Unemployment In France on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The economy of


 In April and May 2012, France held a
In April and May 2012, France held a
 The following table shows the main economic indicators in 1980–2021 (with IMF staff estimates in 2022–2027). Inflation below 5% is in green.
The following table shows the main economic indicators in 1980–2021 (with IMF staff estimates in 2022–2027). Inflation below 5% is in green.
 In 2019, France was the world's 8th largest manufacturer in terms of
In 2019, France was the world's 8th largest manufacturer in terms of

 France is the world's sixth largest agricultural producer and EU's leading agricultural power, accounting for about one-third of all agricultural land within the EU. In the early 1980s, France was the leading producer of the three principal grains of wheat, barley, and maize. Back in 1983, France produced around 24.8 million tonnes, ahead of the United Kingdom and West Germany, the next two largest wheat producers.
Northern France is characterised by large wheat farms. Dairy products, pork, poultry, and apple production are concentrated in the western region. Beef production is located in central France, while the production of fruits, vegetables, and wine ranges from central to southern France. France is a large producer of many agricultural products and is currently expanding its forestry and fishery industries. The implementation of the Common Agricultural Policy (CAP) and the Uruguay Round of the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) have resulted in reforms in the agricultural sector of the economy.
As the world's second-largest agricultural exporter, France ranks just after the United States. The destination of 49% of its exports is other EU members states. France also provides agricultural exports to many poor African countries (including its former colonies) which face serious food shortages. Wheat, beef, pork, poultry, and dairy products are the principal exports.
Exports from the United States face stiff competition from domestic production, other EU member states, and third-world countries in France. US agricultural exports to France, totaling some $600 million annually, consist primarily of soybeans and soybean products, feeds and fodders, seafood, and consumer products, especially snack foods and nuts. French exports to the United States are much more high-value products such as French cheese, its cheese, processed products and French wine, its wine.
The French agricultural sector receives almost €11 billion in EU subsidies. France produced in 2018 39.5 million tons of sugar beet (2nd largest producer in the world, just behind Russia), which serves to produce sugar and ethanol; 35.8 million tons of wheat (5th largest producer in the world); 12.6 million tons of maize (11th largest producer in the world); 11.2 million tons of barley (2nd largest producer in the world, only behind Russia); 7.8 million tons of potato (8th largest producer in the world); 6.2 million tons of grape (5th largest producer in the world); 4.9 million tons of rapeseed (4th largest producer in the world, behind Canada, China and India); 2.2 million tons of sugarcane; 1.7 million tons of apple (9th largest producer in the world); 1.3 million tons of triticale (4th largest producer in the world, only behind Poland, Germany and Belarus); 1.2 million tons of sunflower seed (9th largest producer in the world); 712 thousand tons of tomatoes; 660 thousand tons of linen; 615 thousand tons of dry pea; 535 thousand tons of carrot; 427 thousand tons of oats; 400 thousand tons of soy; in addition to smaller productions of other agricultural products.
France is the world's sixth largest agricultural producer and EU's leading agricultural power, accounting for about one-third of all agricultural land within the EU. In the early 1980s, France was the leading producer of the three principal grains of wheat, barley, and maize. Back in 1983, France produced around 24.8 million tonnes, ahead of the United Kingdom and West Germany, the next two largest wheat producers.
Northern France is characterised by large wheat farms. Dairy products, pork, poultry, and apple production are concentrated in the western region. Beef production is located in central France, while the production of fruits, vegetables, and wine ranges from central to southern France. France is a large producer of many agricultural products and is currently expanding its forestry and fishery industries. The implementation of the Common Agricultural Policy (CAP) and the Uruguay Round of the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) have resulted in reforms in the agricultural sector of the economy.
As the world's second-largest agricultural exporter, France ranks just after the United States. The destination of 49% of its exports is other EU members states. France also provides agricultural exports to many poor African countries (including its former colonies) which face serious food shortages. Wheat, beef, pork, poultry, and dairy products are the principal exports.
Exports from the United States face stiff competition from domestic production, other EU member states, and third-world countries in France. US agricultural exports to France, totaling some $600 million annually, consist primarily of soybeans and soybean products, feeds and fodders, seafood, and consumer products, especially snack foods and nuts. French exports to the United States are much more high-value products such as French cheese, its cheese, processed products and French wine, its wine.
The French agricultural sector receives almost €11 billion in EU subsidies. France produced in 2018 39.5 million tons of sugar beet (2nd largest producer in the world, just behind Russia), which serves to produce sugar and ethanol; 35.8 million tons of wheat (5th largest producer in the world); 12.6 million tons of maize (11th largest producer in the world); 11.2 million tons of barley (2nd largest producer in the world, only behind Russia); 7.8 million tons of potato (8th largest producer in the world); 6.2 million tons of grape (5th largest producer in the world); 4.9 million tons of rapeseed (4th largest producer in the world, behind Canada, China and India); 2.2 million tons of sugarcane; 1.7 million tons of apple (9th largest producer in the world); 1.3 million tons of triticale (4th largest producer in the world, only behind Poland, Germany and Belarus); 1.2 million tons of sunflower seed (9th largest producer in the world); 712 thousand tons of tomatoes; 660 thousand tons of linen; 615 thousand tons of dry pea; 535 thousand tons of carrot; 427 thousand tons of oats; 400 thousand tons of soy; in addition to smaller productions of other agricultural products.
 France is the world's most popular tourist destination with more than 83.7 million foreign tourists in 2014, ahead of Spain (58.5 million in 2006) and the United States (51.1 million in 2006). This figure excludes people staying less than 24 hours in France, such as northern Europeans crossing France on their way to Spain or Italy during the summer.
According to figures from 2003, some popular tourist sites include (in visitors per year): Eiffel Tower (6.2 million), Louvre Museum (5.7 million), Palace of Versailles (2.8 million), Cité des Sciences et de l'Industrie (2.6 million), Musée d'Orsay (2.1 million), Arc de Triomphe (1.2 million), Centre Georges Pompidou, Centre Pompidou (1.2 million), Mont-Saint-Michel (1 million), Château de Chambord (711,000), Sainte-Chapelle (683,000), Château du Haut-Kœnigsbourg (549,000), Puy-de-Dôme (mountain), Puy de Dôme (500,000), Musée Picasso (441,000), Carcassonne (362,000). However, the most popular site in France is Disneyland Paris, with 9.7 million visitors in 2017
France is the world's most popular tourist destination with more than 83.7 million foreign tourists in 2014, ahead of Spain (58.5 million in 2006) and the United States (51.1 million in 2006). This figure excludes people staying less than 24 hours in France, such as northern Europeans crossing France on their way to Spain or Italy during the summer.
According to figures from 2003, some popular tourist sites include (in visitors per year): Eiffel Tower (6.2 million), Louvre Museum (5.7 million), Palace of Versailles (2.8 million), Cité des Sciences et de l'Industrie (2.6 million), Musée d'Orsay (2.1 million), Arc de Triomphe (1.2 million), Centre Georges Pompidou, Centre Pompidou (1.2 million), Mont-Saint-Michel (1 million), Château de Chambord (711,000), Sainte-Chapelle (683,000), Château du Haut-Kœnigsbourg (549,000), Puy-de-Dôme (mountain), Puy de Dôme (500,000), Musée Picasso (441,000), Carcassonne (362,000). However, the most popular site in France is Disneyland Paris, with 9.7 million visitors in 2017
, Deloitte Moreover, France also possesses 3 of the top 10 luxury goods companies by sales (
 Transportation in France relies on one of the densest networks in the world with 146 km of road and 6.2 km of rail lines per 100 km2. It is built as a web with Paris at its centre. The highly subsidised rail transport in France, rail transport network makes up a relatively small portion of travel, most of which is done by car. However, the high-speed TGV trains make up a large proportion of long-distance travel, partially because intercity buses were prevented from operating until 2015.
With 3,220 kilometers of high-speed train lines, France boast the 2nd most expansive network in the world, only after China. Charles de Gaulle Airport is one of the busiest airports in the world by passenger traffic. Charles de Gaulle airport is third globally in the number of destinations served, and first in the number of countries served with non-stop flights.
France also boasts a number of seaports and harbours, including Bayonne, Bordeaux, Boulogne-sur-Mer, Brest, Finistère, Brest, Calais, Cherbourg-Octeville, Dunkerque, Fos-sur-Mer, La Pallice, Le Havre, Lorient,
Transportation in France relies on one of the densest networks in the world with 146 km of road and 6.2 km of rail lines per 100 km2. It is built as a web with Paris at its centre. The highly subsidised rail transport in France, rail transport network makes up a relatively small portion of travel, most of which is done by car. However, the high-speed TGV trains make up a large proportion of long-distance travel, partially because intercity buses were prevented from operating until 2015.
