Typhoon Alley on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
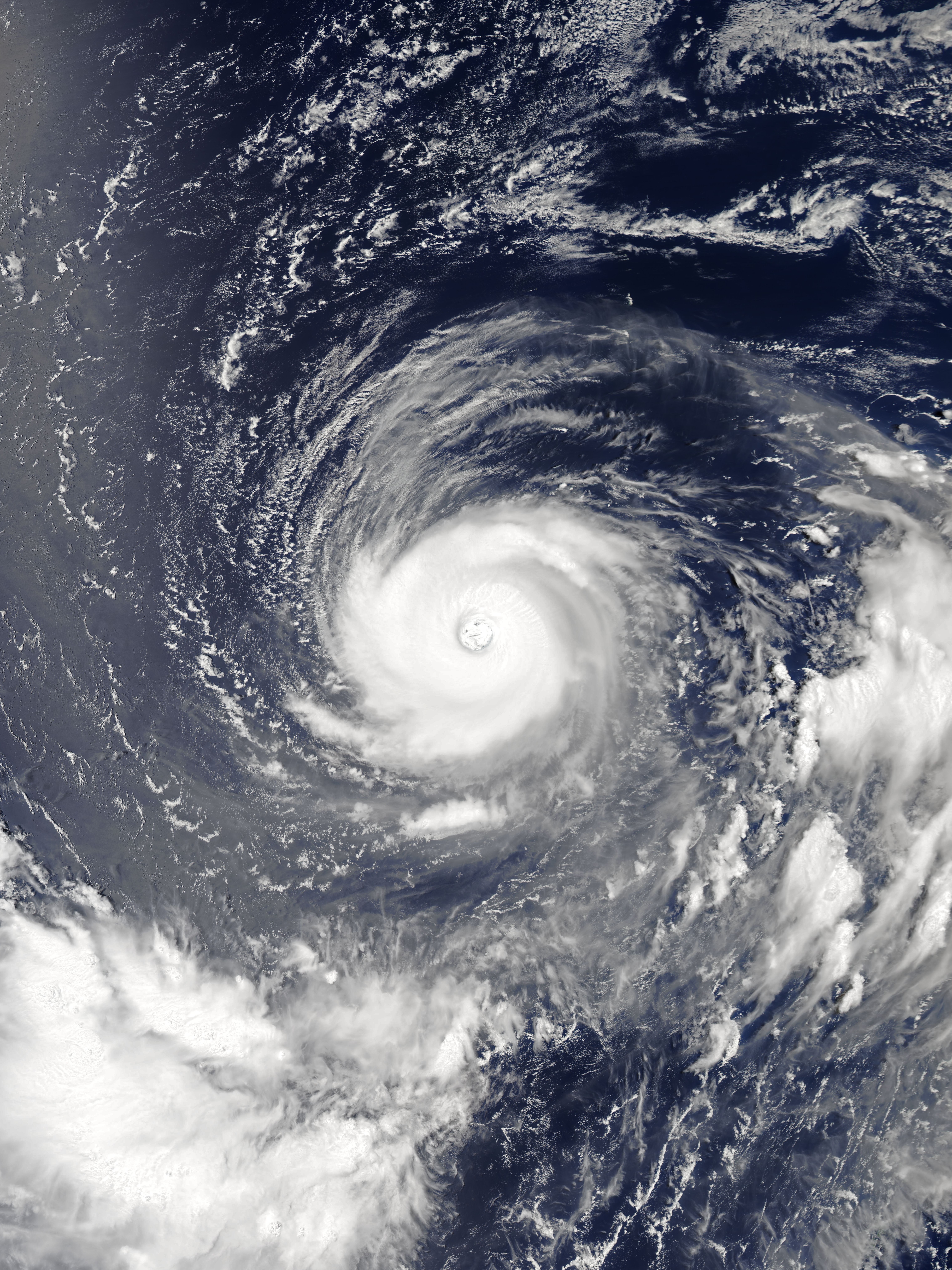 A typhoon is a
A typhoon is a
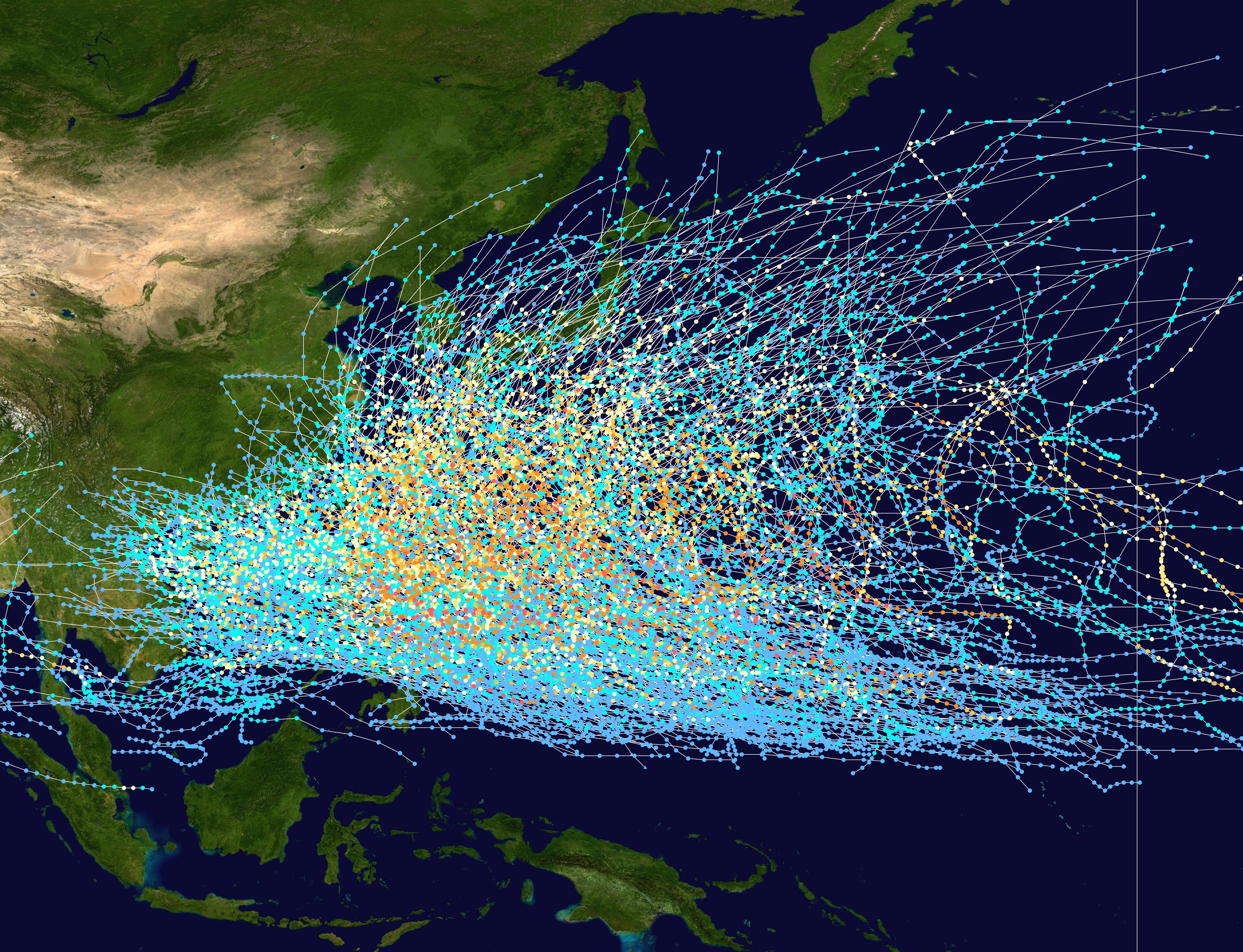 Most tropical cyclones form on the side of the subtropical ridge closer to the equator, then move poleward past the ridge axis before recurving north and northeast into the main belt of the
Most tropical cyclones form on the side of the subtropical ridge closer to the equator, then move poleward past the ridge axis before recurving north and northeast into the main belt of the
 A typhoon is a
A typhoon is a tropical cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system with a low-pressure area, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depending on its locat ...
that develops between 180° and 100°E in the Northern Hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of Earth that is north of the equator. For other planets in the Solar System, north is defined by humans as being in the same celestial sphere, celestial hemisphere relative to the invariable plane of the Solar ...
and which produces sustained hurricane-force winds of at least . This region is referred to as the Northwestern Pacific Basin, accounting for almost one third of the world's tropical cyclones. For organizational purposes, the northern Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five Borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is ...
is divided into three regions: the eastern (North America to 140°W), central (140°W to 180°), and western (180° to 100°E). The Regional Specialized Meteorological Center
A Regional Specialized Meteorological Centre (RSMC) is responsible for the distribution of information, advisories, and warnings regarding the specific program they have a part of, agreed by consensus at the World Meteorological Organization as ...
(RSMC) for tropical cyclone forecasts is in Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
, with other tropical cyclone warning centres for the northwest Pacific in Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; ) is an island U.S. state, state of the United States, in the Pacific Ocean about southwest of the U.S. mainland. One of the two Non-contiguous United States, non-contiguous U.S. states (along with Alaska), it is the only sta ...
(the Joint Typhoon Warning Center
The Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) is a joint United States Navy – United States Air Force command in Pearl Harbor, Hawaii. The JTWC is responsible for the issuing of tropical cyclone warnings in the North-West Pacific Ocean, South P ...
), the Philippines
The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. Located in the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of List of islands of the Philippines, 7,641 islands, with a tot ...
, and Hong Kong
Hong Kong)., Legally Hong Kong, China in international treaties and organizations. is a special administrative region of China. With 7.5 million residents in a territory, Hong Kong is the fourth most densely populated region in the wor ...
. Although the RSMC names each system, the main name list itself is coordinated among 18 countries that have territories threatened by typhoons each year.
