Ultraviolet index on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The ultraviolet index, or UV index, is an international standard measurement of the strength of the
The ultraviolet index, or UV index, is an international standard measurement of the strength of the
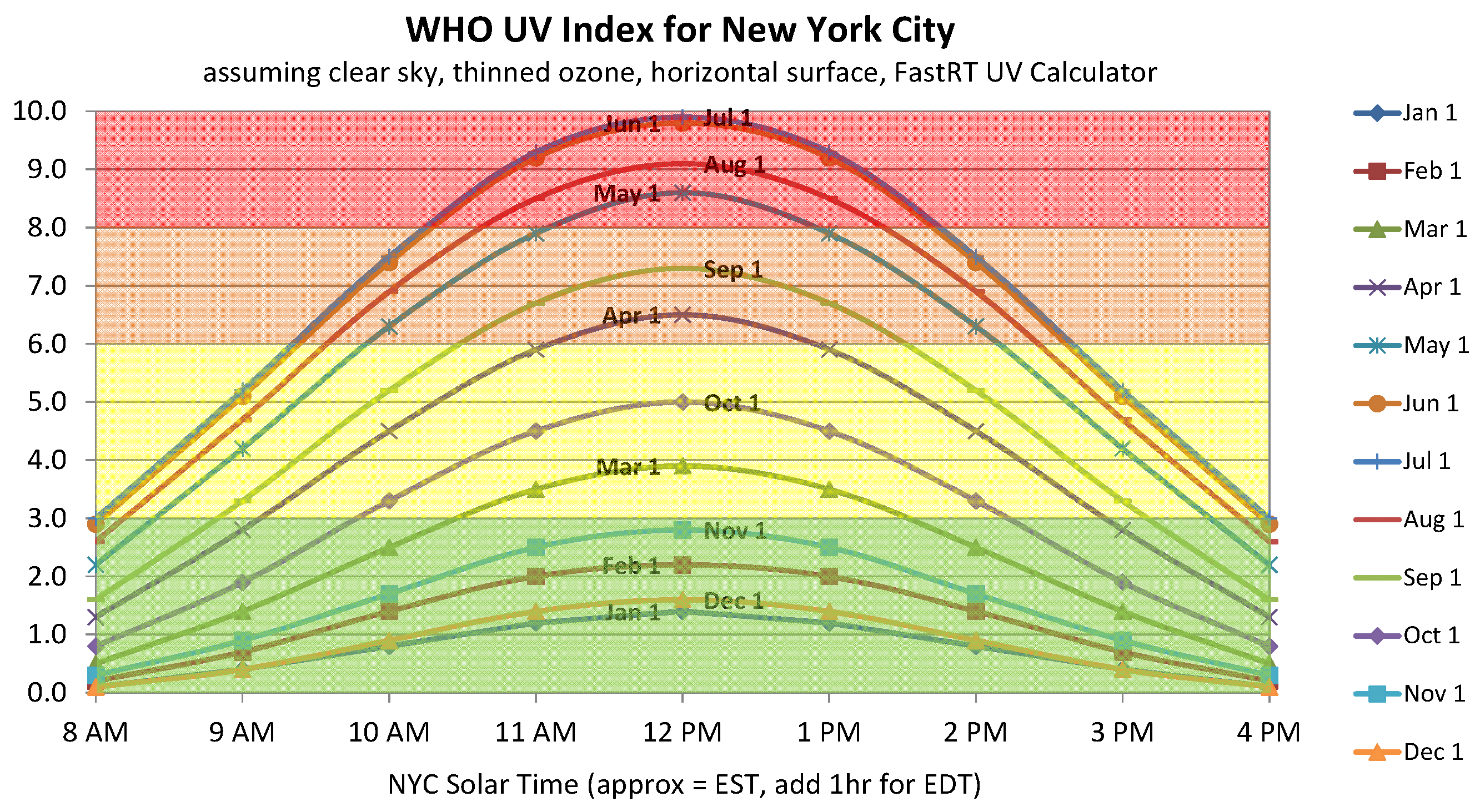 The UV index is a linear scale that measures the intensity of UV radiation with respect to sunburn. For example, assuming similar
The UV index is a linear scale that measures the intensity of UV radiation with respect to sunburn. For example, assuming similar
 The UV index is a number linearly related to the intensity of sunburn-producing UV radiation at a given point on the Earth's surface. It cannot be simply related to the
The UV index is a number linearly related to the intensity of sunburn-producing UV radiation at a given point on the Earth's surface. It cannot be simply related to the
Real-time Global Ultraviolet Index
- A graphical view of the current UV index for the globe.
