Tunis Light Metro on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Tunis Light Metro (, meaning Tunis light rail, , ''el-metrū el-khfīf li-mdīnat tūnis'') is the
/ref> The ''Société du métro léger de Tunis'' (SMLT) was founded in 1981 to manage the operation. Public transport is overseen by Tunisia’s Ministry of Transport, with constituent bodies operating the various modes. The Société Nationale des Chemins de Fer Tunisiens (SNCFT) has continued development of the heavy rail standard and metre gauge routes, initiated under French control, with the operation centred on Tunis. Tunis is set on low-lying land around several lakes just inland from the Mediterranean Sea coast. The heart of the city, the Medina, has a street pattern that long pre-dates the industrial era or motorised transport. In 2003, the city’s road and rail public transport modes came together under the jurisdiction of the Société des Transports de Tunis, operating under the Transtu name. Accounting for almost three-quarters of revenue (2006), the company operates 217 bus routes over with a fleet of 1,114 vehicles. As with most other large cities, road congestion is a feature of Tunis, although the challenge for public transport is as much about increasing the capacity of their already well-used services as it is about stemming the rise in car use. Construction on Line 1 started in 1981, and passenger services commenced in 1985. In 1989, Line 2 became operational, with Lines 3 and 4 following the next year. Line 5 became operative in 1992, while in the same year, Line 3 was extended to its current length. In 1997, the extension of Line 4 was inaugurated, and further construction for an extension to La Manouba began in 2007. The '' Société des transports de Tunis'' took over management in 2003; it was formed by joining the SMLT and the ''Société nationale de transports'' (SNT, founded in 1963) that was responsible for the TGM railway. A new Line 6 was planned to link Tunis with El Mourouj and its construction began in 2005. This new line was completed in 2009. New
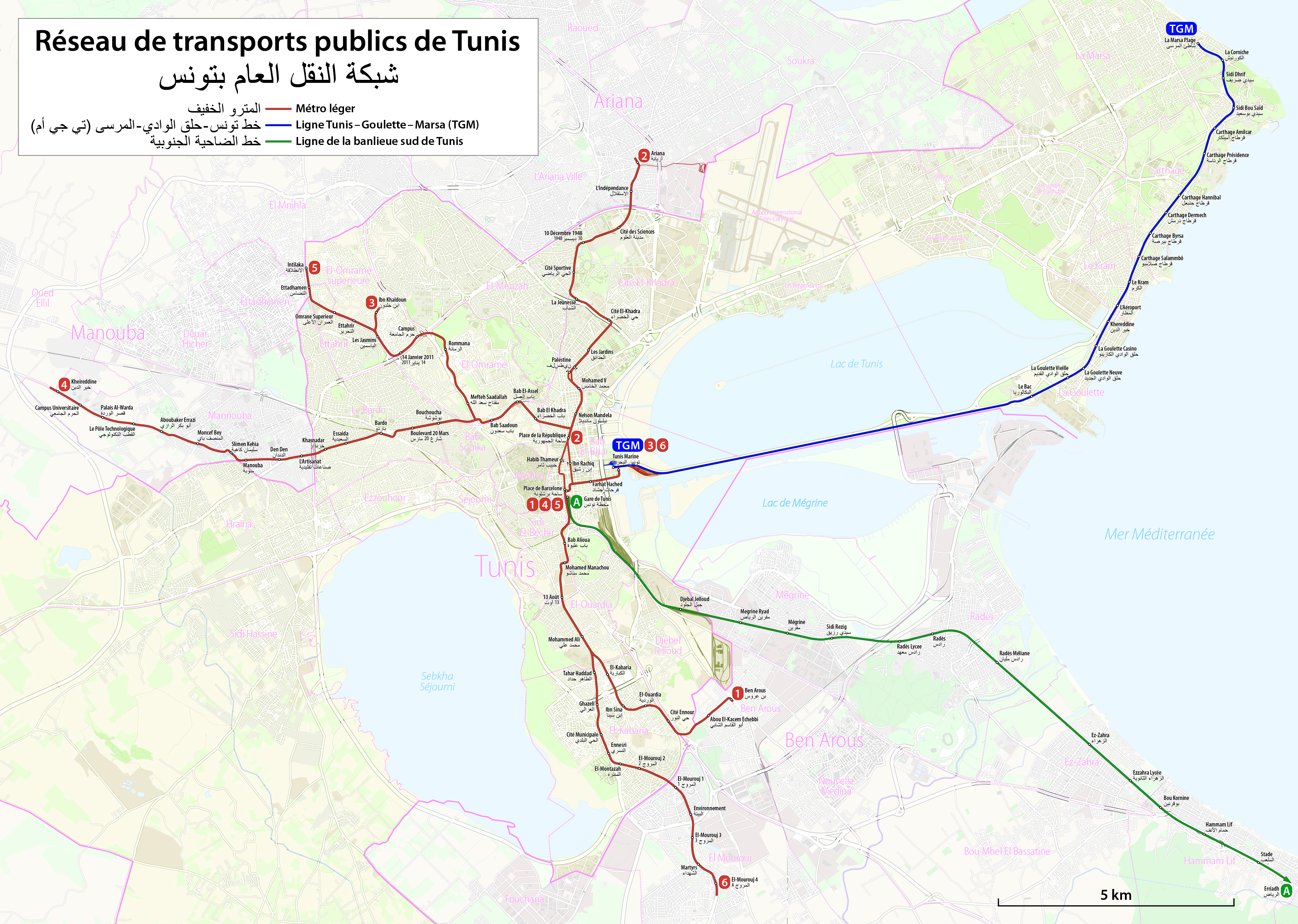
 With the city set for continuing population growth, preliminary studies for light rail, the Métro Léger, began in 1974. A Siemens-led consortium won the contract to create the 1,435mm, overhead supply surface network. Line 1,
With the city set for continuing population growth, preliminary studies for light rail, the Métro Léger, began in 1974. A Siemens-led consortium won the contract to create the 1,435mm, overhead supply surface network. Line 1,
