USS Milwaukee (CL-5) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
USS ''Milwaukee'' (CL-5) was an
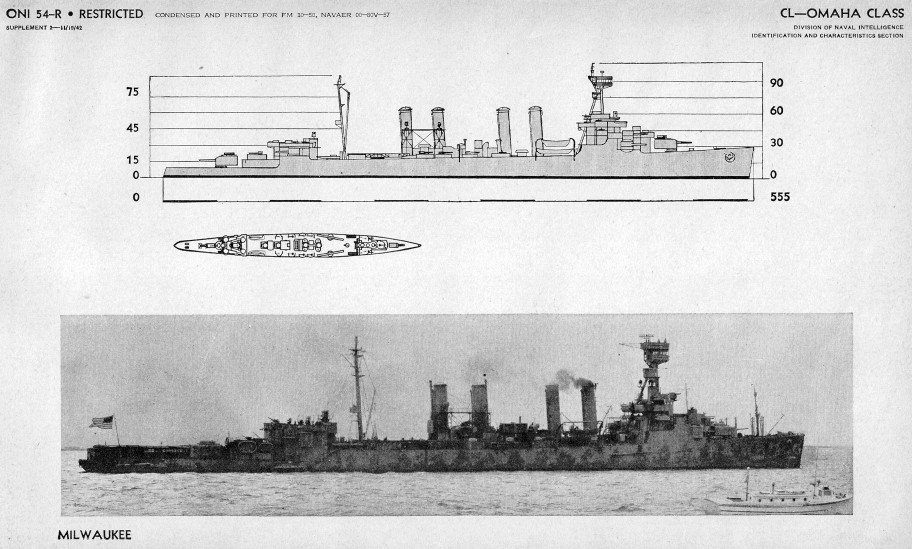 ''Milwaukee'' was long at the waterline and long
''Milwaukee'' was long at the waterline and long
Navy photos of ''Milwaukee''
{{DEFAULTSORT:Milwaukee (CL-5) Omaha-class cruisers Ships built in Tacoma, Washington 1922 ships World War II cruisers of the United States Ships transferred from the United States Navy to the Soviet Navy Cruisers of the Soviet Navy World War II cruisers of the Soviet Union
light cruiser
A light cruiser is a type of small or medium-sized warship. The term is a shortening of the phrase "light armored cruiser", describing a small ship that carried armor in the same way as an armored cruiser: a protective belt and deck. Prior to thi ...
built for the United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the naval warfare, maritime military branch, service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is the world's most powerful navy with the largest Displacement (ship), displacement, at 4.5 millio ...
during the 1920s. The ship spent most of her early career assigned to the Asiatic and Battle Fleet
The United States Battle Fleet or Battle Force was part of the organization of the United States Navy from 1922 to 1941.
The General Order of 6 December 1922 organized the United States Fleet, with the Battle Fleet as the Pacific presence. Thi ...
s. In 1941, she was assigned to the Neutrality Patrol
On September 3, 1939, the British and French declarations of war on Germany initiated the Battle of the Atlantic. The United States Navy Chief of Naval Operations (CNO) established a combined air and ship patrol of the United States Atlantic co ...
until she was refitted in New York in late 1941. She escorted a troop convoy to the Pacific in early 1942 before returning to the South Atlantic where she patrolled for German commerce raider
Commerce raiding is a form of naval warfare used to destroy or disrupt logistics of the enemy on the open sea by attacking its merchant shipping, rather than engaging its combatants or enforcing a blockade against them. Privateering is a fo ...
s and blockade runner
A blockade runner is a merchant vessel used for evading a naval blockade of a port or strait. It is usually light and fast, using stealth and speed rather than confronting the blockaders in order to break the blockade. Blockade runners usua ...
s. In November, she intercepted one of the latter, but it scuttled
Scuttling is the act of deliberately sinking a ship by allowing water to flow into the hull, typically by its crew opening holes in its hull.
Scuttling may be performed to dispose of an abandoned, old, or captured vessel; to prevent the vesse ...
itself before it could be captured. In 1944, she was temporarily transferred to the Soviet Navy
The Soviet Navy was the naval warfare Military, uniform service branch of the Soviet Armed Forces. Often referred to as the Red Fleet, the Soviet Navy made up a large part of the Soviet Union's strategic planning in the event of a conflict with t ...
and commissioned as ''Murmansk''. The ship was returned by the Soviets in 1949 and sold for scrap
Scrap consists of recyclable materials, usually metals, left over from product manufacturing and consumption, such as parts of vehicles, building supplies, and surplus materials. Unlike waste, scrap can have monetary value, especially recover ...
in December.
