Treaties Of Utrecht on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Peace of Utrecht was a series of
 On 2 January 1710, King
On 2 January 1710, King
"The Peace of Utrecht and the Balance of Power"
''Oxford Public International Law''. Several other treaties came out of the congress of Utrecht. France signed treaties of commerce and navigation with Great Britain and the Dutch Republic (11 April 1713). Great Britain signed a like treaty with Spain (9 December 1713).
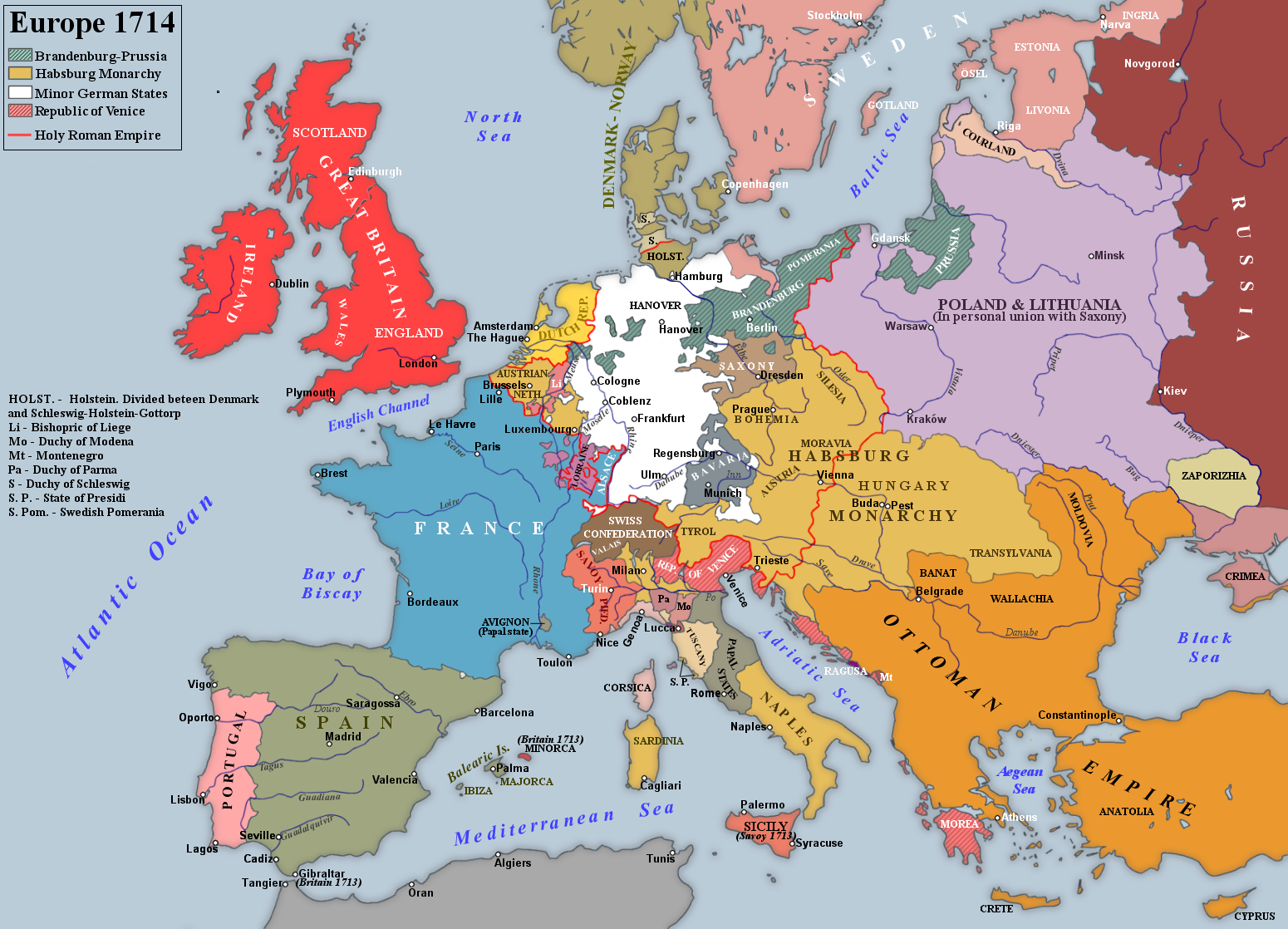 The Peace confirmed the Bourbon candidate as
The Peace confirmed the Bourbon candidate as  Under Article XIII and, despite the British demands to preserve Catalan constitutions and rights in return for Catalonia's support for the Allies during the war, Spain only agreed to grant an amnesty to Hapsburg supporters, thus implying the imposition of the laws and institutions of Castile to the
Under Article XIII and, despite the British demands to preserve Catalan constitutions and rights in return for Catalonia's support for the Allies during the war, Spain only agreed to grant an amnesty to Hapsburg supporters, thus implying the imposition of the laws and institutions of Castile to the
 The treaty's territorial provisions did not go as far as the Whigs in Britain would have liked, considering that the French had made overtures for peace in 1706 and again in 1709. The Whigs considered themselves the heirs of the staunch anti-French policies of
The treaty's territorial provisions did not go as far as the Whigs in Britain would have liked, considering that the French had made overtures for peace in 1706 and again in 1709. The Whigs considered themselves the heirs of the staunch anti-French policies of
 Spain retained the majority of its Empire and recovered remarkably quickly; the recapture of Naples and Sicily in 1718 was only prevented by British naval power and a second attempt was successful in 1734. The 1707, 1715 and 1716 ''Nueva Planta'' decrees abolished regional political structures in the kingdoms of
Spain retained the majority of its Empire and recovered remarkably quickly; the recapture of Naples and Sicily in 1718 was only prevented by British naval power and a second attempt was successful in 1734. The 1707, 1715 and 1716 ''Nueva Planta'' decrees abolished regional political structures in the kingdoms of
online
* * Churchill, Winston (2002). ''Marlborough: His Life and Times, Bk. 2, vols. iii & iv''. University of Chicago Press.