Official site of the ''Société des transports de Tunis''
{{DEFAULTSORT:Metro Leger Rapid transit in Tunisia Tram transport in Tunisia Transport in Tunis 750 V DC railway electrification Railway lines opened in 1985 Standard-gauge railways in Tunisia
light rail
Light rail (or light rail transit, abbreviated to LRT) is a form of passenger urban rail transit that uses rolling stock derived from tram technology National Conference of the Transportation Research Board while also having some features from ...
network serving the Tunis
Tunis (, ') is the capital city, capital and largest city of Tunisia. The greater metropolitan area of Tunis, often referred to as "Grand Tunis", has about 2,700,000 inhabitants. , it is the third-largest city in the Maghreb region (after Casabl ...
metropolitan area. It began operation in 1985.
Tunis's light rail system has its track at a surface level generally with its rail bed, but at key intersections, the system goes underground to avoid congestion or has the right of way
A right of way (also right-of-way) is a specific route that people, animals, vehicles, watercraft, or utility lines travel, or the legal status that gives them the right to do so. Rights-of-way in the physical sense include controlled-access h ...
. Together with the TGM commuter rail line, it is managed by the parastatal
A state-owned enterprise (SOE) is a business entity created or owned by a national or local government, either through an executive order or legislation. SOEs aim to generate profit for the government, prevent private sector monopolies, provide goo ...
transport authority Société des transports de Tunis (''Transtu'').
While some African cities once had traditional electric tram
A tram (also known as a streetcar or trolley in Canada and the United States) is an urban rail transit in which Rolling stock, vehicles, whether individual railcars or multiple-unit trains, run on tramway tracks on urban public streets; some ...
systems, all but the Alexandria Tram
The Alexandria tramway network serves the city of Alexandria, Egypt. It began operating in 1863 and consists of 20 lines operating on of the track, serving 140 stops. It is one of only a few tram systems in the world that uses double-deck cars; ...
were discontinued. The Tunis modern light rail system was originally unique in Africa, but there are now modern trams in Algeria and Morocco
Morocco, officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It has coastlines on the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to Algeria–Morocc ...
, as well.
