Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (abbreviated as UPPP or UP3) is a type of
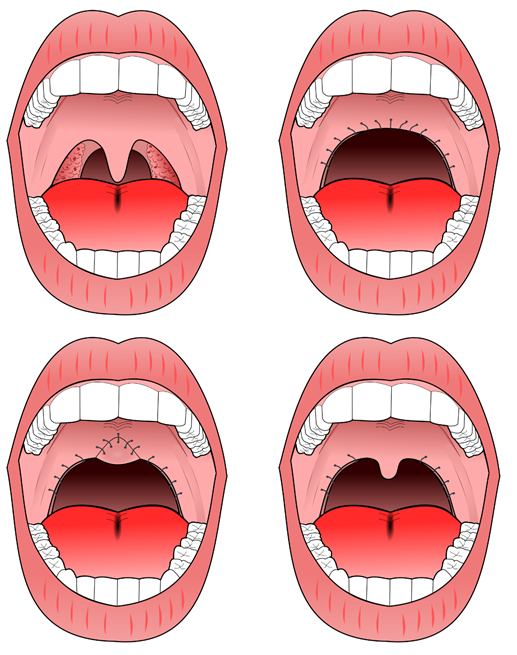 First, the surgeon cuts into the soft palate starting from a point above the palatal tonsil towards the uvula. Then, the mucosa of the soft palate, tonsillar fossa, and side of the uvula is separated from the underlying tissue layers and removed, leaving any excess nasal mucosa. The edges of the remaining mucosa are sutured back together and the tonsillar pillars may be sutured closed. If the uvula is long, it is shortened or removed completely. Often, the palatal tonsils are removed at the same time, if they have not already been removed. The result of UPPP is that the soft palate is shortened by removing a wedge of excess mucosa from the palate. UPPP decreases the amount of anterior-posterior (front to back) palatal collapse and widens the pharyngeal airway.
UPPP may be combined with other types of sleep surgery to address airway obstruction at different sites. This is termed the multilevel surgery. The effectiveness of UPPP is increased when it is combined with another procedure as a multilevel surgery. Examples include UPPP with tonsillectomy or UPPP with a hypopharyngeal procedure such as tongue base reduction or hyoid suspension or UPPP with radiofrequency ablation.
First, the surgeon cuts into the soft palate starting from a point above the palatal tonsil towards the uvula. Then, the mucosa of the soft palate, tonsillar fossa, and side of the uvula is separated from the underlying tissue layers and removed, leaving any excess nasal mucosa. The edges of the remaining mucosa are sutured back together and the tonsillar pillars may be sutured closed. If the uvula is long, it is shortened or removed completely. Often, the palatal tonsils are removed at the same time, if they have not already been removed. The result of UPPP is that the soft palate is shortened by removing a wedge of excess mucosa from the palate. UPPP decreases the amount of anterior-posterior (front to back) palatal collapse and widens the pharyngeal airway.
UPPP may be combined with other types of sleep surgery to address airway obstruction at different sites. This is termed the multilevel surgery. The effectiveness of UPPP is increased when it is combined with another procedure as a multilevel surgery. Examples include UPPP with tonsillectomy or UPPP with a hypopharyngeal procedure such as tongue base reduction or hyoid suspension or UPPP with radiofrequency ablation.
sleep surgery
Sleep surgery is a range of surgical procedures to treat sleep-related breathing disorders (sleep-disordered breathing), especially obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). The spectrum of sleep-related breathing disorders also includes Snoring, primary snor ...
, which are surgical procedures for sleep-related breathing disorder A sleep-related breathing disorder is a sleep disorder in which abnormalities in breathing occur during sleep which may or may not be present while awake. According to the International Classification of Sleep Disorders, sleep-related breathing diso ...
s, especially obstructive sleep apnea
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is the most common sleep-related breathing disorder and is characterized by recurrent episodes of complete or partial airway obstruction, obstruction of the respiratory tract#Upper respiratory tract, upper airway lea ...
(OSA). Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty involves removal and/or remodeling of tissues in the throat in order to prevent obstruction of the airway during sleep. Tissues which may typically be removed include the paryngeal tonsil
The tonsils ( ) are a set of lymphoid organs facing into the aerodigestive tract, which is known as Waldeyer's tonsillar ring and consists of the adenoid tonsil (or pharyngeal tonsil), two tubal tonsils, two palatine tonsils, and the lingual t ...
s and the adenoid
In anatomy, the pharyngeal tonsil, also known as the nasopharyngeal tonsil or adenoid, is the superior-most of the tonsils. It is a mass of lymphoid tissue located behind the nasal cavity, in the roof and the posterior wall of the nasopharyn ...
tonsil. Tissues which may typically be remodeled include the uvula
The uvula (: uvulas or uvulae), also known as the palatine uvula or staphyle, is a conic projection from the back edge of the middle of the soft palate, composed of connective tissue containing a number of racemose glands, and some muscular fi ...
