Turkeys on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The turkey is a large
The turkey is a large  The earliest turkeys evolved in North America over 20 million years ago. They share a recent common ancestor with grouse, pheasants, and other fowl. The wild turkey species is the ancestor of the domestic turkey, which was domesticated approximately 2,000 years ago.
The earliest turkeys evolved in North America over 20 million years ago. They share a recent common ancestor with grouse, pheasants, and other fowl. The wild turkey species is the ancestor of the domestic turkey, which was domesticated approximately 2,000 years ago.
 The linguist Mario Pei proposes two possible explanations for the name ''turkey''. One theory suggests that when Europeans first encountered turkeys in the Americas, they incorrectly identified the birds as a type of guineafowl, which were already being imported into Europe by English merchants to the Levant via
The linguist Mario Pei proposes two possible explanations for the name ''turkey''. One theory suggests that when Europeans first encountered turkeys in the Americas, they incorrectly identified the birds as a type of guineafowl, which were already being imported into Europe by English merchants to the Levant via
 Turkeys were likely first domesticated in Pre-Columbian Mexico, where they held a cultural and symbolic importance."Turkey." ''Britannica Library'', Encyclopædia Britannica, 13 Feb. 2019. Accessed 25 May 2022. The Classical Nahuatl word for the turkey, ( in Spanish), is still used in modern Mexico, in addition to the general term . Mayan aristocrats and priests appear to have had a special connection to ocellated turkeys, with
Turkeys were likely first domesticated in Pre-Columbian Mexico, where they held a cultural and symbolic importance."Turkey." ''Britannica Library'', Encyclopædia Britannica, 13 Feb. 2019. Accessed 25 May 2022. The Classical Nahuatl word for the turkey, ( in Spanish), is still used in modern Mexico, in addition to the general term . Mayan aristocrats and priests appear to have had a special connection to ocellated turkeys, with
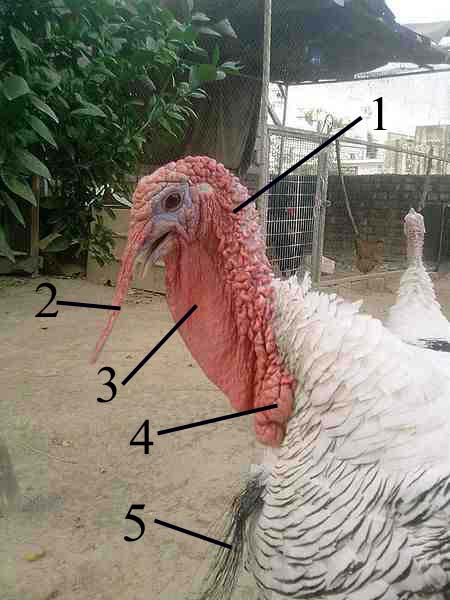 In anatomical terms, a ''snood'' is an erectile, fleshy protuberance on the forehead of turkeys. Most of the time when the turkey is in a relaxed state, the snood is pale and 2–3 cm long. However, when the male begins strutting (the courtship display), the snood engorges with blood, becomes redder and elongates several centimeters, hanging well below the beak (see image).
Snoods are just one of the caruncles (small, fleshy excrescences) that can be found on turkeys.
While fighting, commercial turkeys often peck and pull at the snood, causing damage and bleeding. This often leads to further injurious pecking by other turkeys and sometimes results in
In anatomical terms, a ''snood'' is an erectile, fleshy protuberance on the forehead of turkeys. Most of the time when the turkey is in a relaxed state, the snood is pale and 2–3 cm long. However, when the male begins strutting (the courtship display), the snood engorges with blood, becomes redder and elongates several centimeters, hanging well below the beak (see image).
Snoods are just one of the caruncles (small, fleshy excrescences) that can be found on turkeys.
While fighting, commercial turkeys often peck and pull at the snood, causing damage and bleeding. This often leads to further injurious pecking by other turkeys and sometimes results in
 The species ''Meleagris gallopavo'' is eaten by humans. They were first domesticated by the indigenous people of
The species ''Meleagris gallopavo'' is eaten by humans. They were first domesticated by the indigenous people of
File:Ocellated Turkey.jpg, Chan Chich Lodge area, Belize: the ocellated turkey is named for the eye-shaped spots (ocelli) on its tail feathers
File:Turkey (Meleagris gallopavo) (16279818861).jpg, A male (tom)
 The turkey is a large
The turkey is a large bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweig ...
in the genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial n ...
