Tundra Orbit on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A Tundra orbit () is a highly elliptical
A Tundra orbit () is a highly elliptical
 Russia currently uses satellites in the Tundra orbit. The EKS (Edinaya Kosmicheskaya Sistema) or Kupol system, which is part of Russia's early warning satellite network, includes satellites that operate in Tundra orbits. These satellites are designed to detect and track ballistic missile launches and provide early warning of potential missile attacks.
From 2000 to 2016,
Russia currently uses satellites in the Tundra orbit. The EKS (Edinaya Kosmicheskaya Sistema) or Kupol system, which is part of Russia's early warning satellite network, includes satellites that operate in Tundra orbits. These satellites are designed to detect and track ballistic missile launches and provide early warning of potential missile attacks.
From 2000 to 2016,
 A Tundra orbit () is a highly elliptical
A Tundra orbit () is a highly elliptical geosynchronous orbit
A geosynchronous orbit (sometimes abbreviated GSO) is an Earth-centered orbit with an orbital period that matches Earth's rotation on its axis, 23 hours, 56 minutes, and 4 seconds (one sidereal day). The synchronization of rotation and orbital ...
with a high inclination
Orbital inclination measures the tilt of an object's orbit around a celestial body. It is expressed as the angle between a reference plane and the orbital plane or axis of direction of the orbiting object.
For a satellite orbiting the Eart ...
(approximately 63.4°), an orbital period
The orbital period (also revolution period) is the amount of time a given astronomical object takes to complete one orbit around another object. In astronomy, it usually applies to planets or asteroids orbiting the Sun, moons orbiting planets ...
of one sidereal day
Sidereal time ("sidereal" pronounced ) is a system of timekeeping used especially by astronomers. Using sidereal time and the celestial coordinate system, it is easy to locate the positions of celestial objects in the night sky. Sidereal t ...
, and a typical eccentricity
Eccentricity or eccentric may refer to:
* Eccentricity (behavior), odd behavior on the part of a person, as opposed to being "normal"
Mathematics, science and technology Mathematics
* Off-Centre (geometry), center, in geometry
* Eccentricity (g ...
between 0.2 and 0.3. A satellite
A satellite or an artificial satellite is an object, typically a spacecraft, placed into orbit around a celestial body. They have a variety of uses, including communication relay, weather forecasting, navigation ( GPS), broadcasting, scient ...
placed in this orbit spends most of its time over a chosen area of the Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all ...
, a phenomenon known as apogee dwell, which makes them particularly well suited for communications satellites
A communications satellite is an artificial satellite that relays and amplifies radio telecommunication signals via a transponder; it creates a communication channel between a source transmitter and a receiver at different locations on Earth. ...
serving high-latitude regions.
The Tundra orbit, like the Molniya orbit
A Molniya orbit ( rus, Молния, p=ˈmolnʲɪjə, a=Ru-молния.ogg, "Lightning") is a type of satellite orbit designed to provide communications and remote sensing coverage over high latitudes. It is a highly elliptical orbit with ...
, was developed by Soviet scientists. The Molniya orbit was specifically designed in the 1960s to provide better communication coverage for high-latitude regions, which geostationary satellites struggled to cover effectively. The Tundra orbit, while similar in its high inclination and elliptical shape, was developed later to offer continuous coverage over specific areas by having satellites spend most of their time over a chosen region. Both orbits were innovative solutions to the unique challenges posed by the Soviet Union's geographical location and the need for reliable communication and surveillance capabilities.
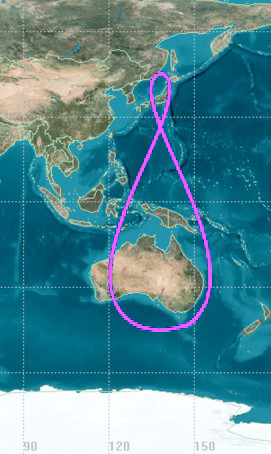
The ground track
A satellite ground track or satellite ground trace is the path on the surface of a planet directly below a satellite's trajectory. It is also known as a suborbital track or subsatellite track, and is the vertical projection of the satellite's ...
of a satellite in a Tundra orbit is a closed figure 8 with a smaller loop over either the northern or southern hemisphere. This differentiates them from Molniya orbit
A Molniya orbit ( rus, Молния, p=ˈmolnʲɪjə, a=Ru-молния.ogg, "Lightning") is a type of satellite orbit designed to provide communications and remote sensing coverage over high latitudes. It is a highly elliptical orbit with ...
s designed to service high-latitude regions, which have the same inclination but half the period and do not loiter over a single region.