With 3,220 kilometers of high-speed train lines, France boast the 2nd most expansive network in the world, only after China. Charles de Gaulle Airport is one of the busiest airports in the world by passenger traffic. Charles de Gaulle airport is third globally in the number of destinations served, and first in the number of countries served with non-stop flights.
France also boasts a number of seaports and harbours, including Bayonne, Bordeaux, Boulogne-sur-Mer, Brest, Finistère, Brest, Calais, Cherbourg-Octeville, Dunkerque, Fos-sur-Mer, La Pallice, Le Havre, Lorient,
, Ernst&Young, EY, 28 May 2020 EY attributed this as a "direct result of Emmanuel Macron, President Macron’s reforms of labor laws and corporate taxation, which were well received by domestic and international investors alike." France scored 5th in the 2019 AT Kearney FDI Confidence Index, up 2 notches from its 2017 ranking.
, World Trade Organization, p. 11 Its foreign trade balance for goods had been in surplus from 1992 until 2001, reaching $25.4 1000000000 (number), billion (25.4 G$) in 1998; however, the French balance of trade was hit by the economic downturn, and went into the red in 2000, reaching a US$15bn deficit in 2003. Total trade for 1998 amounted to $730 billion, or 50% of GDP—imports plus exports of goods and services. Trade with European Union countries accounts for 60% of French trade. In 1998, US–France trade stood at about $47 billion – goods only. According to French trade data, US exports accounted for 8.7% – about $25 billion – of France's total imports. US industrial chemicals, aircraft and engines, electronic components, telecommunications, computer software, computers and peripherals, analytical and scientific instrumentation, medical instruments and supplies, broadcasting equipment, and programming and franchising are particularly attractive to French importers. The principal French exports to the US are aircraft and engines, beverages, electrical equipment, chemicals, cosmetics, luxury products and perfume. France is the ninth-largest trading partner of the US. In August 2023, the French current account deficit shrank by €29.7 billion in the past six months, from −€39.3 billion to −€9.6 billion, primarily due to a fall in energy prices.
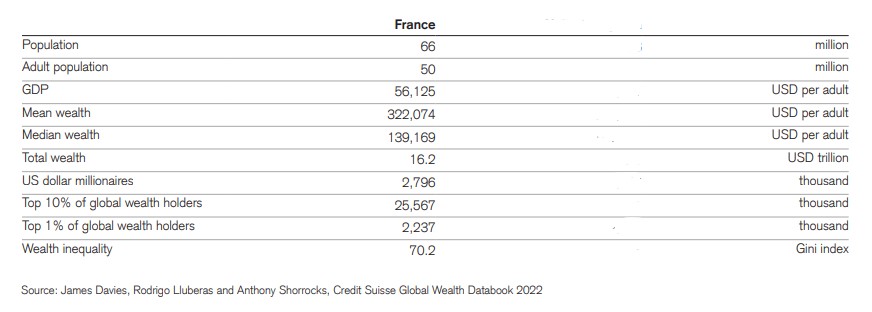 The wealthiest man in France is the
The wealthiest man in France is the
National Institute of Statistics and Economic Studies – InseeBanque de FranceWorld Bank: France Trade StatisticsFrance – OECDFrance profile
at the CIA World Factbook
France profile
at The World Bank
France Business Facts
{{Authority control Economy of France, European Union member economies, France World Trade Organization member economies, France OECD member economies, France Economies of Europe by country, France
France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
is a highly developed social market economy
The social market economy (SOME; ), also called Rhine capitalism, Rhine-Alpine capitalism, the Rhenish model, and social capitalism, is a socioeconomic model combining a free-market capitalist economic system with social policies and enough re ...
with notable state participation in strategic sectors. It is the world's seventh-largest economy by nominal GDP and the ninth-largest economy by PPP, constituting around 4% of world GDP. Due to a volatile currency exchange rate
In finance, an exchange rate is the rate at which one currency will be exchanged for another currency. Currencies are most commonly national currencies, but may be sub-national as in the case of Hong Kong or supra-national as in the case of ...
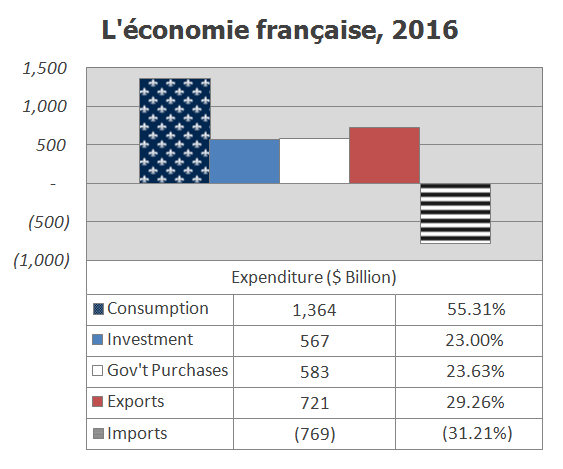
, France's GDP as measured in dollars fluctuates sharply, being smaller in 2024 than in 2008. France has a diversified economy, that is dominated by the service sector
The tertiary sector of the economy, generally known as the service sector, is the third of the three economic sectors in the three-sector model (also known as the economic cycle). The others are the primary sector (raw materials) and the ...
(which in 2017 represented 78.8% of its GDP), whilst the industrial sector
In macroeconomics, the secondary sector of the economy is an economic sector in the three-sector theory that describes the role of manufacturing. It encompasses industries that produce a finished, usable product or are involved in construc ...
accounted for 19.5% of its GDP and the primary sector
The primary sector of the economy includes any industry involved in the extraction and production of raw materials, such as farming, logging, fishing, forestry and mining.
The primary sector tends to make up a larger portion of the economy in d ...
accounted for the remaining 1.7%. In 2020, France was the largest Foreign Direct Investment
A foreign direct investment (FDI) is an ownership stake in a company, made by a foreign investor, company, or government from another country. More specifically, it describes a controlling ownership an asset in one country by an entity based i ...
recipient in Europe, and Europe's second largest spender in research and development
Research and development (R&D or R+D), known in some countries as OKB, experiment and design, is the set of innovative activities undertaken by corporations or governments in developing new services or products. R&D constitutes the first stage ...
. It was ranked among the 10 most innovative
Innovation is the practical implementation of ideas that result in the introduction of new goods or services or improvement in offering goods or services. ISO TC 279 in the standard ISO 56000:2020 defines innovation as "a new or changed ent ...
countries in the world by the 2020 Bloomberg Innovation Index
Bloomberg L.P. is an American privately-held financial, software, data, and media company headquartered in Midtown Manhattan, New York City. It was co-founded by Michael Bloomberg in 1981, with Thomas Secunda, Duncan MacMillan (Bloomberg), Du ...
, as well as the 15th most competitive nation globally according to the 2019 Global Competitiveness Report
The ''Global Competitiveness Report'' (GCR) was a yearly report published by the World Economic Forum. Between 2004 and 2020, the ''Global Competitiveness Report'' ranked countries based on the Global Competitiveness Index, developed by Xavier Sa ...
(up 2 notches compared to 2018). It was the fifth-largest trading nation in the world (and second in Europe after Germany). France is also the most visited destination in the world, as well as the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
's leading agricultural power.
According to the International Monetary Fund
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is a major financial agency of the United Nations, and an international financial institution funded by 191 member countries, with headquarters in Washington, D.C. It is regarded as the global lender of las ...
(IMF), in 2023, France was the world's 23rd country by GDP per capita with $44,408 per inhabitant. In 2021, France was listed on the United Nations's Human Development Index
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a statistical composite index of life expectancy, Education Index, education (mean years of schooling completed and expected years of schooling upon entering the education system), and per capita income i ...
with a value of 0.903 (indicating very high human development) and 22nd on the Corruption Perceptions Index
The Corruption Perceptions Index (CPI) is an index that scores and ranks countries by their perceived levels of public sector corruption, as assessed by experts and business executives. The CPI generally defines corruption as an "abuse of entr ...
in 2021. Among OECD
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; , OCDE) is an international organization, intergovernmental organization with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate economic progress and international trade, wor ...
members, France has a highly efficient and strong social security system, which comprises roughly 31.7% of GDP.
Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, largest city of France. With an estimated population of 2,048,472 residents in January 2025 in an area of more than , Paris is the List of ci ...
is a leading global city
A global city (also known as a power city, world city, alpha city, or world center) is a city that serves as a primary node in the global economic network. The concept originates from geography and urban studies, based on the thesis that glo ...