''Meleagris'', native to North America. There are two extant turkey species: the wild turkey
The wild turkey (''Meleagris gallopavo'') is an upland ground bird native to North America, one of two extant species of turkey and the heaviest member of the order Galliformes. It is the ancestor to the domestic turkey, which was originally ...
(''Meleagris gallopavo'') of eastern and central North America and the ocellated turkey (''Meleagris ocellata'') of the Yucatán Peninsula
The Yucatán Peninsula (, also , ; es, Península de Yucatán ) is a large peninsula in southeastern Mexico and adjacent portions of Belize and Guatemala. The peninsula extends towards the northeast, separating the Gulf of Mexico to the north ...
in Mexico. Males of both turkey species have a distinctive fleshy wattle
Wattle or wattles may refer to:
Plants
*''Acacia sensu lato'', polyphyletic genus of plants commonly known as wattle, especially in Australia and South Africa
**''Acacia'', large genus of shrubs and trees, native to Australasia
**Black wattle, c ...
, called a snood, that hangs from the top of the beak. They are among the largest birds in their ranges. As with many large ground-feeding birds (order Galliformes
Galliformes is an order of heavy-bodied ground-feeding birds that includes turkeys, chickens, quail, and other landfowl. Gallinaceous birds, as they are called, are important in their ecosystems as seed dispersers and predators, and are ofte ...
), the male is bigger and much more colorful than the female.
Native to North America, the wild species was bred as domesticated turkey by indigenous peoples. It was this domesticated turkey that later reached Eurasia, during the Columbian exchange
The Columbian exchange, also known as the Columbian interchange, was the widespread transfer of plants, animals, precious metals, commodities, culture, human populations, technology, diseases, and ideas between the New World (the Americas) in ...
. In English, "turkey" probably got its name from the domesticated variety being imported to Britain in ships coming from the Turkish Levant
The Levant () is an approximation, approximate historical geography, historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology an ...
via Spain. The British at the time therefore associated the bird with the country Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with ...
and the name prevailed. An alternative theory posits that another bird, a guinea fowl native to Madagascar introduced to England by Turkish merchants, was the original source, and that the term was then transferred to the New World bird by English colonizers with knowledge of the previous species.
 The earliest turkeys evolved in North America over 20 million years ago. They share a recent common ancestor with grouse, pheasants, and other fowl. The wild turkey species is the ancestor of the domestic turkey, which was domesticated approximately 2,000 years ago.
The earliest turkeys evolved in North America over 20 million years ago. They share a recent common ancestor with grouse, pheasants, and other fowl. The wild turkey species is the ancestor of the domestic turkey, which was domesticated approximately 2,000 years ago.
Taxonomy
Thegenus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial n ...
''Meleagris'' was introduced in 1758 by the Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (; 23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after his ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné Blunt (2004), p. 171. (), was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, taxonomist, and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, ...
in the tenth edition of his ''Systema Naturae
' (originally in Latin written ' with the ligature æ) is one of the major works of the Swedish botanist, zoologist and physician Carl Linnaeus (1707–1778) and introduced the Linnaean taxonomy. Although the system, now known as binomial nom ...
''. The genus name is from the Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic p ...
μελεαγρις, ''meleagris'' meaning "guineafowl". The type species
In zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the species that contains the biological type specimen( ...
is the wild turkey
The wild turkey (''Meleagris gallopavo'') is an upland ground bird native to North America, one of two extant species of turkey and the heaviest member of the order Galliformes. It is the ancestor to the domestic turkey, which was originally ...
(''Meleagris gallopavo'').
Turkeys are classed in the family Phasianidae
The Phasianidae are a family of heavy, ground-living birds, which includes pheasants, partridges, junglefowl, chickens, turkeys, Old World quail, and peafowl. The family includes many of the most popular gamebirds. The family is a large one and i ...