Description
 ''Milwaukee'' was long at the waterline and long
''Milwaukee'' was long at the waterline and long overall
Overalls or bib-and-brace overalls, also called dungarees in British English, are a type of garment usually used as protective clothing when working. The garments are commonly referred to as a "pair of overalls" by analogy with "pair of trousers ...
, with a beam of and a mean draft
Draft, the draft, or draught may refer to:
Watercraft dimensions
* Draft (hull), the distance from waterline to keel of a vessel
* Draft (sail), degree of curvature in a sail
* Air draft, distance from waterline to the highest point on a v ...
of . Her standard displacement
The displacement or displacement tonnage of a ship is its weight. As the term indicates, it is measured indirectly, using Archimedes' principle, by first calculating the volume of water displaced by the ship, then converting that value into wei ...
was and at full load
The displacement or displacement tonnage of a ship is its weight. As the term indicates, it is measured indirectly, using Archimedes' principle, by first calculating the volume of water displaced by the ship, then converting that value into weig ...
.Whitley, p. 228 Her crew consisted of 29 officers and 429 enlisted men.Friedman, p. 469 The ship was fitted with a powerful echo sounder.
The ship was powered by four Westinghouse geared steam turbine
A steam turbine or steam turbine engine is a machine or heat engine that extracts thermal energy from pressurized steam and uses it to do mechanical work utilising a rotating output shaft. Its modern manifestation was invented by Sir Charles Par ...
s, each driving one propeller shaft, using steam generated by 12 Yarrow boiler
Yarrow boilers are an important class of high-pressure water-tube boilers. They were developed by
Yarrow Shipbuilders, Yarrow & Co. (London), Shipbuilders and Engineers and were widely used on ships, particularly warships.
The Yarrow boiler desi ...
s. The engines were rated at and designed to reach a top speed of . At deep load she carried of fuel oil
Fuel oil is any of various fractions obtained from the distillation of petroleum (crude oil). Such oils include distillates (the lighter fractions) and residues (the heavier fractions). Fuel oils include heavy fuel oil (bunker fuel), marine f ...
that provided her a range of at a speed of .Friedman, pp. 78, 469
''Milwaukee'' mounted a dozen 53-caliber
In guns, particularly firearms, but not #As a measurement of length, artillery, where a different definition may apply, caliber (or calibre; sometimes abbreviated as "cal") is the specified nominal internal diameter of the gun barrel Gauge ( ...
guns; four in two twin gun turret
A gun turret (or simply turret) is a mounting platform from which weapons can be fired that affords protection, visibility and ability to turn and aim. A modern gun turret is generally a rotatable weapon mount that houses the crew or mechanis ...
s and eight in tiered casemate
A casemate is a fortified gun emplacement or armoured structure from which guns are fired, in a fortification, warship, or armoured fighting vehicle.Webster's New Collegiate Dictionary
When referring to antiquity, the term "casemate wall" ...
s fore and aft. Her secondary armament initially consisted of two 50-caliber anti-aircraft
Anti-aircraft warfare (AAW) is the counter to aerial warfare and includes "all measures designed to nullify or reduce the effectiveness of hostile air action".AAP-6 It encompasses surface-based, subsurface ( submarine-launched), and air-ba ...
(AA) guns in single mounts, but this was doubled to four guns during construction. ''Milwaukee'' was initially built with the capacity to carry 224 mines, but these were removed early in her career to make more space for crew accommodations. The ship carried above-water two triple and two twin torpedo tube
A torpedo tube is a cylindrical device for launching torpedoes.