Within most of the northwestern Pacific, there are no official typhoon seasons as tropical cyclones form throughout the year. Like any tropical cyclone, there are several main requirements for typhoon formation and development. It must be in sufficiently warm sea surface temperature
Sea surface temperature (or ocean surface temperature) is the ocean temperature, temperature of ocean water close to the surface. The exact meaning of ''surface'' varies in the literature and in practice. It is usually between and below the sea ...
s, atmospheric instability, high humidity
Humidity is the concentration of water vapor present in the air. Water vapor, the gaseous state of water, is generally invisible to the human eye. Humidity indicates the likelihood for precipitation (meteorology), precipitation, dew, or fog t ...
in the lower-to-middle levels of the troposphere
The troposphere is the lowest layer of the atmosphere of Earth. It contains 80% of the total mass of the Atmosphere, planetary atmosphere and 99% of the total mass of water vapor and aerosols, and is where most weather phenomena occur. From the ...
, have enough Coriolis effect
In physics, the Coriolis force is a pseudo force that acts on objects in motion within a frame of reference that rotates with respect to an inertial frame. In a reference frame with clockwise rotation, the force acts to the left of the moti ...
to develop a low pressure centre, a pre-existing low level focus or disturbance, and a low vertical wind shear
Wind shear (; also written windshear), sometimes referred to as wind gradient, is a difference in wind speed and/or direction over a relatively short distance in the atmosphere. Atmospheric wind shear is normally described as either vertical ...
. Although the majority of storms form between June and November, a few storms may occur between December and May (although tropical cyclone formation is very rare during that time). On average, the northwestern Pacific features the most numerous and intense tropical cyclones globally. Like other basins, they are steered by the subtropical ridge
The horse latitudes are the latitudes about 30 degrees north and south of the Equator. They are characterized by sunny skies, calm winds, and very little precipitation. They are also known as subtropical ridges or highs. It is a high-pressur ...
towards the west or northwest, with some systems recurving near and east of Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
. The Philippines receive the brunt of the landfalls, with China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
and Japan being less often impacted. However, some of the deadliest typhoons in history have struck China. Southern China has the longest record of typhoon impacts for the region, with a thousand-year sample via documents within their archives. Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
has received the wettest known typhoon on record for the northwest Pacific tropical cyclone basin
Traditionally, areas of tropical cyclone formation are divided into seven basins. These include the North Atlantic Ocean, the eastern and western parts of the North Pacific Ocean, the Southwest Pacific, the Southwest and Southeast Indian Oceans, ...
s. However, Vietnam recognises its typhoon season as lasting from the beginning of June through to the end of November, with an average of four to six typhoons hitting the country annually.
According to the statistics of the Joint Typhoon Warning Center, from 1950 to 2022, the Northwest Pacific generated an average of 26.5 named tropical cyclones each year, of which an average of 16.6 reached typhoon standard or above as defined by the Joint Typhoon Warning Center.
Nomenclature
Etymology
The etymology of typhoon is either Chinese or Persian-Hindustani origin. Typhoon may trace to (meaning "winds which long last"), first attested in 1124 in China. It was pronounced as inMin Chinese
Min ( zh, t=, s=闽语, p=Mǐnyǔ, poj=Bân-gú / Bân-gír / Bân-gí; Bàng-uâ-cê, BUC: ''Mìng-ngṳ̄'') is a broad group of Sinitic languages with about 75 million native speakers. These languages are spoken in Fujian province and Chaoshan ...
at the time, but later evolved to ɔŋ tʰai New characters were created to match the sound, no later than 1566.; ; . As cited in ; ; The word was introduced to Mandarin Chinese
Mandarin ( ; zh, s=, t=, p=Guānhuà, l=Mandarin (bureaucrat), officials' speech) is the largest branch of the Sinitic languages. Mandarin varieties are spoken by 70 percent of all Chinese speakers over a large geographical area that stretch ...
in the inverted Mandarin order , later picked up by foreign sailors to appear as typhoon.; ; ; The usage of was not dominant until Chu Coching
Coching Chu (; March 7, 1890 – February 7, 1974), also romanized as Zhu Kezhen, was a Chinese geologist and meteorologist.
Life and career
Born in Shangyu, Zhejiang, Chu received his secondary education at the Tangshan School of Rail and ...
, the head of meteorology of the national academy
A national academy is an organizational body, usually operating with state financial support and approval, that co-ordinates scholarly research activities and standards for academic disciplines, and serves as a public policy advisors, research ...
from 1929 to 1936, declared it to be the standard term. There were 29 alternative terms for typhoon recorded in a chronicle in 1762, now mostly replaced by , although or continues to be used in Min Chinese
Min ( zh, t=, s=闽语, p=Mǐnyǔ, poj=Bân-gú / Bân-gír / Bân-gí; Bàng-uâ-cê, BUC: ''Mìng-ngṳ̄'') is a broad group of Sinitic languages with about 75 million native speakers. These languages are spoken in Fujian province and Chaoshan ...
- and Wu Chinese
, region = Shanghai, Zhejiang, southern Jiangsu, parts of Anhui and Jiangxi provinces; overseas and migrant communities
, ethnicity = Wu
, speakers = million
, date = 2021
, ref = e27
, fa ...
- speaking areas from Chaozhou
Chaozhou ( zh, t=潮州), alternatively Chiuchow, Chaochow or Teochew, is a city in the eastern Guangdong province of China. It borders Shantou to the south, Jieyang to the southwest, Meizhou to the northwest, the province of Fujian to the east, ...