(pheasant
Pheasants ( ) are birds of several genera within the family Phasianidae in the order Galliformes. Although they can be found all over the world in introduced (and captive) populations, the pheasant genera native range is restricted to Eurasia ...
s, partridge
A partridge is a medium-sized galliform bird in any of several genera, with a wide native distribution throughout parts of Europe, Asia and Africa. Several species have been introduced to the Americas. They are sometimes grouped in the Perdic ...
s, francolin
Francolins are birds in the tribe Gallini that traditionally have been placed in the genus ''Francolinus'', but now commonly are divided into multiple genera.
As previously defined, they were paraphyletic as the genus '' Pternistis'', which wa ...
s, junglefowl, grouse
Grouse are a group of birds from the order (biology), order Galliformes, in the family (biology), family Phasianidae. Grouse are presently assigned to the Tribe (biology), tribe Tetraonini (formerly the subfamily Tetraoninae and the family Tetr ...
, and relatives thereof) in the taxonomic order
Order, ORDER or Orders may refer to:
* Categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood
* Heterarchy, a system of organization wherein the elements have the potential to be ranked a number of d ...
Galliformes
Galliformes is an order of heavy-bodied ground-feeding birds that includes turkeys, chickens, quail, and other landfowl. Gallinaceous birds, as they are called, are important in their ecosystems as seed dispersers and predators, and are ofte ...
. They are close relatives of the grouse
Grouse are a group of birds from the order (biology), order Galliformes, in the family (biology), family Phasianidae. Grouse are presently assigned to the Tribe (biology), tribe Tetraonini (formerly the subfamily Tetraoninae and the family Tetr ...
and are classified alongside them in the tribe Tetraonini.
Extant species
The genus contains two species.Fossil species
* ''Meleagris californica''Californian turkey
The Californian turkey (''Meleagris californica'') is an extinct species of turkey indigenous to the Pleistocene and Early Holocene of California. It has been estimated that the Californian turkey went extinct about 10,000 years ago.
Fossil ev ...
– Southern California
* ''Meleagris crassipes'' Southwestern turkey - New MexicoTyrberg, T. (2008). The Late Pleistocene continental avian extinction—An evaluation of the fossil evidence. Oryctos, 7, 249-269.
Names
 The linguist Mario Pei proposes two possible explanations for the name ''turkey''. One theory suggests that when Europeans first encountered turkeys in the Americas, they incorrectly identified the birds as a type of guineafowl, which were already being imported into Europe by English merchants to the Levant via
The linguist Mario Pei proposes two possible explanations for the name ''turkey''. One theory suggests that when Europeans first encountered turkeys in the Americas, they incorrectly identified the birds as a type of guineafowl, which were already being imported into Europe by English merchants to the Levant via Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth ( Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis ( ...
. The birds were therefore nicknamed ''turkey coqs''. The name of the North American bird may have then become ''turkey fowl'' or ''Indian turkeys'', which was eventually shortened to ''turkeys''.
A second theory arises from turkeys coming to England not directly from the Americas, but via merchant ships from the Middle East, where they were domesticated successfully. Again the importers lent the name to the bird; hence'' turkey-cocks'' and ''turkey-hens'', and soon thereafter, ''turkeys''.
In 1550, the English navigator William Strickland, who had introduced the turkey into England, was granted a coat of arms including a "turkey-cock in his pride proper". William Shakespeare
William Shakespeare ( 26 April 1564 – 23 April 1616) was an English playwright, poet and actor. He is widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's pre-eminent dramatist. He is often called England's natio ...
used the term in ''Twelfth Night
''Twelfth Night'', or ''What You Will'' is a romantic comedy by William Shakespeare, believed to have been written around 1601–1602 as a Twelfth Night's entertainment for the close of the Christmas season. The play centres on the twins V ...
'', believed to be written in 1601 or 1602. The lack of context around his usage suggests that the term was already widespread.
Other European names for turkeys incorporate an assumed Indian origin, such as ('from India') in French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
, (, 'bird of India') in Russian, in Polish and Ukrainian, and ('Indian') in Turkish
Turkish may refer to:
*a Turkic language spoken by the Turks
* of or about Turkey
** Turkish language
*** Turkish alphabet
** Turkish people, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
*** Turkish citizen, a citizen of Turkey
*** Turkish communities and mi ...
. These are thought to arise from the supposed belief of Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus
* lij, Cristoffa C(or)ombo
* es, link=no, Cristóbal Colón
* pt, Cristóvão Colombo
* ca, Cristòfor (or )
* la, Christophorus Columbus. (; born between 25 August and 31 October 1451, died 20 May 1506) was a ...
that he had reached India rather than the Americas on his voyage. In Portuguese a turkey is a ; the name is thought to derive from 'Peru'.