online abridged edition
* Gregory, Desmond: ''Minorca, the Illusory Prize: A History of the British Occupations of Minorca Between 1708 and 1802'' (Associated University Press, 1990) * Lesaffer, Randall
"The peace of Utrecht and the balance of power"
''Oxford Historical Treaties'' 10 Nov 1914 online * Lynn, John A (1999). ''The Wars of Louis XIV, 1667–1714''. Longman. * Mowat, Robert B. ''History of European diplomacy, 1451–1789'' (1928) pp. 141–154
online
pp. 165–182. * Sichel, Walter. ''Bolingbroke And His Times'', 2 vols. (1901–02
''Vol. 1 The Reign of Queen Anne''
* Stanhope, Philip: ''History of England, Comprising the Reign of Queen Anne until the Peace of Utrecht'' (London: 1870) * Trevelyan, G. M (1930–34). ''England Under Queen Anne''. 3 volumes. Longmans, Green and co. * *
"The Treaties of Utrecht (1713)"
Brief discussion and extracts of the various treaties on François Velde's ''Heraldica'' website, with particular focus on the renunciations and their later reconfirmations. {{DEFAULTSORT:Utrecht, Treaty of History of Gibraltar War of the Spanish Succession New France Gibraltar–Spain border Peace treaties of the Kingdom of Great Britain 1713 treaties Peace treaties of the Netherlands Peace treaties of Spain Peace treaties of the Ancien Régime Treaties of the Duchy of Savoy Treaties of the Dutch Republic Treaties of the Spanish Empire History of Utrecht (city) 1713 in the Dutch Republic 1713 in France 1713 in Gibraltar 1713 in Great Britain 1713 in Portugal 1713 in Spain Queen Anne's War Charles VI, Holy Roman Emperor Louis XIV Anne, Queen of Great Britain Frederick William I of Prussia Philip V of Spain
peace treaties
A peace treaty is an agreement between two or more hostile parties, usually countries or governments, which formally ends a state of war between the parties. It is different from an armistice, which is an agreement to stop hostilities; a surr ...
signed by the belligerents in the War of the Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was a European great power conflict fought between 1701 and 1714. The immediate cause was the death of the childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700, which led to a struggle for control of the Spanish E ...
, in the Dutch city of Utrecht
Utrecht ( ; ; ) is the List of cities in the Netherlands by province, fourth-largest city of the Netherlands, as well as the capital and the most populous city of the Provinces of the Netherlands, province of Utrecht (province), Utrecht. The ...
between April 1713 and February 1715. The war involved three contenders for the vacant throne of Spain, and had involved much of Europe for over a decade. Essentially, the treaties allowed Philip V (grandson of King Louis XIV
LouisXIV (Louis-Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was King of France from 1643 until his death in 1715. His verified reign of 72 years and 110 days is the List of longest-reign ...
of France) to keep the Spanish throne in return for permanently renouncing his claim to the French throne, along with other necessary guarantees that would ensure that France and Spain should not merge, thus preserving the balance of power in Europe.
The treaties between several European states, including Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
, Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-west coast of continental Europe, consisting of the countries England, Scotland, and Wales. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the List of European ...
, France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
, Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic, is a country on the Iberian Peninsula in Southwestern Europe. Featuring Cabo da Roca, the westernmost point in continental Europe, Portugal borders Spain to its north and east, with which it share ...
, Savoy
Savoy (; ) is a cultural-historical region in the Western Alps. Situated on the cultural boundary between Occitania and Piedmont, the area extends from Lake Geneva in the north to the Dauphiné in the south and west and to the Aosta Vall ...
and the Dutch Republic
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, commonly referred to in historiography as the Dutch Republic, was a confederation that existed from 1579 until the Batavian Revolution in 1795. It was a predecessor state of the present-day Netherlands ...
, helped end the war. The treaties were concluded between the representatives of Louis XIV of France and of his grandson Philip on one hand, and representatives of Queen Anne of Great Britain, King Victor Amadeus II of Sardinia, King John V of Portugal and the United Provinces of the Netherlands
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, commonly referred to in historiography as the Dutch Republic, was a confederation that existed from 1579 until the Batavian Revolution in 1795. It was a predecessor state of the present-day Netherla ...
on the other. Though the king of France ensured the Spanish crown for his dynasty, the treaties marked the end of French ambitions of hegemony
Hegemony (, , ) is the political, economic, and military predominance of one State (polity), state over other states, either regional or global.
