Usedom on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Usedom ( , ) is a
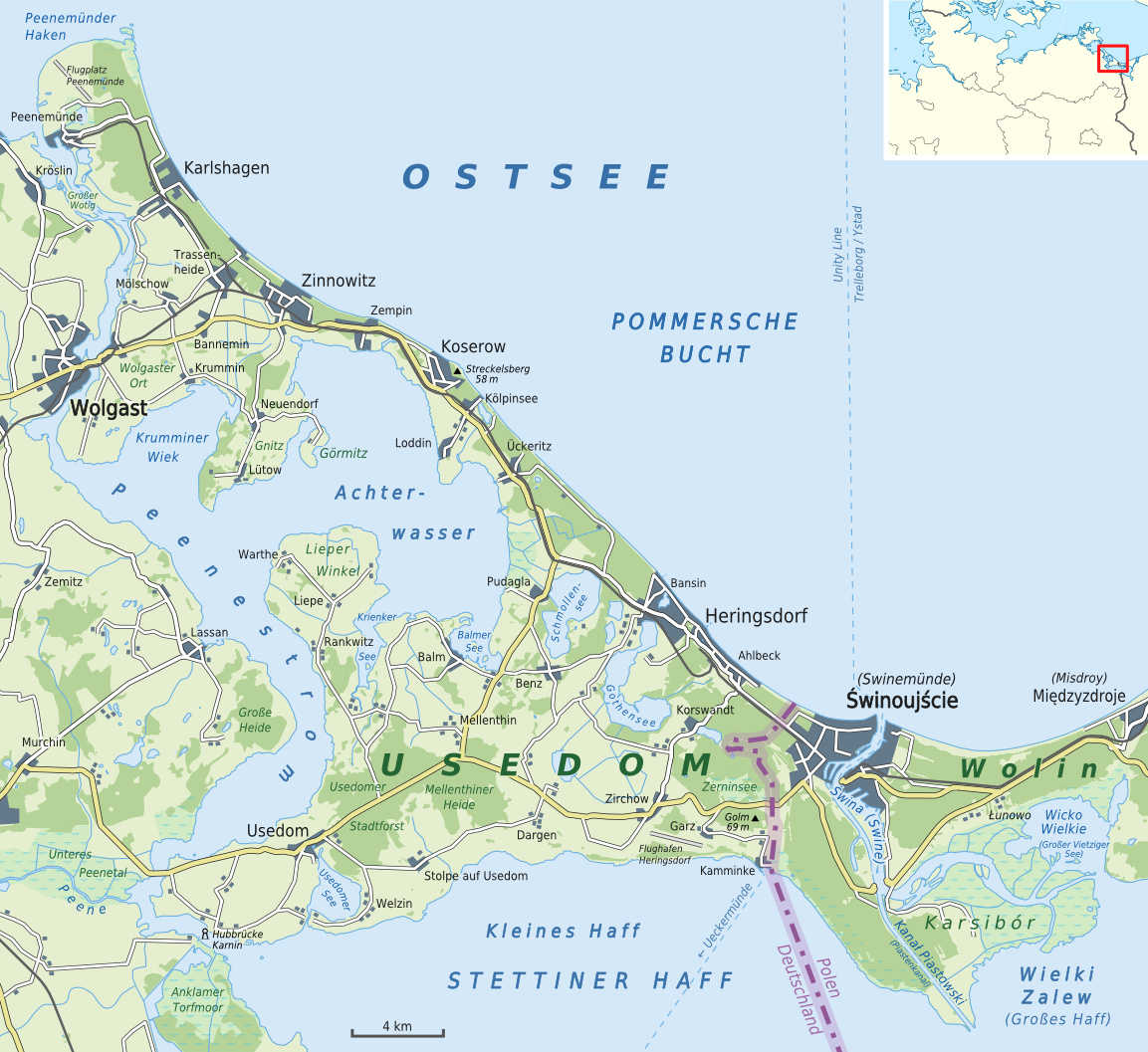 The island is separated from the neighbouring island of Wolin to the east by the Strait of Świna, which is the main route connecting Szczecin Bay with Pomeranian Bay, a part of the Baltic Sea. The strait between the island and the mainland is called the Peenestrom; it is a downstream extension of the valley of the Peene river, which flows into the westernmost part of the Szczecin Lagoon. The island is mostly flat, and partly covered by marshes.