Several other birds that are sometimes called turkeys are not particularly closely related: the brushturkeys are megapodes, and the bird sometimes known as the ''Australian turkey'' is the Australian bustard (''Ardeotis australis''). The anhinga (''Anhinga anhinga'') is sometimes called the ''water turkey'', from the shape of its tail when the feathers are fully spread for drying.
An infant turkey is called a ''chick'' or ''poult''.
History
 Turkeys were likely first domesticated in Pre-Columbian Mexico, where they held a cultural and symbolic importance."Turkey." ''Britannica Library'', Encyclopædia Britannica, 13 Feb. 2019. Accessed 25 May 2022. The Classical Nahuatl word for the turkey, ( in Spanish), is still used in modern Mexico, in addition to the general term . Mayan aristocrats and priests appear to have had a special connection to ocellated turkeys, with
Turkeys were likely first domesticated in Pre-Columbian Mexico, where they held a cultural and symbolic importance."Turkey." ''Britannica Library'', Encyclopædia Britannica, 13 Feb. 2019. Accessed 25 May 2022. The Classical Nahuatl word for the turkey, ( in Spanish), is still used in modern Mexico, in addition to the general term . Mayan aristocrats and priests appear to have had a special connection to ocellated turkeys, with ideogram
An ideogram or ideograph (from Greek "idea" and "to write") is a graphic symbol that represents an idea or concept, independent of any particular language, and specific words or phrases. Some ideograms are comprehensible only by familiarit ...
s of those birds appearing in Mayan manuscripts. Spanish chroniclers, including Bernal Díaz del Castillo and Father Bernardino de Sahagún, describe the multitude of food (both raw fruits and vegetables as well as prepared dishes) that were offered in the vast markets () of Tenochtitlán, noting there were tamale
A tamale, in Spanish tamal, is a traditional Mesoamerican dish made of masa, a dough made from nixtamalized corn, which is steamed in a corn husk or banana leaf. The wrapping can either be discarded prior to eating or used as a plate. Tam ...
s made of turkeys, iguanas, chocolate, vegetables, fruits and more.
Turkeys were first exported to Europe via Spain around 1519, where they gained immediate popularity among the aristocratic classes. Turkeys arrived in England in 1541. From there, English settlers brought turkeys to North America during the 17th century.
Destruction and re-introduction in the United States
In what is now the United States, there were an estimated 10 million turkeys in the 17th century. By the 1930s, only 30,000 remained. In the 1960s and 1970s, biologists started trapping wild turkeys from the few places they remained (including the Ozarks and New York), and re-introducing them into other states, including Minnesota and Vermont.Human conflicts with wild turkeys
Turkeys have been known to be aggressive toward humans and pets in residential areas. Wild turkeys have a social structure and pecking order and habituated turkeys may respond to humans and animals as they do other turkeys. Habituated turkeys may attempt to dominate or attack people that the birds view as subordinates. In 2017, the town ofBrookline, Massachusetts
Brookline is a town in Norfolk County, Massachusetts, in the United States, and part of the Boston metropolitan area. Brookline borders six of Boston's neighborhoods: Brighton, Allston, Fenway–Kenmore, Mission Hill, Jamaica Plain, and ...
, recommended a controversial approach when confronted with wild turkeys. Besides taking a step forward to intimidate the birds, officials also suggested "making noise (clanging pots or other objects together); popping open an umbrella; shouting and waving your arms; squirting them with a hose; allowing your leashed dog to bark at them; and forcefully fending them off with a broom". This advice was quickly rescinded and replaced with a caution that "being aggressive toward wild turkeys is not recommended by State wildlife officials.”
Fossil record
A number of turkeys have been described fromfossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
s. The Meleagridinae are known from the Early Miocene
The Early Miocene (also known as Lower Miocene) is a sub-epoch of the Miocene Epoch made up of two stages: the Aquitanian and Burdigalian stages.