History
Tunis had an older electrictram
A tram (also known as a streetcar or trolley in Canada and the United States) is an urban rail transit in which Rolling stock, vehicles, whether individual railcars or multiple-unit trains, run on tramway tracks on urban public streets; some ...
system that, like in many cities, eventually was dismantled. With the post-war growth of the metropolitan area and the traffic congestion that followed, the need for a commuter transportation system became evident. The city eventually decided to link the suburbs to the city centre with a modern network of light rail. Preliminary studies were undertaken in 1974. The system was delivered as a turnkey
A turnkey, a turnkey project, or a turnkey operation (also spelled turn-key) is a type of project that is constructed so that it can be sold to any buyer as a completed product. This is contrasted with build to order, where the constructor builds ...
operation by a consortium led by Siemens
Siemens AG ( ) is a German multinational technology conglomerate. It is focused on industrial automation, building automation, rail transport and health technology. Siemens is the largest engineering company in Europe, and holds the positi ...
.Urbanrail.net information page/ref> The ''Société du métro léger de Tunis'' (SMLT) was founded in 1981 to manage the operation. Public transport is overseen by Tunisia’s Ministry of Transport, with constituent bodies operating the various modes. The Société Nationale des Chemins de Fer Tunisiens (SNCFT) has continued development of the heavy rail standard and metre gauge routes, initiated under French control, with the operation centred on Tunis. Tunis is set on low-lying land around several lakes just inland from the Mediterranean Sea coast. The heart of the city, the Medina, has a street pattern that long pre-dates the industrial era or motorised transport. In 2003, the city’s road and rail public transport modes came together under the jurisdiction of the Société des Transports de Tunis, operating under the Transtu name. Accounting for almost three-quarters of revenue (2006), the company operates 217 bus routes over with a fleet of 1,114 vehicles. As with most other large cities, road congestion is a feature of Tunis, although the challenge for public transport is as much about increasing the capacity of their already well-used services as it is about stemming the rise in car use. Construction on Line 1 started in 1981, and passenger services commenced in 1985. In 1989, Line 2 became operational, with Lines 3 and 4 following the next year. Line 5 became operative in 1992, while in the same year, Line 3 was extended to its current length. In 1997, the extension of Line 4 was inaugurated, and further construction for an extension to La Manouba began in 2007. The '' Société des transports de Tunis'' took over management in 2003; it was formed by joining the SMLT and the ''Société nationale de transports'' (SNT, founded in 1963) that was responsible for the TGM railway. A new Line 6 was planned to link Tunis with El Mourouj and its construction began in 2005. This new line was completed in 2009. New
Alstom Citadis
The Alstom Citadis is a family of low-floor trams and light rail vehicles built by Alstom. , over 2,300 Citadis trams have been sold and 1,800 tramways are in revenue service throughout the world, with operations in all six inhabited continents ...
trams to supplement the earlier Siemens trams were introduced in 2007.
Network

Line 1
;Place de Barcelone – Ben Arous *''Opened: 1985'' *''Number of stations: 11 '' Line 1 is the oldest and it is the shortest line compared to the 5 other lines. It has 11 stations. Work on line 1, which began in 1981, was completed with the commissioning of the line (towards Ben Arous) in 1985. The connection between bus lines and line 1 at the El Ouardia station was put in place a year later, in 1986.Line 2
;Place de la République – Ariana *''Opened: 1989'' *''Number of stations: 12 '' Line 2 is the oldest and it is the shortest line after Line 1. It has 12 stations. Construction on Line 2 started in 1981 and passenger services commenced in 1989.Line 3
;Tunis Marine – Ibn Khaldoun *''Opened: 1990'' *''Number of stations: 14 '' Line 3 is composed of 14 stations and passenger services commenced in 1990. In 2017, the Tunis Transport Company announced the removal of the Habib-Thameur station following a fire that destroyed the ticket sales point. The station ofTunis Marine
Tunis Marine is a railway station in Tunis, the capital of Tunisia, and forms the southern terminus of the standard gauge Tunis-Goulette-Marsa, Tunis-Goulette-Marsa railway or "TGM", which was inaugurated in 1872. The line and the station are man ...
has also a line of TGM. It's the only station that is both a Metro station and a TGM station.