There are two main types of torpedo tube: underwater tubes fitted to submarines and some surface ships, and deck-mounted units (also referred to as torpedo launchers) installed aboa ...
mounts for torpedo
A modern torpedo is an underwater ranged weapon launched above or below the water surface, self-propelled towards a target, with an explosive warhead designed to detonate either on contact with or in proximity to the target. Historically, such ...
es. The triple mounts were fitted on the upper deck, aft of the aircraft catapult
An aircraft catapult is a device used to help fixed-wing aircraft gain enough airspeed and lift for takeoff from a limited distance, typically from the deck of a ship. They are usually used on aircraft carrier flight decks as a form of assist ...
s, and the twin mounts were one deck lower, covered by hatches in the side of the hull. These lower mounts proved to be very wet and were removed, and the openings plated over, before the start of World War II. Another change made before the war was to increase the guns to four, all mounted in the ship's waist.
The ship lacked a full-length waterline
The waterline is the line where the hull of a ship meets the surface of the water.
A waterline can also refer to any line on a ship's hull that is parallel to the water's surface when the ship is afloat in a level trimmed position. Hence, wate ...
armor belt
Belt armor is a layer of heavy metal armor plated onto or within the outer hulls of warships, typically on battleships, battlecruisers and cruisers, and aircraft carriers.
The belt armor is designed to prevent projectiles from penetrating to ...
. The sides of her boiler and engine rooms and steering gear were protected by of armor. The transverse bulkheads at the end of her machinery rooms were thick forward and three inches thick aft. The deck over the machinery spaces and steering gear had a thickness of 1.5 inches. The gun turrets were only protected against muzzle blast
A muzzle blast is an explosive shockwave created at the muzzle of a firearm during shooting. Before a projectile leaves the gun barrel, it obturates the bore and "plugs up" the pressurized gaseous products of the propellant combustion behind ...
and the conning tower had 1.5 inches of armor. ''Milwaukee'' carried two floatplane
A floatplane is a type of seaplane with one or more slender floats mounted under the fuselage to provide buoyancy. By contrast, a flying boat uses its fuselage for buoyancy. Either type of seaplane may also have landing gear suitable for land, ...
s aboard that were stored on the two catapults. Initially these were probably Vought VE-9s, but the ship operated Curtiss SOC Seagull
The Curtiss SOC Seagull was an American single-engined scout observation seaplane, designed by Alexander Solla of the Curtiss-Wright Corporation for the United States Navy. The aircraft served on battleships and cruisers in a seaplane configurat ...
s from 1935 and Vought OS2U Kingfisher
The Vought OS2U Kingfisher is an American catapult-launched observation floatplane. It was a compact mid-wing monoplane, with a large central float and small stabilizing floats. Performance was modest because of its low-powered engine. The OS2U ...
s after 1940.Whitley, p. 229
Wartime changes
After 1940 the lower aft six-inch guns were removed and the casemates plated over. The ship's anti-aircraft armament was augmented by two quadruple 1.1-inch gun mounts by early 1942, although these were replaced by twin Bofors 40 mm gun mounts later in the war. At about the same time, ''Milwaukee'' received eightOerlikon 20 mm cannon
The Oerlikon 20 mm cannon is a series of autocannons based on an original German Becker Type M2 20 mm cannon design that appeared very early in World War I. It was widely produced by Oerlikon Contraves and others, with various models empl ...
.
Service history
Inter-war period
The contract for ''Milwaukee'', the third ship named for the city ofMilwaukee, Wisconsin
Milwaukee is the List of cities in Wisconsin, most populous city in the U.S. state of Wisconsin. Located on the western shore of Lake Michigan, it is the List of United States cities by population, 31st-most populous city in the United States ...
, was signed on 27 August 1917, and the ship was laid down
Laying the keel or laying down is the formal recognition of the start of a ship's construction. It is often marked with a ceremony attended by dignitaries from the shipbuilding company and the ultimate owners of the ship.
Keel laying is one ...
by Todd Dry Dock and Construction Company, at their Tacoma
Tacoma ( ) is the county seat of Pierce County, Washington, United States. A port city, it is situated along Washington's Puget Sound, southwest of Seattle, southwest of Bellevue, northeast of the state capital, Olympia, northwest of Mount ...
, Washington
Washington most commonly refers to:
* George Washington (1732–1799), the first president of the United States
* Washington (state), a state in the Pacific Northwest of the United States
* Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States
** A ...
shipyard on 13 December 1918. She was launched on 24 March 1921 and was commissioned on 20 June 1923. During the ship's shakedown cruise
Shakedown cruise is a nautical term in which the performance of a ship is tested. Generally, shakedown cruises are performed before a ship enters service or after major changes such as a crew change, repair, refit or overhaul. The shakedown ...