The sub-epoch lasted from 23.03 ± 0.05 Ma to 15.97 ± 0.05 Ma (million years ago). It was p ...
( mya
Mya may refer to:
Brands and product names
* Mya (program), an intelligent personal assistant created by Motorola
* Mya (TV channel), an Italian Television channel
* Midwest Young Artists, a comprehensive youth music program
Codes
* Burmese ...
) onwards, with the extinct genera
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial ...
'' Rhegminornis'' (Early Miocene of Bell, U.S.) and '' Proagriocharis'' (Kimball Late Miocene
The Late Miocene (also known as Upper Miocene) is a sub-epoch of the Miocene Epoch made up of two stages. The Tortonian and Messinian stages comprise the Late Miocene sub-epoch, which lasted from 11.63 Ma (million years ago) to 5.333 Ma.
The ...
/Early Pliocene
Early may refer to:
History
* The beginning or oldest part of a defined historical period, as opposed to middle or late periods, e.g.:
** Early Christianity
** Early modern Europe
Places in the United States
* Early, Iowa
* Early, Texas
* Early ...
of Lime Creek, U.S.). The former is probably a basal turkey
Basal or basilar is a term meaning ''base'', ''bottom'', or ''minimum''.
Science
* Basal (anatomy), an anatomical term of location for features associated with the base of an organism or structure
* Basal (medicine), a minimal level that is nece ...
, the other a more contemporary bird not very similar to known turkeys; both were much smaller birds. A turkey fossil not assignable to genus but similar to ''Meleagris'' is known from the Late Miocene of Westmoreland County, Virginia. In the modern genus ''Meleagris'', a considerable number of species have been described, as turkey fossils are robust and fairly often found, and turkeys show great variation among individuals. Many of these supposed fossilized species are now considered junior synonyms. One, the well-documented California turkey ''Meleagris californica'', became extinct recently enough to have been hunted by early human settlers. It has been suggested that its demise was due to the combined pressures of human hunting and climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
at the end of the last glacial period.
The Oligocene
The Oligocene ( ) is a geologic epoch of the Paleogene Period and extends from about 33.9 million to 23 million years before the present ( to ). As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that define the epoch are well identified but ...
fossil ''Meleagris antiquus
''Paracrax'' ("near curassow") is a genus of extinct North American flightless birds, possibly related to modern seriemas and the extinct terror birds. Part of Bathornithidae (though some analysis recover it as closer to the living seriemas inste ...
'' was first described by Othniel Charles Marsh in 1871. It has since been reassigned to the genus '' Paracrax'', first interpreted as a cracid, then soon after as a bathornithid Cariamiformes.
Fossil species
* ''Meleagris'' sp. (Early Pliocene of Bone Valley, U.S.) * ''Meleagris'' sp. (Late Pliocene of Macasphalt Shell Pit, U.S.) * '' Meleagris californica'' (Late Pleistocene of southwestern U.S.)formerly ''Parapavo/Pavo'' * ''Meleagris crassipes'' (Late Pleistocene of southwestern North America) Turkeys have been considered by many authorities to be their own family—the Meleagrididae—but a recent genomic analysis of a retrotransposon marker groups turkeys in the familyPhasianidae
The Phasianidae are a family of heavy, ground-living birds, which includes pheasants, partridges, junglefowl, chickens, turkeys, Old World quail, and peafowl. The family includes many of the most popular gamebirds. The family is a large one and i ...
. In 2010, a team of scientists published a draft sequence of the domestic turkey (''Meleagris gallopavo'') genome.
Anatomy
 In anatomical terms, a ''snood'' is an erectile, fleshy protuberance on the forehead of turkeys. Most of the time when the turkey is in a relaxed state, the snood is pale and 2–3 cm long. However, when the male begins strutting (the courtship display), the snood engorges with blood, becomes redder and elongates several centimeters, hanging well below the beak (see image).
Snoods are just one of the caruncles (small, fleshy excrescences) that can be found on turkeys.