In Ancient Greece (ca. 8th BC – AD 6th c.), hegemony denoted the politico-military dominance of ...
in Europe expressed in the continuous wars of Louis XIV, and paved the way to the European system based on the balance of power.
Negotiations
 On 2 January 1710, King
On 2 January 1710, King Louis XIV
LouisXIV (Louis-Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was King of France from 1643 until his death in 1715. His verified reign of 72 years and 110 days is the List of longest-reign ...
of France agreed to commence .
France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
and Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-west coast of continental Europe, consisting of the countries England, Scotland, and Wales. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the List of European ...
had come to terms in October 1711, when the preliminaries of peace had been signed in London
London is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of both England and the United Kingdom, with a population of in . London metropolitan area, Its wider metropolitan area is the largest in Wester ...
. The preliminaries were based on a tacit acceptance of the partition of Spain's European possessions. Following this, the Congress of Utrecht opened on 29 January 1712, with the British representatives being John Robinson, Bishop of Bristol, and Thomas Wentworth, Lord Strafford. Reluctantly the United Provinces accepted the preliminaries and sent representatives, but Emperor Charles VI refused to do so until he was assured that the preliminaries were not binding. This assurance was given, and so in February the Imperial representatives made their appearance. As Philip
Philip, also Phillip, is a male name derived from the Macedonian Old Koine language, Greek (''Philippos'', lit. "horse-loving" or "fond of horses"), from a compound of (''philos'', "dear", "loved", "loving") and (''hippos'', "horse"). Prominen ...
was not yet recognized as its king, Spain did not at first send plenipotentiaries, but the Duke of Savoy
The titles of the count of Savoy, and then duke of Savoy, are titles of nobility attached to the historical territory of Savoy. Since its creation, in the 11th century, the House of Savoy held the county. Several of these rulers ruled as kings at ...
sent one, and the Kingdom of Portugal
The Kingdom of Portugal was a Portuguese monarchy, monarchy in the western Iberian Peninsula and the predecessor of the modern Portuguese Republic. Existing to various extents between 1139 and 1910, it was also known as the Kingdom of Portugal a ...
was represented by Luís da Cunha. One of the first questions discussed was the nature of the guarantees to be given by France and Spain that their crowns would be kept separate, and little progress was made until 10 July 1712, when Philip signed a renunciation.
With Great Britain, France and Spain having agreed to a "suspension of arms" (armistice) covering Spain on 19 August in Paris, the pace of negotiation quickened. The first treaty signed at Utrecht was the truce between France and Portugal on 7 November, followed by the truce between France and Savoy on 14 March 1713. That same day, Spain, Great Britain, France and the Empire agreed to the evacuation of Catalonia
Catalonia is an autonomous community of Spain, designated as a ''nationalities and regions of Spain, nationality'' by its Statute of Autonomy of Catalonia of 2006, Statute of Autonomy. Most of its territory (except the Val d'Aran) is situate ...
and an armistice
An armistice is a formal agreement of warring parties to stop fighting. It is not necessarily the end of a war, as it may constitute only a cessation of hostilities while an attempt is made to negotiate a lasting peace. It is derived from t ...
in Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
. The main treaties of peace followed on 11 April 1713. These were five separate treaties between France and Great Britain, the Dutch Republic
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, commonly referred to in historiography as the Dutch Republic, was a confederation that existed from 1579 until the Batavian Revolution in 1795. It was a predecessor state of the present-day Netherlands ...
, Savoy
Savoy (; ) is a cultural-historical region in the Western Alps. Situated on the cultural boundary between Occitania and Piedmont, the area extends from Lake Geneva in the north to the Dauphiné in the south and west and to the Aosta Vall ...
, Prussia
Prussia (; ; Old Prussian: ''Prūsija'') was a Germans, German state centred on the North European Plain that originated from the 1525 secularization of the Prussia (region), Prussian part of the State of the Teutonic Order. For centuries, ...
and Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic, is a country on the Iberian Peninsula in Southwestern Europe. Featuring Cabo da Roca, the westernmost point in continental Europe, Portugal borders Spain to its north and east, with which it share ...
. Spain under Philip V signed separate peace treaties with Savoy and Great Britain at Utrecht on 13 July. Negotiations at Utrecht dragged on into the next year, for the peace treaty between Spain and the Netherlands was only signed on 26 June 1714 and that between Spain and Portugal on 6 February 1715.
Randall Lesaffer"The Peace of Utrecht and the Balance of Power"
''Oxford Public International Law''. Several other treaties came out of the congress of Utrecht. France signed treaties of commerce and navigation with Great Britain and the Dutch Republic (11 April 1713). Great Britain signed a like treaty with Spain (9 December 1713).
Treaties
Principal provisions
 The Peace confirmed the Bourbon candidate as
The Peace confirmed the Bourbon candidate as Philip V of Spain
Philip V (; 19 December 1683 – 9 July 1746) was List of Spanish monarchs, King of Spain from 1 November 1700 to 14 January 1724 and again from 6 September 1724 to his death in 1746. His total reign (45 years and 16 days) is the longest in the ...
to remain as king. In return, Philip renounced the French throne, both for himself and his descendants, with reciprocal renunciations by French Bourbons of the Spanish throne, including Louis XIV's nephew Philippe of Orléans. These became increasingly important after a series of deaths between 1712 and 1714 left the five year old Louis XV
Louis XV (15 February 1710 – 10 May 1774), known as Louis the Beloved (), was King of France from 1 September 1715 until his death in 1774. He succeeded his great-grandfather Louis XIV at the age of five. Until he reached maturity (then defi ...
as his great-grandfather's heir.