(see uvulotomy), the soft palate
The soft palate (also known as the velum, palatal velum, or muscular palate) is, in mammals, the soft biological tissue, tissue constituting the back of the roof of the mouth. The soft palate is part of the palate of the mouth; the other part is ...
, and parts of the pharynx
The pharynx (: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the human mouth, mouth and nasal cavity, and above the esophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs respectively). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates ...
. UPPP is the most common surgical procedure performed for OSA.
Background
OSA is one of the most common types ofsleep-related breathing disorder A sleep-related breathing disorder is a sleep disorder in which abnormalities in breathing occur during sleep which may or may not be present while awake. According to the International Classification of Sleep Disorders, sleep-related breathing diso ...
. It involves obstruction of the upper airway during sleep. Loud snoring and apnea
Apnea (also spelled apnoea in British English) is the temporary cessation of breathing. During apnea, there is no movement of the muscles of inhalation, and the volume of the lungs initially remains unchanged. Depending on how blocked the ...
(periods of no breathing) followed by gasping and choking are signs of the condition. The main treatment is continuous positive airway pressure
Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) is a form of positive airway pressure (PAP) ventilation in which a constant level of pressure greater than atmospheric pressure is continuously applied to the upper respiratory tract of a person. The a ...
and a range of other measures such sleeping on the side and mandibular advancement splint
A mandibular splint or mandibular advancement splint is a prescription custom-made medical device worn in the mouth used to treat sleep-related breathing disorders including: obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), snoring, and Temporomandibular joint dysf ...
s.
Definition
Exactly what procedures fall under the category UPPP is poorly defined. Some consider all of the following to be UPPP: *Tonsillectomy
Tonsillectomy is a surgical procedure in which both palatine tonsils are fully removed from the back of the throat. The procedure is mainly performed for recurrent tonsillitis, throat infections and obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). For those wit ...
* UPPP with tonsillectomy / adenoidectomy
* Laser assisted uvulopalatoplasty (LAUP)
* Palatal stiffening (pillar procedure
Sleep surgery is a range of surgical procedures to treat sleep-related breathing disorders (sleep-disordered breathing), especially obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). The spectrum of sleep-related breathing disorders also includes primary snoring (no ...
)
* Cautery assisted palatal stiffening operation (CAPSO)
* Relocation pharyngoplasty
* Lateral pharyngoplasty
* Expansion sphincter pharyngoplasty
* Barbed reposition pharyngoplasty
* Palatal advancement pharyngoplasty
Indications
UPPP may be indicated if all of the following are true: * Diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnea * Failure of non invasive treatments (e.g.,continuous positive airway pressure
Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) is a form of positive airway pressure (PAP) ventilation in which a constant level of pressure greater than atmospheric pressure is continuously applied to the upper respiratory tract of a person. The a ...
, mandibular advancement splint
A mandibular splint or mandibular advancement splint is a prescription custom-made medical device worn in the mouth used to treat sleep-related breathing disorders including: obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), snoring, and Temporomandibular joint dysf ...
)
* Site of airway obstruction identified (soft palate) and amenable to correction with UPPP
Sleep surgery generally aims to correct one or more of the following three types of airway obstruction in OSA:
* Too little space (craniofacial anomaly)
* Too much tissue (tissue hypertrophy or obesity)
* Tissue too lax (nerve damage, poor muscle tone)
Of the above, UPPP is indicated in cases where there is too much tissue. It removes excess soft tissue from the back of the soft palate, thereby increasing the amount of space in the airway. UPPP also reduces the collapsibility of the upper airway.
Patient selection
It is difficult to predict which individuals will benefit from UPPP and which will not. The important factors may be the position of the palate with respect to the tongue, the size of the tonsils, and the individual's body mass index. The Friedman tongue position / palate position is one method to assess the level of obstruction in the pharynx.Contra-indications
Contraindications for UPPP include: * Morbid obesity / Body mass index more than 40kg/m2. *Retrognathia
Retrognathia is a type of malocclusion which refers to an abnormal posterior positioning of the maxilla or Human mandible, mandible, particularly the mandible, relative to the facial skeleton and soft tissues.
A retrognathic mandible is commonly ...
(small lower jaw).
* Retroglossia (tongue positioned further back than normal).
* Narrowing of the hypopharynx (laryngopharynx). Success rate is only 5% when hypopharyneal narrowing is present. If combined with maxillomandibular advancement, UPPP may still be possible.