Radiation: The ultraviolet (UV) index
- World Health Organization
Europe UV Index Forecast
- European Climate and Health Observatory
Australian UV Index Forecast
- Australian Bureau of Meteorology
United States UV index forecast
- National Weather Service: Climate Prediction Center
UV Index Forecasts
- UV Index Today: Hourly USA UV Index Forecasts Sun tanning Atmospheric radiation Ozone depletion Meteorological indices Hazard scales
 The ultraviolet index, or UV index, is an international standard measurement of the strength of the
The ultraviolet index, or UV index, is an international standard measurement of the strength of the sunburn
Sunburn is a form of radiation burn that affects living tissue, such as skin, that results from an overexposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, usually from the Sun. Common symptoms in humans and other animals include red or reddish skin tha ...
-producing ultraviolet
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of ...
(UV) radiation
In physics, radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or a material medium. This includes:
* ''electromagnetic radiation'' consisting of photons, such as radio waves, microwaves, infr ...
at a particular place and time. It is primarily used in daily and hourly forecasts aimed at the general public. The UV index is designed as an open-ended linear scale
A linear scale, also called a bar scale, scale bar, graphic scale, or graphical scale, is a means of visually showing the scale of a map, nautical chart, engineering drawing, or architectural drawing. A scale bar is common element of map layo ...
, directly proportional to the intensity of UV radiation, and adjusting for wavelength based on what causes human skin
The human skin is the outer covering of the body and is the largest organ of the integumentary system. The skin has up to seven layers of ectodermal tissue (biology), tissue guarding Skeletal muscle, muscles, bones, ligaments and organ (anato ...
to sunburn. The purpose of the UV index is to help people effectively protect themselves from UV radiation, which has health benefits in moderation but in excess causes sunburn, skin aging, DNA damage, skin cancer
Skin cancers are cancers that arise from the Human skin, skin. They are due to the development of abnormal cells (biology), cells that have the ability to invade or metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. It occurs when skin cells grow ...
, immunosuppression
Immunosuppression is a reduction of the activation or efficacy of the immune system. Some portions of the immune system itself have immunosuppressive effects on other parts of the immune system, and immunosuppression may occur as an adverse react ...
, and eye
An eye is a sensory organ that allows an organism to perceive visual information. It detects light and converts it into electro-chemical impulses in neurons (neurones). It is part of an organism's visual system.
In higher organisms, the ey ...
damage, such as cataract
A cataract is a cloudy area in the lens (anatomy), lens of the eye that leads to a visual impairment, decrease in vision of the eye. Cataracts often develop slowly and can affect one or both eyes. Symptoms may include faded colours, blurry or ...
s.
The scale was developed by Canadian scientists in 1992, and then adopted and standardized by the UN's World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Gen ...
and World Meteorological Organization
The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for promoting international cooperation on atmospheric science, climatology, hydrology an ...
in 1994. Public health organizations recommend that people protect themselves (for example, by applying sunscreen to the skin and wearing a hat and sunglasses
Sunglasses or sun glasses (informally called shades or sunnies; more names Sunglasses#Other names, below) are a form of Eye protection, protective eyewear designed primarily to prevent bright sunlight and high-energy visible light from damagin ...
) if they spend substantial time outdoors when the UV index is 3 or higher; see the table below for more detailed recommendations.
Description
 The UV index is a linear scale that measures the intensity of UV radiation with respect to sunburn. For example, assuming similar
The UV index is a linear scale that measures the intensity of UV radiation with respect to sunburn. For example, assuming similar spectral power distribution
In radiometry, photometry (optics), photometry, and color science, a spectral power distribution (SPD) measurement describes the Power (physics), power per unit area per unit wavelength of an illumination (lighting), illumination (radiant exitan ...
s, radiation with a UV index of 12 is twice as intense as radiation at a UV index of 6. For a wide range of timescales, sunburn in response to controlled UV radiation occurs in proportion to the total number of photons delivered, not varying with the intensity or duration of exposure. Therefore, under similar conditions, a person who develops a sunburn after 30 minutes of exposure to UV index 6 radiation would most likely develop a sunburn after 15 minutes of exposure to UV index 12 radiation, since it is twice the intensity but half the duration. This linear scale is unlike other common environmental scales such as decibel
The decibel (symbol: dB) is a relative unit of measurement equal to one tenth of a bel (B). It expresses the ratio of two values of a Power, root-power, and field quantities, power or root-power quantity on a logarithmic scale. Two signals whos ...
s or the Richter scale
The Richter scale (), also called the Richter magnitude scale, Richter's magnitude scale, and the Gutenberg–Richter scale, is a measure of the strength of earthquakes, developed by Charles Richter in collaboration with Beno Gutenberg, and pr ...
, which are logarithmic (the severity multiplies for each step on the scale, growing exponentially).
