Ur (cuneiform) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

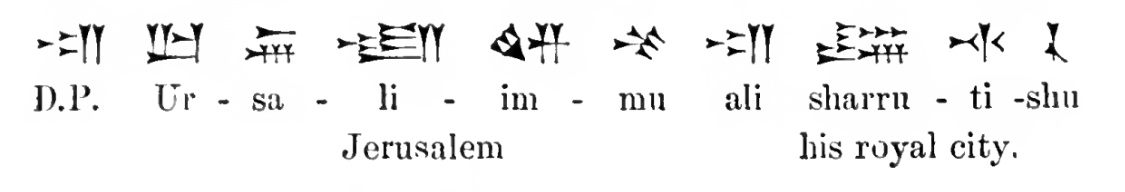 The
The
 The
The cuneiform
Cuneiform is a Logogram, logo-Syllabary, syllabic writing system that was used to write several languages of the Ancient Near East. The script was in active use from the early Bronze Age until the beginning of the Common Era. Cuneiform script ...
sign ur () is a common-use sign in the ''Epic of Gilgamesh
The ''Epic of Gilgamesh'' () is an epic poetry, epic from ancient Mesopotamia. The literary history of Gilgamesh begins with five Sumerian language, Sumerian poems about Gilgamesh (formerly read as Sumerian "Bilgames"), king of Uruk, some of ...
'', the Amarna letters, and other cuneiform texts. It has multiple sub-uses in the ''Epic of Gilgamesh'', as well as use for the Sumerogram
A Sumerogram is the use of a Sumerian cuneiform character or group of characters as an ideogram or logogram rather than a syllabogram in the graphic representation of a language other than Sumerian, such as Akkadian, Eblaite, or Hittite. Th ...
(capital letter (majuscule
Letter case is the distinction between the letters that are in larger uppercase or capitals (more formally '' majuscule'') and smaller lowercase (more formally '' minuscule'') in the written representation of certain languages. The writing syste ...
)), UR. In the Epic, ''UR'' is used to spell Akkadian language
Akkadian ( ; )John Huehnergard & Christopher Woods, "Akkadian and Eblaite", ''The Cambridge Encyclopedia of the World's Ancient Languages''. Ed. Roger D. Woodard (2004, Cambridge) Pages 218–280 was an East Semitic language that is attested ...
''barbaru'', "wolf", as ''UR.BAR.RA'' (in Tablet VI, and Tablet XI).
Cuneiform ''ur'' is a syllabic for "ur", and an alphabetic for "u", or "r". In the Amarna letters, usage is sumerogrammic for English language
English is a West Germanic language that developed in early medieval England and has since become a English as a lingua franca, global lingua franca. The namesake of the language is the Angles (tribe), Angles, one of the Germanic peoples th ...
"dog", spelled either ''UR.KI'', or ''UR.KU'', but the 'dog' reference can be found in many Amarna letters.
The cuneiform ''ur'' cuneiform
Cuneiform is a Logogram, logo-Syllabary, syllabic writing system that was used to write several languages of the Ancient Near East. The script was in active use from the early Bronze Age until the beginning of the Common Era. Cuneiform script ...
character (no. 575) is built in a 'rectangular box form', sitting upon a long horizontal stroke. It contains the 2-verticals at left and 1-vertical at right. Three other signs are similarly built, but contain 1-vertical at left, with 2-verticals at right for lu (cuneiform) (with 3-short horizontals in the center, no. 537), and the same but only 1-short horizontal at center, ib (cuneiform)
The cuneiform sign ib, (or ip) is a common-use sign in the ''Epic of Gilgamesh'', the Amarna letters, and other cuneiform texts. Its common usage is syllabic for ''ib'' (or ''ip''), or alphabetic for ''i'' or ''b''/''p''; the "i" is also exc ...
(also ''ip'', no. 535). The third similar sign, (no. 536) has 1-vertical left and right, ku (cuneiform)
Ku, KU, or Kū may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* Ku (fictional language), a constructed language created for the 2005 film The Interpreter
* Esther Ku, a Korean-American comedian
* Shawn Ku, U.S. choreographer and motion picture director
* K ...
. It also has 3-short verticals in the center, but is often such a compressed cuneiform character that individual strokes are overwritten, and difficult to identify.
''Epic of Gilgamesh'' usage
Cuneiform ''ur'' has many sub-uses in the ''Epic of Gilgamesh''. The following can be found: ''leq''--(1) time, ''lik''--(37), ''liq''--(3), ''tas''--(1), ''taṣ''--(2), ''taš''--(15), ''tés''--(1), ''téš''--(1), ''ur''--(93), ''UR''--(16) times.References
Citations
Bibliography
* Moran, William L. 1987, 1992. ''The Amarna Letters.'' Johns Hopkins University Press, 1987, 1992. 393 pages.(softcover, {{ISBN, 0-8018-6715-0) * Parpola, 1971. ''The Standard BabylonianEpic of Gilgamesh
The ''Epic of Gilgamesh'' () is an epic poetry, epic from ancient Mesopotamia. The literary history of Gilgamesh begins with five Sumerian language, Sumerian poems about Gilgamesh (formerly read as Sumerian "Bilgames"), king of Uruk, some of ...
'', Parpola, Simo, Neo-Assyrian Text Corpus Project
The Neo-Assyrian Text Corpus Project is an international scholarly project aimed at collecting and publishing ancient Assyrian texts of the Neo-Assyrian Empire and studies based on them. Its headquarters are in Helsinki in Finland.
State Archives ...
, c 1997, Tablet I thru Tablet XII, Index of Names, Sign List, and Glossary-(pp. 119–145), 165 pages.
Sumerian words and phrases
Cuneiform signs