Geographical features include a number of lakes:
The island is separated from the neighbouring island of Wolin to the east by the Strait of Świna, which is the main route connecting Szczecin Bay with Pomeranian Bay, a part of the Baltic Sea. The strait between the island and the mainland is called the Peenestrom; it is a downstream extension of the valley of the Peene river, which flows into the westernmost part of the Szczecin Lagoon. The island is mostly flat, and partly covered by marshes.
Geographical features include a number of lakes:
 The largest town on the island is Świnoujście, which has a total population of 41,500. The western part of Świnoujście covers the entire Polish part of the island. Another town, Usedom, gives its name to the island. The largest municipalities in the German part are Heringsdorf (from 2005 to 2006 called ''Dreikaiserbäder'', literally "The Three Imperial Spas") and Zinnowitz.
There are many
The largest town on the island is Świnoujście, which has a total population of 41,500. The western part of Świnoujście covers the entire Polish part of the island. Another town, Usedom, gives its name to the island. The largest municipalities in the German part are Heringsdorf (from 2005 to 2006 called ''Dreikaiserbäder'', literally "The Three Imperial Spas") and Zinnowitz.
There are many
 Settled since the
Settled since the
 Usedom is one of Germany's major holiday and recreation areas due to its beaches, its natural environment, and seaside towns such as Ahlbeck, Heringsdorf and Bansin, which, since the
Usedom is one of Germany's major holiday and recreation areas due to its beaches, its natural environment, and seaside towns such as Ahlbeck, Heringsdorf and Bansin, which, since the
 The Polish Naval Base Świnoujście is located on the island.
The Polish Naval Base Świnoujście is located on the island.
Usedom.de: Official Usedom webpageVisitusedom.com: Official Island of Usedom tourism website
* {{Authority control German islands in the Baltic Polish islands in the Baltic International islands Islands of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania Landforms of West Pomeranian Voivodeship Pomerania
Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by the countries of Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden, and the North European Plain, North and Central European Plain regions. It is the ...
island
An island or isle is a piece of land, distinct from a continent, completely surrounded by water. There are continental islands, which were formed by being split from a continent by plate tectonics, and oceanic islands, which have never been ...
in Pomerania
Pomerania ( ; ; ; ) is a historical region on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in Central Europe, split between Poland and Germany. The central and eastern part belongs to the West Pomeranian Voivodeship, West Pomeranian, Pomeranian Voivod ...
, divided between Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
and Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukrai ...
. It is the second largest Pomeranian island after Rügen
Rügen (; Rani: ''Rȯjana'', ''Rāna''; , ) is Germany's largest island. It is located off the Pomeranian coast in the Baltic Sea and belongs to the state of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania.
The "gateway" to Rügen island is the Hanseatic ci ...
, and the most populous island in the Baltic Sea.
It lies north of the Szczecin Lagoon estuary
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime enviro ...
of the Oder
The Oder ( ; Czech and ) is a river in Central Europe. It is Poland's second-longest river and third-longest within its borders after the Vistula and its largest tributary the Warta. The Oder rises in the Czech Republic and flows through wes ...
river. About 80% of the island belongs to the German district of Vorpommern-Greifswald
Vorpommern-Greifswald is a district in the east of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany. It is bounded by (from the west and clockwise) the districts of Mecklenburgische Seenplatte and Vorpommern-Rügen, the Baltic Sea, Poland (West Pomeranian Voiv ...
in the state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern
Mecklenburg-Vorpommern (MV; ; ), also known by its Anglicisation, anglicized name Mecklenburg–Western Pomerania, is a Federated state, state in the north-east of Germany. Of the country's States of Germany, sixteen states, Mecklenburg-Vorpom ...