* Pharyngeal wall bulging.
* Sagittal (front-to-back) orientation of airway.
Technique
 First, the surgeon cuts into the soft palate starting from a point above the palatal tonsil towards the uvula. Then, the mucosa of the soft palate, tonsillar fossa, and side of the uvula is separated from the underlying tissue layers and removed, leaving any excess nasal mucosa. The edges of the remaining mucosa are sutured back together and the tonsillar pillars may be sutured closed. If the uvula is long, it is shortened or removed completely. Often, the palatal tonsils are removed at the same time, if they have not already been removed. The result of UPPP is that the soft palate is shortened by removing a wedge of excess mucosa from the palate. UPPP decreases the amount of anterior-posterior (front to back) palatal collapse and widens the pharyngeal airway.
UPPP may be combined with other types of sleep surgery to address airway obstruction at different sites. This is termed the multilevel surgery. The effectiveness of UPPP is increased when it is combined with another procedure as a multilevel surgery. Examples include UPPP with tonsillectomy or UPPP with a hypopharyngeal procedure such as tongue base reduction or hyoid suspension or UPPP with radiofrequency ablation.
First, the surgeon cuts into the soft palate starting from a point above the palatal tonsil towards the uvula. Then, the mucosa of the soft palate, tonsillar fossa, and side of the uvula is separated from the underlying tissue layers and removed, leaving any excess nasal mucosa. The edges of the remaining mucosa are sutured back together and the tonsillar pillars may be sutured closed. If the uvula is long, it is shortened or removed completely. Often, the palatal tonsils are removed at the same time, if they have not already been removed. The result of UPPP is that the soft palate is shortened by removing a wedge of excess mucosa from the palate. UPPP decreases the amount of anterior-posterior (front to back) palatal collapse and widens the pharyngeal airway.
UPPP may be combined with other types of sleep surgery to address airway obstruction at different sites. This is termed the multilevel surgery. The effectiveness of UPPP is increased when it is combined with another procedure as a multilevel surgery. Examples include UPPP with tonsillectomy or UPPP with a hypopharyngeal procedure such as tongue base reduction or hyoid suspension or UPPP with radiofrequency ablation.
Modifications of uvulopalatopharyngoplasty
Different modifications of the original UPPP technique have been developed, termed modified uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (modUPPP or mUPPP). To distinguish them, the original procedure is sometimes termed standard, conventional, or traditional UPPP. These modifications were deeveloped because the original UPPP for OSA was quite invasive and involved removal of a relatively large amount of soft tissue. This sometimes results in significant complications. Modifications of UPPP and the year they were introduced are listed below: * Powell’s uvulopalatal flap (introduced in 1996). * Extended uvulopalatal flap (EUPF; 2003). * Lateral pharyngoplasty (LP; 2003). * Z-palatoplasty (ZPP; 2004). * Han-UPPP (2005). * Expansion sphincter pharyngoplasty (ESP; 2007). * Microdebrider-assisted extended uvulopalatoplasty (MEUP; 2008). * Relocation pharyngoplasty (rPP; 2009). * Z-palatopharyngoplasty (Z-PPP; 2010). * Soft palate webbing flap (SPWF; 2015).Uvuloplalatal flap with uvular preservation
This variant of UPPP reduces the risk of velopharyngeal incompetence and has less pain.Anterior advancement palatoplasty
This variant of UPPP preserves the back edge of the soft palate while moving the soft palate forwards.Expansion sphincter pharyngoplasty
The palatopharyngeal muscle is repositioned anteriorly (in a more forwards position).Recovery
UPPP may be carried out asoutpatient surgery
Outpatient surgery, also known as ambulatory surgery, day surgery, day case surgery, or same-day surgery, is surgery that does not require an overnight hospital stay.The International Association for Ambulatory Surgery (IAAS) would not consider al ...
(day case surgery), but it is sometimes done as an inpatient
A patient is any recipient of health care services that are performed by healthcare professionals. The patient is most often ill or injured and in need of treatment by a physician, nurse, optometrist, dentist, veterinarian, or other heal ...
procedure.
Complications
Possible short-term complications include: *Intubation
Intubation (sometimes entubation) is a medical procedure involving the insertion of a tube into the body. Most commonly, intubation refers to tracheal intubation, a procedure during which an endotracheal tube is inserted into the trachea to supp ...
not possible.
* Negative-pressure pulmonary edema
Negative-pressure pulmonary edema (NPPE), also known as Postobstructive Pulmonary Edema, is a clinical phenomenon that results from the generation of large negative pressures in the airways during attempted inspiration against some form of obstruc ...
(post-obstructive pulmonary edema).
* Bleeding (1-2% risk, which may occur at any time in the first 2 weeks after the procedure).