, Guangdong to Taizhou, Zhejiang.
Some English linguists proposed the English word typhoon traced to the Cantonese pronunciation of (correspond to Mandarin ), in turn the Cantonese word traced to Arabic. This claim contradicts the fact that the Cantonese term for typhoon was before the national promotion of . (meaning "winds which long last") was first attested in 280, being the oldest Chinese term for typhoon. Not one Chinese historical record links to an Arabic or foreign origin. On the other hand, Chinese records consistently assert foreigners refer typhoon as "black wind". "Black wind" eventually enters the vocabulary of Jin Chinese
Jin () is a group of Chinese linguistic varieties spoken by roughly 48 million people in northern China, including most of Shanxi province, much of central Inner Mongolia, and adjoining areas in Hebei, Henan, and Shaanxi provinces. The status ...
as .
Alternatively, some dictionaries propose that typhoon derived from (طوفان) ''tūfān'', meaning storm in Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
and Hindustani. The root
In vascular plants, the roots are the plant organ, organs of a plant that are modified to provide anchorage for the plant and take in water and nutrients into the plant body, which allows plants to grow taller and faster. They are most often bel ...
of (طوفان) ''tūfān'' possibly traces to the Ancient Greek mythological creature '' Typhôn''. In French
French may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France
** French people, a nation and ethnic group
** French cuisine, cooking traditions and practices
Arts and media
* The French (band), ...
''typhon'' was attested as storm in 1504. Portuguese traveler Fernão Mendes Pinto
Fernão Mendes Pinto (; 1509 – 8 July 1583) was a Portuguese people, Portuguese explorer and writer. His voyages are recorded in ''Pilgrimage'' (), his autobiographical memoir, which was published posthumously in 1614. The historical accura ...
referred to a ''tufão'' in his memoir published in 1614. The earliest form in English was "touffon" (1588), later as touffon, tuffon, tufon, tuffin, tuffoon, tayfun, tiffoon, typhawn.
Intensity classifications
A ''tropical depression'' is the lowest category that theJapan Meteorological Agency
The Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA; ''気象庁, Kishō-chō'') is a division of the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism dedicated to the Scientific, scientific observation and research of natural phenomena. Headquartered ...
uses and is the term used for a tropical system that has wind speeds not exceeding . A tropical depression is upgraded to a ''tropical storm'' should its sustained wind speeds exceed . Tropical storms also receive official names from RSMC Tokyo. Should the storm intensify further and reach sustained wind speeds of then it will be classified as a ''severe tropical storm''. Once the system's maximum sustained winds reach wind speeds of , the JMA will designate the tropical cyclone as a ''typhoon''—the highest category on its scale.
Since 2009 the Hong Kong Observatory
The Hong Kong Observatory is a weather forecast agency of the government of Hong Kong. The Observatory forecasts the weather and issues warnings on weather-related hazards. It also monitors and makes assessments on radiation levels in Hong ...
has divided typhoons into three different classifications: ''typhoon'', ''severe typhoon'' and ''super typhoon''. A ''typhoon'' has wind speed of , a severe typhoon has winds of at least , and a super typhoon has winds of at least . The United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
' Joint Typhoon Warning Center
The Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) is a joint United States Navy – United States Air Force command in Pearl Harbor, Hawaii. The JTWC is responsible for the issuing of tropical cyclone warnings in the North-West Pacific Ocean, South P ...
(JTWC) unofficially classifies typhoons with wind speeds of at least —the equivalent of a strong Category 4 storm in the Saffir-Simpson scale—as ''super typhoons''. However, the maximum sustained wind speed measurements that the JTWC uses are based on a 1-minute averaging period, akin to the U.S.'s National Hurricane Center
The National Hurricane Center (NHC) is the division of the United States' NOAA/National Weather Service responsible for tracking and predicting tropical weather systems between the IERS Reference Meridian, Prime Meridian and the 140th meridian ...
and Central Pacific Hurricane Center
The Central Pacific Hurricane Center (CPHC) of the United States National Weather Service is the official body responsible for tracking and issuing tropical cyclone warnings, watches, advisories, discussions, and statements for the Central Pacif ...
. As a result, the JTWC's wind reports are higher than JMA's measurements, as the latter is based on a 10-minute averaging interval.
Genesis
There are six main requirements for tropical cyclogenesis: sufficiently warm sea surface temperatures, atmospheric instability, highhumidity
Humidity is the concentration of water vapor present in the air. Water vapor, the gaseous state of water, is generally invisible to the human eye. Humidity indicates the likelihood for precipitation (meteorology), precipitation, dew, or fog t ...
in the lower to middle levels of the troposphere
The troposphere is the lowest layer of the atmosphere of Earth. It contains 80% of the total mass of the Atmosphere, planetary atmosphere and 99% of the total mass of water vapor and aerosols, and is where most weather phenomena occur. From the ...
