VSS (voltage) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
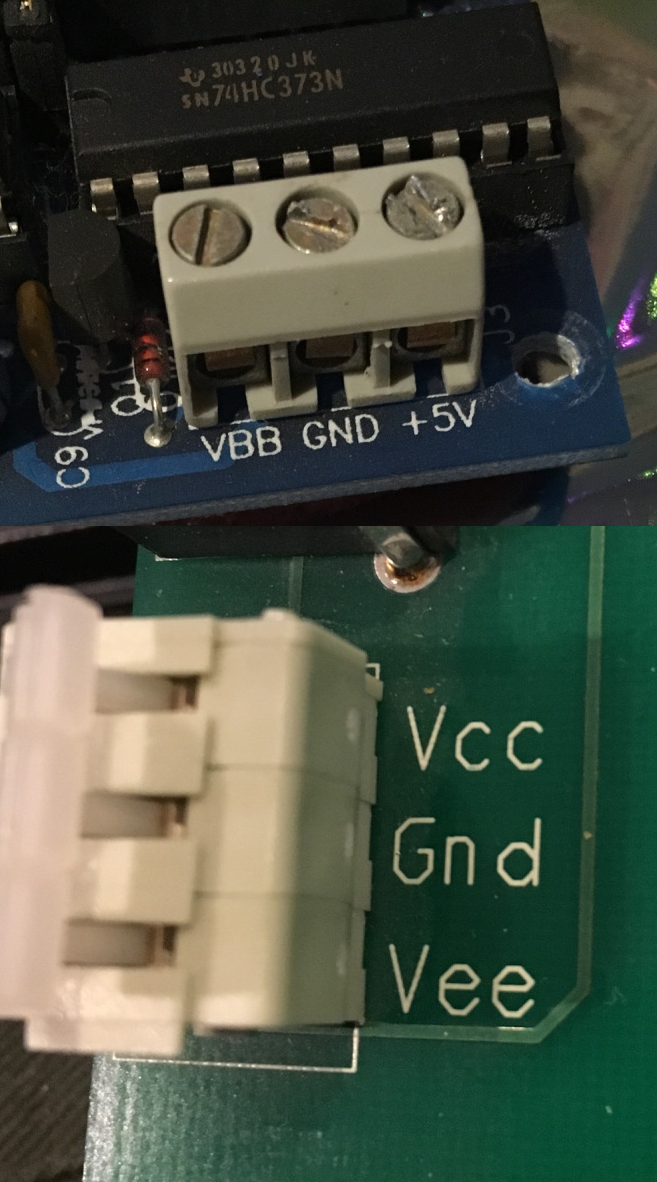 IC power-supply pins are voltage and current supply terminals found on
IC power-supply pins are voltage and current supply terminals found on Op-amps: Some Standard Conconfigurations and Applications, Fall 2012
Washington and Lee University, Lexington, VA.
 IC power-supply pins are voltage and current supply terminals found on
IC power-supply pins are voltage and current supply terminals found on integrated circuits
An integrated circuit (IC), also known as a microchip or simply chip, is a set of electronic circuits, consisting of various electronic components (such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors) and their interconnections. These components a ...
(ICs) in electrical engineering
Electrical engineering is an engineering discipline concerned with the study, design, and application of equipment, devices, and systems that use electricity, electronics, and electromagnetism. It emerged as an identifiable occupation in the l ...
, electronic engineering
Electronic engineering is a sub-discipline of electrical engineering that emerged in the early 20th century and is distinguished by the additional use of active components such as semiconductor devices to amplify and control electric current flo ...
, and integrated circuit design
Integrated circuit design, semiconductor design, chip design or IC design, is a sub-field of electronics engineering, encompassing the particular Boolean logic, logic and circuit design techniques required to design integrated circuits (ICs). A ...
. ICs have at least two pins that connect to the power rails of the circuit in which they are installed. These are known as the power-supply pins. However, the labeling of the pins varies by IC family and manufacturer. The double-subscript notation usually corresponds to a first letter in a given IC family (transistors) notation of the terminals (e.g. VDD supply for a drain terminal in FETs etc.).