An index of 0 corresponds to zero UV radiation, as is essentially the case at night. An index of 10 corresponds roughly to midday summer sunlight in the tropics with a clear sky when the UV index was originally designed; now summertime index values in the tens are common for tropical latitudes, mountainous altitudes, areas with ice/water reflectivity and areas with above-average ozone layer depletion.
While the UV index can be calculated from a direct measurement of the UV spectral power at a given location, as some inexpensive portable devices are able to approximate, the value given in weather reports is usually a prediction based on a computer model. Although this may be in error (especially when cloud conditions are unexpectedly heavy or light), it is usually within ±1 UV index unit as that which would be measured.
When the UV index is presented on a daily basis, it represents UV intensity around the sun's highest point in the day, called solar noon
Noon (also known as noontime or midday) is 12 o'clock in the daytime. It is written as 12 noon, 12:00 m. (for '' meridiem'', literally 12:00 midday), 12 p.m. (for ''post meridiem'', literally "after midday"), 12 pm, or 12:00 (using a 24-hour clo ...
, halfway between sunrise
Sunrise (or sunup) is the moment when the upper rim of the Sun appears on the horizon in the morning, at the start of the Sun path. The term can also refer to the entire process of the solar disk crossing the horizon.
Terminology
Although the S ...
and sunset
Sunset (or sundown) is the disappearance of the Sun at the end of the Sun path, below the horizon of the Earth (or any other astronomical object in the Solar System) due to its Earth's rotation, rotation. As viewed from everywhere on Earth, it ...
. This typically occurs between 11:30 and 12:30, or between 12:30 and 13:30 in areas where daylight saving time
Daylight saving time (DST), also referred to as daylight savings time, daylight time (Daylight saving time in the United States, United States and Daylight saving time in Canada, Canada), or summer time (British Summer Time, United Kingdom, ...
is being observed. Predictions are made by a computer model that accounts for the effects of sun-earth distance, solar zenith angle
The solar zenith angle is the zenith angle of the sun, i.e., the angle between the sun’s rays and the vertical direction. It is the complement to the solar altitude or solar elevation, which is the altitude angle or elevation angle between the ...
, total ozone amount, tropospheric aerosol optical depth, elevation, snow/ice reflectivity and cloud transmission, all of which influence the amount of UV radiation at the surface.
Technical definition
irradiance
In radiometry, irradiance is the radiant flux ''received'' by a ''surface'' per unit area. The SI unit of irradiance is the watt per square metre (symbol W⋅m−2 or W/m2). The CGS unit erg per square centimetre per second (erg⋅cm−2⋅s−1) ...
(measured in W/ m2) because the UV of greatest concern occupies a spectrum of wavelengths from 295 to 325 nm, and shorter wavelengths have already been absorbed a great deal when they arrive at the Earth's surface. However, skin damage from sunburn is related to wavelength, the shorter wavelengths being much more damaging. The UV power spectrum (expressed as watts per square meter per nanometer of wavelength) is therefore multiplied by a weighting curve
A weighting curve is a graph of a set of factors, that are used to 'weight' measured values of a variable according to their importance in relation to some outcome. An important example is frequency weighting in sound level measurement where a spec ...
known as the CIE-standard McKinlay–Diffey erythemal action spectrum. There are some older formulas for the spectrum, resulting in differences of up to 2%. The result is integrated over the whole spectrum. This gives a weighted figure called the Diffey-weighted UV irradiance (DUV) or the erythemal dose rate. Since the normalization weight is 1 for wavelengths between 250nm and 298nm, a source of a given DUV irradiance causes roughly as much sunburn as a radiation source emitting those wavelengths at the same intensity, although inaccuracies in the spectrum definition and varying reactions by skin type may mean this relationship does not actually hold. When the index was designed, the typical midday summer sunlight was around 250 mW/m2. Thus, for convenience, the DUV is divided by 25 mW/m2 to produce an index (This source contains some numerical errors.) nominally from 0 to 11+, though ozone depletion is now resulting in higher values.
To illustrate the spectrum weighting principle, the incident power density in midday summer sunlight is typically 0.6 mW/(nm m2) at 295 nm, 74 mW/(nm m2) at 305 nm, and 478 mW/(nm m2) at 325 nm. (Note the huge absorption that has already taken place in the atmosphere at short wavelengths.)
The erythemal weighting factors applied to these figures are 1.0, 0.22, and 0.003 respectively. (Also note the huge increase in sunburn damage caused by the shorter wavelengths; e.g., for the same irradiance, 305 nm is 22% as damaging as 295 nm, and 325 nm is 0.3% as damaging as 295 nm.) Integration of these values using all the intermediate weightings over the full spectral range of 290 nm to 400 nm produces a figure of 264 mW/m2 (the DUV), which is then divided by 25 mW/m2 to give a UV index of 10.6.
