Type 89 machine gun on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Type 89 refers to two unrelated
 The first machine gun is a recoil-operated, licensed copy of the Vickers Class E machine gun re-chambered to 7.7x58mmSR Type 89 cartridge, it is referred to as the "fixed type". It was used in synchronized applications in fighter cowls and in wing gun applications. It was
The first machine gun is a recoil-operated, licensed copy of the Vickers Class E machine gun re-chambered to 7.7x58mmSR Type 89 cartridge, it is referred to as the "fixed type". It was used in synchronized applications in fighter cowls and in wing gun applications. It was
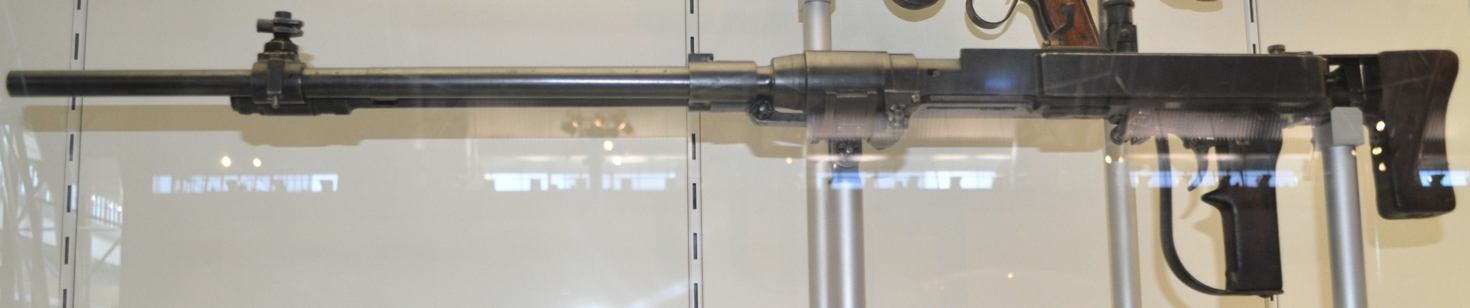 The second machine gun is
The second machine gun is
pwencycl.kgbudge.com Japanese_7p7mm_Type_89_gun.htmalternathistory.org.ua
Aircraft guns World War II weapons of Japan Machine guns of Japan
Imperial Japanese Army
The was the official ground-based armed force of the Empire of Japan from 1868 to 1945. It was controlled by the Imperial Japanese Army General Staff Office and the Ministry of the Army, both of which were nominally subordinate to the Emperor ...
aircraft machine gun
A machine gun is a fully automatic, rifled autoloading firearm designed for sustained direct fire with rifle cartridges. Other automatic firearms such as automatic shotguns and automatic rifles (including assault rifles and battle rifl ...
s. Its Imperial Japanese Navy
The Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN; Kyūjitai: Shinjitai: ' 'Navy of the Greater Japanese Empire', or ''Nippon Kaigun'', 'Japanese Navy') was the navy of the Empire of Japan from 1868 to 1945, when it was dissolved following Japan's surrender ...
counterparts are the Type 97 machine gun (fixed), and Type 92 machine gun (a Lewis gun copy).
Type 89 fixed
belt-fed
upright=1.35, An 7.62×51mm_NATO.html" ;"title="M60 machine gun belt loaded with 7.62×51mm NATO">M60 machine gun belt loaded with 7.62×51mm NATO cartridges, aboard a U.S. Navy patrol craft
An ammunition belt is a firearm device used to packag ...
, using a steel link disintegrating belt. The fixed Type 89 was used in the Nakajima Ki-27
The was the main fighter aircraft used by the Imperial Japanese Army Air Service up until 1940. Its Allied nickname was "Nate", although it was called "Abdul" in the "China Burma India" (CBI) theater by many post war sources; Allied Intellig ...
, Ki-43
The Nakajima Ki-43 ''Hayabusa'' (, "Peregrine falcon", "Army Type 1 Fighter" ) is a single-engine land-based tactical fighter used by the Imperial Japanese Army Air Service in World War II.
The Allied reporting name was "Oscar", but it was ...
, early Ki-44 fighters, the Mitsubishi Ki-30
The was a Japanese light bomber of World War II. It was a single-engine, mid-wing, cantilever monoplane of stressed-skin construction with a fixed tailwheel undercarriage and a long transparent cockpit canopy. The type had significance in ...
and Ki-51 light bomber
A light bomber is a relatively small and fast type of Military aircraft, military bomber Fixed-wing aircraft, aircraft that was primarily employed before the 1950s. Such Fixed-wing aircraft, aircraft would typically not carry more than one ton ...
s, the Kawasaki Ki-32
The was a Japanese light bomber aircraft of World War II. It was a single-engine, two-seat, mid-wing, cantilever monoplane with a fixed tailwheel undercarriage. An internal bomb bay accommodated a offensive load, supplemented by of bombs on ex ...
light bomber and various others. Communist forces used some ex-Japanese Type 89s during the Korean War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Korean War
, partof = the Cold War and the Korean conflict
, image = Korean War Montage 2.png
, image_size = 300px
, caption = Clockwise from top: ...