The simplest labels are V+ and V−, but internal design and historical traditions have led to a variety of other labels being used. V+ and V− may also refer to the non-inverting (+) and inverting (−) voltage inputs of ICs like op amp
An operational amplifier (often op amp or opamp) is a DC-coupled electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input, a (usually) single-ended output, and an extremely high gain. Its name comes from its original use of performing mathema ...
s.
For power supplies, sometimes one of the supply rails is referred to as ground
Ground may refer to:
Geology
* Land, the solid terrestrial surface of the Earth
* Soil, a mixture of clay, sand and organic matter present on the surface of the Earth
Electricity
* Ground (electricity), the reference point in an electrical circ ...
(abbreviated "GND") positive and negative voltages are relative to the ground. In digital electronics, negative voltages are seldom present, and the ground nearly always is the lowest voltage level. In analog electronics (e.g. an audio power amplifier
An audio power amplifier (or power amp) amplifies low-power electronic audio signals, such as the signal from a radio receiver or an electric guitar pickup, to a level that is high enough for driving loudspeakers or headphones. Audio power a ...
) the ground can be a voltage level between the most positive and most negative voltage level.
While double-subscript notation, where subscripted letters denote the difference between two points, uses similar-looking placeholders with subscripts, the double-letter supply voltage subscript notation is not directly linked (though it may have been an influencing factor).Washington and Lee University, Lexington, VA.
BJTs
ICs usingbipolar junction transistor
A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a type of transistor that uses both electrons and electron holes as charge carriers. In contrast, a unipolar transistor, such as a field-effect transistor (FET), uses only one kind of charge carrier. A ...
s have ''VCC'' (+, positive) and ''VEE'' (-, negative) power-supply pins though ''VCC'' is also often used for CMOS devices as well.
In circuit diagram
A circuit diagram (or: wiring diagram, electrical diagram, elementary diagram, electronic schematic) is a graphical representation of an Electrical network, electrical circuit. A pictorial circuit diagram uses simple images of components, whil ...
s and circuit analysis, there are long-standing conventions regarding the naming of voltages, currents, and some components. In the analysis of a bipolar junction transistor, for example, in a common-emitter
In electronics, a common-emitter amplifier is one of three basic single-stage bipolar-junction-transistor (BJT) amplifier topologies, typically used as a voltage amplifier. It offers high current gain (typically 200), medium input resistance ...
configuration, the DC voltage at the collector, emitter, and base (with respect to ground) may be written as ''V''C, ''V''E, and ''V''B respectively.
Resistors associated with these transistor terminals may be designated ''RC'', ''RE'', and ''RB''. In order to create the DC voltages, the furthest voltage, beyond these resistors or other components if present, was often referred to as ''VCC'', ''VEE'', and ''VBB''. In practice ''VCC'' and ''VEE'' then refer to the positive and negative supply lines respectively in common
Common may refer to:
As an Irish surname, it is anglicised from Irish Gaelic surname Ó Comáin.
Places
* Common, a townland in County Tyrone, Northern Ireland
* Boston Common, a central public park in Boston, Massachusetts
* Cambridge Com ...
NPN circuits. Note that ''VCC'' would be negative, and ''VEE'' would be positive in equivalent PNP circuits.
The ''VBB'' specifies reference bias supply voltage in ECL logic.
FETs
Exactly analogous conventions were applied tofield-effect transistor
The field-effect transistor (FET) is a type of transistor that uses an electric field to control the current through a semiconductor. It comes in two types: junction FET (JFET) and metal-oxide-semiconductor FET (MOSFET). FETs have three termi ...
s with their drain, source and gate terminals. This led to ''VD'' and ''VS'' being created by supply voltages designated ''VDD'' and ''VSS'' in the more common circuit configurations. In equivalence to the difference between NPN and PNP bipolars, ''VDD'' is positive with regard to ''VSS'' in the case of ''n''-channel FETs and MOSFET
upright=1.3, Two power MOSFETs in amperes">A in the ''on'' state, dissipating up to about 100 watt">W and controlling a load of over 2000 W. A matchstick is pictured for scale.