, enough Coriolis force
In physics, the Coriolis force is a pseudo force that acts on objects in motion within a frame of reference that rotates with respect to an inertial frame. In a reference frame with clockwise rotation, the force acts to the left of the motio ...
to develop a low pressure center, a pre-existing low level focus or disturbance, and low vertical wind shear. While these conditions are necessary for tropical cyclone formation, they do not guarantee that a tropical cyclone will form. Normally, an ocean temperature of spanning through a depth of at least is considered the minimum to maintain the special mesocyclone
A mesocyclone is a meso-gamma mesoscale (or storm scale) region of rotation ( vortex), typically around in diameter, most often noticed on radar within thunderstorms. In the Northern Hemisphere, it is usually located in the right rear flank ( ...
that is the tropical cyclone. These warm waters are needed to maintain the warm core
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system with a low-pressure area, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depending on its locat ...
that fuels tropical systems. A minimum distance of from the equator
The equator is the circle of latitude that divides Earth into the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Southern Hemisphere, Southern Hemispheres of Earth, hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, about in circumferen ...
is normally needed for tropical cyclogenesis.
Whether it be a depression in the Intertropical Convergence Zone
The Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ , or ICZ), known by sailors as the doldrums or the calms because of its monotonous windless weather, is the area where the northeast and the southeast trade winds converge. It encircles Earth near the t ...
(ITCZ) or monsoon trough
The monsoon trough is a convergence zone between the wind patterns of the southern and northern hemispheres. It is a portion of the Intertropical Convergence Zone in the Western Pacific,Bin WangThe Asian Monsoon.Retrieved 2008-05-03. and is dep ...
, a broad surface front, or an outflow boundary
An outflow boundary, also known as a gust front, is a storm-scale or mesoscale meteorology, mesoscale boundary separating thunderstorm-cooled air (Outflow (meteorology), outflow) from the surrounding air; similar in effect to a cold front, with ...
, a low level feature with sufficient vorticity
In continuum mechanics, vorticity is a pseudovector (or axial vector) field that describes the local spinning motion of a continuum near some point (the tendency of something to rotate), as would be seen by an observer located at that point an ...
and convergence is required to begin tropical cyclogenesis. About 85 to 90 percent of Pacific typhoons form within the monsoon trough
The monsoon trough is a convergence zone between the wind patterns of the southern and northern hemispheres. It is a portion of the Intertropical Convergence Zone in the Western Pacific,Bin WangThe Asian Monsoon.Retrieved 2008-05-03. and is dep ...
. Even with perfect upper-level conditions and the required atmospheric instability, the lack of a surface focus will prevent the development of organized convection and a surface low. Vertical wind shear of less than between the ocean surface and the tropopause
The tropopause is the atmospheric boundary that demarcates the lowest two layers of the atmosphere of Earth – the troposphere and stratosphere – which occurs approximately above the equatorial regions, and approximately above the polar regi ...
is required for tropical cyclone development. Typically with Pacific typhoons, there are two jets of outflow
Outflow may refer to:
*Capital outflow, the capital leaving a particular economy
*Bipolar outflow, in astronomy, two continuous flows of gas from the poles of a star
* Outflow (hydrology), the discharge of a lake or other reservoir system
*Outflow ...
: one to the north ahead of an upper trough in the westerlies
The westerlies, anti-trades, or prevailing westerlies, are prevailing winds from the west toward the east in the middle latitudes between 30 and 60 degrees latitude. They originate from the high-pressure areas in the horse latitudes (about ...
, and a second towards the equator.
In general, the westerly wind increases associated with the Madden–Julian oscillation
The Madden–Julian oscillation (MJO) is the largest element of the intraseasonal (30- to 90-day) variability in the tropical atmosphere. It was discovered in 1971 by Roland Madden and Paul Julian of the American National Center for Atmospheric ...
lead to increased tropical cyclogenesis in all tropical cyclone basins
Traditionally, areas of tropical cyclone formation are divided into seven basins. These include the North Atlantic Ocean, the eastern and western parts of the North Pacific Ocean, the Southwest Pacific, the Southwest and Southeast Indian Oceans, ...
. As the oscillation propagates from west to east, it leads to an eastward march in tropical cyclogenesis with time during that hemisphere's summer season. On average, twice per year twin tropical cyclones will form in the western Pacific Ocean, near the 5th parallel north
Following are whole degree circles of latitude between the Equator and the 5th parallel north:
1st parallel north
The 1st parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 1 degree (angle), degree true north, north of the Earth, Earth's equator, ...
and the 5th parallel south
Following are circles of latitude between the Equator and the 5th parallel south:
1st parallel south
The 1st parallel south is a circle of latitude that is 1 degree (69.2 miles/111.36 kilometers) south of the Earth's equatorial plane. It cros ...
, along the same meridian, or line of longitude. There is an inverse relationship between tropical cyclone activity in the western Pacific basin and the North Atlantic basin, however. When one basin is active, the other is normally quiet, and vice versa. The main reason for this appears to be the phase of the Madden–Julian oscillation, or MJO, which is normally in opposite modes between the two basins at any given time.
Frequency
Nearly one-third of the world's tropical cyclones form within the western Pacific. This makes this basin the most active on Earth. Pacific typhoons have formed year-round, with peak months from August to October. The peak months correspond to that of theAtlantic hurricane season
The Atlantic hurricane season is the period in a year, from June 1 through November 30, when Tropical cyclone, tropical or subtropical cyclones are most likely to form in the North Atlantic Ocean. These dates, adopted by convention ...
s. Along with a high storm frequency, this basin also features the most globally intense storms on record. One of the most recent busy seasons was 2013
2013 was the first year since 1987 to contain four unique digits (a span of 26 years).