. The eastern part and the largest city on the island, Świnoujście, are part of the Polish West Pomeranian Voivodeship
West Pomeranian Voivodeship is a Voivodeships of Poland, voivodeship (province) in northwestern Poland. Its capital and largest city is Szczecin. Its area equals , and in 2021, it was inhabited by 1,682,003 people.
It was established on 1 Janua ...
. The island's total area is – in the German part and in the Polish part. Its population is 76,500 (German part 31,500; Polish part 45,000).
With an annual average of 1,906 hours of sunshine, Usedom is the sunniest region of both Germany and Poland, and it is also one of the sunniest islands in the Baltic Sea, hence its nickname "Sun Island" (, ).
The island has been a tourist destination since the Gründerzeit
The (; ) was a period of Economic history of Europe (1000 AD–present), European economic history in mid- and late-19th century German Empire, Germany and Austria-Hungary between Industrialization in Germany, industrialization and the great P ...
in the 19th century, and features resort architecture. Seaside resorts include Zinnowitz and the Amber Spas in the west, the Kaiserbad and Świnoujście in the east.
Geography
 The island is separated from the neighbouring island of Wolin to the east by the Strait of Świna, which is the main route connecting Szczecin Bay with Pomeranian Bay, a part of the Baltic Sea. The strait between the island and the mainland is called the Peenestrom; it is a downstream extension of the valley of the Peene river, which flows into the westernmost part of the Szczecin Lagoon. The island is mostly flat, and partly covered by marshes.
Geographical features include a number of lakes:
The island is separated from the neighbouring island of Wolin to the east by the Strait of Świna, which is the main route connecting Szczecin Bay with Pomeranian Bay, a part of the Baltic Sea. The strait between the island and the mainland is called the Peenestrom; it is a downstream extension of the valley of the Peene river, which flows into the westernmost part of the Szczecin Lagoon. The island is mostly flat, and partly covered by marshes.
Geographical features include a number of lakes:
 The largest town on the island is Świnoujście, which has a total population of 41,500. The western part of Świnoujście covers the entire Polish part of the island. Another town, Usedom, gives its name to the island. The largest municipalities in the German part are Heringsdorf (from 2005 to 2006 called ''Dreikaiserbäder'', literally "The Three Imperial Spas") and Zinnowitz.
There are many
The largest town on the island is Świnoujście, which has a total population of 41,500. The western part of Świnoujście covers the entire Polish part of the island. Another town, Usedom, gives its name to the island. The largest municipalities in the German part are Heringsdorf (from 2005 to 2006 called ''Dreikaiserbäder'', literally "The Three Imperial Spas") and Zinnowitz.
There are many seaside resort
A seaside resort is a city, resort town, town, village, or hotel that serves as a Resort, vacation resort and is located on a coast. Sometimes the concept includes an aspect of an official accreditation based on the satisfaction of certain requi ...
s on the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by the countries of Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden, and the North European Plain, North and Central European Plain regions. It is the ...
coast, including Zinnowitz and Koserow in the west – and the three Imperial Spas Ahlbeck, Heringsdorf, and Bansin forming a town, as well as neighbouring Świnoujście in the east of Usedom.
The hinterland is called ''Achterland'', referring to the Achterwasser lagoon
A lagoon is a shallow body of water separated from a larger body of water by a narrow landform, such as reefs, barrier islands, barrier peninsulas, or isthmuses. Lagoons are commonly divided into ''coastal lagoons'' (or ''barrier lagoons'') an ...
(''Rear Waters''). It is characterized by unspoilt forests, lagoon landscapes, and hills, as well as calm villages such as Loddin and Balmer See with its golf course
A golf course is the grounds on which the sport of golf is played. It consists of a series of holes, each consisting of a teeing ground, tee box, a #Fairway and rough, fairway, the #Fairway and rough, rough and other hazard (golf), hazards, and ...
.
Main economic activities include tourism
Tourism is travel for pleasure, and the Commerce, commercial activity of providing and supporting such travel. World Tourism Organization, UN Tourism defines tourism more generally, in terms which go "beyond the common perception of tourism as ...