.
Type 89 flexible type
 The second machine gun is
The second machine gun is gas-operated
Gas-operation is a system of operation used to provide energy to operate locked breech, autoloading firearms. In gas-operation, a portion of high-pressure gas from the cartridge being fired is used to power a mechanism to dispose of the spen ...
, it consists of two modified Type 11 machine guns paired into a single unit, similar to the German MG 81Z. It is commonly referred to as the "flexible type". It was derived from ''otsu-gou'' - an experimental machine gun (1922-1929) which was a Type 11 turned on its side and fed from a pan magazine. The machine gun was chambered in the 7.7x58mmSR Type 89 cartridge, it used a "Y"-shaped metallic stock, spade grips, the barrels had no cooling fins (contrary to Type 11), it was fed from two quadrant-shaped 45-round pan magazines (each magazine has a place for nine 5-round stripper clip
A stripper clip (also known as a charger or charger clip, especially in British and in Commonwealth military vocabulary) is a speedloader that holds several cartridges (usually between 5 and 10) together in a single unit for easier and faster ...
s).
The machine gun was used as a rear gun on aircraft and some were pressed into ground and anti-aircraft use. Single or doubled Type 89s were used in most Imperial Japanese Army aircraft that had flexible defensive weapons, including the Mitsubishi Ki-21
The ( Allied reporting name: "Sally" /"Gwen") was a Japanese heavy bomber during World War II. It began operations during the Second Sino-Japanese War participating in the Nomonhan Incident, and in the first stages of the Pacific War, includ ...
, Ki-67 and Nakajima Ki-49
The Nakajima Ki-49 ''Donryu'' (呑龍, "Storm Dragon")Francillon, 1970, p.223 was a twin-engine Japanese World War II heavy bomber. It was designed to carry out daylight bombing missions, without the protection of escort fighters. Consequently, ...
heavy bombers, the Mitsubishi Ki-30
The was a Japanese light bomber of World War II. It was a single-engine, mid-wing, cantilever monoplane of stressed-skin construction with a fixed tailwheel undercarriage and a long transparent cockpit canopy. The type had significance in ...
, Ki-51 and Kawasaki Ki-32
The was a Japanese light bomber aircraft of World War II. It was a single-engine, two-seat, mid-wing, cantilever monoplane with a fixed tailwheel undercarriage. An internal bomb bay accommodated a offensive load, supplemented by of bombs on ex ...
light bombers, the Tachikawa Ki-9
The was an intermediate training aircraft of the Imperial Japanese Army Air Force built by Tachikawa Aircraft Company Ltd in the 1930s. It was known to the Allies under the nickname of "Spruce" during World War II.
Design and development
T ...
(for training purposes only), and various other aircraft in the Army Air Force inventory.
Additionally, there was also the Te-4 machine gun (the ''Te'' designation was given to firearms under 11mm, and ''Ho'' to larger weapons such as the 12.7mm Ho-103 heavy machine gun
A heavy machine gun (HMG) is significantly larger than light, medium or general-purpose machine guns. HMGs are typically too heavy to be man-portable (carried by one person) and require mounting onto a weapons platform to be operably stable o ...
and 20mm
20 mm caliber is a specific size of popular autocannon ammunition. It is typically used to distinguish smaller-caliber weapons, commonly called "guns", from larger-caliber "cannons" (e.g. machine gun vs. autocannon). All 20 mm cartridges ha ...
Ho-5
The Ho-5 (Army Type 2) was a Japanese aircraft autocannon used during World War II. Developed from the Ho-103 machine gun, it was a version of the American Model 1921 Browning aircraft machine gun. It replaced the Ho-1 and Ho-3 (Army Type 97 ...
autocannon
An autocannon, automatic cannon or machine cannon is a fully automatic gun that is capable of rapid-firing large-caliber ( or more) armour-piercing, explosive or incendiary shells, as opposed to the smaller-caliber kinetic projectiles (bulle ...
), the machine gun bore a strong resemblance to ''otsu-gou'' (of which the Type 89 "flexible" was a derivative), due to that fact it was assumed to be a further modification of the double-barrelled machine gun, as such it was referred to as Type 89 "modified single".
See also
* Type 97 machine gun *Type 92 machine gun
The was developed for aerial use for the Imperial Japanese Navy in 1932. The Type 92 is a light machine gun and not to be confused with the similarly named Type 92 heavy machine gun.
Description
It was the standard hand-held machine gun in mu ...
* Type 100 machine gun
References
Bibliography
*External links
{{commons category, Type 89 aircraft machine gunpwencycl.kgbudge.com Japanese_7p7mm_Type_89_gun.htm
Aircraft guns World War II weapons of Japan Machine guns of Japan