2013 was designated as:
*International Year of Water Cooperation
*International Year of Quinoa
Events
January
* January 5 – 2013 Craig, Alask ...
. Tropical cyclones form in any month of the year across the northwest Pacific Ocean and concentrate around June and November in the northern Indian Ocean. The area just northeast of the Philippines is the most active place on Earth for tropical cyclones to exist.
Across the Philippines themselves, activity reaches a minimum in February, before increasing steadily through June and spiking from July through October, with September being the most active month for tropical cyclones across the archipelago
An archipelago ( ), sometimes called an island group or island chain, is a chain, cluster, or collection of islands. An archipelago may be in an ocean, a sea, or a smaller body of water. Example archipelagos include the Aegean Islands (the o ...
. Activity falls off significantly in November, although Typhoon Haiyan
Typhoon Haiyan, known in the Philippines as Super Typhoon Yolanda, was an extremely powerful and catastrophic tropical cyclone that is among List of the most intense tropical cyclones, the most powerful tropical cyclones ever recorded. Upon ...
, the strongest Philippine typhoon on record, was a November typhoon. The most frequently impacted areas of the Philippines by tropical cyclones are northern and central Luzon
Luzon ( , ) is the largest and most populous List of islands in the Philippines, island in the Philippines. Located in the northern portion of the List of islands of the Philippines, Philippine archipelago, it is the economic and political ce ...
and eastern Visayas
The Visayas ( ), or the Visayan Islands (Bisayan languages, Visayan: ''Kabisay-an'', ; Filipino language, Filipino: ''Kabisayaan'' ), are one of the three Island groups of the Philippines, principal geographical divisions of the Philippines, a ...
. A ten-year average of satellite determined precipitation showed that at least 30 percent of the annual rainfall in the northern Philippines could be traced to tropical cyclones, while the southern islands receive less than 10 percent of their annual rainfall from tropical cyclones. The genesis and intensity of typhoons are also modulated by slow variation of the sea surface temperature and circulation features following a near-10-year frequency.
Paths
 Most tropical cyclones form on the side of the subtropical ridge closer to the equator, then move poleward past the ridge axis before recurving north and northeast into the main belt of the
Most tropical cyclones form on the side of the subtropical ridge closer to the equator, then move poleward past the ridge axis before recurving north and northeast into the main belt of the westerlies
The westerlies, anti-trades, or prevailing westerlies, are prevailing winds from the west toward the east in the middle latitudes between 30 and 60 degrees latitude. They originate from the high-pressure areas in the horse latitudes (about ...
. Most typhoons form in a region in the northwest Pacific known as typhoon alley, where the planet's most powerful tropical cyclones most frequently develop. When the subtropical ridge shifts due to El Niño
EL, El or el may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Fictional entities
* El, a character from the manga series ''Shugo Chara!'' by Peach-Pit
* Eleven (''Stranger Things'') (El), a fictional character in the TV series ''Stranger Things''
* El, fami ...
, so will the preferred tropical cyclone tracks. Areas west of Japan and Korea
Korea is a peninsular region in East Asia consisting of the Korean Peninsula, Jeju Island, and smaller islands. Since the end of World War II in 1945, it has been politically Division of Korea, divided at or near the 38th parallel north, 3 ...
tend to experience many fewer September–November tropical cyclone impacts during El Niño and neutral years. During El Niño years, the break in the subtropical ridge tends to lie near 130°E, which would favor the Japanese archipelago. During La Niña years, the formation of tropical cyclones, and the subtropical ridge position, shift westward across the western Pacific Ocean, which increases the landfall threat to China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
and greater intensity to Philippines
The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. Located in the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of List of islands of the Philippines, 7,641 islands, with a tot ...
. Those that form near the Marshall Islands
The Marshall Islands, officially the Republic of the Marshall Islands, is an island country west of the International Date Line and north of the equator in the Micronesia region of the Northwestern Pacific Ocean.
The territory consists of 29 c ...
find their way to Jeju Island
Jeju Island (Jeju language, Jeju/) is South Korea's largest island, covering an area of , which is 1.83% of the total area of the country. Alongside outlying islands, it is part of Jeju Province and makes up the majority of the province.
The i ...
, Korea. Typhoon paths follow three general directions.
* Straight track (or straight runner). A general westward path affects the Philippines
The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. Located in the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of List of islands of the Philippines, 7,641 islands, with a tot ...
, southern China, Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
, and Vietnam
Vietnam, officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam (SRV), is a country at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of about and a population of over 100 million, making it the world's List of countries and depende ...
.
* A parabolic recurving track. Storms recurving affect the eastern Philippines, eastern China, Taiwan, Korea, Japan, and the Russian Far East.
* Northward track. From point of origin, the storm follows a northerly direction, only affecting small islands.
A rare few storms, like Hurricane John
Hurricane John was a powerful and devastating tropical cyclone that caused deadly flooding and record rainfall across southern Mexico for several days in September 2024. The eleventh named storm, fourth hurricane, and second major hurricane of ...