Line 4
;Place de Barcelone – Kheireddine *''Opened: 1990'' *''Number of stations: 20 '' Line 4 is the longest compared to the other 5 lines. It has 20 stations and passenger services commenced in 1990.Line 5
;Place de Barcelone – Intilaka *''Opened: 1992'' *''Number of stations: 14 '' Line 5 has 14 stations since 2017 after a fire that burned the Habib-Thameur station. The line links important locations such as the campus of the University of El Manar and Bab Saadoun.Line 6
;Place de Barcelone – Intilaka *''Opened: 2008'' *''Number of stations: 18 '' Line 6 has 18 stations and is the longest line after line 4. On 12 November 2008, the new line 6 (6.8 kilometers long and initially serving eleven stations between Place de Barcelona and El Mourouj 4) came into service after work on the line had started in 2005. Like line 3, line 6 has a TGM line inTunis Marine
Tunis Marine is a railway station in Tunis, the capital of Tunisia, and forms the southern terminus of the standard gauge Tunis-Goulette-Marsa, Tunis-Goulette-Marsa railway or "TGM", which was inaugurated in 1872. The line and the station are man ...
station.
Infrastructure
Tunis Marine
Tunis Marine is a railway station in Tunis, the capital of Tunisia, and forms the southern terminus of the standard gauge Tunis-Goulette-Marsa, Tunis-Goulette-Marsa railway or "TGM", which was inaugurated in 1872. The line and the station are man ...
(also the city terminus for the TGM) to Ben Arous
Ben Arous ( ) is a city in north-eastern Tunisia, part the agglomeration of Tunis, also called Grand Tunis. It is located south of Tunis city center and is the capital of the Ben Arous Governorate.
Information about Ben Arous
East Ben Arous i ...
in the south, opened in 1985.
Tram vehicles
By 2006, 136 articulated passenger trams were in operation. They were built bySiemens
Siemens AG ( ) is a German multinational technology conglomerate. It is focused on industrial automation, building automation, rail transport and health technology. Siemens is the largest engineering company in Europe, and holds the positi ...
and delivered between 1984 and 1997. These trams were derived from the TW 6000
The TW 6000 is a type of articulated light rail vehicle used on the Hanover Stadtbahn system, manufactured by Duewag, Linke-Hofmann-Busch, AEG, Kiepe and Siemens.
The vehicle can serve both high platforms and street-level stops; it has cabs a ...
originally developed for Hanover Stadtbahn
Hanover Stadtbahn is a light urban rail transport (Stadtbahn, ) system in the city of Hanover, the capital of Lower Saxony, Germany. It opened on 29 September 1975, gradually replacing the city's tramway () network over the course of the subsequ ...
. The bi-directional trams are powered via a 750 V DC overhead wire and run on a track. The trams have a green livery with white and blue lines. Each tram consists of two units each of which has:
* bogies typ Bo-2-2-Bo
* electric motors 2 x 240 kW
* weight of 40.3 tonnes
* length of 30 meters
* width of 2.47 meters
* access from low and high platforms
In 2004, an agreement between the French and Tunisian governments led to the order of 30 new Alstom Citadis
The Alstom Citadis is a family of low-floor trams and light rail vehicles built by Alstom. , over 2,300 Citadis trams have been sold and 1,800 tramways are in revenue service throughout the world, with operations in all six inhabited continents ...
trams. Each tram consists of two units 64 metres in length and can hold 208 people standing and 58 sitting places. The first such trams started to operate on 17 September 2007. 16 more trams were ordered from Alstom in July 2010.
See also
* List of Tunis Metro stations *List of town tramway systems in Africa
This is a list of African cities and towns that have, or once had, town tramway (urban tramway, or streetcar) systems as part of their public transport system.
Algeria
Democratic Republic of the Congo
Egypt
Eritrea
Ethiopia
Ghana
...
* Réseau Ferroviaire Rapide
* Transport in Tunisia
Tunisia has a number of international airports to service its sizable tourist trade. Tunis is the center of the transport system as the largest city having the largest port and a light transit system.
Railways
Tunisia inherited much of its r ...
References
External links
Official site of the ''Société des transports de Tunis''
{{DEFAULTSORT:Metro Leger Rapid transit in Tunisia Tram transport in Tunisia Transport in Tunis 750 V DC railway electrification Railway lines opened in 1985 Standard-gauge railways in Tunisia