, and has one of the largest city GDP in the world. It ranks as the first city in Europe (and 3rd worldwide) by the number of companies classified in ''Fortune
Fortune may refer to:
General
* Fortuna or Fortune, the Roman goddess of luck
* Luck
* Wealth
* Fate
* Fortune, a prediction made in fortune-telling
* Fortune, in a fortune cookie
Arts and entertainment Film and television
* ''The Fortune'' (19 ...
s Fortune Global 500
The ''Fortune'' Global 500, also known as Global 500, is an annual ranking of the top 500 corporations worldwide as measured by revenue. The list is compiled and published annually by '' Fortune'' magazine.
Methodology
Until 1989, it listed o ...
. Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, largest city of France. With an estimated population of 2,048,472 residents in January 2025 in an area of more than , Paris is the List of ci ...
produced US$738 billion (or US$882 billion at market exchange rates) or around 1/3 of the French economy in 2018 while the economy of the Paris metropolitan area
The Paris metropolitan area () is a statistical area that describes the reach of commuter movement to and from Paris, France and its surrounding suburbs.
Overview
In 2020, France's national INSEE statistical bureau introduced the concept "ai ...
—the largest in Europe with London—generates around 1/3 of France's GDP or around $1.0 trillion. Paris has been ranked as the 2nd most attractive global city in the world in 2019 by KPMG
KPMG is a multinational professional services network, based in London, United Kingdom. As one of the Big Four accounting firms, along with Ernst & Young (EY), Deloitte, and PwC. KPMG is a network of firms in 145 countries with 275,288 emplo ...
. La Défense
La Défense () is a major business district in France's Paris metropolitan area, west of the city limits. It is located in Île-de-France region's Departments of France, department of Hauts-de-Seine in the Communes of France, communes of Courbe ...
, Paris's Central Business District, was ranked by Ernst & Young
EY, previously known as Ernst & Young, is a multinational corporation, multinational professional services partnership, network based in London, United Kingdom. Along with Deloitte, KPMG and PwC, it is one of the Big Four accounting firms, Big F ...
in 2017 as the leading business district in continental Europe
Continental Europe or mainland Europe is the contiguous mainland of Europe, excluding its surrounding islands. It can also be referred to ambiguously as the European continent, – which can conversely mean the whole of Europe – and, by som ...
, and fourth in the world. The OECD
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; , OCDE) is an international organization, intergovernmental organization with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate economic progress and international trade, wor ...
is headquartered in Paris, the nation's financial capital. The other major economic centres of the country include Lyon
Lyon (Franco-Provençal: ''Liyon'') is a city in France. It is located at the confluence of the rivers Rhône and Saône, to the northwest of the French Alps, southeast of Paris, north of Marseille, southwest of Geneva, Switzerland, north ...
, Toulouse
Toulouse (, ; ; ) is a city in southern France, the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Haute-Garonne department and of the Occitania (administrative region), Occitania region. The city is on the banks of the Garonne, River Garonne, from ...
(centre of the European aerospace industry), Marseille
Marseille (; ; see #Name, below) is a city in southern France, the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Departments of France, department of Bouches-du-Rhône and of the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur Regions of France, region. Situated in the ...
and Lille
Lille (, ; ; ; ; ) is a city in the northern part of France, within French Flanders. Positioned along the Deûle river, near France's border with Belgium, it is the capital of the Hauts-de-France Regions of France, region, the Prefectures in F ...
.
France's economy entered the recession of the late 2000s later and appeared to leave it earlier than most affected economies, only enduring four-quarters of contraction. However, France experienced stagnant growth between 2012 and 2014, with the economy expanding by 0% in 2012, 0.8% in 2013 and 0.2% in 2014. Growth picked up in 2015 with a growth of 0.8%. This was followed by a growth of 1.1% for 2016, a growth of 2.2% for 2017, and a growth of 2.1% for 2018.
According to INSEE (2021), non-financial and non-agricultural medium-sized firms employed 3 million full-time equivalent employees (24.3% of the workforce), accounted for 27% of investment, 30% of turnover, and 26% of value added, despite accounting for only 1.6% of total firms in France.
Corporations
With 31 companies that are part of the world's biggest 500 companies, France was in 2020 the most represented European country in the 2020Fortune Global 500
The ''Fortune'' Global 500, also known as Global 500, is an annual ranking of the top 500 corporations worldwide as measured by revenue. The list is compiled and published annually by '' Fortune'' magazine.
Methodology
Until 1989, it listed o ...
, ahead of Germany (27 companies) and the UK (22).
As of August 2020, France was also the country that weighed the most on the Eurozone's EURO STOXX 50 (representing 36.4% of all total assets), ahead of Germany (35.2%).
Several French corporations rank amongst the largest in their industries such as AXA
Axa S.A. is a French multinational insurance corporation headquartered in the 8th arrondissement of Paris. It also provides investment management and other financial services via its subsidiaries. As of 2024, it is the fourth largest financi ...
in insurance and Air France
Air France (; legally ''Société Air France, S.A.''), stylised as AIRFRANCE, is the flag carrier of France, and is headquartered in Tremblay-en-France. The airline is a subsidiary of the Air France-KLM Group and is one of the founding members ...
in air transportation. Luxury and consumer goods are particularly relevant, with L'Oreal being the world's largest cosmetic company while LVMH
LVMH Moët Hennessy Louis Vuitton SE (), commonly known as LVMH, is a French multinational holding company and conglomerate that specializes in luxury goods and has its headquarters in Paris, France. The company was formed in 1987 through the ...
and Kering
Kering S.A. () is a French multinational holding company specializing in luxury goods, headquartered in Paris. It owns the brands Yves Saint Laurent, Gucci, Balenciaga, Bottega Veneta, Creed, Maui Jim, and Alexander McQueen.
The timber-tradin ...
are the world's two largest luxury product companies. In energy and utilities, GDF-Suez and EDF EDF may refer to:
Organisations
* Eclaireurs de France, a French Scouting association
* Électricité de France, a French energy company
** EDF Energy, their British subsidiary
** EDF Luminus, their Belgian subsidiary
* Environmental Defense Fund, ...
are amongst the largest energy companies in the world, and Areva
Areva S.A. was a French multinational group specializing in nuclear power, active between 2001 and 2018. It was headquartered in Courbevoie, France. Before its 2016 corporate restructuring, Areva was majority-owned by the French state through t ...
is a large nuclear-energy company; Veolia Environnement
Veolia Environnement S.A., branded as Veolia, is a French transnational company with activities in three main service and utility areas traditionally managed by public authorities – water management, waste management and energy services. In 2 ...
is the world's largest environmental services and water management company; Vinci SA
Vinci (; corporately styled VINCI) is a French concessions and construction company founded in 1899 as Société Générale d'Entreprises. Its head office is in Nanterre, in the western suburbs of Paris. Vinci is listed on Euronext's Paris st ...
, Bouygues
Bouygues S.A. () is a French engineering group headquartered in the 8th arrondissement of Paris, 8th arrondissement of Paris, France. Bouygues is listed on the Euronext, Euronext Paris exchange and is a blue chip (stock market), blue chip in the ...
and Eiffage
Eiffage S.A. () is a French civil engineering construction company. it was the third largest company of its type in France, and the fifth largest in Europe.
History
The company was formed in 1992 through the merger of several long standing comp ...
are large construction companies; Michelin
Michelin ( , ), in full ("General Company of the Michelin Enterprises P.L.S."), is a French multinational tyre manufacturing company based in Clermont-Ferrand in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes '' région'' of France. It is the second largest t ...
ranks in the top 3 tire manufacturers; JCDecaux is the world's largest outdoor advertising corporation; BNP Paribas
BNP Paribas (; sometimes referred to as BNPP or BNP) is a French multinational universal bank and financial services holding company headquartered in Paris. It was founded in 2000 from the merger of two of France's foremost financial instituti ...
, Credit Agricole and Société Générale
Société Générale S.A. (), colloquially known in English-speaking countries as SocGen (), is a French multinational universal bank and financial services company founded in 1864. It is registered in downtown Paris and headquartered nearby i ...
rank amongst the largest banks in the world by assets. Capgemini
Capgemini SE is a French Multinational corporation, multinational information technology (IT) services and consulting company, headquartered in Paris, France.
History
Capgemini was founded by Serge Kampf in 1967 as an enterprise management and d ...
and Atos
Atos SE is a European multinational information technology (IT) service and consulting company with headquarters in Bezons suburb of Paris, France, and offices worldwide. It specialises in hi-tech transactional services, unified communicat ...
are among the largest technology consulting companies.