Uses
Tundra and Molniya orbits are used to provide high-latitude
In geography, latitude is a geographic coordinate system, geographic coordinate that specifies the north-south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from −90° at t ...
users with higher elevation
The elevation of a geographic location (geography), ''location'' is its height above or below a fixed reference point, most commonly a reference geoid, a mathematical model of the Earth's sea level as an equipotential gravitational equipotenti ...
angles than a geostationary orbit
A geostationary orbit, also referred to as a geosynchronous equatorial orbit''Geostationary orbit'' and ''Geosynchronous (equatorial) orbit'' are used somewhat interchangeably in sources. (GEO), is a circular orbit, circular geosynchronous or ...
. This is desirable as broadcasting to these latitudes from a geostationary orbit (above the Earth's equator
The equator is the circle of latitude that divides Earth into the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Southern Hemisphere, Southern Hemispheres of Earth, hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, about in circumferen ...
) requires considerable power due to the low elevation angles, and the extra distance and atmospheric attenuation that comes with it. Sites located above 81° latitude are unable to view geocentric satellites at all, and as a rule of thumb, elevation angles of less than 10° can cause problems, depending on the communications frequency.
Highly elliptical orbits provide an alternative to geostationary ones, as they remain over their desired high-latitude regions for long periods of time at the apogee. Their convenience is mitigated by cost, however: two satellites are required to provide continuous coverage from a Tundra orbit (three from a Molniya orbit).
A ground station receiving data from a satellite constellation in a highly elliptical orbit must periodically switch between satellites and deal with varying signal strengths, latency and Doppler shift
The Doppler effect (also Doppler shift) is the change in the frequency of a wave in relation to an observer who is moving relative to the source of the wave. The ''Doppler effect'' is named after the physicist Christian Doppler, who described t ...
s as the satellite's range changes throughout its orbit. These changes are less pronounced for satellites in a Tundra orbit, given their increased distance from the surface, making tracking and communication more efficient. Additionally, unlike the Molniya orbit, a satellite in a Tundra orbit avoids passing through the Van Allen belts
The Van Allen radiation belt is a zone of energy, energetic charged particles, most of which originate from the solar wind, that are captured by and held around a planet by that planet's magnetosphere. Earth has two such belts, and sometimes ot ...
.
Despite these advantages the Tundra orbit is used less often than a Molniya orbit in part due to the higher launch energy required.
Proposed uses
In 2017 the ESA Space Debris office released a paper proposing that a Tundra-like orbit be used as a disposal orbit for old high-inclination geosynchronous satellites, as opposed to traditionalgraveyard orbit
A graveyard orbit, also called a junk orbit or disposal orbit, is an Orbit (physics), orbit that lies away from common operational orbits. One significant graveyard orbit is a supersynchronous orbit well beyond geosynchronous orbit. Some satellit ...
s.
Properties
A typical Tundra orbit has the following properties: * Inclination: 63.4° * Argument of perigee: 270° * Period: 1436 minutes * Eccentricity: 0.24–0.4 * Semi-major axis:Orbital inclination
In general, theoblateness
Flattening is a measure of the compression of a circle or sphere along a diameter to form an ellipse or an ellipsoid of revolution (spheroid) respectively. Other terms used are ellipticity, or oblateness. The usual notation for flattening is f ...
of the Earth perturbs a satellite's argument of perigee () such that it gradually changes with time. If we only consider the first-order coefficient , the perigee will change according to equation , unless it is constantly corrected with station-keeping thruster burns.
where is the orbital inclination, is the eccentricity, is mean motion in degrees per day, is the perturbing factor, is the radius of the Earth, is the semimajor axis, and is in degrees per day.
To avoid this expenditure of fuel, the Tundra orbit uses an inclination of 63.4°, for which the factor is zero, so that there is no change in the position of perigee over time. This is called the critical inclination, and an orbit designed in this manner is called a frozen orbit
In orbital mechanics, a frozen orbit is an orbit for an artificial satellite in which perturbations have been minimized by careful selection of the orbital parameters. Perturbations can result from natural drifting due to the central body's shap ...
.
Argument of perigee
An argument of perigee of 270° places apogee at the northernmost point of the orbit. An argument of perigee of 90° would likewise serve the high southern latitudes. An argument of perigee of 0° or 180° would cause the satellite to dwell over the equator, but there would be little point to this as this could be better done with a conventionalgeostationary orbit
A geostationary orbit, also referred to as a geosynchronous equatorial orbit''Geostationary orbit'' and ''Geosynchronous (equatorial) orbit'' are used somewhat interchangeably in sources. (GEO), is a circular orbit, circular geosynchronous or ...
