Tropical Rain Belt on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Rainfall and the
/ref> This causes the air at ground level in the tropics to warm up. Because hot air is less dense than cold air, the hot air rises into the upper levels of the
tropical climate
Tropical climate is the first of the five major climate groups in the Köppen climate classification identified with the letter A. Tropical climates are defined by a monthly average temperature of or higher in the coolest month, featuring hot te ...
dominate the tropical
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the equator, where the sun may shine directly overhead. This contrasts with the temperate or polar regions of Earth, where the Sun can never be directly overhead. This is because of Earth's ax ...
rain belt, which oscillates from the northern to the southern tropics
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the equator, where the sun may shine directly overhead. This contrasts with the temperate or polar regions of Earth, where the Sun can never be directly overhead. This is because of Earth's ax ...
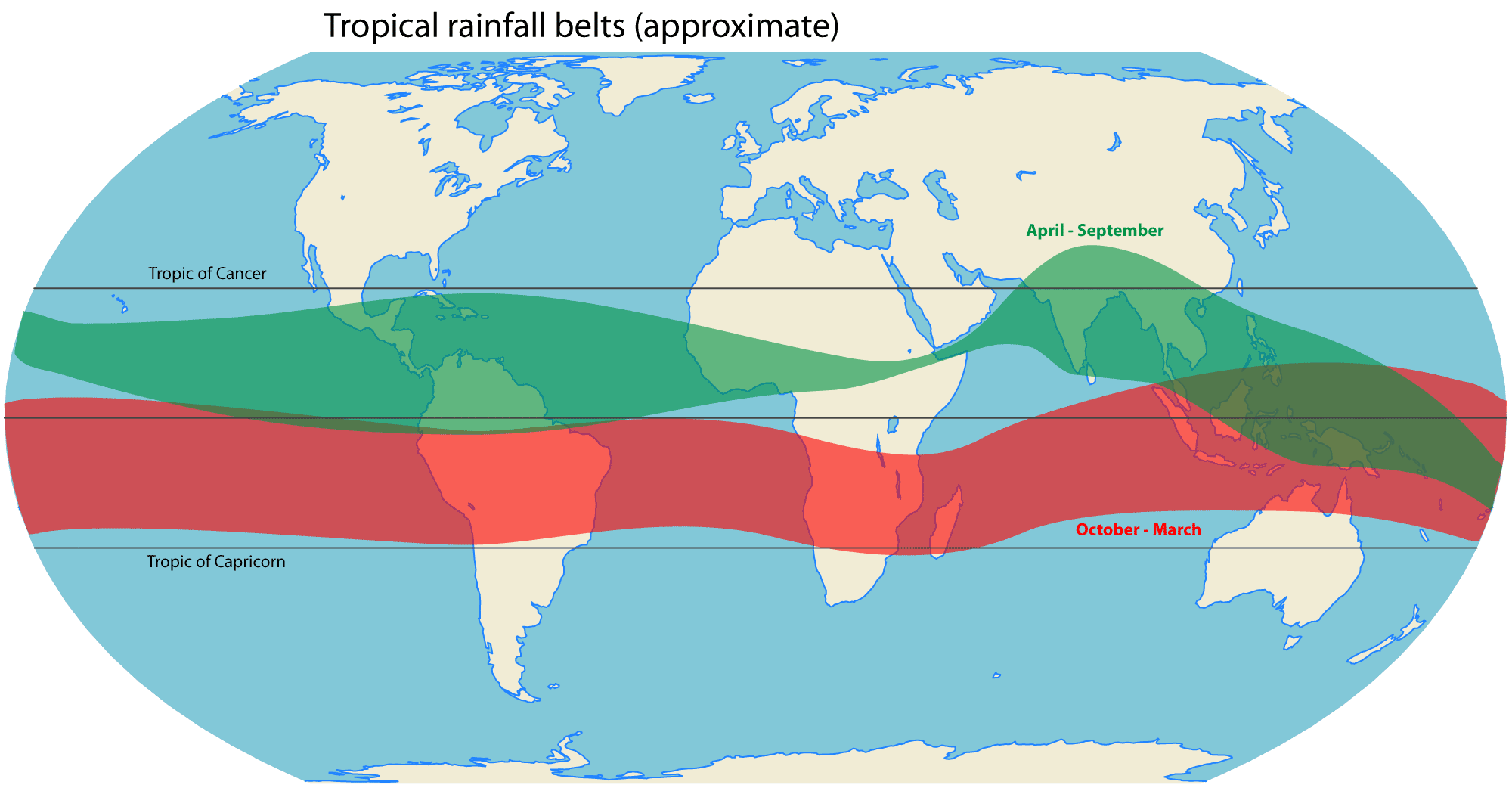
over the course of the year, roughly following the solar equator. The tropical rain belt is an area of active rain that is positioned mostly around the tropics.