, were redesignated as typhoons as they originated in the Eastern/Central Pacific and moved into the western Pacific.
Basin monitoring
Within the Western Pacific, RSMC Tokyo-Typhoon Center, part of theJapan Meteorological Agency
The Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA; ''気象庁, Kishō-chō'') is a division of the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism dedicated to the Scientific, scientific observation and research of natural phenomena. Headquartered ...
, has had the official warning responsibility for the whole of the Western Pacific since 1989, and the naming responsibility for systems of tropical storm strength or greater since 2000. However each National Meteorological and Hydrological Service within the western Pacific has the responsibility for issuing warnings for land areas about tropical cyclones affecting their country, such as the Joint Typhoon Warning Center for United States agencies, the Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration
The Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration (, abbreviated as PAGASA , which means "hope" as in the Tagalog word ''pag-asa'') is the National Meteorological and Hydrological Services (NMHS) agency of the P ...
(PAGASA) for interests in the island archipelago nation, and the Hong Kong Observatory
The Hong Kong Observatory is a weather forecast agency of the government of Hong Kong. The Observatory forecasts the weather and issues warnings on weather-related hazards. It also monitors and makes assessments on radiation levels in Hong ...
for storms that come close enough to cause the issuance of warning signals.
Name sources and name list
The list of names consists of entries from 14 southeast and east Asian nations and regions and the United States who have territories directly affected by typhoons. The submitted names are arranged into a list, the names on the list will be used from up to down, from left to right. When all names on the list are used, it will start again from the left-top corner. When a typhoon causes damage in a region, the affected region can request for retiring the name in the next session of the ESCAP/WMO Typhoon Committee. A new name will be decided by the region whose name was retired. Unlike tropical cyclones in other parts of the world, typhoons are not named after people. Instead, they generally refer to animals, flowers, astrological signs, and a few personal names. However, Philippines (PAGASA) retains its own naming list, which consists of both human names and other objects. Japan and some other East Asian countries also assign numbers to typhoons. Storms that cross the date line from the central Pacific retain their original name, but the designation of hurricane becomes typhoon.Records
The most active Western Pacific typhoon season was in1964
Events January
* January 1 – The Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland is dissolved.
* January 5 – In the first meeting between leaders of the Roman Catholic and Orthodox churches since the fifteenth century, Pope Paul VI and Patria ...
, when 39 storms of tropical storm strength formed. Only 15 seasons had 30 or more storms developing since reliable records began. The least activity seen in the northwest Pacific Ocean was during the 2010 Pacific typhoon season
The 2010 Pacific typhoon season, with 14 named storms, was the least active Pacific typhoon season on record. Seven of them strengthened into typhoons while one reached super typhoon intensity. All of the 14 named storms developed west of 150 ...
, when only 14 tropical storms and seven typhoons formed. In the Philippines, the most active season since 1945 for tropical cyclone strikes was 1993
The United Nations General Assembly, General Assembly of the United Nations designated 1993 as:
* International Year for the World's Indigenous People
The year 1993 in the Kwajalein Atoll in the Marshall Islands had only 364 days, since its ...
, when nineteen tropical cyclones moved through the country. There was only one tropical cyclone that moved through the Philippines in 1958
Events
January
* January 1 – The European Economic Community (EEC) comes into being.
* January 3 – The West Indies Federation is formed.
* January 4
** Edmund Hillary's Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition completes the thir ...
. The 2004 Pacific typhoon season
The 2004 Pacific typhoon season was an extremely active season that featured the second-highest ACE ever recorded in a single season, second only to 1997, which featured 29 named storms, nineteen typhoons, and six super typhoons. It was an event ...
was the busiest for Okinawa since 1957. Within Guangdong
) means "wide" or "vast", and has been associated with the region since the creation of Guang Prefecture in AD 226. The name "''Guang''" ultimately came from Guangxin ( zh, labels=no, first=t, t= , s=广信), an outpost established in Han dynasty ...
in southern China, during the past thousand years, the most active decades for typhoon strikes were the 1660s and 1670s.
The highest reliably-estimated maximum sustained wind
The maximum sustained wind associated with a tropical cyclone is a common
indicator of the intensity of the storm. Within a mature tropical cyclone, it is found within the eyewall at a certain distance from the center, known as the radius of ma ...
s on record for a typhoon was that of Typhoon Haiyan
Typhoon Haiyan, known in the Philippines as Super Typhoon Yolanda, was an extremely powerful and catastrophic tropical cyclone that is among List of the most intense tropical cyclones, the most powerful tropical cyclones ever recorded. Upon ...
at shortly before its landfall in the central Philippines
The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. Located in the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of List of islands of the Philippines, 7,641 islands, with a tot ...
on November 8, 2013. The most intense storm based on minimum pressure was Typhoon Tip
Typhoon Tip, known in the Philippines as Super Typhoon Warling, was the largest and most intense tropical cyclone ever recorded. The forty-third tropical depression, nineteenth tropical storm, twelfth typhoon, and third super typhoon of the 1 ...
in the northwestern Pacific Ocean in 1979, which reached a minimum pressure of and maximum sustained wind speeds of . The deadliest typhoon of the 20th century was Typhoon Nina, which killed nearly 100,000 in China in 1975 due to a flood that caused 12 reservoirs to fail. After Typhoon Morakot
Typhoon Morakot, known in the Philippines as Typhoon Kiko, was the wettest and deadliest typhoon to impact Taiwan in recorded history. The eighth named storm and fourth typhoon of the 2009 Pacific typhoon season, Morakot wrought catastrophic d ...
landed in Taiwan at midnight on August 8, 2009, almost the entire southern region of Taiwan (Chiayi County
Chiayi is a County (Taiwan), county in Taiwan. Located in Regions of Taiwan, southwestern Taiwan surrounding but not including Chiayi City, it is the sixth largest county in the island of Taiwan. Its major tourist destination is Alishan Natio ...