Carrefour
Carrefour Group, S.A. (, ), is a French multinational retail and wholesaling corporation headquartered in Massy, Essonne, Massy, France. It operates a chain of hypermarkets, grocery stores and convenience stores. By 2024, the group had 14,000 ...
is the world's second-largest retail group in terms of revenue; Total
Total may refer to:
Mathematics
* Total, the summation of a set of numbers
* Total order, a partial order without incomparable pairs
* Total relation, which may also mean
** connected relation (a binary relation in which any two elements are comp ...
is the world's fourth-largest private oil company; Lactalis
Groupe Lactalis S.A. (doing business as Lactalis) is a French multinational dairy products corporation, owned by the Besnier family and based in Laval, Mayenne, France. The company's former name was Besnier S.A.
Lactalis is the largest dairy pr ...
is the world's largest dairy products group; Sanofi
Sanofi S.A. is a French Multinational corporation, multinational pharmaceutical and healthcare company headquartered in Paris, France. The corporation was established in 1973 and merged with Synthélabo in 1999 to form Sanofi-Synthélabo. In 200 ...
is the world's fifth-largest pharmaceutical company; Publicis
Publicis Groupe S.A. is a French multinational advertising and public relations company. As of 2024, the company is the largest advertising company in the world by revenue. Based in Paris, it is one of the 'Big Four' advertising commpanies, al ...
is the world's third-largest advertising company; Groupe PSA
Peugeot S.A., trading as Groupe PSA () (formerly PSA Peugeot Citroën from 1991 to 2016) was a French multinational automotive manufacturing company which produced automobiles and motorcycles under the Peugeot, Citroën, DS, Opel and Vauxhal ...
is the world's 6th and Europe's 2nd largest automaker; Accor
Accor S.A. is a French multinational hospitality company that owns, manages and franchises hotels, resorts and vacation properties. It is the largest hospitality company in Europe, and the sixth largest hospitality company worldwide.
Accor ope ...
is the leading European hotel group; Alstom
Alstom SA () is a French multinational rolling stock manufacturer which operates worldwide in rail transport markets. It is active in the fields of passenger transportation, signaling, and locomotives, producing high-speed, suburban, regional ...
is one of the world's leading conglomerates in rail transport.
In 2022, the sector with the highest number of companies registered in France is Finance, Insurance, and Real Estate with 2,656,178 companies followed by Services and Retail Trade with 2,090,320 and 549,395 companies respectively.
Rise and decline of dirigisme
France embarked on an ambitious and very successful programme of modernisation under state coordination. This programme of ''dirigisme
Dirigisme or dirigism () is an economic doctrine in which the state plays a strong directive (policies) role, contrary to a merely regulatory or non-interventionist role, over a market economy. As an economic doctrine, dirigisme is the opposite ...
'', mostly implemented by governments between 1944 and 1983, involved the state control of certain industries such as transportation, energy and telecommunications as well as various incentives for private corporations to merge or engage in certain projects.
The 1981 election of president François Mitterrand
François Maurice Adrien Marie Mitterrand (26 October 19168 January 1996) was a French politician and statesman who served as President of France from 1981 to 1995, the longest holder of that position in the history of France. As a former First ...
saw a short-lived increase in governmental control of the economy, nationalizing many industries and private banks. This form of increased ''dirigisme'', was criticised as early as 1982. By 1983, the government decided to renounce ''dirigisme'' and start an era of rigueur ("rigor") or corporation. As a result, the government largely retreated from economic intervention; ''dirigisme'' has now essentially receded, though some of its traits remain. The French economy grew and changed under government direction and planning much more than in other European countries.
Despite being a widely liberalised economy, the government continues to play a significant role in the economy: government spending, at 56% of GDP in 2014, is the second-highest in the European Union. Labor conditions and wages are highly regulated. The government continues to own shares in corporations in several sectors, including energy production and distribution, automobiles, aerospace industry, shipbuilding, the arms industry, electronics industry, machine industry, metallurgy, fuels, chemical industry, transportation, and telecommunications.
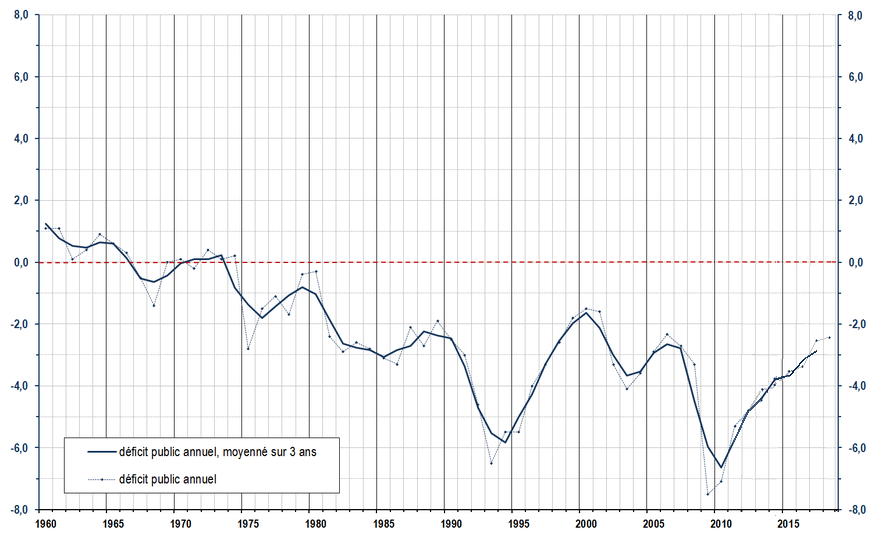
Government finance



 In April and May 2012, France held a
In April and May 2012, France held a presidential election
A presidential election is the election of any head of state whose official title is President.
Elections by country
Albania
The president of Albania is elected by the Assembly of Albania who are elected by the Albanian public.
Chile
The p ...
in which the winner François Hollande
François Gérard Georges Nicolas Hollande (; born 12 August 1954) is a French politician who served as President of France from 2012 to 2017. Before his presidency, he was First Secretary of the Socialist Party (France), First Secretary of th ...
had opposed austerity measures, promising to eliminate France's budget deficit by 2017. The new government stated that it aimed to cancel recently enacted tax cuts and exemptions for the wealthy, raising the top tax bracket rate to 75% on incomes over a million euros, restoring the retirement age to 60 with a full pension for those who have worked 42 years, restoring 60,000 jobs recently cut from public education, regulating rent increases; and building additional public housing for the poor.
In June 2012, Hollande's Socialist Party
Socialist Party is the name of many different political parties around the world. All of these parties claim to uphold some form of socialism, though they may have very different interpretations of what "socialism" means. Statistically, most of th ...
won an overall majority in the legislative elections
A general election is an electoral process to choose most or all members of a governing body at the same time. They are distinct from by-elections, which fill individual seats that have become vacant between general elections. General elections ...
, giving it the capability to amend the French Constitution and allowing immediate enactment of the promised reforms. French government bond interest rates fell 30% to record lows, less than 50 basis point
A basis point (often abbreviated as bp, often pronounced as "bip" or "beep") is one hundredth of 1 percentage point. Changes of interest rates are often stated in basis points. For example, if an existing interest rate of 10 percent is increased ...
s above German government bond rates.
Hollande's successor as President of France, Emmanuel Macron
Emmanuel Jean-Michel Frédéric Macron (; born 21 December 1977) is a French politician who has served as President of France and Co-Prince of Andorra since 2017. He was Ministry of Economy and Finance (France), Minister of Economics, Industr ...
, a centrist politician, took office in May 2017. His aim was to revive the euro zone’s second-largest economy.
In July 2020, during the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic (also known as the coronavirus pandemic and COVID pandemic), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), began with an disease outbreak, outbreak of COVID-19 in Wuhan, China, in December ...
, the French government issued 10-years bonds which had negative interest rates, for the first time in its history (which means that investors buying French bonds will pay, rather than receive, interest for owning French sovereign debt).
France possesses in 2020 the fourth-largest gold reserves in the world.
Macron vowed in May 2023 to build factories, boost job creations and make France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
more independent, shaked by pension protests.
National debt
The Government of France has run abudget deficit
Within the budgetary process, deficit spending is the amount by which spending exceeds revenue over a particular period of time, also called simply deficit, or budget deficit, the opposite of budget surplus. The term may be applied to the budg ...
each year since the early 1970s. As of 2021, French government debt reached an equivalent of 118.6% of French GDP.
Under European Union rules, member states are supposed to limit their debt to 60% of output or be reducing the ratio structurally towards this ceiling, and run public deficits of no more than 3.0% of GDP.