, she visited Sydney
Sydney is the capital city of the States and territories of Australia, state of New South Wales and the List of cities in Australia by population, most populous city in Australia. Located on Australia's east coast, the metropolis surrounds Syd ...
, Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
, during the Pan-Pacific Scientific Congress which opened on 23 August. With her new depth–finding equipment, ''Milwaukee'' surveyed the floor of the Pacific en route. "The Milwaukee Seamount
A seamount is a large submarine landform that rises from the ocean floor without reaching the water surface (sea level), and thus is not an island, islet, or cliff-rock. Seamounts are typically formed from extinct volcanoes that rise abruptly a ...
s in the Northern Pacific are named after a set of soundings taken by ''Milwaukee'' in 1929."
During Fleet Problem VI, she collided with her sister ship
A sister ship is a ship of the same Ship class, class or of virtually identical design to another ship. Such vessels share a nearly identical hull and superstructure layout, similar size, and roughly comparable features and equipment. They o ...
in Guantanamo Bay, Cuba, on 1 February 1926, although neither ship was seriously damaged. ''Milwaukee'' and the destroyer
In naval terminology, a destroyer is a fast, maneuverable, long-endurance warship intended to escort
larger vessels in a fleet, convoy, or carrier battle group and defend them against a wide range of general threats. They were conceived i ...
assisted victims of a fierce hurricane which had devastated the Isle of Pines in October. She was assigned to Cruiser Division 2 of the Asiatic Fleet in 1928. During an engagement with "enemy" cruisers during Fleet Problem IX on 16 April 1930, the ship was ruled to have been knocked out by the exercise's umpires. Three years later, during Fleet Problem XIV, ''Milwaukee'' was spotted by fighters from the aircraft carrier and "sunk" by some of the opposing cruisers. In 1933, the ship was assigned to Cruiser Division 3 of the Battle Fleet. After the Panay Incident
The USS ''Panay'' incident was a Japanese bombing attack on the U.S. Navy river gunboat and three Standard Oil Company tankers on the Yangtze River near the Chinese capital of Nanjing on 12 December 1937. Japan and the United States were not at ...
in December 1937, ''Milwaukee'' made a cruise through the Western Pacific from January to April 1938.
While steaming north of Hispaniola
Hispaniola (, also ) is an island between Geography of Cuba, Cuba and Geography of Puerto Rico, Puerto Rico in the Greater Antilles of the Caribbean. Hispaniola is the most populous island in the West Indies, and the second-largest by List of C ...
and Puerto Rico
; abbreviated PR), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, is a Government of Puerto Rico, self-governing Caribbean Geography of Puerto Rico, archipelago and island organized as an Territories of the United States, unincorporated territo ...
on 14 February 1939, ''Milwaukee'' discovered the deepest place in the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the ...
. The spot—which has a depth of —is now known as the "Milwaukee Deep
Milwaukee Deep, also known as the Milwaukee Depth, is the deepest part of the Puerto Rico Trench, constituting the deepest points in the Atlantic Ocean. Together with the surrounding seabed area, known as Brownson Deep, the Milwaukee Deep forms ...
". By January 1941, the ship had returned to Cruiser Division 2 which was now assigned to the Caribbean Patrol, commanded by Rear Admiral
Rear admiral is a flag officer rank used by English-speaking navies. In most European navies, the equivalent rank is called counter admiral.
Rear admiral is usually immediately senior to commodore and immediately below vice admiral. It is ...
Jonas H. Ingram
Jonas Howard Ingram (October 15, 1887 – September 9, 1952) was an officer in the United States Navy during World War I and World War II. He commanded the United States Atlantic Fleet during World War II and was a recipient of the Medal of Hon ...
, part of the Neutrality Patrol established after the war began. Cruiser Division 2 was ordered to patrol the Atlantic between Trinidad
Trinidad is the larger, more populous island of the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago, the country. The island lies off the northeastern coast of Venezuela and sits on the continental shelf of South America. It is the southernmost island in ...