, health and life sciences
This list of life sciences comprises the branches of science that involve the scientific study of life – such as microorganisms, plants, and animals including human beings. This science is one of the two major branches of natural science, ...
, retail
Retail is the sale of goods and services to consumers, in contrast to wholesaling, which is the sale to business or institutional customers. A retailer purchases goods in large quantities from manufacturers, directly or through a wholes ...
, agriculture
Agriculture encompasses crop and livestock production, aquaculture, and forestry for food and non-food products. Agriculture was a key factor in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created ...
, fishing, animal husbandry, food processing, and timber production.
History
 Settled since the
Settled since the Stone Age
The Stone Age was a broad prehistory, prehistoric period during which Rock (geology), stone was widely used to make stone tools with an edge, a point, or a percussion surface. The period lasted for roughly 3.4 million years and ended b ...
, the area was probably inhabited by Germanic Rugians, before the Polabian Slavs
Polabian Slavs, also known as Elbe Slavs
and more broadly as Wends, is a collective term applied to a number of Lechites, Lechitic (West Slavs, West Slavic) tribes who lived scattered along the Elbe river in what is today eastern Germany. The ...
moved in during the fifth, sixth, and seventh centuries. Around the island, Wendish/ Scandinavian trade centres such as Vineta/ Jomsborg and Menzlin were established. In the 1110s, the town of Uznam was destroyed by the Danes
Danes (, ), or Danish people, are an ethnic group and nationality native to Denmark and a modern nation identified with the country of Denmark. This connection may be ancestral, legal, historical, or cultural.
History
Early history
Denmark ...
. In the 1120s, the island along with Western Pomerania came under Polish suzerainty under Bolesław III Wrymouth
Bolesław III Wrymouth (; 20 August 1086 – 28 October 1138), also known as Boleslaus the Wry-mouthed, was the duke of Lesser Poland, Silesia and Sandomierz between 1102 and 1107 and over the whole of Poland between 1107 and 1138. He was the onl ...
, and became part of a newly formed vassal state of Poland, the Duchy of Pomerania
The Duchy of Pomerania (; ; Latin: ''Ducatus Pomeraniae'') was a duchy in Pomerania on the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, ruled by dukes of the House of Pomerania (''Griffins''). The country existed in the Middle Ages between years 1121–11 ...
. The Polish ruler initiated Christianization
Christianization (or Christianisation) is a term for the specific type of change that occurs when someone or something has been or is being converted to Christianity. Christianization has, for the most part, spread through missions by individu ...
, entrusting this task to Otto of Bamberg, and in 1128 the Slavic Pomeranian Duke Wartislaw I was converted to Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose ...
through the efforts of Otto. In 1155 the Premonstratensian
The Order of Canons Regular of Prémontré (), also known as the Premonstratensians, the Norbertines and, in Britain and Ireland, as the White Canons (from the colour of their habit), is a religious order of canons regular in the Catholic Chur ...
s established a monastery in Grobe, generally known as Usedom Abbey
Usedom Abbey () was a medieval Premonstratensian monastery on the isle of Usedom (Western Pomerania, Germany) near the Usedom (town), town of Usedom. It was founded in Grobe and later moved to nearby Pudagla, and is thus also known as Grobe Abbey ...
, which in 1309 was moved to the village of Pudagla. In the meantime, a Cistercian
The Cistercians (), officially the Order of Cistercians (, abbreviated as OCist or SOCist), are a Catholic religious order of monks and nuns that branched off from the Benedictines and follow the Rule of Saint Benedict, as well as the contri ...
nunnery was founded in Krummin and soon almost the whole island was in the possession of one or the other of the ecclesiastical orders. In the 1170s, the island was ravaged by King Valdemar I of Denmark
Valdemar I Knudsen (14 January 1131 – 12 May 1182), also known as Valdemar the Great (), was King of Denmark from 1154 until his death in 1182. The reign of King Valdemar I saw the rise of Denmark, which reached its medieval zenith under his s ...
. During the Reformation
The Reformation, also known as the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation, was a time of major Theology, theological movement in Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the p ...