/Chiayi City
Chiayi (,), officially known as Chiayi City, is a Provincial city (Taiwan), city located in Chianan Plain in Regions of Taiwan, southwestern Taiwan, surrounded by Chiayi County with a population of 263,188 inhabitants as of January 2023.
The H ...
, Tainan County
Tainan County was a County (Taiwan), county in southern Taiwan between 1945 and 2010. The county seat was in Xinying District, Sinying City.
History
Tainan County was established on 7 January 1946 on the territory of Tainan Prefecture () sh ...
/Tainan City
Tainan (), officially Tainan City, is a special municipality in southern Taiwan, facing the Taiwan Strait on its western coast. Tainan is the oldest city on the island and commonly called the " prefectural capital" for its over 260-year histo ...
(now merged as Tainan), Kaohsiung County
Kaohsiung County was a county in southern Taiwan between 1945 and 2010. The county seat was located in Fongshan City.
History
Kaohsiung County was established on 6 December 1945 on the territory of Takao Prefecture () shortly after the end ...
/Kaohsiung City
Kaohsiung, officially Kaohsiung City, is a Special municipality (Taiwan), special municipality located in southern Taiwan. It ranges from the coastal urban center to the rural Yushan Range with an area of . Kaohsiung City has a population of ...
(now merged as Kaohsiung), and Pingtung County
Pingtung () is a County (Taiwan), county located in southern Taiwan. It has a warm tropical monsoon climate and is known for its agriculture and tourism. Kenting National Park, Taiwan's oldest national park, is located in the county. The county ...
) and parts of Taitung County
Taitung () is the third largest county in Taiwan, located primarily on the island's southeastern coast and also including Green Island, Orchid Island and Lesser Orchid Island. The seat is located in Taitung City.
Name
While its name means "East ...
and Nantou County
Nantou is the second largest County (Taiwan), county of Taiwan by area, located in the central part of the country. It is also the only non-coastal county in Taiwan. Its name derives from the Hoanya people, Hoanya Taiwanese aborigines, Taiwanese ...
were flooded by record-breaking heavy rain. The rainfall in Pingtung County
Pingtung () is a County (Taiwan), county located in southern Taiwan. It has a warm tropical monsoon climate and is known for its agriculture and tourism. Kenting National Park, Taiwan's oldest national park, is located in the county. The county ...
reached , breaking all rainfall records of any single place in Taiwan induced by a single typhoon, and making the cyclone the wettest known typhoon.
See also
* Pacific typhoon season * Tropical cyclones in * Pacific typhoon season *Effects of tropical cyclones
The effects of tropical cyclones include heavy rain, strong wind, large storm surges near landfall, and tornadoes. The destruction from a tropical cyclone, such as a hurricane or tropical storm, depends mainly on its intensity, its size, and its ...
* China tropical cyclone rainfall climatology
China is a mountainous country, which leads to rapid dissipation of cyclones that move inland as well as significant amounts of rain from those dissipating cyclones. Typhoon Nina in 1975 caused the collapse of two huge reservoirs and ten smaller ...
For storms that have affected countries in this basin:
* Tropical cyclones in Malaysia
Malaysia is a country in the southern part of Southeast Asia and is located to the south of the South China Sea. The sea separates two regions which consists of Peninsular Malaysia, located within the Malay Peninsula, and East Malaysia, located ...
* Tropical cyclones in Vietnam
Vietnam is a southeast Asian country, and is the easternmost country of mainland Southeast Asia. It borders the South China Sea, hence, seeing the increased likeliness of tropical cyclones. Tropical cyclones in this area are considered to be part ...
* Typhoons in the Korean peninsula
The Korean Peninsula is a peninsula region located over Eastern Asia. The region is divided into North Korea and South Korea.
Climatologically, in the Northwest Pacific basin, most tropical cyclones tend to develop between May and October. Typho ...
* Typhoons in the Philippines
The Philippines is a typhoon-prone country, with approximately twenty tropical cyclones entering its area of responsibility per year. Locally known generally as (),Glossary of Meteorology. These 20 Tropical Cyclones can vary from Tropical ...
* Typhoons in Japan
Japan is one of the countries frequently hit by typhoons, with the nation giving its own names to particularly destructive storms.
Since records began in 1951, an average of 2.6 typhoons reached the main islands of Kyushu, Shikoku, Honshu and Ho ...
References
External links
{{DEFAULTSORT:Pacific Typhoon Tropical cyclone meteorology