, the Cape Verde Islands
Cape Verde or Cabo Verde, officially the Republic of Cabo Verde, is an island country and archipelagic state of West Africa in the central Atlantic Ocean, consisting of ten volcanic islands with a combined land area of about . These islands ...
and the eastern bulge of Brazil in April, although ''Milwaukee'' was not immediately available. The ship, escorted by the destroyers and , began her first patrol in May, making a port visit to Recife
Recife ( , ) is the Federative units of Brazil, state capital of Pernambuco, Brazil, on the northeastern Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic coast of South America. It is the largest urban area within both the North Region, Brazil, North and the Northeast R ...
, Brazil, on 1 June, before returning to San Juan, Puerto Rico
San Juan ( , ; Spanish for "Saint John the Baptist, John") is the capital city and most populous Municipalities of Puerto Rico, municipality in the Commonwealth (U.S. insular area), Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, an unincorporated territory of the ...
. These patrols continued in the same manner for most of the rest of the year.
World War II
South Atlantic
''Milwaukee'', commanded byCaptain
Captain is a title, an appellative for the commanding officer of a military unit; the supreme leader or highest rank officer of a navy ship, merchant ship, aeroplane, spacecraft, or other vessel; or the commander of a port, fire or police depa ...
Forrest B. Royal, was being overhauled in the Brooklyn Navy Yard
The Brooklyn Navy Yard (originally known as the New York Navy Yard) is a shipyard and industrial complex in northwest Brooklyn in New York City, New York (state), New York, U.S. The Navy Yard is located on the East River in Wallabout Bay, a se ...
when the Japanese attacked Pearl Harbor on 7 December. The ship escorted a convoy to the Caribbean
The Caribbean ( , ; ; ; ) is a region in the middle of the Americas centered around the Caribbean Sea in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, mostly overlapping with the West Indies. Bordered by North America to the north, Central America ...
from New York on 31 December and then escorted eight troop transports from the Panama Canal
The Panama Canal () is an artificial waterway in Panama that connects the Caribbean Sea with the Pacific Ocean. It cuts across the narrowest point of the Isthmus of Panama, and is a Channel (geography), conduit for maritime trade between th ...
to the Society Islands
The Society Islands ( , officially ; ) are an archipelago in the South Pacific Ocean that includes the major islands of Tahiti, Mo'orea, Moorea, Raiatea, Bora Bora and Huahine. Politically, they are part of French Polynesia, an overseas country ...
. She rejoined the South Atlantic Patrol Force upon her return and spend the next two years making patrols between Brazil and the African coast. On 19 May she received an SOS
SOS is a Morse code distress signal (), used internationally, originally established for maritime use. In formal notation SOS is written with an overscore line (), to indicate that the Morse code equivalents for the individual letters of "SOS" a ...
from the Brazilian cargo ship SS ''Commandante Lyra'', which had been torpedoed by the off the coast of Brazil. ''Milwaukee'' found the freighter abandoned, burning, and listing to port. She rescued 25 survivors from their lifeboats
Lifeboat may refer to:
Rescue vessels
* Lifeboat (shipboard), a small craft aboard a ship to allow for emergency escape
* Lifeboat (rescue), a boat designed for sea rescues
* Airborne lifeboat, an air-dropped boat used to save downed airmen
...
, including the ship's master. Reinforced by her sister and the destroyer , the fires were brought under control, cargo was jettisoned to lighten the ship, and ''Commandante Lyra'' was towed to Fortaleza
Fortaleza ( ; ; ) is the state capital of Ceará, located in Northeast Region, Brazil, Northeastern Brazil. It is Brazil's 4th largest city—Fortaleza surpassed Salvador, Bahia, Salvador in 2022 census with a population of slightly over 2.4 mi ...
, Brazil. Shortly after, on the night of 20 May, she was attacked by the ''Barbarigo'', commanded by Enzo Grossi (who mistook her for a " ''Maryland''- or ''California''- type battleship") with two torpedoes, which missed and were not even noticed by the American ships; however, Grossi claimed to have sunk his target, and was promoted to ''Capitano di Fregata'' (Commander) and decorated with the Gold Medal of Military Valour
The Gold Medal of Military Valor () is an Italian medal established on 21 May 1793 by King Victor Amadeus III of Sardinia for deeds of outstanding gallantry in war by junior officers and soldiers.