, ownership passed to the Slavic dukes of Pomerania, who took over the island.
During the Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War, fought primarily in Central Europe between 1618 and 1648, was one of the most destructive conflicts in History of Europe, European history. An estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died from battle, famine ...
, on June 26, 1630, the Swedish Army
The Swedish Army () is the army, land force of the Swedish Armed Forces of the Kingdom of Sweden. Beginning with its service in 1521, the Swedish Army has been active for more than 500 years.
History
Svea Life Guards dates back to the year 1 ...
under King Gustavus Adolphus
Gustavus Adolphus (9 December N.S 19 December">Old_Style_and_New_Style_dates.html" ;"title="/nowiki>Old Style and New Style dates">N.S 19 December15946 November Old Style and New Style dates">N.S 16 November] 1632), also known in English as ...
landed in the village of Peenemünde
Peenemünde (, ) is a municipality on the Baltic Sea island of Usedom in the Vorpommern-Greifswald district in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern in north-eastern Germany. It is part of the ''Amt (country subdivision), Amt'' (collective municipality) of Used ...
, located on the Peenestrom strait. In 1637 the last duke of Pomerania Bogislaw XIV died, the House of Griffin
The House of Griffin or Griffin dynasty, (; , ; Latin: ''Gryphes''), or House of Pomerania (see ), was a dynasty ruling the Duchy of Pomerania from the 12th century until 1637. The name "Griffins" was used by the dynasty after the 15th century ...
became extinct and the duchy ceased to exist. Usedom was annexed by Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic count ...
after the war for almost a century, until in 1720 it was sold for 2 million thaler
A thaler or taler ( ; , previously spelled ) is one of the large silver coins minted in the states and territories of the Holy Roman Empire and the Habsburg monarchy during the Early Modern period. A ''thaler'' size silver coin has a diameter o ...
s to Prussian King Frederick William I. In 1740 Frederick the Great
Frederick II (; 24 January 171217 August 1786) was the monarch of Prussia from 1740 until his death in 1786. He was the last Hohenzollern monarch titled ''King in Prussia'', declaring himself ''King of Prussia'' after annexing Royal Prussia ...
of Prussia developed a seaport in Świnoujście (then ''Swinemünde''). With the Kingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (, ) was a German state that existed from 1701 to 1918.Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. Rev. ed. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1946. It played a signif ...
the island became part of the German Empire
The German Empire (),; ; World Book, Inc. ''The World Book dictionary, Volume 1''. World Book, Inc., 2003. p. 572. States that Deutsches Reich translates as "German Realm" and was a former official name of Germany. also referred to as Imperia ...
in 1871.
The small village of Peenemünde came to prominence again during World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
. The Luftwaffe
The Luftwaffe () was the aerial warfare, aerial-warfare branch of the before and during World War II. German Empire, Germany's military air arms during World War I, the of the Imperial German Army, Imperial Army and the of the Imperial Ge ...
tested missile
A missile is an airborne ranged weapon capable of self-propelled flight aided usually by a propellant, jet engine or rocket motor.
Historically, 'missile' referred to any projectile that is thrown, shot or propelled towards a target; this ...
s and rocket
A rocket (from , and so named for its shape) is a vehicle that uses jet propulsion to accelerate without using any surrounding air. A rocket engine produces thrust by reaction to exhaust expelled at high speed. Rocket engines work entirely ...
s, including the V-1 and V-2 nearby. Germany used thousands of slave laborers on Usedom during World War II. During the war, a subcamp of the Sachsenhausen concentration camp
Sachsenhausen () or Sachsenhausen-Oranienburg was a German Nazi concentration camp in Oranienburg, Germany, used from 1936 until April 1945, shortly before the defeat of Nazi Germany in May later that year. It mainly held political prisoners t ...
was located in the town of Usedom. In the final stages of the war, in 1945, German-perpetrated death marches of Allied prisoners-of-war from the Stalag XX-B and Stalag Luft IV POW camps passed through the island.
