling in small blood vessels, causing the vessels to narrow or become blocked by blood clots
A thrombus ( thrombi) is a solid or semisolid aggregate from constituents of the blood (platelets, fibrin, red blood cells, white blood cells) within the circulatory system during life. A blood clot is the final product of the blood coagulati ...
.
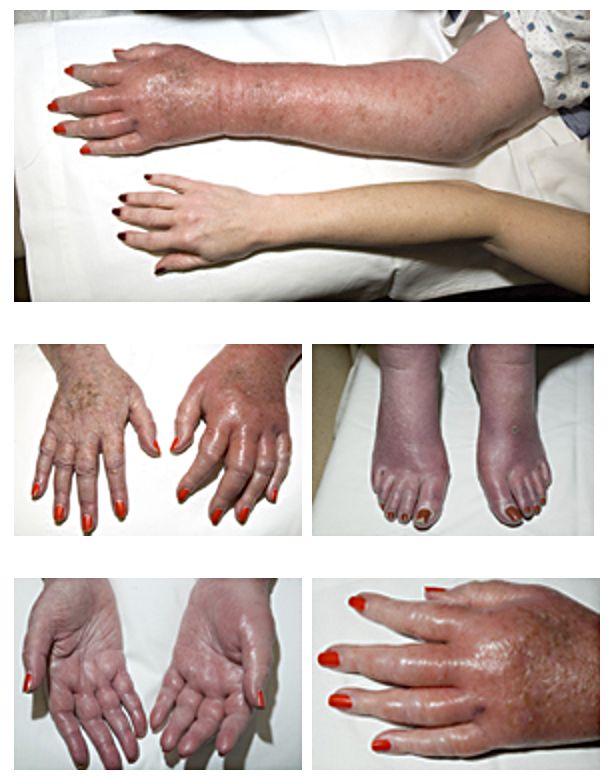
* Raynaud syndrome
Raynaud syndrome, also known as Raynaud's phenomenon, is a medical condition in which the spasm of small arteries causes episodes of reduced blood flow to end arterioles. Typically the fingers, and, less commonly, the toes, are involved. Rare ...
– a peripheral vascular disorder that causes constriction of the peripheral blood vessels in the fingers and toes when a person is cold or experiencing stress.
* Disseminated intravascular coagulation
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) is a condition in which blood clots form throughout the body, blocking Microvessel, small blood vessels. Symptoms may include chest pain, shortness of breath, leg pain, problems speaking, or problems ...
– a widespread activation of clotting in the smaller blood vessels.
* Cerebrovascular disease
Cerebrovascular disease includes a variety of medical conditions that affect the blood vessels of the brain and the cerebral circulation. Arteries supplying oxygen and nutrients to the brain are often damaged or deformed in these disorders. Th ...
– a group of vascular diseases that affect brain
The brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head (cephalization), usually near organs for ...
function, most commonly a stroke
Stroke is a medical condition in which poor cerebral circulation, blood flow to a part of the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: brain ischemia, ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and intracranial hemorrhage, hemor ...
.
* Vasculitis
Vasculitis is a group of disorders that destroy blood vessels by inflammation. Both artery, arteries and veins are affected. Lymphangitis (inflammation of lymphatic vessels) is sometimes considered a type of vasculitis. Vasculitis is primarily c ...
- inflammation of blood vessels, either arteries or veins
Lymphatic disease
*Lymphangitis
Lymphangitis is an inflammation or an infection of the lymphatic channels that occurs as a result of infection at a site distal to the channel. It may present as long red streaks spreading away from the site of infection. It is a possible medic ...
Mechanism
 Vascular disease is a pathological state of large and medium muscular arteries and is triggered by
Vascular disease is a pathological state of large and medium muscular arteries and is triggered by endothelial cell
The endothelium (: endothelia) is a single layer of squamous endothelial cells that line the interior surface of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels. The endothelium forms an interface between circulating blood or lymph in the lumen and th ...
dysfunction.