In late 2012, credit-rating agencies warned that growing French government debt levels risked France's AAA credit rating, raising the possibility of a future credit downgrade and subsequent higher borrowing costs for the French government. In 2012 France was downgraded by ratings agencies Moody's
Moody's Ratings, previously and still legally known as Moody's Investors Service and often referred to as Moody's, is the bond credit rating business of Moody's Corporation, representing the company's traditional line of business and its histo ...
, Standard & Poor
S&P Global Ratings (previously Standard & Poor's and informally known as S&P) is an American credit rating agency (CRA) and a division of S&P Global that publishes financial research and analysis on stocks, bonds, and commodities. S&P is cons ...
's (S&P), and Fitch to an AA+ credit rating.
In December 2014 France's credit rating was further downgraded by Fitch and S&P to AA.
Macron, shaken by pension protests, vowed in May 2023 to build factories, boost job creations and make France more independent.
The Government of France experienced a significant shift in its bond market
The bond market (also debt market or credit market) is a financial market in which participants can issue new debt, known as the primary market, or buy and sell debt security (finance), securities, known as the secondary market. This is usually in ...
position on September 26, 2024, when its bond yield surpassed that of Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
for the first time since 2007. The yield on 10-year French bonds reached 2.97%, slightly exceeding the yield on Spanish bonds of similar maturity, despite France's typically higher credit rating
A credit rating is an evaluation of the credit risk of a prospective debtor (an individual, a business, company or a government). It is the practice of predicting or forecasting the ability of a supposed debtor to pay back the debt or default. The ...
.
This development raised concerns among investors about France's ability to manage its public finances
Public finance refers to the monetary resources available to governments and also to the study of finance within government and role of the government in the economy. Within academic settings, public finance is a widely studied subject in man ...
effectively. France's bond yields were reported to be higher than those of Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic, is a country on the Iberian Peninsula in Southwestern Europe. Featuring Cabo da Roca, the westernmost point in continental Europe, Portugal borders Spain to its north and east, with which it share ...
and approaching levels seen in Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
and Greece
Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. Located on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, it shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to th ...
, countries traditionally viewed as having higher economic risks in the Eurozone
The euro area, commonly called the eurozone (EZ), is a Monetary union, currency union of 20 Member state of the European Union, member states of the European Union (EU) that have adopted the euro (Euro sign, €) as their primary currency ...
.
Furthermore, France faces a budget crisis in 2024, with the deficit at risk of exceeding 6% of GDP, significantly higher than the previous government's estimate of 5.1%. Newly appointed Finance Minister Antoine Armand and Budget Minister Laurent Saint-Martin pledged to focus on spending cuts before considering tax
A tax is a mandatory financial charge or levy imposed on an individual or legal entity by a governmental organization to support government spending and public expenditures collectively or to regulate and reduce negative externalities. Tax co ...
increases to address the fiscal shortfall. Prime Minister Michel Barnier
Michel Jean Barnier (; born 9 January 1951) is a French politician who was Prime Minister of France from September to December 2024. A member of a series of Gaullist parties ( UDR, RPR, UMP, LR), Barnier has served in several French cabinet p ...
was tasked with finalizing the 2025 budget within days, amidst pressure to present realistic plans for deficit reduction.
Data
 The following table shows the main economic indicators in 1980–2021 (with IMF staff estimates in 2022–2027). Inflation below 5% is in green.
The following table shows the main economic indicators in 1980–2021 (with IMF staff estimates in 2022–2027). Inflation below 5% is in green.
Economic sectors
Industry
 In 2019, France was the world's 8th largest manufacturer in terms of
In 2019, France was the world's 8th largest manufacturer in terms of value added
Value added is a term in economics for calculating the difference between market value of a product or service, and the sum value of its constituents. It is relatively expressed by the supply-demand curve for specific units of sale. Value added ...
, according to the World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and Grant (money), grants to the governments of Least developed countries, low- and Developing country, middle-income countries for the purposes of economic development ...
.
The leading industrial sectors in France are telecommunications (including communication satellites), aerospace and defence, ship building, pharmaceuticals, construction and civil engineering, chemicals, textiles, and automobile production. The chemical industry
The chemical industry comprises the companies and other organizations that develop and produce industrial, specialty and other chemicals. Central to the modern world economy, the chemical industry converts raw materials ( oil, natural gas, air, ...
is a key sector for France, helping to develop other manufacturing activities and contributing to economic growth.
Research and development
Research and development (R&D or R+D), known in some countries as OKB, experiment and design, is the set of innovative activities undertaken by corporations or governments in developing new services or products. R&D constitutes the first stage ...
spending is also high in France at 2.26% of GDP, the fourth-highest in the OECD.
Industry contributes to French exports: as of 2018, the Observatory of Economic Complexity
The Observatory of Economic Complexity (OEC) is an online data visualization and distribution platform for international trade data designed and owned bDatawheel Through interactive visualizations, the OEC aims to make global trade data accessib ...
estimates that France's largest exports "are led by planes, helicopters, and spacecraft ($43.8 billion), cars ($26 billion), packaged medicaments ($25.7 billion), vehicle parts ($16.5 billion), and gas turbine
A gas turbine or gas turbine engine is a type of Internal combustion engine#Continuous combustion, continuous flow internal combustion engine. The main parts common to all gas turbine engines form the power-producing part (known as the gas gene ...
s ($14.4 billion)."
In December 2023, industrial production in France experienced its most significant change since May of the same year, with a notable increase of 1.1%.
Energy
France is the world-leading country in nuclear energy, home of global energy giantsAreva
Areva S.A. was a French multinational group specializing in nuclear power, active between 2001 and 2018. It was headquartered in Courbevoie, France. Before its 2016 corporate restructuring, Areva was majority-owned by the French state through t ...
, EDF EDF may refer to:
Organisations
* Eclaireurs de France, a French Scouting association
* Électricité de France, a French energy company
** EDF Energy, their British subsidiary
** EDF Luminus, their Belgian subsidiary
* Environmental Defense Fund, ...
and GDF Suez
Engie SA (stylised in all caps as ENGIE) is a French multinational electric utility company, headquartered in La Défense, Courbevoie. Its activities cover electricity generation and distribution, natural gas, nuclear power, renewable energy ...
: nuclear power
Nuclear power is the use of nuclear reactions to produce electricity. Nuclear power can be obtained from nuclear fission, nuclear decay and nuclear fusion reactions. Presently, the vast majority of electricity from nuclear power is produced by ...
now accounts for about 78% of the country's electricity production, up from only 8% in 1973, 24% in 1980, and 75% in 1990. Nuclear waste
Radioactive waste is a type of hazardous waste that contains radioactive material. It is a result of many activities, including nuclear medicine, nuclear research, nuclear power generation, nuclear decommissioning, rare-earth mining, and nuclear ...
is stored on site at reprocessing facilities. Due to its Nuclear power in France, heavy investment in nuclear power, France is the smallest emitter of Greenhouse gas, carbon dioxide among the seven most industrialised countries in the world. Due to its overwhelming reliance on nuclear power, Renewable energy in France, renewable energies have seen relatively little growth compared to other Western countries.
In 2006, electricity generated in France amounted to 548.8 Watt-hour#Multiples, TWh, of which:
*428.7 TWh (78.1%) were produced by Nuclear reactor technology, nuclear power generation
*60.9 TWh (11.1%) were produced by hydroelectric power generation
*52.4 TWh (9.5%) were produced by fossil-fuel power generation
**21.6 TWh (3.9%) by coal power
**20.9 TWh (3.8%) by natural-gas power
**9.9 TWh (1.8%) by other fossil fuel generation (fuel oil and gases by-products of industry such as blast furnace gases)
*6.9 TWh (1.3%) were produced by other types of power generation (essentially waste-to-energy and wind turbines)
**The electricity produced by wind turbines increased from 0.596 TWh in 2004, to 0.963 TWh in 2005, and 2.15 TWh in 2006, but this still accounted only for 0.4% of the total production of electricity (as of 2006).
In November 2004, EDF EDF may refer to:
Organisations
* Eclaireurs de France, a French Scouting association
* Électricité de France, a French energy company
** EDF Energy, their British subsidiary
** EDF Luminus, their Belgian subsidiary
* Environmental Defense Fund, ...
(which stands for Electricité de France), one of the world's largest utility company and France's largest electricity provider, was floated with huge success on the French stock market. However, the French state still retains 70% of the capital. Other electricity providers include Compagnie nationale du Rhône (CNR) and Endesa (Spain), Endesa (through Société nationale d'électricité et de thermique, SNET).