The face of the medal displayed the profile o ...
and the Iron Cross
The Iron Cross (, , abbreviated EK) was a military decoration in the Kingdom of Prussia, the German Empire (1871–1918), and Nazi Germany (1933–1945). The design, a black cross pattée with a white or silver outline, was derived from the in ...
. Two subsequent commissions in 1949 and 1962 would eventually reverse the promotion and the decorations.
Rear Admiral Oliver M. Read assumed command of Cruiser Division 2 in October and hoisted his flag aboard ''Milwaukee''. On 21 November, ''Milwaukee'', her sister and the destroyer ''Somers'' intercepted the German blockade runner . When ''Somers'' had closed to , the German ship scuttled herself to prevent capture. ''Milwaukee'' rescued 62 of the ship's crew. On 2 May 1943, while the ship was under repair at Recife, her crew helped to fight a fire on the oil tanker
An oil tanker, also known as a petroleum tanker, is a ship designed for the bulk cargo, bulk transport of petroleum, oil or its products. There are two basic types of oil tankers: crude tankers and product tankers. Crude tankers move large quant ...
. ''Milwaukee'' and ''Omaha'' collided on 31 May off the coast of Brazil, although the extent of the damage is not known. The ship sailed for the Brooklyn Navy Yard on 8 February 1944, preparatory to her temporary transfer to the Soviet Union in lieu of Italian ships allotted after the Italian surrender that could not be delivered. She escorted a convoy to Belfast
Belfast (, , , ; from ) is the capital city and principal port of Northern Ireland, standing on the banks of the River Lagan and connected to the open sea through Belfast Lough and the North Channel (Great Britain and Ireland), North Channel ...
, Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland ( ; ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, part of the United Kingdom in the north-east of the island of Ireland. It has been #Descriptions, variously described as a country, province or region. Northern Ireland shares Repub ...
, on 8 March before forming part of the escort of Convoy JW 58
Convoy JW 58 was an Arctic convoy sent from Britain by the Western Allies to aid the Soviet Union during World War II. It sailed in March 1944, reaching the Soviet northern ports in early April. All ships arrived safely. JW 58 was attacked by G ...
during her voyage to Murmansk
Murmansk () is a port city and the administrative center of Murmansk Oblast in the far Far North (Russia), northwest part of Russia. It is the world's largest city north of the Arctic Circle and sits on both slopes and banks of a modest fjord, Ko ...
beginning on 29 March.
Soviet service
On 20 April, the ship was transferred on loan to the SovietNorthern Fleet
The Northern Fleet (, ''Severnyy flot'') is the Naval fleet, fleet of the Russian Navy in the Arctic.
According to the Russian ministry of defence: "The Northern Fleet dates its history back to a squadron created in 1733 to protect the terri ...
in Murmansk
Murmansk () is a port city and the administrative center of Murmansk Oblast in the far Far North (Russia), northwest part of Russia. It is the world's largest city north of the Arctic Circle and sits on both slopes and banks of a modest fjord, Ko ...
. She was commissioned in the Soviet Navy as ''Murmansk'' and performed convoy and patrol duty in the Arctic Ocean
The Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five oceanic divisions. It spans an area of approximately and is the coldest of the world's oceans. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, ...
for the remainder of the war. Afterward, she became a training ship
A training ship is a ship used to train students as sailors. The term is mostly used to describe ships employed by navies to train future officers. Essentially there are two types: those used for training at sea and old hulks used to house class ...
and participated in the 1948 fleet maneuvers. On 16 March 1949, ''Milwaukee'' was transferred back to the United States. She was the first of 15 American warships returned by the Soviet Union. She entered the Philadelphia Naval Shipyard on 18 March 1949, and was sold for scrapping on 10 December to the American Shipbreakers, Inc. of Wilmington, Delaware
Wilmington is the List of municipalities in Delaware, most populous city in the U.S. state of Delaware. The city was built on the site of Fort Christina, the first Swedish colonization of the Americas, Swedish settlement in North America. It lie ...
.
Footnotes
References
* * * * * * *Further reading
* *External links
Navy photos of ''Milwaukee''
{{DEFAULTSORT:Milwaukee (CL-5) Omaha-class cruisers Ships built in Tacoma, Washington 1922 ships World War II cruisers of the United States Ships transferred from the United States Navy to the Soviet Navy Cruisers of the Soviet Navy World War II cruisers of the Soviet Union