Mechanism
The reason the rain belt is situated near the tropics can be attributed to the fact that the Sun's radiation is strongest near the equator, which is located in the middle of the tropics. Thissolar radiation
Sunlight is the portion of the electromagnetic radiation which is emitted by the Sun (i.e. solar radiation) and received by the Earth, in particular the visible light perceptible to the human eye as well as invisible infrared (typically p ...
generates large amounts of heat near the equator.Annual Migration of Tropical Rain Belt/ref> This causes the air at ground level in the tropics to warm up. Because hot air is less dense than cold air, the hot air rises into the upper levels of the
atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gases that envelop an astronomical object, held in place by the gravity of the object. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A stellar atmosph ...
, cooling as it rises.
However, cooler air cannot hold as much moisture as hot air, so when the air rises and cools, its water condenses, forming clouds which cause rain in the form of thunderstorms and rain showers.
Location
The tropical rain belt is located along theequator
The equator is the circle of latitude that divides Earth into the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Southern Hemisphere, Southern Hemispheres of Earth, hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, about in circumferen ...
, but they will extend out to the Tropic of Cancer
The Tropic of Cancer, also known as the Northern Tropic, is the Earth's northernmost circle of latitude where the Sun can be seen directly overhead. This occurs on the June solstice, when the Northern Hemisphere is tilted toward the Sun ...
, which is the 23.5 north latitude, as well as the Tropic of Capricorn, which is the 23.5 south latitude. It moves north in the Northern hemisphere summer and south in the Northern hemisphere winter, following the thermal equator where temperatures are highest at each point in the year. It is a manifestation of the Intertropical Convergence Zone
The Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ , or ICZ), known by sailors as the doldrums or the calms because of its monotonous windless weather, is the area where the northeast and the southeast trade winds converge. It encircles Earth near the t ...
.
The tropical rain belt lies in the southern hemisphere of the Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or approximately 20% of the water area of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia (continent), ...
and western Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five Borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is ...
roughly from October to March, and during this time the northern tropics experience a dry season
The dry season is a yearly period of low rainfall, especially in the tropics. The weather in the tropics is dominated by the tropical rain belt, which moves from the northern to the southern tropics and back over the course of the year. The t ...
in which precipitation is very rare, and days are typically hot and sunny throughout. From April to September, the rain belt lies in the northern hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of Earth that is north of the equator. For other planets in the Solar System, north is defined by humans as being in the same celestial sphere, celestial hemisphere relative to the invariable plane of the Solar ...
, and a wet season
The wet season (sometimes called the rainy season or monsoon season) is the time of year when most of a region's average annual rainfall occurs. Generally, the season lasts at least one month. The term ''green season'' is also sometimes used a ...
occurs there, while the southern tropics experience their dry season
The dry season is a yearly period of low rainfall, especially in the tropics. The weather in the tropics is dominated by the tropical rain belt, which moves from the northern to the southern tropics and back over the course of the year. The t ...
.
The rain belt reaches roughly as far north as the Tropic of Cancer and as far south as the Tropic of Capricorn in the western Pacific Ocean. Its variation in the Western Hemisphere
The Western Hemisphere is the half of the planet Earth that lies west of the Prime Meridian (which crosses Greenwich, London, United Kingdom) and east of the 180th meridian.- The other half is called the Eastern Hemisphere. Geopolitically, ...
is minimal, roughly between the equator
The equator is the circle of latitude that divides Earth into the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Southern Hemisphere, Southern Hemispheres of Earth, hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, about in circumferen ...
and the 15th parallel north latitude
In geography, latitude is a geographic coordinate system, geographic coordinate that specifies the north-south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from −90° at t ...
. Near these latitudes, there is one wet season and one dry season annually. On the equator, there are two wet and two dry seasons as the rain belt passes over twice a year, one moving north and one moving south. Between the tropics and the equator, locations may experience both a short wet and a long wet season. Local geography may substantially modify these climate patterns.

Effects of climate change
As the earth warms, the rain belt is projected to move north of the current position. Recent climate change can be attributed to risingcarbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at norma ...
concentrations in the atmosphere; caused by the burning of fossil fuels
A fossil fuel is a flammable carbon compound- or hydrocarbon-containing material formed naturally in the Earth's crust from the buried remains of prehistoric organisms (animals, plants or microplanktons), a process that occurs within geologica ...
. The correlation between the concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere and average global temperature is undeniably direct, meaning that as more carbon dioxide is released into the atmosphere, the temperature of the Earth is expected to rise as well. Even though the Earth is warming as a whole entity, the Northern Hemisphere is warming faster than the Southern because of melting Arctic sea ice.