Agriculture
 France is the world's sixth largest agricultural producer and EU's leading agricultural power, accounting for about one-third of all agricultural land within the EU. In the early 1980s, France was the leading producer of the three principal grains of wheat, barley, and maize. Back in 1983, France produced around 24.8 million tonnes, ahead of the United Kingdom and West Germany, the next two largest wheat producers.
Northern France is characterised by large wheat farms. Dairy products, pork, poultry, and apple production are concentrated in the western region. Beef production is located in central France, while the production of fruits, vegetables, and wine ranges from central to southern France. France is a large producer of many agricultural products and is currently expanding its forestry and fishery industries. The implementation of the Common Agricultural Policy (CAP) and the Uruguay Round of the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) have resulted in reforms in the agricultural sector of the economy.
As the world's second-largest agricultural exporter, France ranks just after the United States. The destination of 49% of its exports is other EU members states. France also provides agricultural exports to many poor African countries (including its former colonies) which face serious food shortages. Wheat, beef, pork, poultry, and dairy products are the principal exports.
Exports from the United States face stiff competition from domestic production, other EU member states, and third-world countries in France. US agricultural exports to France, totaling some $600 million annually, consist primarily of soybeans and soybean products, feeds and fodders, seafood, and consumer products, especially snack foods and nuts. French exports to the United States are much more high-value products such as French cheese, its cheese, processed products and French wine, its wine.
The French agricultural sector receives almost €11 billion in EU subsidies. France produced in 2018 39.5 million tons of sugar beet (2nd largest producer in the world, just behind Russia), which serves to produce sugar and ethanol; 35.8 million tons of wheat (5th largest producer in the world); 12.6 million tons of maize (11th largest producer in the world); 11.2 million tons of barley (2nd largest producer in the world, only behind Russia); 7.8 million tons of potato (8th largest producer in the world); 6.2 million tons of grape (5th largest producer in the world); 4.9 million tons of rapeseed (4th largest producer in the world, behind Canada, China and India); 2.2 million tons of sugarcane; 1.7 million tons of apple (9th largest producer in the world); 1.3 million tons of triticale (4th largest producer in the world, only behind Poland, Germany and Belarus); 1.2 million tons of sunflower seed (9th largest producer in the world); 712 thousand tons of tomatoes; 660 thousand tons of linen; 615 thousand tons of dry pea; 535 thousand tons of carrot; 427 thousand tons of oats; 400 thousand tons of soy; in addition to smaller productions of other agricultural products.
France is the world's sixth largest agricultural producer and EU's leading agricultural power, accounting for about one-third of all agricultural land within the EU. In the early 1980s, France was the leading producer of the three principal grains of wheat, barley, and maize. Back in 1983, France produced around 24.8 million tonnes, ahead of the United Kingdom and West Germany, the next two largest wheat producers.
Northern France is characterised by large wheat farms. Dairy products, pork, poultry, and apple production are concentrated in the western region. Beef production is located in central France, while the production of fruits, vegetables, and wine ranges from central to southern France. France is a large producer of many agricultural products and is currently expanding its forestry and fishery industries. The implementation of the Common Agricultural Policy (CAP) and the Uruguay Round of the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) have resulted in reforms in the agricultural sector of the economy.
As the world's second-largest agricultural exporter, France ranks just after the United States. The destination of 49% of its exports is other EU members states. France also provides agricultural exports to many poor African countries (including its former colonies) which face serious food shortages. Wheat, beef, pork, poultry, and dairy products are the principal exports.
Exports from the United States face stiff competition from domestic production, other EU member states, and third-world countries in France. US agricultural exports to France, totaling some $600 million annually, consist primarily of soybeans and soybean products, feeds and fodders, seafood, and consumer products, especially snack foods and nuts. French exports to the United States are much more high-value products such as French cheese, its cheese, processed products and French wine, its wine.
The French agricultural sector receives almost €11 billion in EU subsidies. France produced in 2018 39.5 million tons of sugar beet (2nd largest producer in the world, just behind Russia), which serves to produce sugar and ethanol; 35.8 million tons of wheat (5th largest producer in the world); 12.6 million tons of maize (11th largest producer in the world); 11.2 million tons of barley (2nd largest producer in the world, only behind Russia); 7.8 million tons of potato (8th largest producer in the world); 6.2 million tons of grape (5th largest producer in the world); 4.9 million tons of rapeseed (4th largest producer in the world, behind Canada, China and India); 2.2 million tons of sugarcane; 1.7 million tons of apple (9th largest producer in the world); 1.3 million tons of triticale (4th largest producer in the world, only behind Poland, Germany and Belarus); 1.2 million tons of sunflower seed (9th largest producer in the world); 712 thousand tons of tomatoes; 660 thousand tons of linen; 615 thousand tons of dry pea; 535 thousand tons of carrot; 427 thousand tons of oats; 400 thousand tons of soy; in addition to smaller productions of other agricultural products.
Tourism
 France is the world's most popular tourist destination with more than 83.7 million foreign tourists in 2014, ahead of Spain (58.5 million in 2006) and the United States (51.1 million in 2006). This figure excludes people staying less than 24 hours in France, such as northern Europeans crossing France on their way to Spain or Italy during the summer.
According to figures from 2003, some popular tourist sites include (in visitors per year): Eiffel Tower (6.2 million), Louvre Museum (5.7 million), Palace of Versailles (2.8 million), Cité des Sciences et de l'Industrie (2.6 million), Musée d'Orsay (2.1 million), Arc de Triomphe (1.2 million), Centre Georges Pompidou, Centre Pompidou (1.2 million), Mont-Saint-Michel (1 million), Château de Chambord (711,000), Sainte-Chapelle (683,000), Château du Haut-Kœnigsbourg (549,000), Puy-de-Dôme (mountain), Puy de Dôme (500,000), Musée Picasso (441,000), Carcassonne (362,000). However, the most popular site in France is Disneyland Paris, with 9.7 million visitors in 2017
France is the world's most popular tourist destination with more than 83.7 million foreign tourists in 2014, ahead of Spain (58.5 million in 2006) and the United States (51.1 million in 2006). This figure excludes people staying less than 24 hours in France, such as northern Europeans crossing France on their way to Spain or Italy during the summer.
According to figures from 2003, some popular tourist sites include (in visitors per year): Eiffel Tower (6.2 million), Louvre Museum (5.7 million), Palace of Versailles (2.8 million), Cité des Sciences et de l'Industrie (2.6 million), Musée d'Orsay (2.1 million), Arc de Triomphe (1.2 million), Centre Georges Pompidou, Centre Pompidou (1.2 million), Mont-Saint-Michel (1 million), Château de Chambord (711,000), Sainte-Chapelle (683,000), Château du Haut-Kœnigsbourg (549,000), Puy-de-Dôme (mountain), Puy de Dôme (500,000), Musée Picasso (441,000), Carcassonne (362,000). However, the most popular site in France is Disneyland Paris, with 9.7 million visitors in 2017
Arms industry
The French government is the French arms industry's main customer, mainly buying warships, guns, nuclear weapons and equipment. During the 2000–2015 period, France was the fourth largest Arms industry#World's largest arms exporters, weapons exporter in the world. French manufacturers export great quantities of weaponry to Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, Brazil, Greece, India, Pakistan, Taiwan, Singapore and many others. It was reported that in 2015, French arms sales internationally amounted to 17.4 billion U.S. dollars, more than double the figure of 2014.Fashion and luxury goods
According to 2017 data compiled by Deloitte, Louis Vuitton Moet Hennessey (LVMH), a French brand, is the largest luxury company in the world by sales, selling more than twice the amount of its nearest competitor.Global Powers of Luxury Goods 2019: Bridging the gap between the old and the new, Deloitte Moreover, France also possesses 3 of the top 10 luxury goods companies by sales (
LVMH
LVMH Moët Hennessy Louis Vuitton SE (), commonly known as LVMH, is a French multinational holding company and conglomerate that specializes in luxury goods and has its headquarters in Paris, France. The company was formed in 1987 through the ...
, Kering SA, L'Oréal), more than any other country in the world.
Paris is considered one of the world's foremost fashion capitals, or even "the world's fashion capital". The French tradition for haute couture has been estimated to start as early as the era of Louis XIV, the Sun King.