Because of factors like pathogen
In biology, a pathogen (, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of"), in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a Germ theory of d ...
s, oxidized
Redox ( , , reduction–oxidation or oxidation–reduction) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of the reactants change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is ...
LDL particles and other inflammatory stimuli endothelial cell
The endothelium (: endothelia) is a single layer of squamous endothelial cells that line the interior surface of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels. The endothelium forms an interface between circulating blood or lymph in the lumen and th ...
s become active.
The process causes thickening of the vessel wall, forming a plaque that consists of proliferating smooth muscle cell
Smooth muscle is one of the three major types of vertebrate muscle tissue, the others being skeletal and cardiac muscle. It can also be found in invertebrates and is controlled by the autonomic nervous system. It is non- striated, so-called becau ...
s, macrophage
Macrophages (; abbreviated MPhi, φ, MΦ or MP) are a type of white blood cell of the innate immune system that engulf and digest pathogens, such as cancer cells, microbes, cellular debris and foreign substances, which do not have proteins that ...
s and lymphocyte
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) in the immune system of most vertebrates. Lymphocytes include T cells (for cell-mediated and cytotoxic adaptive immunity), B cells (for humoral, antibody-driven adaptive immunity), an ...
s.
The plaque results in restricted blood flow, decreasing the amount of oxygen and nutrients that reach certain organs.
This plaque can also rupture, causing the formation of clots.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing vascular disease can be complex due to the variety of symptoms vascular diseases can cause. Reviewing a patient'sfamily history
Genealogy () is the study of families, family history, and the tracing of their lineages. Genealogists use oral interviews, historical records, genetic analysis, and other records to obtain information about a family and to demonstrate kins ...
and conducting a physical examination
In a physical examination, medical examination, clinical examination, or medical checkup, a medical practitioner examines a patient for any possible medical signs or symptoms of a Disease, medical condition. It generally consists of a series of ...
are important steps in making a diagnosis. Physical exams may differ depending on the type of vascular disease suspected. For example, in the case of a peripheral vascular disease
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is a vascular disorder that causes abnormal narrowing of arteries other than those that supply the heart or brain. PAD can happen in any blood vessel, but it is more common in the legs than the arms.
When narro ...
, a physical exam consists of checking blood flow
Hemodynamics American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, or haemodynamics are the Fluid dynamics, dynamics of blood flow. The circulatory system is controlled by homeostasis, homeostatic mechanisms of autoregulation, just as hydrau ...
in a patient's legs.
Treatment
 Treatment varies based on the type of vascular disease being treated. In treating renal artery disease, a 2014 study indicates that balloon angioplasty can improve diastolic blood pressure and potentially reduce antihypertensive drug requirements. In the case of peripheral artery disease, treatment to prevent complications is important; without treatment, sores or
Treatment varies based on the type of vascular disease being treated. In treating renal artery disease, a 2014 study indicates that balloon angioplasty can improve diastolic blood pressure and potentially reduce antihypertensive drug requirements. In the case of peripheral artery disease, treatment to prevent complications is important; without treatment, sores or gangrene
Gangrene is a type of tissue death caused by a lack of blood supply. Symptoms may include a change in skin color to red or black, numbness, swelling, pain, skin breakdown, and coolness. The feet and hands are most commonly affected. If the ga ...
(tissue death) may occur.
More generally, treatments for vascular disease may include:
* Lowering cholesterol
Cholesterol is the principal sterol of all higher animals, distributed in body Tissue (biology), tissues, especially the brain and spinal cord, and in Animal fat, animal fats and oils.
Cholesterol is biosynthesis, biosynthesized by all anima ...
levels
* Lowering blood pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of Circulatory system, circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term ...
* Lowering blood glucose
* Changes in diet
* Increasing physical activity (as recommended by a healthcare provider)
* Weight loss
* Quitting smoking
* Stress reduction
References
Further reading
*External links
{{Medicine Vascular diseases Diseases of veins, lymphatic vessels and lymph nodes