Urban Plague on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
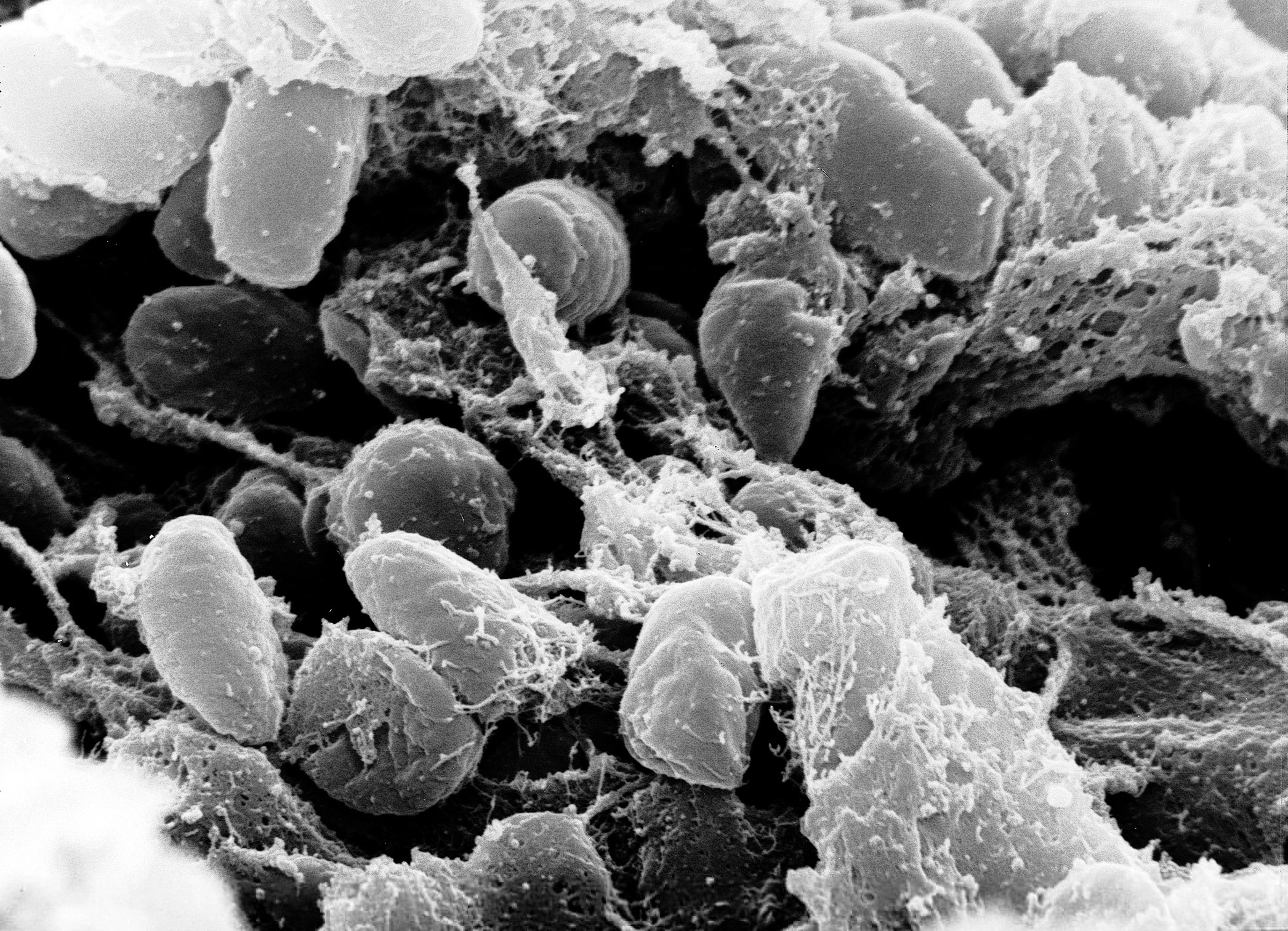 Urban plague is an infectious disease among rodent species that live in close association with humans in urban areas. It is caused by the bacterium ''
Urban plague is an infectious disease among rodent species that live in close association with humans in urban areas. It is caused by the bacterium ''
Black Death
at
 Urban plague is an infectious disease among rodent species that live in close association with humans in urban areas. It is caused by the bacterium ''
Urban plague is an infectious disease among rodent species that live in close association with humans in urban areas. It is caused by the bacterium ''Yersinia pestis
''Yersinia pestis'' (''Y. pestis''; formerly ''Pasteurella pestis'') is a Gram-negative bacteria, gram-negative, non-motile bacteria, non-motile, coccobacillus Bacteria, bacterium without Endospore, spores. It is related to pathogens ''Yer ...
'' which is the same bacterium that causes bubonic and pneumonic plague in humans. Plague was first introduced into the United States in 1900 by rat–infested steamships that had sailed from affected areas, mostly from Asia. Urban plague spread from urban rats to rural rodent species, especially among prairie dogs in the western United States.
Vector reservoir
Common vectors for urban plague are house mice, black rats, and Norway rats.Transmission
Urban plague can be spread from animals to humans via flea bites and handling of infected fluids and tissues. Human to human infection occurs from droplets that contain plague bacteria which are produced when an infected person coughs.See also
*Sylvatic plague
Sylvatic plague is an infectious bacterial disease caused by the plague bacterium (''Yersinia pestis'') that primarily affects rodents, such as prairie dogs. It is the same bacterium that causes bubonic and pneumonic plague in humans. Sylvatic, ...
*Epizootic
In epizoology, an epizootic (or epizoötic, from Greek: ''epi-'' "upon" + ''zoon'' "animal") is a disease event in a nonhuman animal population analogous to an epidemic in humans. An epizootic disease (or ) may occur in a specific locale (an ...
References
External links
*Black Death
at
BBC
The British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) is a British public service broadcaster headquartered at Broadcasting House in London, England. Originally established in 1922 as the British Broadcasting Company, it evolved into its current sta ...
{{Black Death, state=expanded
Plague (disease)
Rodent-carried diseases