Great Britain was the main beneficiary; Utrecht marked the point at which it became the primary European commercial power. In Article X, Spain ceded the strategic ports of Gibraltar
Gibraltar ( , ) is a British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory and British overseas cities, city located at the southern tip of the Iberian Peninsula, on the Bay of Gibraltar, near the exit of the Mediterranean Sea into the A ...
and Menorca
Menorca or Minorca (from , later ''Minorica'') is one of the Balearic Islands located in the Mediterranean Sea belonging to Spain. Its name derives from its size, contrasting it with nearby Mallorca. Its capital is Maó, situated on the isl ...
.
The British emerged from the treaty with the ''Asiento de Negros
The () was a monopoly contract between the Spanish Crown and various merchants for the right to provide enslaved Africans to colonies in the Spanish Americas. The Spanish Empire rarely engaged in the transatlantic slave trade directly from A ...
'', which referred to the monopoly contract granted by the Spanish government
The government of Spain () is the central government which leads the executive branch and the General State Administration of the Kingdom of Spain.
The Government consists of the Prime Minister and the Ministers; the prime minister has the o ...
to other European nations to supply slaves to Spain's colonies in the Americas. The ''Asiento de Negros'' had come about because the Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire, sometimes referred to as the Hispanic Monarchy (political entity), Hispanic Monarchy or the Catholic Monarchy, was a colonial empire that existed between 1492 and 1976. In conjunction with the Portuguese Empire, it ushered ...
rarely participated in the transatlantic slave trade
The Atlantic slave trade or transatlantic slave trade involved the transportation by slave traders of Slavery in Africa, enslaved African people to the Americas. European slave ships regularly used the triangular trade route and its Middle Pass ...
itself, preferring to outsource this to foreign merchants. Bourbon France had previously held the ''Asiento de Negros'', allowing French slave traders to supply 5,000 slaves to the Spanish Empire each year; France had gained control over this contract after Philip V had become King of Spain. After the British government gained access to the ''Asiento de Negros'', the economic prominence held by Dutch Sephardic Jewish
Sephardic Jews, also known as Sephardi Jews or Sephardim, and rarely as Iberian Peninsular Jews, are a Jewish diaspora population associated with the historic Jewish communities of the Iberian Peninsula (Spain and Portugal) and their descendant ...
slaveowners began to fade, while the South Sea Company
The South Sea Company (officially: The Governor and Company of the merchants of Great Britain, trading to the South Seas and other parts of America and for the encouragement of the Fishery) was a British joint-stock company founded in Ja ...
was established in hopes of gaining exclusive access to the contract. The British government sought to reduce its debt by increasing the volume of trade it had with Spain, which required gaining access to the ''Asiento de Negros''; as historian G.M. Trevelyan noted: "The finances of the country were based in May 1711 on the assumption that the Asiento, or monopoly of the slave trade with Spanish America, would be wrested from France as an integral part of the terms of peace". Following the passage of the treaty, the British government gained access for thirty years to the ''Asiento de Negros''.
The importance placed by British negotiators on commercial interests was demonstrated by their demand for France to "level the fortifications of Dunkirk
Dunkirk ( ; ; ; Picard language, Picard: ''Dunkèke''; ; or ) is a major port city in the Departments of France, department of Nord (French department), Nord in northern France. It lies from the Belgium, Belgian border. It has the third-larg ...
, block up the port and demolish the sluices that scour the harbour, hich
Ij () is a village in Golabar Rural District of the Central District in Ijrud County, Zanjan province, Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq ...
shall never be reconstructed". This was because Dunkirk was the primary base for French privateer
A privateer is a private person or vessel which engages in commerce raiding under a commission of war. Since robbery under arms was a common aspect of seaborne trade, until the early 19th century all merchant ships carried arms. A sovereign o ...
s, as it was possible to reach the North Sea in a single tide and escape British patrols in the English Channel.
Principality of Catalonia
The Principality of Catalonia (; ; ; ) was a Middle Ages, medieval and early modern state (polity), state in the northeastern Iberian Peninsula. During most of its history it was in dynastic union with the Kingdom of Aragon, constituting together ...
, as it already happened in 1707 to the other occupied kingdoms of the Crown of Aragon. Spanish territories in Italy and Flanders
Flanders ( or ; ) is the Dutch language, Dutch-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to culture, la ...
were divided, with Savoy
Savoy (; ) is a cultural-historical region in the Western Alps. Situated on the cultural boundary between Occitania and Piedmont, the area extends from Lake Geneva in the north to the Dauphiné in the south and west and to the Aosta Vall ...
receiving Sicily
Sicily (Italian language, Italian and ), officially the Sicilian Region (), is an island in the central Mediterranean Sea, south of the Italian Peninsula in continental Europe and is one of the 20 regions of Italy, regions of Italy. With 4. ...
and parts of the Duchy of Milan
The Duchy of Milan (; ) was a state in Northern Italy, created in 1395 by Gian Galeazzo Visconti, then the lord of Milan, and a member of the important Visconti of Milan, Visconti family, which had been ruling the city since 1277. At that time, ...