In electronics, the metal–oxide–semiconductor field- ...
s and negative for circuits based on ''p''-channel FETs and MOSFETs.
CMOS
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS, pronounced "sea-moss
", , ) is a type of MOSFET, metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) semiconductor device fabrication, fabrication process that uses complementary an ...
ICs have generally borrowed the NMOS convention of ''VDD'' for positive and ''VSS'' for negative, even though both positive and negative supply rails connect to source terminals (the positive supply goes to PMOS sources, the negative supply to NMOS sources).
In many single-supply digital and analog circuits the negative power supply is also called "GND". In "split-rail" supply systems there are multiple supply voltages. Examples of such systems include modern cell phones, with GND and voltages such as 1.2 V, 1.8 V, 2.4 V, 3.3 V, and PCs, with GND and voltages such as −5 V, 3.3 V, 5 V, 12 V. Power-sensitive designs often have multiple power rails at a given voltage, using them to conserve energy by switching off supplies to components that are not in active use.
More advanced circuits often have pins carrying voltage levels for more specialized functions, and these are generally labeled with some abbreviation of their purpose. For example, VUSB for the supply delivered to a USB
Universal Serial Bus (USB) is an industry standard, developed by USB Implementers Forum (USB-IF), for digital data transmission and power delivery between many types of electronics. It specifies the architecture, in particular the physical ...
device (nominally 5 V), VBAT for a battery, or Vref for the reference voltage for an analog-to-digital converter
In electronics, an analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A-to-D) is a system that converts an analog signal, such as a sound picked up by a microphone or light entering a digital camera, into a Digital signal (signal processing), digi ...
. Systems combining both digital and analog circuits often distinguish digital and analog grounds (GND and AGND), helping isolate digital noise from sensitive analog circuits. High-security cryptographic devices and other secure systems sometimes require separate power supplies for their unencrypted and encrypted ( red/black) subsystems to prevent leakage of sensitive plaintext.
BJTs and FETs mixed
Although still in relatively common use, there is limited relevance of these device-specific power-supply designations in circuits that use a mixture of bipolar and FET elements, or in those that employ either both NPN and PNP transistors or both ''n''- and ''p''-channel FETs. This latter case is very common in modern chips, which are often based onCMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS, pronounced "sea-moss
", , ) is a type of MOSFET, metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) semiconductor device fabrication, fabrication process that uses complementary an ...
technology, where the ''C'' stands for ''complementary'', meaning that complementary pairs of ''n''- and ''p''-channel devices are common throughout.
These naming conventions were part of a bigger picture, where, to continue with bipolar-transistor examples, although the FET
The field-effect transistor (FET) is a type of transistor that uses an electric field to control the current through a semiconductor. It comes in two types: junction FET (JFET) and metal-oxide-semiconductor FET (MOSFET). FETs have three termi ...
remains entirely analogous, DC or bias
Bias is a disproportionate weight ''in favor of'' or ''against'' an idea or thing, usually in a way that is inaccurate, closed-minded, prejudicial, or unfair. Biases can be innate or learned. People may develop biases for or against an individ ...
currents into or out of each terminal may be written ''IC'', ''IE'', and ''IB''. Apart from DC or bias conditions, many transistor circuits also process a smaller audio-, video-, or radio-frequency signal that is superimposed on the bias at the terminals. Lower-case letters and subscripts are used to refer to these signal levels at the terminals, either peak-to-peak
The amplitude of a Periodic function, periodic Variable (mathematics), variable is a measure of its change in a single Period (mathematics), period (such as frequency, time or Wavelength, spatial period). The amplitude of a non-periodic signal is ...
or RMS as required. So we see ''vc'', ''ve'', and ''vb'', as well as ''ic'', ''ie'', and ''ib''. Using these conventions, in a common-emitter amplifier, the ratio ''vc''/''vb'' represents the small-signal voltage gain at the transistor, and ''vc''/''ib'' the small-signal ''trans-resistance'', from which the name ''transistor'' is derived by contraction. In this convention, ''vi'' and ''vo'' usually refer to the external input and output voltages of the circuit or stage.