As the Northern Hemisphere warms, a temperature gradient is established between the Northern and Southern hemispheres. The warmer temperatures in the Northern parts of the tropics foster an environment more conducive to the development of moisture. The additional moisture is met with a low-level atmosphere that is cooler because the warm air has risen to the higher levels of the atmosphere.
This scenario leads to increased precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls from clouds due to gravitational pull. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, rain and snow mixed ("sleet" in Commonwe ...
and is a fundament behind the idea that the rain belt is moving north. The contrast in temperature is only a part of the entire process that is driving the tropical rain belt northward. Another factor that influences the tropical rain belt is ocean circulation. Ocean Overturning Circulation is a process that involves ocean circulation between the Antarctic
The Antarctic (, ; commonly ) is the polar regions of Earth, polar region of Earth that surrounds the South Pole, lying within the Antarctic Circle. It is antipodes, diametrically opposite of the Arctic region around the North Pole.
The Antar ...
and Arctic regions.
Dargan Frierson explains that in this process, the Northern Hemisphere receives more heat than the Southern because the overturning circulation brings more heat into the Northern Hemisphere as opposed to the Southern. He also states that as a result, the extra heat is transferred to the tropical regions in the Northern Hemisphere, causing warm ocean water to be situated in the northern tropics. This warm ocean water is what eventually generates rain and thunderstorms, and because there is more warm water in the northern tropics, it is obvious that the tropical rain belt is moving northward. Due to global climate change, the circulation of ocean currents and ocean temperatures might adjust in favor of pushing the belt further north into the region of oscillation.
However, there is also the possibility that climate change will slow down ocean currents and circulation, which can change the present-day dynamic and send the rain belt to the south. Therefore, ocean circulation, ocean temperature
The ocean temperature plays a crucial role in the global climate system, ocean currents and for marine habitats. It varies depending on depth, geographical location and season. Not only does the temperature differ in seawater, so does the salin ...
, and the temperature of the earth are all attributing to the movement of the tropical rain belt. It is evident that the trend is northward and the belt is currently situated in the northern tropics, but the possibility of southward movement does exist. The northward movement does affect many countries and crops because the tropical rain belt is essential to food production in areas that rely on heavy precipitation.
The tropical regions will be affected most by the northward movement of the rain. The banana and coffee crops in Guatemala
Guatemala, officially the Republic of Guatemala, is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the north and west by Mexico, to the northeast by Belize, to the east by Honduras, and to the southeast by El Salvador. It is hydrologically b ...
and Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania, between the Indian Ocean, Indian and Pacific Ocean, Pacific oceans. Comprising over List of islands of Indonesia, 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, ...
will become compromised by the loss of precipitation. In addition, the effects of a drier climate in Mexico
Mexico, officially the United Mexican States, is a country in North America. It is the northernmost country in Latin America, and borders the United States to the north, and Guatemala and Belize to the southeast; while having maritime boundar ...
could push the Mexican desert into southern portions of Texas
Texas ( , ; or ) is the most populous U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. It borders Louisiana to the east, Arkansas to the northeast, Oklahoma to the north, New Mexico to the we ...
, New Mexico
New Mexico is a state in the Southwestern United States, Southwestern region of the United States. It is one of the Mountain States of the southern Rocky Mountains, sharing the Four Corners region with Utah, Colorado, and Arizona. It also ...
and other areas in the southern U.S. Areas in the Middle East
The Middle East (term originally coined in English language) is a geopolitical region encompassing the Arabian Peninsula, the Levant, Turkey, Egypt, Iran, and Iraq.
The term came into widespread usage by the United Kingdom and western Eur ...
, Western America
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
, and the Amazon rainforest
The Amazon rainforest, also called the Amazon jungle or Amazonia, is a Tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests, moist broadleaf tropical rainforest in the Amazon biome that covers most of the Amazon basin of South America. This basin ...
risk the possibility of becoming drier and less humid. In contrast, the northward trend could bring more rain to areas in Asia
Asia ( , ) is the largest continent in the world by both land area and population. It covers an area of more than 44 million square kilometres, about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which ...
already exposed to monsoons
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal oscil ...
.
An increase of moisture in monsoon prone areas could be catastrophic as massive floods could follow the large amounts of rain added to preexisting rain from monsoons. Using geographical information, it is possible that the northward movement of the rain belt is already evident because of droughts in the western US, Syria
Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to Syria–Turkey border, the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, t ...
and northern China
Northern China () and Southern China () are two approximate regions that display certain differences in terms of their geography, demographics, economy, and culture.
Extent
The Qinling, Qinling–Daba Mountains serve as the transition zone ...
. Although the possible adversarial effects of the movement can be devastating, the northward movement of the rain belt could bring an increase of rain to areas that have been decimated by droughts, which could prove to be very beneficial.
References
{{Reflist Tropical meteorology Atmospheric dynamics Belt regions