. The former Spanish Netherlands
The Spanish Netherlands (; ; ; ) (historically in Spanish: , the name "Flanders" was used as a '' pars pro toto'') was the Habsburg Netherlands ruled by the Spanish branch of the Habsburgs from 1556 to 1714. They were a collection of States of t ...
, the Kingdom of Naples
The Kingdom of Naples (; ; ), officially the Kingdom of Sicily, was a state that ruled the part of the Italian Peninsula south of the Papal States between 1282 and 1816. It was established by the War of the Sicilian Vespers (1282–1302). Until ...
, Sardinia
Sardinia ( ; ; ) is the Mediterranean islands#By area, second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, and one of the Regions of Italy, twenty regions of Italy. It is located west of the Italian Peninsula, north of Tunisia an ...
, and the bulk of the Duchy of Milan went to Emperor Charles VI.
In South America, Spain returned Colónia do Sacramento
Colonia del Sacramento (; ) is a city in southwestern Uruguay, by the Río de la Plata, facing Buenos Aires, Argentina. It is one of the oldest towns in Uruguay and the capital of the Colonia Department. As of the 2023 census, it has a populati ...
in modern Uruguay to Portugal and recognised Portuguese sovereignty over the lands between the Amazon and Oyapock rivers, now in Brazil
Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil, is the largest country in South America. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, fifth-largest country by area and the List of countries and dependencies by population ...
. The British agreed to prevent their citizens from visiting Spanish colonies in America without prior approval from colonial officials.
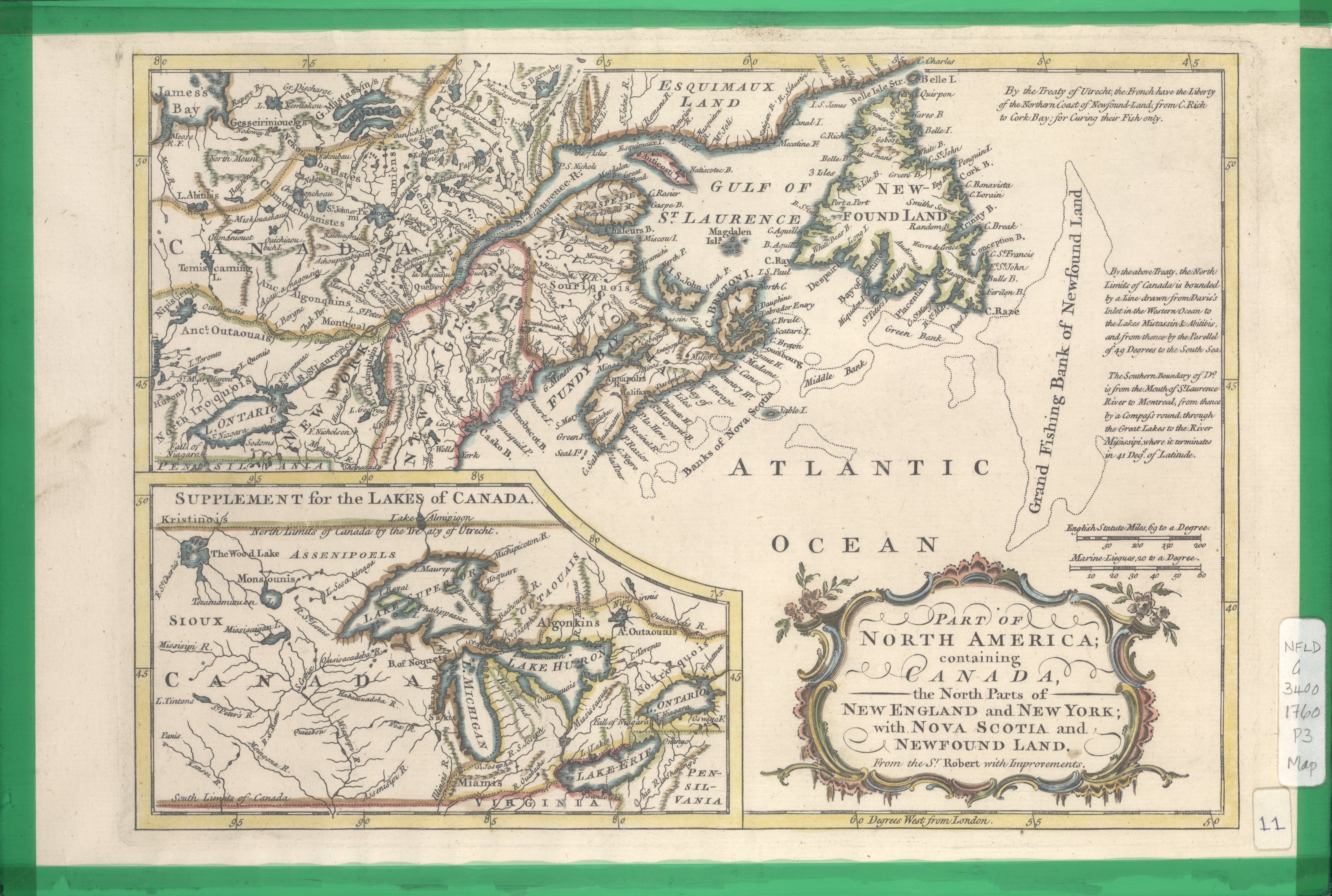
In North America, France recognised British suzerainty
A suzerain (, from Old French "above" + "supreme, chief") is a person, state (polity)">state or polity who has supremacy and dominant influence over the foreign policy">polity.html" ;"title="state (polity)">state or polity">state (polity)">st ...