Similar conventions were applied to circuits involving vacuum tube
A vacuum tube, electron tube, thermionic valve (British usage), or tube (North America) is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric voltage, potential difference has been applied. It ...
s, or ''thermionic valves'', as they were known outside of the U.S. Therefore, we see ''VP'', ''VK'', and ''VG'' referring to plate (or ''anode'' outside of the U.S.), cathode (note ''K'', not ''C'') and grid voltages in analyses of vacuum triode
A triode is an electronic amplifier, amplifying vacuum tube (or ''thermionic valve'' in British English) consisting of three electrodes inside an evacuated glass envelope: a heated Electrical filament, filament or cathode, a control grid, grid ...
, tetrode
A tetrode is a vacuum tube (called ''valve'' in British English) having four active electrodes. The four electrodes in order from the centre are: a thermionic cathode, first and second grids, and a plate electrode, plate (called ''anode'' in Bri ...
, and pentode
A pentode is an electronic device having five electrodes. The term most commonly applies to a three-grid amplifying vacuum tube or thermionic valve that was invented by Gilles Holst and Bernhard D.H. Tellegen in 1926. The pentode (called a ''tri ...
circuits.
See also
*4000 series
The 4000 series is a CMOS logic family of integrated circuits (ICs) first introduced in 1968 by RCA. It was slowly migrated into the 4000B buffered series after about 1975. It had a much wider supply voltage range than any contemporary logic fami ...
*7400 series
The 7400 series is a popular logic family of transistor–transistor logic (TTL) integrated circuits (ICs).
In 1964, Texas Instruments introduced the SN5400 series of logic chips, in a ceramic semiconductor package. A low-cost plastic package ...
*Bob Widlar
Robert John Widlar (pronounced ''wide-lar''; November 30, 1937 – February 27, 1991) was an American electronics engineer and a designer of linear integrated circuits (ICs).
Early years
Widlar was born November 30, 1937, in Cleveland to p ...
*Common collector
In electronics, a common collector amplifier (also known as an emitter follower) is one of three basic single-stage bipolar junction transistor (BJT) amplifier topologies, typically used as a voltage buffer.
In this circuit, the base term ...
*Differential amplifier
A differential amplifier is a type of electronic amplifier that amplifies the difference between two input voltages but suppresses any voltage common to the two inputs. It is an analog circuit with two inputs V_\text^- and V_\text^+ and one outp ...
* Letter and numeral code for voltages
*List of 4000 series integrated circuits
The following is a list of CMOS 4000-series digital logic integrated circuits. In 1968, the original 4000-series was introduced by RCA. Although more recent parts are considerably faster, the 4000 devices operate over a wide power supply range ( ...
*List of 7400 series integrated circuits
The following is a list of 7400-series digital logic integrated circuits. In the mid-1960s, the original 7400-series integrated circuits, 7400-series integrated circuits were introduced by Texas Instruments with the prefix "SN" to create the name ...
*Logic family
In computer engineering, a logic family is one of two related concepts:
* A logic family of monolithic digital integrated circuit devices is a group of electronic logic gates constructed using one of several different designs, usually with compati ...
*Logic gate
A logic gate is a device that performs a Boolean function, a logical operation performed on one or more binary inputs that produces a single binary output. Depending on the context, the term may refer to an ideal logic gate, one that has, for ...
*Open collector
Open collector, open drain, open emitter, and open source refer to integrated circuit (IC) output pin configurations that process the IC's internal function through a transistor with an exposed terminal that is internally unconnected (i.e. "ope ...
*Operational amplifier applications
This article illustrates some typical operational amplifier applications. Operational amplifiers are optimised for use with negative feedback, and this article discusses only negative-feedback applications. When positive feedback is required, a ...
* Pin-compatibility
*Reference designator
A reference designator unambiguously identifies the location of a component within an electrical schematic or on a printed circuit board. The reference designator usually consists of one or two letters followed by a number, e.g. C3, D1, R4, U15. ...
Notes
References
{{reflist Integrated circuits fr:Boîtier de circuit intégré#Broches d'alimentation d'un circuit intégré