History
After sporadic attempts by various meteorologists to define a "sunburn index" and growing concern aboutozone depletion
Ozone depletion consists of two related events observed since the late 1970s: a lowered total amount of ozone in Earth, Earth's upper atmosphere, and a much larger springtime decrease in stratospheric ozone (the ozone layer) around Earth's polar ...
, Environment Canada
Environment and Climate Change Canada (ECCC; )Environment and Climate Change Canada is the applied title under the Federal Identity Program; the legal title is Department of the Environment (). is the Ministry (government department), department ...
scientists James B. Kerr, C. Thomas McElroy, and David I. Wardle invented the modern UV index in Toronto, Ontario. Environment Canada launched it as part of the weather forecast on May 27, 1992, making Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
the first country in the world to issue official predictions of UV levels for the next day. Many other countries followed suit with their own UV indices. Initially, the methods of calculating and reporting a UV index varied significantly from country to country. A global UV index, first standardized by the World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Gen ...
and World Meteorological Organization
The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for promoting international cooperation on atmospheric science, climatology, hydrology an ...
in 1994, gradually replaced the inconsistent regional versions, specifying not only a uniform calculation method (the Canadian definition) but also standard colors and graphics for visual media.
On December 29, 2003, a world-record ground-level UV index of 43.3 was detected at Bolivia
Bolivia, officially the Plurinational State of Bolivia, is a landlocked country located in central South America. The country features diverse geography, including vast Amazonian plains, tropical lowlands, mountains, the Gran Chaco Province, w ...
's Licancabur
Licancabur () is a prominent, stratovolcano on the Bolivia–Chile border in the Central Volcanic Zone of the Andes. It is capped by a wide summit crater which contains Licancabur Lake, a Volcanic crater lake, crater lake that is among the hig ...
volcano, though other scientists dispute readings higher than 26.
In 2005, Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
and the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
launched the UV Alert. While the two countries have different baseline UV intensity requirements before issuing an alert, their common goal is to raise awareness of the dangers of over-exposure to the Sun on days with intense UV radiation.
In 2007, the United Nations honored UV index inventors Kerr, McElroy, and Wardle with the Innovators Award for their far-reaching work on reducing public health risks from UV radiation. In the same year, a survey among meteorologists ranked the development of the UV index as #11 on The Weather Channel
The Weather Channel (TWC) is an American pay television television channel, channel owned by Weather Group, LLC, a subsidiary of Allen Media Group. The channel's headquarters are located in Atlanta, Georgia. Launched on May 2, 1982, the channel ...
's '' 100 Biggest Weather Moments''.
Index usage
The recommendations below are for average adults with lightly tanned skin ( Fitzpatrick scale of skin colour: Type II). Those with darker skin (Type IV+) are more likely to withstand greater sun exposure, while extra precautions are needed for children, seniors, particularly fair-skinned adults, and those who have greater sun sensitivity for medical reasons or from UV exposure in previous days. When the day's predicted UV index is within various numerical ranges, the recommendations for protection are as follows: Some sunshine prediction and advice apps have been released. These use the UV index and Fitzpatrick scale skin type to calculate the maximum exposure time before receiving a sunburn. The Fitzpatrick scale is not sufficient to precisely estimate the minimum radiation dose needed for sunburn. Research has found broad variation within and between populations, e.g. for skin type V subjects the MED in the US is 60–100 mJ/cm2 vs. 120–240 mJ/cm2 in Taiwan. Neglecting weighting, 9 mJ/cm2 is 1 UV index hour.See also
* Fitzpatrick scale * Health effects of sunlight exposure *Sun protective clothing
Sun protective clothing is clothing specifically designed for sun protection and is produced from a fabric rated for its level of ultraviolet (UV) protection. A novel weave structure and denier (related to thread count per inch) may produce sun p ...
* Sunscreen
Sunscreen, also known as sunblock, sun lotion or sun cream, is a photoprotection, photoprotective topical product for the Human skin, skin that helps protect against sunburn and prevent skin cancer. Sunscreens come as lotions, sprays, gels, fo ...
References
External links
{{CommonsReal-time Global Ultraviolet Index
- A graphical view of the current UV index for the globe.
Radiation: The ultraviolet (UV) index
- World Health Organization
Europe UV Index Forecast
- European Climate and Health Observatory
Australian UV Index Forecast
- Australian Bureau of Meteorology
United States UV index forecast
- National Weather Service: Climate Prediction Center
UV Index Forecasts
- UV Index Today: Hourly USA UV Index Forecasts Sun tanning Atmospheric radiation Ozone depletion Meteorological indices Hazard scales