over the Iroquois
The Iroquois ( ), also known as the Five Nations, and later as the Six Nations from 1722 onwards; alternatively referred to by the Endonym and exonym, endonym Haudenosaunee ( ; ) are an Iroquoian languages, Iroquoian-speaking Confederation#Ind ...
, and ceded Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada, located on its east coast. It is one of the three Maritime Canada, Maritime provinces and Population of Canada by province and territory, most populous province in Atlan ...
and its claims to Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region of Labrador, having a total size of . As of 2025 the population ...
and territories in Rupert's Land
Rupert's Land (), or Prince Rupert's Land (), was a territory in British North America which comprised the Hudson Bay drainage basin. The right to "sole trade and commerce" over Rupert's Land was granted to Hudson's Bay Company (HBC), based a ...
. The French portion of Saint Kitts
Saint Kitts, officially Saint Christopher, is an island in the West Indies. The west side of the island borders the Caribbean Sea, and the eastern coast faces the Atlantic Ocean. Saint Kitts and the neighbouring island of Nevis constitute one ...
in the West Indies
The West Indies is an island subregion of the Americas, surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea, which comprises 13 independent island country, island countries and 19 dependent territory, dependencies in thr ...
was also ceded in its entirety to Britain. France retained its other pre-war North American possessions, including Cape Breton Island
Cape Breton Island (, formerly '; or '; ) is a rugged and irregularly shaped island on the Atlantic coast of North America and part of the province of Nova Scotia, Canada.
The island accounts for 18.7% of Nova Scotia's total area. Although ...
, where it built the Fortress of Louisbourg
The Fortress of Louisbourg () is a tourist attraction as a National Historic Sites of Canada, National Historic Site and the location of a one-quarter partial reconstruction of an 18th-century Kingdom of France, French fortress at Louisbourg, Nov ...
, then the most expensive military installation in North America.
The successful French Rhineland campaign of 1713 finally induced Charles to sign the 1714 treaties of Rastatt
Rastatt () is a town with a Baroque core, District of Rastatt, Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It is located in the Upper Rhine Plain on the Murg river, above its junction with the Rhine and has a population of around 51,000 (2022). Rastatt was an ...
and Baden
Baden (; ) is a historical territory in southern Germany. In earlier times it was considered to be on both sides of the Upper Rhine, but since the Napoleonic Wars, it has been considered only East of the Rhine.
History
The margraves of Ba ...
, although terms were not agreed with Spain until the 1720 Treaty of The Hague.
Responses to the treaties
 The treaty's territorial provisions did not go as far as the Whigs in Britain would have liked, considering that the French had made overtures for peace in 1706 and again in 1709. The Whigs considered themselves the heirs of the staunch anti-French policies of
The treaty's territorial provisions did not go as far as the Whigs in Britain would have liked, considering that the French had made overtures for peace in 1706 and again in 1709. The Whigs considered themselves the heirs of the staunch anti-French policies of William III of England
William III (William Henry; ; 4 November 1650 – 8 March 1702), also known as William of Orange, was the sovereign Prince of Orange from birth, Stadtholder of County of Holland, Holland, County of Zeeland, Zeeland, Lordship of Utrecht, Utrec ...
and of John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough
General (United Kingdom), General John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough, 1st Prince of Mindelheim, 1st Count of Nellenburg, Prince of the Holy Roman Empire, (26 May 1650 – 16 June 1722 Old Style and New Style dates, O.S.) was a Briti ...
. The Whigs were now a minority in the house, but still pushing their anti-peace agenda. The Whigs opposed peace every step of the way. The Whigs even called the treaty a sellout for letting the duke of Anjou stay on the Spanish throne.
However, in the Parliament of 1710 the Tories had gained control of the House of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the Bicameralism, bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of ...
, and they wished for an end to Great Britain's participation in a European war. Queen Anne and her advisors had also come to agree.
The party in the administration of Robert Harley (created Earl of Oxford and Mortimer on 23 May 1711) and the Viscount Bolingbroke proved more flexible at the bargaining table and were characterized by the Whigs as "pro-French"; Oxford and Bolingbroke persuaded the Queen to create twelve new "Tory peers" to ensure ratification of the treaty in the House of Lords
The House of Lords is the upper house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Like the lower house, the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, House of Commons, it meets in the Palace of Westminster in London, England. One of the oldest ext ...
. The opponents of the treaty tried to rally support under the slogan of '' No Peace Without Spain''.