* Dehydration
In physiology, dehydration is a lack of total body water that disrupts metabolic processes. It occurs when free water loss exceeds intake, often resulting from excessive sweating, health conditions, or inadequate consumption of water. Mild deh ...
.
* Persistent pain (more than 2 weeks after the procedure).
Upper airway edema may be too much when UPPP is done at the same time as maxillomandibular advancement.
Possible long-term complications:
* Dysphagia
Dysphagia is difficulty in swallowing. Although classified under " symptoms and signs" in ICD-10, in some contexts it is classified as a condition in its own right.
It may be a sensation that suggests difficulty in the passage of solids or l ...
(possibly related to undiagnosed gastroesophageal reflux disease
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is a chronic upper gastrointestinal disease in which stomach content persistently and regularly flows up into the esophagus, resulting in symptoms and/or ...
).
* Dysgeusia
Dysgeusia, also known as parageusia, is a distortion of the sense of taste. Dysgeusia is also often associated with ageusia, which is the complete lack of taste, and hypogeusia, which is a decrease in taste sensitivity. An alteration in taste or ...
(change in sense of taste).
* Globus pharyngis
Globus pharyngeus (also termed globus sensation) is the persistent but painless sensation of having a pill, food bolus, or some other sort of obstruction in the throat when there is none. Swallowing is typically performed normally, so it is not ...
(a sensation of something being stuck in the throat; in up to 31% of cases).
* Velopharyngeal insufficiency
Velopharyngeal insufficiency is a disorder of structure that causes a failure of the velum (soft palate) to close against the posterior Pharynx, pharyngeal wall (back wall of the throat) during speech in order to close off the nasal cavity durin ...
(rare).
* Nasopharyngeal stenosis.
* Xerostomia
Xerostomia, also known as dry mouth, is a subjective complaint of dryness in the mouth, which may be associated with a change in the composition of saliva, reduced salivary flow, or have no identifiable cause.
This symptom is very common and is o ...
(dry mouth) and dry throat, which may be related to loss of the uvula.
The overall rate of complications is about 35%. Some of the complications are significant, such as velopharyngeal insufficiency and globus pharyngeus.
Effectiveness
Obstructive sleep apnea
Systematic reviews have reported successful outcome after UPPP for OSA in the range of 35-95%. The AHI reduces by an average of 18.6 events per hour. The Epworth sleepiness scale changes by an average of 5.4. The effect of UPPP often reduces over time. UPPP may also reduce the risk of conditions linked to OSA, such ascongestive heart failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome caused by an impairment in the heart's ability to fill with and pump blood.
Although symptoms vary based on which side of the heart is affected, HF typically pr ...
and atrial fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation (AF, AFib or A-fib) is an Heart arrhythmia, abnormal heart rhythm (arrhythmia) characterized by fibrillation, rapid and irregular beating of the Atrium (heart), atrial chambers of the heart. It often begins as short periods ...
. UPPP may also reduce depression.
In recent years, UPPP has become less popular among surgeons. This is related to the rate of complications and its overall low cure rate in unselected patients with OSA (40%). The 40% success rate was from a landmark study in 1996 which defined successful outcome after surgery as AHI score less than 20 and over 50% reduction in AHI compared to before surgery. UPPP by itself has limited effectiveness for OSA. Now UPPP is often combined with other procedures as a multilevel surgery, giving improved outcomes. For example, uvula preserving UPPP with maxillomandibular advancement was found to be a more effective combination when compared to several other types of maxillomandibular advancement.
Since many people have collapse of the lateral walls of the pharynx, another procedure called expansion sphincter palatoplasty has become more popular. Hypoglossal nerve stimulation
Hypoglossal nerve stimulation (HNS) is a treatment for obstructive sleep apnea. It involves implanting a small device that sends electrical impulses to the hypoglossal nerve (the twelfth cranial nerve) during sleep, causing the tongue to move forw ...
may have superior results to UPPP.
History
UPPP was originally devised in 1964 by Ikematsu as a treatment for snoring.Ikematsu, T (1964). "Study of snoring". Therapy. ''J Jpn Otol Rhinol Laryngol Soc'' 64: 434–435 It was not until the years after 1965 that OSA began to be recognized as a distinct condition. UPPP was first used for OSA in 1981 in the USA by Shiro Fujita and colleagues. This was the same year that CPAP was introduced. The UPPP for OSA was more invasive than the original UPPP for snoring. After its introduction, UPPP quickly became the most popular surgical treatment for OSA. Several modifications of the UPPP technique were introduced from about 1996 to 2015.References
{{Procedures on the mouth and pharynx Sleep surgery Palate surgery Otorhinolaryngology