Transition Metal Silane Complexes on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
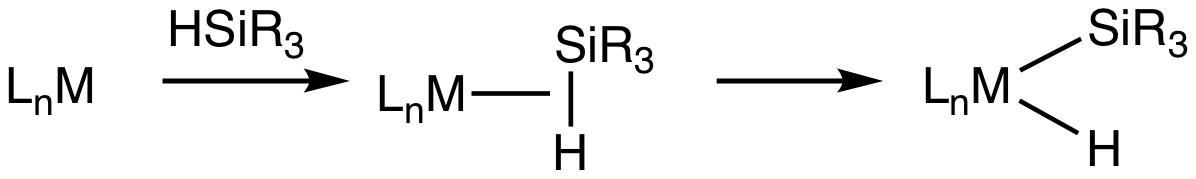 Transition metal silane complexes are
Transition metal silane complexes are  Evidence for sigma-silane complexes is provided by proton NMR spectroscopy. For (MeC5H4)Mn(CO)2(η2-HSiPh3), J(29Si,1H) = 65 Hz compared to 180 Hz in free diphenylsilane. In silyl hydride complexes, the coupling in about 6 Hz.
Evidence for sigma-silane complexes is provided by proton NMR spectroscopy. For (MeC5H4)Mn(CO)2(η2-HSiPh3), J(29Si,1H) = 65 Hz compared to 180 Hz in free diphenylsilane. In silyl hydride complexes, the coupling in about 6 Hz.
 Transition metal silane complexes are
Transition metal silane complexes are coordination compound
A coordination complex consists of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the ''coordination centre'', and a surrounding array of bound molecules or ions, that are in turn known as ''ligands'' or complexing agents. Many ...
s containing hydrosilane ligands. An early example is (MeC5H4)Mn(CO)2(η2-HSiPh3) (Ph = C6H5).
The bonding in silane sigma complexes is similar to that invoked in agostic interactions. The metal center engages the Si-H entity via a 3-center, 2-electron bond. It is widely assumed that these sigma complexes are intermediates in the oxidative addition
Oxidative addition and reductive elimination are two important and related classes of reactions in organometallic chemistry. Oxidative addition is a process that increases both the oxidation state and coordination number of a metal centre. Oxid ...
of hydrosilanes to give metal silyl hydrides. This transformation is invoked in hydrosilylation Hydrosilylation, also called catalytic hydrosilation, describes the addition of Si-H bonds across unsaturated bonds."Hydrosilylation A Comprehensive Review on Recent Advances" B. Marciniec (ed.), Advances in Silicon Science, Springer Science, 2009 ...
catalysis.
 Evidence for sigma-silane complexes is provided by proton NMR spectroscopy. For (MeC5H4)Mn(CO)2(η2-HSiPh3), J(29Si,1H) = 65 Hz compared to 180 Hz in free diphenylsilane. In silyl hydride complexes, the coupling in about 6 Hz.
Evidence for sigma-silane complexes is provided by proton NMR spectroscopy. For (MeC5H4)Mn(CO)2(η2-HSiPh3), J(29Si,1H) = 65 Hz compared to 180 Hz in free diphenylsilane. In silyl hydride complexes, the coupling in about 6 Hz. Neutron diffraction
Neutron diffraction or elastic neutron scattering is the application of neutron scattering to the determination of the atomic and/or magnetic structure of a material. A sample to be examined is placed in a beam of thermal or cold neutrons to ob ...
studies reveal a Si-H distance of 1.802(5) Å in the corresponding η2-HSiFPh2 complex vs 1.48 Å in free HSiFPh2. Elongated Si-H bonds are characteristic of these sigma complexes.
References