Although the fate of the Spanish Netherlands
The Spanish Netherlands (; ; ; ) (historically in Spanish: , the name "Flanders" was used as a '' pars pro toto'') was the Habsburg Netherlands ruled by the Spanish branch of the Habsburgs from 1556 to 1714. They were a collection of States of t ...
in particular was of interest to the United Provinces, Dutch influence on the outcome of the negotiations was fairly insignificant, even though the talks were held on their territory. The French negotiator Melchior de Polignac taunted the Dutch with the scathing remark ''de vous, chez vous, sans vous'', meaning that negotiations would be held "about you, around you, without you". The fact that Bolingbroke had secretly ordered the British commander, the Duke of Ormonde, to withdraw from the Allied forces before the Battle of Denain (informing the French but not the Allies), and the fact that they secretly arrived at separate peace with France was a ''fait accompli'', made the objections of the Allies pointless. In any case, the Dutch achieved their condominium
A condominium (or condo for short) is an ownership regime in which a building (or group of buildings) is divided into multiple units that are either each separately owned, or owned in common with exclusive rights of occupation by individual own ...
in the Austrian Netherlands
The Austrian Netherlands was the territory of the Burgundian Circle of the Holy Roman Empire between 1714 and 1797. The period began with the acquisition by the Austrian Habsburg monarchy of the former Spanish Netherlands under the Treaty of Ras ...
with the Austro-Dutch Barrier Treaty of 1715.
Aftermath
The Treaty stipulated that "because of the great danger which threatened the liberty and safety of all Europe, from the too close conjunction of the kingdoms of Spain and France, ... one and the same person should never become King of both kingdoms". Some historians argue this makes it a significant milestone in the evolution of the modern nation state and concept of a balance of power. First mentioned in 1701 by Charles Davenant in his ''Essays on the Balance of Power'', it was widely publicised in Britain by author and Tory satiristDaniel Defoe
Daniel Defoe (; born Daniel Foe; 1660 – 24 April 1731) was an English writer, merchant and spy. He is most famous for his novel ''Robinson Crusoe'', published in 1719, which is claimed to be second only to the Bible in its number of translati ...
in his 1709 article ''A Review of the Affairs of France''. The idea was reflected in the wording of the treaties and resurfaced after the defeat of Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte (born Napoleone di Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French general and statesman who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led Military career ...
in the 1815 Concert of Europe
The Concert of Europe was a general agreement among the great powers of 19th-century Europe to maintain the European balance of power, political boundaries, and spheres of influence. Never a perfect unity and subject to disputes and jockeying ...
that dominated Europe in the 19th century.
For the individual signatories, Britain established naval superiority over its competitors, commercial access to Spain and America, and control of Menorca and Gibraltar; it retains the latter territory to this day. France accepted the Protestant succession on the British throne, ensuring a smooth transition when Anne died in August 1714, and ended its support for the Stuarts under the 1716 Anglo-French Treaty. While the war left all participants with unprecedented levels of government debt, only Great Britain successfully financed it.
 Spain retained the majority of its Empire and recovered remarkably quickly; the recapture of Naples and Sicily in 1718 was only prevented by British naval power and a second attempt was successful in 1734. The 1707, 1715 and 1716 ''Nueva Planta'' decrees abolished regional political structures in the kingdoms of
Spain retained the majority of its Empire and recovered remarkably quickly; the recapture of Naples and Sicily in 1718 was only prevented by British naval power and a second attempt was successful in 1734. The 1707, 1715 and 1716 ''Nueva Planta'' decrees abolished regional political structures in the kingdoms of Aragon
Aragon ( , ; Spanish and ; ) is an autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community in Spain, coextensive with the medieval Kingdom of Aragon. In northeastern Spain, the Aragonese autonomous community comprises three provinces of Spain, ...
, Valencia
Valencia ( , ), formally València (), is the capital of the Province of Valencia, province and Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Valencian Community, the same name in Spain. It is located on the banks of the Turia (r ...
, Majorca
Mallorca, or Majorca, is the largest of the Balearic Islands, which are part of Spain, and the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, seventh largest island in the Mediterranean Sea.
The capital of the island, Palma, Majorca, Palma, i ...
and the Principality of Catalonia
The Principality of Catalonia (; ; ; ) was a Middle Ages, medieval and early modern state (polity), state in the northeastern Iberian Peninsula. During most of its history it was in dynastic union with the Kingdom of Aragon, constituting together ...
, although Catalonia and Aragon retained some of these rights until 1767.
Despite failure in Spain, Austria secured its position in Italy and Hungary, allowing it to continue expansion into areas of South-East Europe previously held by the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
. Even after paying expenses associated with the Dutch Barrier, increased tax revenues from the Austrian Netherlands
The Austrian Netherlands was the territory of the Burgundian Circle of the Holy Roman Empire between 1714 and 1797. The period began with the acquisition by the Austrian Habsburg monarchy of the former Spanish Netherlands under the Treaty of Ras ...
funded a significant upgrade of the Austrian military. However, these gains were diminished by various factors, chiefly the disruption of the Pragmatic Sanction of 1713 caused by Charles disinheriting his nieces in favour of his daughter Maria Theresa
Maria Theresa (Maria Theresia Walburga Amalia Christina; 13 May 1717 – 29 November 1780) was the ruler of the Habsburg monarchy from 1740 until her death in 1780, and the only woman to hold the position suo jure, in her own right. She was the ...
.