.
Period
The period of one sidereal day ensures that the satellites follows the same ground track over time. This is controlled by the semi-major axis of the orbit.Eccentricity
The eccentricity is chosen for the dwell time required, and changes the shape of the ground track. A Tundra orbit generally has an eccentricity of about 0.2; one with an eccentricity of about 0.4, changing the ground track from a figure 8 to a teardrop, is called a Supertundra orbit.Semi-major axis
The exact height of a satellite in a Tundra orbit varies between missions, but a typical orbit will have a perigee of approximately and an apogee of , for a semi-major axis of .Spacecraft using Tundra orbits
 Russia currently uses satellites in the Tundra orbit. The EKS (Edinaya Kosmicheskaya Sistema) or Kupol system, which is part of Russia's early warning satellite network, includes satellites that operate in Tundra orbits. These satellites are designed to detect and track ballistic missile launches and provide early warning of potential missile attacks.
From 2000 to 2016,
Russia currently uses satellites in the Tundra orbit. The EKS (Edinaya Kosmicheskaya Sistema) or Kupol system, which is part of Russia's early warning satellite network, includes satellites that operate in Tundra orbits. These satellites are designed to detect and track ballistic missile launches and provide early warning of potential missile attacks.
From 2000 to 2016, Sirius Satellite Radio
Sirius Satellite Radio was a satellite radio ( SDARS) service that operated in the United States and Canada. Sirius launched in 2002, and primarily competed with XM Satellite Radio, until the two services merged in 2008 to form Sirius XM.
Li ...
, now part of Sirius XM Holdings
Sirius XM Holdings Inc. is an American broadcasting corporation headquartered in Midtown Manhattan, New York City, that provides satellite radio and online radio services operating in the United States. The company was formed by the 2008 merge ...
, operated a constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object.
The first constellati ...
of three satellites in Tundra orbits for satellite radio
Satellite radio is defined by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU)'s ITU Radio Regulations (RR) as a '' broadcasting-satellite service''. The satellite's signals are broadcast nationwide, across a much wider geographical area than te ...
. The RAAN and mean anomaly
In celestial mechanics, the mean anomaly is the fraction of an elliptical orbit's period that has elapsed since the orbiting body passed periapsis, expressed as an angle which can be used in calculating the position of that body in the classical ...
of each satellite were offset by 120° so that when one satellite moved out of position, another had passed perigee and was ready to take over. The constellation was developed to better reach consumers in far northern latitudes, reduce the impact of urban canyons and required only 130 repeaters compared to 800 for a geostationary system. After Sirius' merger with XM it changed the design and orbit of the FM-6 replacement satellite from a tundra to a geostationary one. This supplemented the already geostationary FM-5 (launched 2009), and in 2016 Sirius discontinued broadcasting from tundra orbits. The Sirius satellites were the only commercial satellites to use a Tundra orbit.
The Japanese Quasi-Zenith Satellite System
The , also known as , is a four-satellite regional satellite navigation system and a GNSS augmentation#Satellite-based augmentation system, satellite-based augmentation system developed by the Japanese government to enhance the United States ...
uses a geosynchronous orbit similar to a Tundra orbit, but with an inclination of only 43°. It includes four satellites following the same ground track. It was tested from 2010 and became fully operational in November 2018.
Proposed systems
The Tundra orbit has been considered for use by the ESA's Archimedes project, a broadcasting system proposed in the 1990s.See also
*Elliptic orbit
In astrodynamics or celestial mechanics, an elliptical orbit or eccentric orbit is an orbit with an eccentricity of less than 1; this includes the special case of a circular orbit, with eccentricity equal to 0. Some orbits have been referre ...
* List of orbits
This is a list of types of gravitational orbit classified by various characteristics.
Common abbreviations
List of abbreviations of common Earth orbits
List of abbreviations of other orbits
Classifications
The following is a list of t ...
* Molniya orbit
A Molniya orbit ( rus, Молния, p=ˈmolnʲɪjə, a=Ru-молния.ogg, "Lightning") is a type of satellite orbit designed to provide communications and remote sensing coverage over high latitudes. It is a highly elliptical orbit with ...
References
{{Portal bar, Astronomy, Stars, Spaceflight, Outer space, Solar System Earth orbits Satellite broadcasting