Education
Education in France is organised in a highly centralised manner, with many subdivisions. It is divided into the three stages of primary education (''enseignement primaire''), secondary education (''enseignement secondaire''), and higher education (''enseignement supérieur''). In French higher education, the following degrees are recognised by the Bologna Process (EU recognition): ''Licence'' and ''Licence Professionnelle'' (bachelor's degrees), and the comparably named ''Master'' and ''Doctorat'' degrees. The Programme for International Student Assessment coordinated by theOECD
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; , OCDE) is an international organization, intergovernmental organization with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate economic progress and international trade, wor ...
currently ranks the overall knowledge and skills of French 15-year-olds as 26th in the world in reading literacy, mathematics, and science, near the OECD average of 493. France's performance in mathematics and science at the middle school level was ranked 23 in the 1995 TIMSS, Trends in International Math and Science Study. The OECD
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; , OCDE) is an international organization, intergovernmental organization with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate economic progress and international trade, wor ...
also found that students in France reported greater concern about discipline and behaviour at school and in classrooms, much more than the rest of Europe. This was higher than all OECD
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; , OCDE) is an international organization, intergovernmental organization with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate economic progress and international trade, wor ...
countries. School principals reported higher staff and material shortage in France, higher than OECD
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; , OCDE) is an international organization, intergovernmental organization with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate economic progress and international trade, wor ...
averages. About 7% of French teachers believe the teaching profession is highly valued in France and in society. School principals noted regular acts of violence/ bullying among their students, higher than averages. The time spent of teaching time spent on keeping classes in good order is one of the largest in France, among all OECD
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; , OCDE) is an international organization, intergovernmental organization with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate economic progress and international trade, wor ...
countries studied. France also has a high Dropping out, drop out rate.
Pupils can take apprenticeships to enter the Labour economics, labour market with the Baccalauréat, Baccalauréat Technologique. It allows pupils pursue short and technical studies (laboratory, design and applied arts, hotel and restaurant, management etc).
Higher education in France was reshaped by the student revolts of May 68, May 1968. During the 1960s, French public universities responded to a massive explosion in the number of students (280,000 in 1962–63 to 500,000 in 1967–68) by stuffing approximately one-third of their students into hastily developed campus annexes (roughly equivalent to American satellite campuses) which lacked decent amenities, resident professors, academic traditions, or the dignity of university status. This is why the French Higher education, higher education economy performs poorly compared with other high-performing countries such as Economy of England, England or Economy of Australia, Australia. France also hosts various Catholic higher education, catholic universities recognised by the state, the largest one being Lille Catholic University, as well branch colleges of foreign universities. They include Baruch College, the University of London Institute in Paris, Parsons Paris School of Art and Design and the American University of Paris. Eighteen million pupils and students are in the education system, over 2.4 million of whom are in higher education.
Transport
 Transportation in France relies on one of the densest networks in the world with 146 km of road and 6.2 km of rail lines per 100 km2. It is built as a web with Paris at its centre. The highly subsidised rail transport in France, rail transport network makes up a relatively small portion of travel, most of which is done by car. However, the high-speed TGV trains make up a large proportion of long-distance travel, partially because intercity buses were prevented from operating until 2015.
With 3,220 kilometers of high-speed train lines, France boast the 2nd most expansive network in the world, only after China. Charles de Gaulle Airport is one of the busiest airports in the world by passenger traffic. Charles de Gaulle airport is third globally in the number of destinations served, and first in the number of countries served with non-stop flights.
France also boasts a number of seaports and harbours, including Bayonne, Bordeaux, Boulogne-sur-Mer, Brest, Finistère, Brest, Calais, Cherbourg-Octeville, Dunkerque, Fos-sur-Mer, La Pallice, Le Havre, Lorient,
Transportation in France relies on one of the densest networks in the world with 146 km of road and 6.2 km of rail lines per 100 km2. It is built as a web with Paris at its centre. The highly subsidised rail transport in France, rail transport network makes up a relatively small portion of travel, most of which is done by car. However, the high-speed TGV trains make up a large proportion of long-distance travel, partially because intercity buses were prevented from operating until 2015.
With 3,220 kilometers of high-speed train lines, France boast the 2nd most expansive network in the world, only after China. Charles de Gaulle Airport is one of the busiest airports in the world by passenger traffic. Charles de Gaulle airport is third globally in the number of destinations served, and first in the number of countries served with non-stop flights.
France also boasts a number of seaports and harbours, including Bayonne, Bordeaux, Boulogne-sur-Mer, Brest, Finistère, Brest, Calais, Cherbourg-Octeville, Dunkerque, Fos-sur-Mer, La Pallice, Le Havre, Lorient, Marseille
Marseille (; ; see #Name, below) is a city in southern France, the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Departments of France, department of Bouches-du-Rhône and of the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur Regions of France, region. Situated in the ...
, Nantes, Nice, Paris, Port-la-Nouvelle, Port-Vendres, Roscoff, Rouen, Saint-Nazaire, Saint-Malo, Sète, Strasbourg and Toulon. There are approximately 470 airports in France and by a 2005 estimate, there are three heliports. 288 of the airports have paved runways, with the remaining 199 being unpaved. The national carrier of France is Air France, a full service global airline which flies to 20 domestic destinations and 150 international destinations in 83 countries (including Overseas France) across all 6 major continents.
Foreign investment
According to a study conducted byErnst & Young
EY, previously known as Ernst & Young, is a multinational corporation, multinational professional services partnership, network based in London, United Kingdom. Along with Deloitte, KPMG and PwC, it is one of the Big Four accounting firms, Big F ...
, France was in 2020 the largest Foreign Direct Investment
A foreign direct investment (FDI) is an ownership stake in a company, made by a foreign investor, company, or government from another country. More specifically, it describes a controlling ownership an asset in one country by an entity based i ...
recipient in Europe, ahead of the UK and Germany.How can Europe reset the investment agenda now to rebuild its future?, Ernst&Young, EY, 28 May 2020 EY attributed this as a "direct result of Emmanuel Macron, President Macron’s reforms of labor laws and corporate taxation, which were well received by domestic and international investors alike." France scored 5th in the 2019 AT Kearney FDI Confidence Index, up 2 notches from its 2017 ranking.
Labour market
According to a 2011 report by the American Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), France's GDP per capita at purchasing power parity is similar to that of the UK, with just over US$35,000 per head. To explain why French per capita GDP is lower than that of the United States, the economist Paul Krugman stated that "French workers are roughly as productive as US workers", but that the French have a ''lower workforce participation rate,'' and "when they work, they work fewer hours". According to Krugman, the difference is due to the French making "different choices about retirement and leisure". France has long suffered a relatively high unemployment rate, even during the years when its macroeconomic performances compared favourably with other advanced economies. The employment rate of the French working-age population is one of the lowest of the OECD countries: in 2020, only 64.4% of the French working-age population were in employment, compared to 77% in Japan, 76.1% in Germany, 75.4% in the UK, but the French employment rate was higher than that of the US, which stood at 62.5%. This gap is due to the low employment rate of those 15–24 years old: 38% in 2012, compared to 47% in the OECD. Since his French presidential election 2017, election in 2017,Emmanuel Macron
Emmanuel Jean-Michel Frédéric Macron (; born 21 December 1977) is a French politician who has served as President of France and Co-Prince of Andorra since 2017. He was Ministry of Economy and Finance (France), Minister of Economics, Industr ...
has introduced several labour market reforms which proved successful in decreasing the unemployment rate before the global COVID-19 recession struck. In late 2019, the French unemployment rate, though still high compared to other developed economies, was the lowest in a decade.
During the 2000s and 2010s, Classical liberalism, classical liberal and Keynesian economics, Keynesian economists sought out different solutions to the unemployment issue in France. Keynesian economists's theories led to the introduction of the 35-hour workweek law in 1999. Between 2004 and 2008, the government attempted to combat unemployment with supply-side reforms, but was met with fierce resistance; the ''contrat nouvelle embauche'' and the ''First Employment Contract, contrat première embauche'' (which allowed more flexible contracts) were of particular concern, and both were eventually repealed. The Sarkozy government used the ''revenu de solidarité active'' (in-work benefits) to redress the ''negative effect'' of the ''revenu minimum d'insertion'' (unemployment benefits which do not depend on previous contributions, unlike normal unemployment benefits in France) on the incentive to accept even jobs which are insufficient to earn a living. Neoliberal economists attribute the low employment rate, particularly evident among young people, to high minimum wages that would prevent low productivity workers from easily entering the labour market.
A December 2012 ''New York Times'' article reported on a "floating generation" in France that formed part of the 14 million unemployed young Europeans documented by the Eurofound research agency. This ''floating generation'' was attributed to a dysfunctional system: "an elitist educational tradition that does not integrate graduates into the work force, a rigid labour market that is hard to enter for newcomers, and a tax system that makes it expensive for companies to hire full-time employees and both difficult and expensive to lay them off". In July 2013, the unemployment rate for France was 11%.