Attempts to ensure its succession involved Austria in wars of little strategic value; much of the fighting in the 1733–1735 War of the Polish Succession
The War of the Polish Succession (; 1733–35) was a major European conflict sparked by a civil war in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth over the succession to Augustus II the Strong, which the other European powers widened in pursuit of ...
taking place in its maritime provinces in Italy. Austria had traditionally relied on naval support from the Dutch, whose own capability had been severely degraded; Britain prevented the loss of Sicily and Naples in 1718 but refused to do so again in 1734. The dispute continued to loosen Habsburg control over the Empire; Bavaria, Hanover, Prussia and Saxony increasingly acted as independent powers and in 1742, Charles of Bavaria became the first non-Habsburg Emperor in over 300 years.
The Dutch Republic ended the war effectively bankrupt, while the damage suffered by the Dutch merchant navy permanently affected their commercial and political strength and it was superseded by Britain as the pre-eminent European mercantile power. The acquisition of the Barrier Fortresses however became an important asset of Dutch foreign policy and enlarged their sphere of influence. Although judged favourably by contemporaries, it was later argued that the barrier proved to be largely illusory when put to the test during the War of Austrian Succession
The War of the Austrian Succession was a European conflict fought between 1740 and 1748, primarily in Central Europe, the Austrian Netherlands, Italy, the Atlantic Ocean and Mediterranean Sea. Related conflicts include King George's War in Nort ...
. The Dutch had in any case successfully defended their positions in the Southern Netherlands and their troops were central in the alliance which halted French territorial expansion in Europe until a new cycle began in 1792
Events
January–March
* January 9 – The Treaty of Jassy ends the Russian Empire's war with the Ottoman Empire over Crimea.
* January 25 – The London Corresponding Society is founded.
* February 18 – Thomas Holcrof ...
.
While the final settlement at Utrecht was far more favourable to France than the Allied offer of 1709 had been, it gained little that had not already been achieved through diplomacy by February 1701. Though France remained a great power, concern at its relative decline in military and economic terms compared to Britain was an underlying cause of the War of the Austrian Succession
The War of the Austrian Succession was a European conflict fought between 1740 and 1748, primarily in Central Europe, the Austrian Netherlands, Italian Peninsula, Italy, the Atlantic Ocean and Mediterranean Sea. Related conflicts include King Ge ...
in 1740.
Evaluations
The British historianG. M. Trevelyan
George Macaulay Trevelyan (16 February 1876 – 21 July 1962) was an English historian and academic. He was a Fellow of Trinity College, Cambridge, from 1898 to 1903. He then spent more than twenty years as a full-time author. He returned to th ...
has argued that:
The British academic Brendan Simms argues that:
See also
* Disputed status of Gibraltar *French Shore
The French Shore (French language, French: ''Côte française de Terre-Neuve''), also called The Treaty Shore, resulted from the 1713 ratifications of the Treaty of Utrecht. The provisions of the treaty allowed the French to fish in season along t ...
* Herman Moll
Herman Moll (mid-17th century – 22 September 1732) was a British cartographer, engraver, and publisher.
Origin and early life
While Moll's exact place and date of birth are unknown, he was probably born in the mid-17th century in German ...
* '' Utrecht Te Deum and Jubilate,'' composition by Handel
References
Bibliography
* Bruin, Renger and Cornelis Haven, eds. ''Performances of Peace: Utrecht 1713'' (2015)online
* * Churchill, Winston (2002). ''Marlborough: His Life and Times, Bk. 2, vols. iii & iv''. University of Chicago Press.
online abridged edition
* Gregory, Desmond: ''Minorca, the Illusory Prize: A History of the British Occupations of Minorca Between 1708 and 1802'' (Associated University Press, 1990) * Lesaffer, Randall
"The peace of Utrecht and the balance of power"
''Oxford Historical Treaties'' 10 Nov 1914 online * Lynn, John A (1999). ''The Wars of Louis XIV, 1667–1714''. Longman. * Mowat, Robert B. ''History of European diplomacy, 1451–1789'' (1928) pp. 141–154
online
pp. 165–182. * Sichel, Walter. ''Bolingbroke And His Times'', 2 vols. (1901–02
''Vol. 1 The Reign of Queen Anne''
* Stanhope, Philip: ''History of England, Comprising the Reign of Queen Anne until the Peace of Utrecht'' (London: 1870) * Trevelyan, G. M (1930–34). ''England Under Queen Anne''. 3 volumes. Longmans, Green and co. * *
External links
"The Treaties of Utrecht (1713)"
Brief discussion and extracts of the various treaties on François Velde's ''Heraldica'' website, with particular focus on the renunciations and their later reconfirmations. {{DEFAULTSORT:Utrecht, Treaty of History of Gibraltar War of the Spanish Succession New France Gibraltar–Spain border Peace treaties of the Kingdom of Great Britain 1713 treaties Peace treaties of the Netherlands Peace treaties of Spain Peace treaties of the Ancien Régime Treaties of the Duchy of Savoy Treaties of the Dutch Republic Treaties of the Spanish Empire History of Utrecht (city) 1713 in the Dutch Republic 1713 in France 1713 in Gibraltar 1713 in Great Britain 1713 in Portugal 1713 in Spain Queen Anne's War Charles VI, Holy Roman Emperor Louis XIV Anne, Queen of Great Britain Frederick William I of Prussia Philip V of Spain