In 1945 the eastern part of the island, together with the city and port of Swinemünde (now Świnoujście), was assigned to Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukrai ...
under border changes promulgated at the Potsdam Conference, and the surviving German inhabitants of the town were expelled to the west. The territory was repopulated with Poles, most of whom had been expelled by the Soviets from what had been eastern Poland.
Tourism
 Usedom is one of Germany's major holiday and recreation areas due to its beaches, its natural environment, and seaside towns such as Ahlbeck, Heringsdorf and Bansin, which, since the
Usedom is one of Germany's major holiday and recreation areas due to its beaches, its natural environment, and seaside towns such as Ahlbeck, Heringsdorf and Bansin, which, since the Gründerzeit
The (; ) was a period of Economic history of Europe (1000 AD–present), European economic history in mid- and late-19th century German Empire, Germany and Austria-Hungary between Industrialization in Germany, industrialization and the great P ...
in the 19th century, have been frequented by the German and international nobility as well as the general public.
According to ''The Guardian
''The Guardian'' is a British daily newspaper. It was founded in Manchester in 1821 as ''The Manchester Guardian'' and changed its name in 1959, followed by a move to London. Along with its sister paper, ''The Guardian Weekly'', ''The Guardi ...
'', the island, as of 2022, "... is known by some as the 'bathtub of Berlin' and by others, slightly more poetically, as 'sun island'," but "... remains largely undiscovered by international visitors."
Hotels and bed and breakfast
A bed and breakfast (typically shortened to B&B or BnB) is a small lodging establishment that offers overnight accommodation and breakfast. In addition, a B&B sometimes has the hosts living in the house.
''Bed and breakfast'' is also used to ...
establishments are available on both sides of the German-Polish border. Many of them are decorated in nautical themes, and seafood is a major drawcard. St. Peter's Church in Benz is featured in the works of several artists, including the German-American painter Lyonel Feininger who spent summer vacations on the island from 1909 to 1918. In addition to the coastline, the hinterland
Hinterland is a German word meaning the 'land behind' a city, a port, or similar. Its use in English was first documented by the geographer George Chisholm in his ''Handbook of Commercial Geography'' (1888). Originally the term was associated wi ...
features nature reserves, castles, lakes and historic villages.
Points of interest in the German part of the island include:
* Usedom Botanical Gardens, Mellenthin, a botanical garden
A botanical garden or botanic gardenThe terms ''botanic'' and ''botanical'' and ''garden'' or ''gardens'' are used more-or-less interchangeably, although the word ''botanic'' is generally reserved for the earlier, more traditional gardens. is ...
* Karnin Lift Bridge, a technical monument to the former bridge over the Peenestrom.
* Dannenfeldt Mausoleum
In the Polish part of the island, points of interest include:
* Karsiborskie Paprocie nature reserve
A nature reserve (also known as a wildlife refuge, wildlife sanctuary, biosphere reserve or bioreserve, natural or nature preserve, or nature conservation area) is a protected area of importance for flora, fauna, funga, or features of geologic ...
* Sea Fishing Museum ('' Muzeum Rybołówstwa Morskiego'')
* Western Fort (''Fort Zachodni''), which houses the Museum of the History of the Świnoujście Fortress ('' Muzeum Historii Twierdzy Świnoujście'')
* Park Zdrojowy
Military
 The Polish Naval Base Świnoujście is located on the island.
The Polish Naval Base Świnoujście is located on the island.
See also
*List of divided islands
This is a list of islands whose land is divided by one or more border, international borders.
Sea islands
Island country, Island countries
Non-island countries
Both island countries and non-island countries
Lake islands
*Amon ...
* V-1 and V-2 intelligence
* Rügen
Rügen (; Rani: ''Rȯjana'', ''Rāna''; , ) is Germany's largest island. It is located off the Pomeranian coast in the Baltic Sea and belongs to the state of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania.
The "gateway" to Rügen island is the Hanseatic ci ...
References
External links
*Usedom.de: Official Usedom webpage
* {{Authority control German islands in the Baltic Polish islands in the Baltic International islands Islands of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania Landforms of West Pomeranian Voivodeship Pomerania