In early April 2014, employers' federations and unions negotiated an agreement with technology and consultancy employers, as employees had been experiencing an extension of their work time through smartphone communication outside of official working hours. Under a new, legally binding labour agreement, around 250,000 employees will avoid handling work-related matters during their leisure time and their employers will, in turn, refrain from engaging with staff during this time.
Every day, about 80,000 French citizens commute to work in neighbouring Luxembourg, making it the biggest cross-border workforce group in the whole of the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
. They are attracted by much higher wages for the different job groups than in their own country and the lack of skilled labour in the booming Luxembourgish economy.
The background of the 2023 2023 French pension reform law, pension reform was about 14% of GDP pension spending in France compared to OECD average of just over 9%. The aim of the pension reform was to reduce cost by increasing the minimum legal retirement age from 62 years to 64 years in 2030. In April 2023, president Emmanuel Macron signed the pension reforms into law.
External trade
In 2018, France was the 5th largest trading nation in the world, as well as the second-largest trading nation in Europe (after Germany).World Trade Statistical Review 2019, World Trade Organization, p. 11 Its foreign trade balance for goods had been in surplus from 1992 until 2001, reaching $25.4 1000000000 (number), billion (25.4 G$) in 1998; however, the French balance of trade was hit by the economic downturn, and went into the red in 2000, reaching a US$15bn deficit in 2003. Total trade for 1998 amounted to $730 billion, or 50% of GDP—imports plus exports of goods and services. Trade with European Union countries accounts for 60% of French trade. In 1998, US–France trade stood at about $47 billion – goods only. According to French trade data, US exports accounted for 8.7% – about $25 billion – of France's total imports. US industrial chemicals, aircraft and engines, electronic components, telecommunications, computer software, computers and peripherals, analytical and scientific instrumentation, medical instruments and supplies, broadcasting equipment, and programming and franchising are particularly attractive to French importers. The principal French exports to the US are aircraft and engines, beverages, electrical equipment, chemicals, cosmetics, luxury products and perfume. France is the ninth-largest trading partner of the US. In August 2023, the French current account deficit shrank by €29.7 billion in the past six months, from −€39.3 billion to −€9.6 billion, primarily due to a fall in energy prices.
Regional economy
The economic disparity between French regions is not as high as that in other European countries such as the UK or Italy and higher than in countries like Sweden or Denmark, or even Spain. However, Europe's wealthiest and second largest regional economy, Ile-de-France (the region surrounding Paris), has long profited from the capital city's economic hegemony. The most important ''régions'' are Île-de-France (Europe's 4th regional economy), Rhône-Alpes (Europe's 5th largest regional economy thanks to its services, high-technologies, chemical industries, wines, tourism), Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur (services, industry, tourism and wines), Nord-Pas-de-Calais (European transport hub, services, industries) and Pays de la Loire (green technologies, tourism). Regions like Alsace, which has a rich past in industry (machine tool) and currently stands as a high income service-specialised region, are very wealthy without ranking very high in absolute terms. The rural areas are mainly in Auvergne (region), Auvergne, Limousin, and Centre-Val de Loire, and wine production accounts for a significant proportion of the economy in Aquitaine (Bordeaux wine, Bordeaux (or claret)), Burgundy wine, Burgundy, and champagne (wine region), champagne produced in Champagne-Ardennes.Departments economy and cities
Departmental income inequalities
In terms of income, important inequalities can be observed among the French départements. According to the 2008 statistics of the INSEE, the Yvelines is the highest income department of the country with an average income of €4,750 per month. Hauts-de-Seine comes second, Essonne third, Paris fourth, Seine-et Marne fifth. Île-de-France (region), Île-de-France is the wealthiest region in the country with an average income of €4,228 per month (and is also the wealthiest region in Europe) compared to €3,081 at the national level. Alsace comes second, Rhône-Alpes third, Picardy (region), Picardy fourth, and Upper Normandy fifth. The poorest parts of France are the Overseas department, French overseas departments, French Guiana being the poorest department with an average household income of €1,826. In Metropolitan France it is Creuse in the Limousin (region), Limousin region which comes bottom of the list with an average household income of €1,849 per month.Urban income inequalities
Huge inequalities can also be found among cities. In theParis metropolitan area
The Paris metropolitan area () is a statistical area that describes the reach of commuter movement to and from Paris, France and its surrounding suburbs.
Overview
In 2020, France's national INSEE statistical bureau introduced the concept "ai ...
, significant differences exist between the higher standard of living of ''Paris Ouest'' and lower standard of living in areas in the northern Banlieue, ''banlieues'' of Paris such as Seine-Saint-Denis.
For cities of over 50,000 inhabitants, Neuilly-sur-Seine, a western suburb of Paris, is the wealthiest city in France with an average household income of €5,939, and 35% earning more than €8,000 per month.
But within Paris, four Arrondissements of Paris, arrondissements surpass wealthy Neuilly-sur-Seine in household income: the 6th arrondissement of Paris, 6th, the 7th arrondissement of Paris, 7th, the 8th arrondissement of Paris, 8th and the 16th arrondissement of Paris, 16th; the 8th arrondissement being the wealthiest district in France (the other three following it closely as 2nd, 3rd and 4th wealthiest ones).
Poverty
OECD
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; , OCDE) is an international organization, intergovernmental organization with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate economic progress and international trade, wor ...
data from 2021 estimate that 8.4% of the French population lived in poverty, compared with 18% in the United States, 11.6% in Canada, and 9.8% in Germany. In 2016, the poverty rate in France stood at 14%, compared to 12.8% in 2004. The northern districts of Marseille
Marseille (; ; see #Name, below) is a city in southern France, the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Departments of France, department of Bouches-du-Rhône and of the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur Regions of France, region. Situated in the ...
represent one of the poorest and unequal areas in France, where poor neighbourhoods rub shoulders with wealthier pockets. The share of people living below the poverty line (949 euro per month) was 28.8% in 2008 in sensitive urban zones (ZUS) compared to 12% in the rest of the territory.
In comparison with the average French workers, foreign workers tended to be employed in the hardest and lowest-paid jobs. They also live in poor conditions. A 1972 study found that foreign workers earned 17% less than their French counterparts, although this national average concealed the extent of inequality. Foreign workers were more likely to be men in their prime working years in the industrial areas, which generally had higher rates of pay than elsewhere.
Wealth
Overview
In 2010, the French had an estimated wealth of US$14.0 trillion for a population of 63 million. *In terms of aggregate wealth, the French are the wealthiest Europeans, accounting for more than a quarter of wealthiest European households. Globally, the French nation ranks fourth-wealthiest. *In 2010, wealth per French adult was a little higher than $290,000, down from a pre-crisis high of $300,000 in 2007. According to this ratio, the French are the wealthiest in Europe. The wealth tax is paid by 1.1 million people in France. Liability to this tax starts from €1.3 million of assets. (There is a discount on the principal residence value.) *Almost every French household has at least $1,000 in assets. Proportionally, there are twice as many French with assets of over $10,000 and four times as many French with assets of over $100,000 than the world average.Millionaires
France has the third-highest number of millionaires in Europe as of 2017. There were 1.617 million millionaire households (measured in US dollars) living in France in 2017, behind the UK (2.225 million) and Germany (1.637 million). The wealthiest man in France is the
The wealthiest man in France is the LVMH
LVMH Moët Hennessy Louis Vuitton SE (), commonly known as LVMH, is a French multinational holding company and conglomerate that specializes in luxury goods and has its headquarters in Paris, France. The company was formed in 1987 through the ...
CEO and owner Bernard Arnault.
By 2022, the combined wealth of France's 500 richest people will be worth 1,170 billion euros, or 45% of GDP. In 2009, this figure was just 194 billion, representing 10% of GDP at the time.
See also
*Economic impacts of climate change in France *Economy of Economy of French Guiana, French Guiana, Economy of French Polynesia, French Polynesia, Economy of Guadeloupe, Guadeloupe, Economy of Martinique, Martinique, Economy of Mayotte, Mayotte, Economy of New Caledonia, New Caledonia, Economy of Réunion, Réunion, Economy of Saint Barthélemy, Saint Barthélemy, Economy of Saint Martin (France), Saint Martin, Economy of Saint Pierre and Miquelon, Saint Pierre and Miquelon or Economy of Wallis and Futuna, Wallis and Futuna *Economy of Paris *Economy of Europe *Economy of the European UnionReferences
External links
National Institute of Statistics and Economic Studies – Insee
at the CIA World Factbook
France profile
at The World Bank
France Business Facts
{{Authority control Economy of France, European Union member economies, France World Trade Organization member economies, France OECD member economies, France Economies of Europe by country, France