While fighting, commercial turkeys often peck and pull at the snood, causing damage and bleeding. This often leads to further injurious pecking by other turkeys and sometimes results in
In anatomical terms, a ''snood'' is an erectile, fleshy protuberance on the forehead of turkeys. Most of the time when the turkey is in a relaxed state, the snood is pale and 2–3 cm long. However, when the male begins strutting (the courtship display), the snood engorges with blood, becomes redder and elongates several centimeters, hanging well below the beak (see image).
Snoods are just one of the caruncles (small, fleshy excrescences) that can be found on turkeys.
While fighting, commercial turkeys often peck and pull at the snood, causing damage and bleeding. This often leads to further injurious pecking by other turkeys and sometimes results in cannibalism
Cannibalism is the act of consuming another individual of the same species as food. Cannibalism is a common ecological interaction in the animal kingdom and has been recorded in more than 1,500 species. Human cannibalism is well documented, b ...
. To prevent this, some farmers cut off the snood when the chick is young, a process known as "de-snooding".
The snood can be between in length depending on the turkey's sex, health, and mood.
Function
The snood functions in both intersexual and intrasexualselection
Selection may refer to:
Science
* Selection (biology), also called natural selection, selection in evolution
** Sex selection, in genetics
** Mate selection, in mating
** Sexual selection in humans, in human sexuality
** Human mating strat ...
. Captive female wild turkeys prefer to mate with long-snooded males, and during dyadic
Dyadic describes the interaction between two things, and may refer to:
*Dyad (sociology), interaction between a pair of individuals
**The dyadic variation of Democratic peace theory
*Dyadic counterpoint, the voice-against-voice conception of polyp ...
interactions, male turkeys defer to males with relatively longer snoods. These results were demonstrated using both live males and controlled artificial models of males. Data on the parasite burdens of free-living wild turkeys revealed a negative correlation between snood length and infection
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable d ...
with intestinal coccidia, deleterious protozoan parasites. This indicates that in the wild, the long-snooded males preferred by females and avoided by males seemed to be resistant to coccidial infection.
Use by humans
Mexico
Mexico ( Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guate ...
from at least 800 BC onwards. By 200 BC, the indigenous people of what is today the American Southwest
The Southwestern United States, also known as the American Southwest or simply the Southwest, is a geographic and cultural region of the United States that generally includes Arizona, New Mexico, and adjacent portions of California, Colorado ...
had domesticated turkeys; though the theory that they were introduced from Mexico was once influential, modern studies suggest that the turkeys of the Southwest were domesticated independently from those in Mexico. Turkeys were used both as a food source and for their feathers and bones, which were used in both practical and cultural contexts. Compared to wild turkeys, domestic turkeys are selectively bred to grow larger in size for their meat.
Turkey forms a central part of modern Thanksgiving
Thanksgiving is a national holiday celebrated on various dates in the United States, Canada, Grenada, Saint Lucia, Liberia, and unofficially in countries like Brazil and Philippines. It is also observed in the Netherlander town of Leiden ...
celebrations in the United States of America
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territor ...
, and is often eaten at similar holiday occasions, such as Christmas
Christmas is an annual festival commemorating the birth of Jesus Christ, observed primarily on December 25 as a religious and cultural celebration among billions of people around the world. A feast central to the Christian liturgical year ...
.
The Norfolk turkeys
In her memoirs,Lady Dorothy Nevill
Lady Dorothy Fanny Nevill (née Walpole; 1 April 1826 in London – 24 March 1913 in London) was an English writer, hostess, horticulturist and plant collector.
She was one of five children of Horatio Walpole, 3rd Earl of Orford and Mary Fawken ...
(1826–1913) recalls that her great-grandfather Horatio Walpole, 1st Earl of Orford (1723–1809), imported a quantity of American turkeys which were kept in the woods around Wolterton Hall and in all probability were the embryo flock for the popular Norfolk turkey breeds of today.
Gallery
wild turkey
The wild turkey (''Meleagris gallopavo'') is an upland ground bird native to North America, one of two extant species of turkey and the heaviest member of the order Galliformes. It is the ancestor to the domestic turkey, which was originally ...
''(Meleagris gallopavo)'' strutting (spreading its feathers) in a field
References
External links
* * {{Taxonbar, from=Q43794 Birds described in 1758 Extant Miocene first appearances Game birds Meleagris Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus