Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) is a
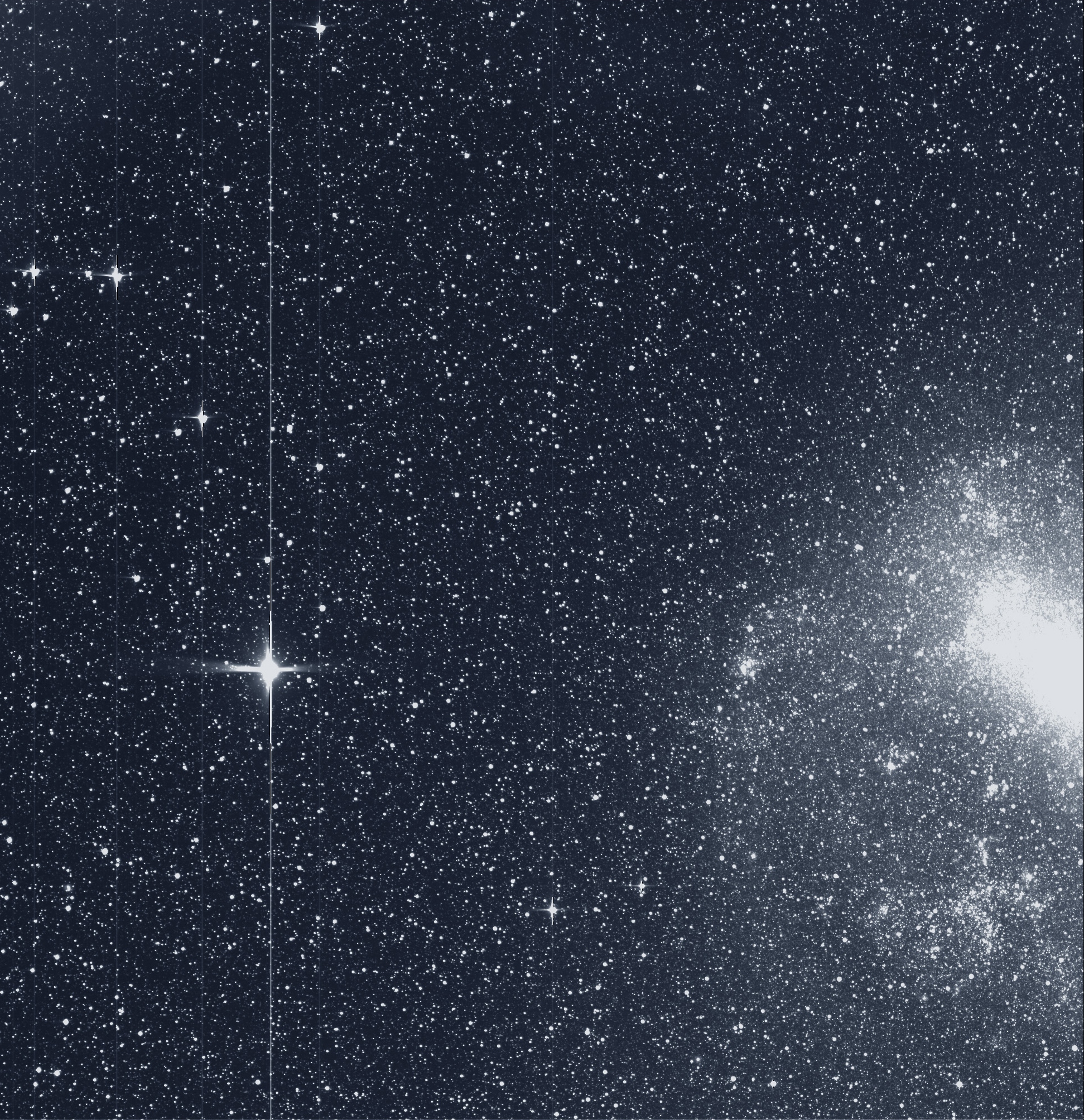

 TESS's two-year all-sky survey would focus on nearby G-, K-, and M-
TESS's two-year all-sky survey would focus on nearby G-, K-, and M-
 In 2013,
In 2013,
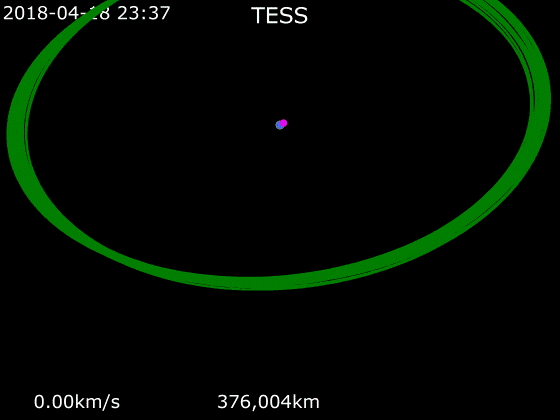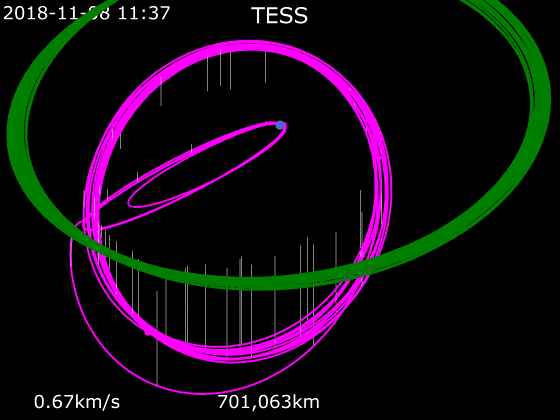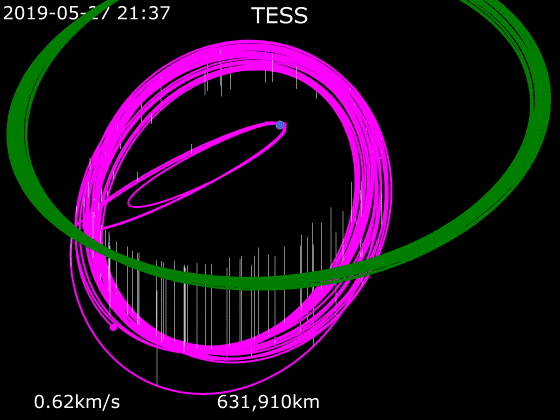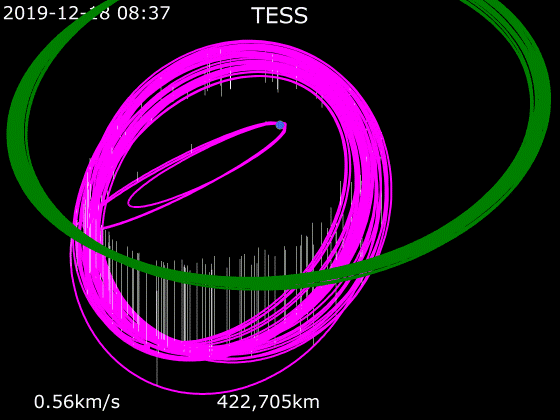
 Once injected into the initial orbit by the Falcon 9 second stage, the spacecraft performed four additional independent burns that placed it into a lunar flyby orbit. On 17 May 2018, the spacecraft underwent a
Once injected into the initial orbit by the Falcon 9 second stage, the spacecraft performed four additional independent burns that placed it into a lunar flyby orbit. On 17 May 2018, the spacecraft underwent a
 The sole instrument on TESS is a package of four wide-field-of-view charge-coupled device (CCD) cameras. Each camera features four low-noise, low-power 4 megapixel CCDs created by
The sole instrument on TESS is a package of four wide-field-of-view charge-coupled device (CCD) cameras. Each camera features four low-noise, low-power 4 megapixel CCDs created by
 Current mission results as of 16 May 2025: 627 confirmed exoplanets discovered by TESS, with 7643 candidate-planets that are still awaiting confirmation or rejection as false positive by the
Current mission results as of 16 May 2025: 627 confirmed exoplanets discovered by TESS, with 7643 candidate-planets that are still awaiting confirmation or rejection as false positive by the 
TESS twitter account
by NASA
TESS website
by NASA Goddard
TESS website
by Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT)
TESS discovered exoplanets
by MIT
TESS website
by the Kavli Foundation
Planet Hunters TESS
anyone can help classifying TESS data
TESS listing of Southern Sky panoramas
(July 18, 2019)
APOD (April 21, 2018)
Interactive 3D simulation of TESS's 2:1 lunar resonant orbit
{{Portal bar, Astronomy, Stars, Spaceflight, Solar System, Science Space probes launched in 2018 Space telescopes Explorers Program NASA space probes NASA programs Exoplanet search projects SpaceX payloads contracted by NASA 2018 establishments in Florida Asteroseismology
space telescope
A space telescope (also known as space observatory) is a telescope in outer space used to observe astronomical objects. Suggested by Lyman Spitzer in 1946, the first operational telescopes were the American Orbiting Astronomical Observatory, OAO ...
for NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States ...
's Explorer program, designed to search for exoplanet
An exoplanet or extrasolar planet is a planet outside the Solar System. The first confirmed detection of an exoplanet was in 1992 around a pulsar, and the first detection around a main-sequence star was in 1995. A different planet, first det ...
s using the transit method
Methods of detecting exoplanets usually rely on indirect strategies – that is, they do not directly image the planet but deduce its existence from another signal. Any planet is an extremely faint light source compared to its parent star. For e ...
in an area 400 times larger than that covered by the Kepler
Johannes Kepler (27 December 1571 – 15 November 1630) was a German astronomer, mathematician, astrologer, natural philosopher and writer on music. He is a key figure in the 17th-century Scientific Revolution, best known for his laws of p ...
mission. It was launched on 18 April 2018, atop a Falcon 9 launch vehicle and was placed into a highly elliptical 13.70-day orbit around the Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all ...
. The first light image from TESS was taken on 7 August 2018, and released publicly on 17 September 2018.
In the two-year primary mission, TESS was expected to detect about 1,250 transiting exoplanets orbiting the targeted star
A star is a luminous spheroid of plasma (physics), plasma held together by Self-gravitation, self-gravity. The List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs, nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night sk ...
s, and an additional 13,000 orbiting stars not targeted but observed. After the end of the primary mission around 4 July 2020, scientists continued to search its data for more planets, while the extended missions acquires additional data. , TESS had identified 7,643 candidate exoplanets, of which 627 had been confirmed.
The primary mission objective for TESS was to survey the brightest stars near the Earth for transiting exoplanets over a two-year period. The TESS satellite uses an array of wide-field cameras to perform a survey of 85% of the sky. With TESS, it is possible to study the mass, size, density and orbit of a large cohort of small planets, including a sample of rocky planets in the habitable zones of their host stars. TESS provides prime targets for further characterization by the James Webb Space Telescope
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is a space telescope designed to conduct infrared astronomy. As the largest telescope in space, it is equipped with high-resolution and high-sensitivity instruments, allowing it to view objects too old, Lis ...
(JWST), as well as other large ground-based and space-based telescopes of the future. While previous sky surveys with ground-based telescopes have mainly detected giant exoplanets and the Kepler space telescope
The Kepler space telescope is a defunct space telescope launched by NASA in 2009 to discover Earth-sized planets orbiting other stars. Named after astronomer Johannes Kepler, the spacecraft was launched into an Earth-trailing heliocentric orb ...
has mostly found planets around distant stars that are too faint for characterization, TESS finds many small planets around the nearest stars in the sky. TESS records the nearest and brightest main sequence stars hosting transiting exoplanets, which are the most favorable targets for detailed investigations. Detailed information about such planetary systems with hot Jupiters makes it possible to better understand the architecture of such systems.
Led by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is a Private university, private research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Established in 1861, MIT has played a significant role in the development of many areas of moder ...
(MIT) with seed funding
Seed money, also known as seed funding or seed capital, is a form of securities offering in which an investor puts capital in a startup company in exchange for an equity stake or convertible note stake in the company. The term ''seed'' suggests ...
from Google
Google LLC (, ) is an American multinational corporation and technology company focusing on online advertising, search engine technology, cloud computing, computer software, quantum computing, e-commerce, consumer electronics, and artificial ...
, on 5 April 2013, it was announced that TESS, along with the Neutron Star Interior Composition Explorer (NICER), had been selected by NASA for launch. On 18 July 2019, after the first year of operation, the southern portion of the survey was completed, and the northern survey was started. The primary mission ended with the completion of the northern survey on 4 July 2020, which was followed by the first extended mission. The first extended mission concluded in September 2022 and the spacecraft entered its second extended mission which should last for another three years.
History
The concept of TESS was first discussed in 2005 by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) and theSmithsonian Astrophysical Observatory
The Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory (SAO) is a research institute of the Smithsonian Institution, concentrating on Astrophysics, astrophysical studies including Galactic astronomy, galactic and extragalactic astronomy, cosmology, Sun, solar ...
(SAO). The genesis of TESS was begun during 2006, when a design was developed from private funding by individuals, Google, and The Kavli Foundation. In 2008, MIT proposed that TESS become a full NASA mission and submitted it for the Small Explorer program at Goddard Space Flight Center
The Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) is a major NASA space research laboratory located approximately northeast of Washington, D.C., in Greenbelt, Maryland, United States. Established on May 1, 1959, as NASA's first space flight center, GSFC ...
, but it was not selected. It was resubmitted in 2010 as an Explorer program mission, and was approved in April 2013 as a Medium Explorer mission. TESS passed its critical design review (CDR) in 2015, allowing production of the satellite to begin. While Kepler had cost US$640 million at launch, TESS cost only US$200 million (plus US$87 million for launch). The mission will find exoplanets that periodically block part of the light from their host stars, events called transits. TESS will survey 200,000 of the brightest stars near the Sun
The Sun is the star at the centre of the Solar System. It is a massive, nearly perfect sphere of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core, radiating the energy from its surface mainly as visible light a ...
to search for transiting exoplanets. TESS was launched on 18 April 2018, aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 launch vehicle.
In July 2019, an Extended Mission 2020 to 2022 was approved. On 3 January 2020, NASA reported that TESS had discovered its first potentially habitable Earth-sized planet, TOI-700 d.
Mission overview
TESS is designed to carry out the first spaceborne all-sky transiting exoplanet survey. It is equipped with four wide-angle telescopes and associatedcharge-coupled device
A charge-coupled device (CCD) is an integrated circuit containing an array of linked, or coupled, capacitors. Under the control of an external circuit, each capacitor can transfer its electric charge to a neighboring capacitor. CCD sensors are a ...
(CCD) detectors. Science data are transmitted to Earth every two weeks. Full-frame images with an effective exposure time of two hours are transmitted as well, enabling scientists to search for unexpected transient phenomena, such as the optical counterparts to gamma-ray burst
In gamma-ray astronomy, gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) are extremely energetic events occurring in distant Galaxy, galaxies which represent the brightest and most powerful class of explosion in the universe. These extreme Electromagnetic radiation, ele ...
s. TESS also hosts a Guest Investigator program, allowing scientists from other organizations to use TESS for their own research. The resources allocated to Guest programs allow an additional 20,000 celestial bodies to be observed.
Orbital dynamics
TESS uses a novel highly elliptical orbit around the Earth with an apogee approximately at the distance of the Moon and aperigee
An apsis (; ) is the farthest or nearest point in the orbit of a planetary body about its primary body. The line of apsides (also called apse line, or major axis of the orbit) is the line connecting the two extreme values.
Apsides perta ...
of . TESS orbits Earth twice during the time the Moon orbits once, a 2:1 resonance
Resonance is a phenomenon that occurs when an object or system is subjected to an external force or vibration whose frequency matches a resonant frequency (or resonance frequency) of the system, defined as a frequency that generates a maximu ...
with the Moon. The orbit is expected to remain stable for a minimum of ten years.
In order to obtain unobstructed imagery of both the northern and southern hemispheres of the sky, TESS utilizes a 2:1 lunar resonant orbit called P/2, an orbit that has never been used before (although Interstellar Boundary Explorer
Interstellar Boundary Explorer (IBEX or Explorer 91 or SMEX-10) is a NASA satellite in Earth orbit that uses energetic neutral atoms (ENAs) to image the interaction region between the Solar System and Outer space, interstellar space. The missi ...
(IBEX) uses a similar P/3 orbit). The highly elliptical orbit
A highly elliptical orbit (HEO) is an elliptic orbit with high eccentricity, usually referring to one around Earth. Examples of inclined HEO orbits include Molniya orbits, named after the Molniya Soviet communication satellites which used them, ...
has a apogee, timed to be positioned approximately 90° away from the position of the Moon to minimize its destabilizing effect. This orbit should remain stable for decades and will keep TESS's cameras in a stable temperature range. The orbit is entirely outside the Van Allen belts to avoid radiation damage to TESS, and most of the orbit is spent far outside the belts. Every 13.70 days at its perigee of , TESS downlinks to Earth over a period of approximately 3 hours the data it has collected during the just finished orbit.
Science objectives

 TESS's two-year all-sky survey would focus on nearby G-, K-, and M-
TESS's two-year all-sky survey would focus on nearby G-, K-, and M-type
Type may refer to:
Science and technology Computing
* Typing, producing text via a keyboard, typewriter, etc.
* Data type, collection of values used for computations.
* File type
* TYPE (DOS command), a command to display contents of a file.
* ...
star
A star is a luminous spheroid of plasma (physics), plasma held together by Self-gravitation, self-gravity. The List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs, nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night sk ...
s with apparent magnitude
Apparent magnitude () is a measure of the Irradiance, brightness of a star, astronomical object or other celestial objects like artificial satellites. Its value depends on its intrinsic luminosity, its distance, and any extinction (astronomy), ...
s brighter than magnitude 12. Approximately 500,000 stars were to be studied, including the 1,000 closest red dwarf
A red dwarf is the smallest kind of star on the main sequence. Red dwarfs are by far the most common type of fusing star in the Milky Way, at least in the neighborhood of the Sun. However, due to their low luminosity, individual red dwarfs are ...
s across the whole sky, an area 400 times larger than that covered by the ''Kepler
Johannes Kepler (27 December 1571 – 15 November 1630) was a German astronomer, mathematician, astrologer, natural philosopher and writer on music. He is a key figure in the 17th-century Scientific Revolution, best known for his laws of p ...
'' mission. TESS was expected to find more than 3,000 transiting exoplanet candidates, including 500 Earth-sized planets and super-Earths. Of those discoveries, an estimated 20 were expected to be super-Earths located in the habitable zone
In astronomy and astrobiology, the habitable zone (HZ), or more precisely the circumstellar habitable zone (CHZ), is the range of orbits around a star within which a planetary surface can support liquid water given sufficient atmospheric pressu ...
around a star. The stated goal of the mission was to determine the masses of at least 50 Earth-sized planets (at most 4 times Earth radius). Most detected exoplanets are expected to be between 30 and 300 light-years away.
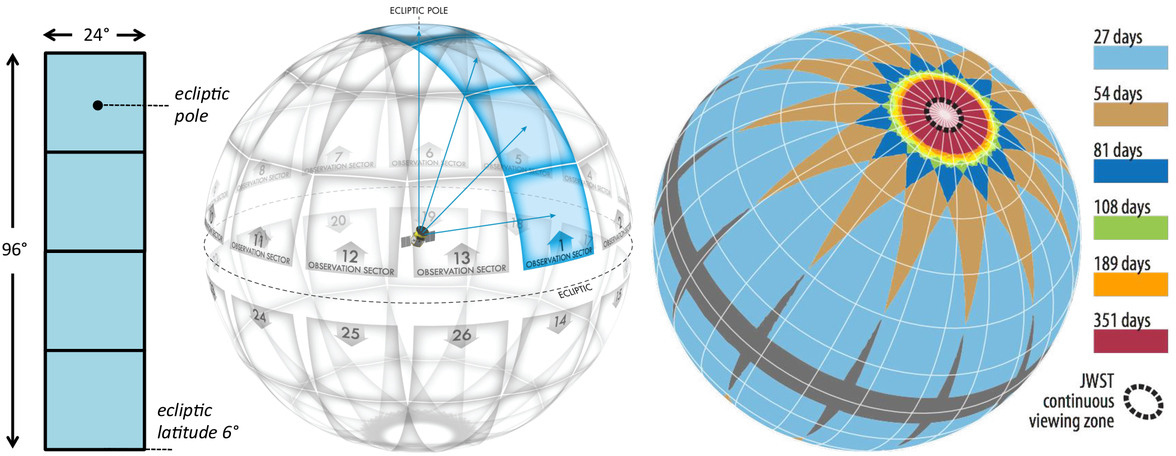
The survey was broken up into 26 observation sectors, each sector being 24° × 96°, with an overlap of sectors at the ecliptic poles to allow additional sensitivity toward smaller and longer-period exoplanets in that region of the celestial sphere. The spacecraft will spend two 13.70-day orbits observing each sector, mapping the southern hemisphere of sky in its first year of operation and the northern hemisphere in its second year. The cameras actually take images every 2 seconds, but all the raw images would represent much more data volume than can be stored or downlinked. To deal with this, cutouts around 15,000 selected stars (per orbit) will be coadded over a 2-minute period and saved on board for downlink, while full-frame images will also be coadded over a 30-minute period and saved for downlink. The actual data downlinks will occur every 13.70 days near perigee. This means that during the 2 years, TESS will continuously survey 85% of the sky for 27 days, with certain parts being surveyed across multiple runs. The survey methodology was designed such that the area that will be surveyed, essentially continuously, over an entire year (351 observation days) and makes up about 5% of the entire sky, will encompass the regions of sky (near the ecliptic poles) which will be observable at any time of year with the James Webb Space Telescope
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is a space telescope designed to conduct infrared astronomy. As the largest telescope in space, it is equipped with high-resolution and high-sensitivity instruments, allowing it to view objects too old, Lis ...
(JWST).
In October 2019, Breakthrough Listen started a collaboration with scientists from the TESS team to look for signs of advanced extraterrestrial life. Thousands of new planets found by TESS will be scanned for "technosignatures" by Breakthrough Listen partner facilities across the globe. Data from TESS monitoring of stars will also be searched for anomalies.
Asteroseismology
The TESS team also plans to use a 30-minute observation cadence for full-frame images, which has been noted for imposing a hardNyquist limit
In signal processing, the Nyquist frequency (or folding frequency), named after Harry Nyquist, is a characteristic of a sampler, which converts a continuous function or signal into a discrete sequence. For a given sampling rate (''samples per ...
that can be problematic for asteroseismology
Asteroseismology is the study of oscillations in stars. Stars have many Resonance, resonant modes and frequencies, and the path of sound waves passing through a star depends on the local speed of sound, which in turn depends on local temperature a ...
of stars. Asteroseismology is the science that studies the internal structure of stars by the interpretation of their frequency spectra. Different oscillation modes penetrate to different depths inside the star. The ''Kepler'' and ''PLATO'' observatories are also intended for asteroseismology.
Extended missions
During the 27 month First Extended Mission, data collection was slightly changed: * A new set of target stars will be selected * The number of stars monitored at 2-minute cadence was increased from 15,000 to 20,000 per observing sector. * Up to 1000 stars per sector will be monitored at a new fast 20-second cadence. * The full-frame image cadence will be increased from every 30 minutes to every 10 minutes. * The pointings and gaps in coverage will be slightly different during the extended mission. * Regions near the ecliptic will be covered. During the second extended mission, the full-frame image cadence will be further increased from every 10 minutes to every 200 seconds, number of 2-minute cadence targets reduced to ~8000 per sector, and number of 20-second cadence targets increased to ~2000 per sector.Launch
In December 2014,SpaceX
Space Exploration Technologies Corp., commonly referred to as SpaceX, is an America, American space technology company headquartered at the SpaceX Starbase, Starbase development site in Starbase, Texas. Since its founding in 2002, the compa ...
was awarded the contract to launch TESS in August 2017, for a total contract value of US$87 million. The spacecraft was originally scheduled to launch on 20 March 2018, but this was pushed back by SpaceX to allow additional time to prepare the launch vehicle and meet NASA launch service requirements. A static fire of the Falcon 9 rocket was completed on 11 April 2018, at approximately 18:30 UTC. The launch was postponed again from 16 April 2018, and TESS was eventually launched on a SpaceX Falcon 9
Falcon 9 is a Reusable launch system#Partial reusable launch systems, partially reusable, two-stage-to-orbit, medium-lift launch vehicle designed and manufactured in the United States by SpaceX. The first Falcon 9 launch was on June 4, 2010, an ...
launch vehicle from the SLC-40 launch site at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
Cape Canaveral Space Force Station (CCSFS) is an installation of the United States Space Force's Space Launch Delta 45, located on Cape Canaveral in Brevard County, Florida.
Headquartered at the nearby Patrick Space Force Base, the sta ...
(CCAFS) on 18 April 2018.
The Falcon 9 launch sequence included a 149-second burn by the first stage, followed by a 6-minute second stage burn. Meanwhile, the first-stage booster performed controlled-reentry maneuvers and successfully landed on the autonomous drone ship ''Of Course I Still Love You''. An experimental water landing was performed for the fairing, as part of SpaceX's attempt to develop fairing reusability.
After coasting for 35 minutes, the second stage performed a final 54-second burn that placed TESS into a supersynchronous transfer orbit of at an inclination
Orbital inclination measures the tilt of an object's orbit around a celestial body. It is expressed as the angle between a reference plane and the orbital plane or axis of direction of the orbiting object.
For a satellite orbiting the Eart ...
of 28.50°. The second stage released the payload, after which the stage itself was placed in a heliocentric orbit
A heliocentric orbit (also called circumsolar orbit) is an orbit around the barycenter of the Solar System, which is usually located within or very near the surface of the Sun. All planets, comets, and asteroids in the Solar System, and the Sun ...
.
Spacecraft
 In 2013,
In 2013, Orbital Sciences Corporation
Orbital Sciences Corporation (commonly referred to as Orbital) was an American company specializing in the design, manufacture, and launch of small- and medium- class space and launch vehicle systems for commercial, military and other governmen ...
received a four-year, US$75 million contract to build TESS for NASA. TESS uses an Orbital Sciences LEOStar-2 satellite bus
A satellite bus (or spacecraft bus) is the main body and structural component of a satellite or spacecraft, in which the payload and all scientific instruments are held.
Bus-derived satellites are less customized than specially-produced satelli ...
, capable of three-axis stabilization using four hydrazine
Hydrazine is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a simple pnictogen hydride, and is a colourless flammable liquid with an ammonia-like odour. Hydrazine is highly hazardous unless handled in solution as, for example, hydraz ...
thrusters plus four reaction wheel
A reaction wheel (RW) is an electric motor attached to a flywheel, which, when its rotation speed is changed, causes a counter-rotation proportionately through conservation of angular momentum. A reaction wheel can rotate only around its center ...
s providing better than three arcsecond
A minute of arc, arcminute (abbreviated as arcmin), arc minute, or minute arc, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of a degree. Since one degree is of a turn, or complete rotation, one arcminute is of a tu ...
fine spacecraft pointing control. Power is provided by two single-axis solar arrays generating 400 watt
The watt (symbol: W) is the unit of Power (physics), power or radiant flux in the International System of Units (SI), equal to 1 joule per second or 1 kg⋅m2⋅s−3. It is used to quantification (science), quantify the rate of Work ...
s. A Ka-band dish antenna provides a 100 Mbit/s
In telecommunications, data transfer rate is the average number of bits (bitrate), characters or symbols (baudrate), or data blocks per unit time passing through a communication link in a data-transmission system. Common data rate units are multi ...
science downlink.
Operational orbit

 Once injected into the initial orbit by the Falcon 9 second stage, the spacecraft performed four additional independent burns that placed it into a lunar flyby orbit. On 17 May 2018, the spacecraft underwent a
Once injected into the initial orbit by the Falcon 9 second stage, the spacecraft performed four additional independent burns that placed it into a lunar flyby orbit. On 17 May 2018, the spacecraft underwent a gravity assist
A gravity assist, gravity assist maneuver, swing-by, or generally a gravitational slingshot in orbital mechanics, is a type of spaceflight flyby (spaceflight), flyby which makes use of the relative movement (e.g. orbit around the Sun) and gra ...
by the Moon at above the surface, and performed the final period adjustment burn on 30 May 2018. It achieved an orbital period of 13.65 days in the desired 2:1 resonance with the Moon, at 90° phase offset to the Moon at apogee, which is expected to be a stable orbit for at least 20 years, thus requiring very little fuel to maintain. The entire maneuvering phase was expected to take a total of two months, and put the craft in an eccentric orbit () at a 37° inclination. The total delta-v
Delta-''v'' (also known as "change in velocity"), symbolized as and pronounced , as used in spacecraft flight dynamics, is a measure of the impulse per unit of spacecraft mass that is needed to perform a maneuver such as launching from or l ...
budget for orbit maneuvers was , which is 80% of the mission's total available reserves. If TESS receives an on-target or slightly above nominal orbit insertion by the Falcon 9, a theoretical mission duration in excess of 15 years would be possible from a consumables standpoint.
Project timeline
The first light image was made on 7 August 2018, and released publicly on 17 September 2018. TESS completed its commissioning phase at the end of July and the science phase officially started on 25 July 2018. For the first two years of operation TESS monitored both the southern (year 1) and northern (year 2) celestial hemispheres. During its nominal mission TESS tiles the sky in 26 separate segments, with a 27.4-day observing period per segment. The first southern survey was completed in July 2019. The first northern survey finished in July 2020. A 27-month First Extended mission ran until September 2022. A second extended mission will run approximately additional three years.Instruments
 The sole instrument on TESS is a package of four wide-field-of-view charge-coupled device (CCD) cameras. Each camera features four low-noise, low-power 4 megapixel CCDs created by
The sole instrument on TESS is a package of four wide-field-of-view charge-coupled device (CCD) cameras. Each camera features four low-noise, low-power 4 megapixel CCDs created by MIT Lincoln Laboratory
The MIT Lincoln Laboratory, located in Lexington, Massachusetts, is a United States Department of Defense federally funded research and development center chartered to apply advanced technology to problems of national security. Research and dev ...
. The four CCDs are arranged in a 2 x 2 detector array for a total of 16 megapixel
In digital imaging, a pixel (abbreviated px), pel, or picture element is the smallest addressable element in a Raster graphics, raster image, or the smallest addressable element in a dot matrix display device. In most digital display devices, p ...
s per camera and 16 CCDs for the entire instrument. Each camera has a 24° × 24° field of view
The field of view (FOV) is the angle, angular extent of the observable world that is visual perception, seen at any given moment. In the case of optical instruments or sensors, it is a solid angle through which a detector is sensitive to elec ...
, a effective pupil diameter, a lens assembly with seven optical elements, and a bandpass range of 600 to 1000 nm. The TESS lenses have a combined field of view of 24° × 96° (2300 deg2, around 5% of the entire sky) and a focal ratio
An f-number is a measure of the light-gathering ability of an optical system such as a camera lens. It is calculated by dividing the system's focal length by the diameter of the entrance pupil ("clear aperture").Smith, Warren ''Modern Optical ...
of f/1.4. The ensquared energy, the fraction of the total energy of the point-spread function that is within a square of the given dimensions centered on the peak, is 50% within 15 × 15 μm and 90% within 60 × 60 μm. For comparison, Kepler's primary mission only covered an area of the sky measuring 105 deg2, though the K2 extension has covered many such areas for shorter times.
The four telescopes in the assembly each have a 10.5-cm diameter lens entrance aperture, with a f/1.4 focal ratio, with a total of seven lenses in the optical train.
Ground operations
The TESS ground system is divided between eight sites around the United States. These includeSpace Network
Space Network (SN) is a NASA program that combines space and ground elements to support spacecraft communications in Earth vicinity. The SN Project Office at Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) manages the SN, which consists of:
* The geosynchr ...
and the Jet Propulsion Laboratory
The Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) is a Federally funded research and development centers, federally funded research and development center (FFRDC) in La Cañada Flintridge, California, Crescenta Valley, United States. Founded in 1936 by Cali ...
's NASA Deep Space Network
The NASA Deep Space Network (DSN) is a worldwide Telecommunications network, network of spacecraft communication ground segment facilities, located in the United States (California), Spain (Madrid), and Australia (Canberra), that supports NASA' ...
for command and telemetry, Orbital ATK
Orbital ATK Inc. was an American aerospace manufacturer and defense industry company. It was formed in February 9, 2015 from the merger of Orbital Sciences Corporation and parts of Alliant Techsystems (ATK). Orbital ATK designed, built, and de ...
's Mission Operations Center, Massachusetts Institute of Technology
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is a Private university, private research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Established in 1861, MIT has played a significant role in the development of many areas of moder ...
's Payload Operations Center, the Ames Research Center
The Ames Research Center (ARC), also known as NASA Ames, is a major NASA research center at Moffett Federal Airfield in California's Silicon Valley. It was founded in 1939 as the second National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) laborat ...
's Science Processing Operations Center, The Goddard Space Flight Center
The Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) is a major NASA space research laboratory located approximately northeast of Washington, D.C., in Greenbelt, Maryland, United States. Established on May 1, 1959, as NASA's first space flight center, GSFC ...
's Flight Dynamics Facility, the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory
The Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory (SAO) is a research institute of the Smithsonian Institution, concentrating on Astrophysics, astrophysical studies including Galactic astronomy, galactic and extragalactic astronomy, cosmology, Sun, solar ...
's TESS Science Office, and the Mikulski Archive for Space Telescopes (MAST).
Stable light source for tests
One of the issues facing the development of this type of instrument is having an ultra-stable light source to test on. In 2015, a group at theUniversity of Geneva
The University of Geneva (French: ''Université de Genève'') is a public university, public research university located in Geneva, Switzerland. It was founded in 1559 by French theologian John Calvin as a Theology, theological seminary. It rema ...
made a breakthrough in the development of a stable light source. While this instrument was created to support ESA's CHEOPS exoplanet observatory, one was also ordered by the TESS program. Although both observatories plan to look at bright nearby stars using the transit method, CHEOPS is focused on collecting more data on known exoplanets, including those found by TESS and other survey missions.
Results
 Current mission results as of 16 May 2025: 627 confirmed exoplanets discovered by TESS, with 7643 candidate-planets that are still awaiting confirmation or rejection as false positive by the
Current mission results as of 16 May 2025: 627 confirmed exoplanets discovered by TESS, with 7643 candidate-planets that are still awaiting confirmation or rejection as false positive by the scientific community
The scientific community is a diverse network of interacting scientists. It includes many "working group, sub-communities" working on particular scientific fields, and within particular institutions; interdisciplinary and cross-institutional acti ...
.
TESS team partners include the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, the Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research, NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, MIT's Lincoln Laboratory, Orbital ATK, NASA's Ames Research Center, the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, and the Space Telescope Science Institute
The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) is the science operations center for the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), science operations and mission operations center for the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), and science operations center for the ...
.
C/2018 N1
TESS started science operations on 25 July 2018. The first announced finding from the mission was the observation ofcomet
A comet is an icy, small Solar System body that warms and begins to release gases when passing close to the Sun, a process called outgassing. This produces an extended, gravitationally unbound atmosphere or Coma (cometary), coma surrounding ...
C/2018 N1.Pi Mensae
The first exoplanet detection announcement was on 18 September 2018, announcing the discovery of a super-Earth in the Pi Mensae system orbiting the star every 6 days, adding to a knownSuper-Jupiter
A super-Jupiter is a gas giant exoplanet that is more massive than the planet Jupiter. For example, substellar companion, companions at the planet–brown dwarf borderline have been called super-Jupiters, such as around the star Kappa Andromedae. ...
orbiting the same star every 5.9 years.LHS 3844 b
On 20 September 2018, the discovery of an ultra-short period planet was announced, slightly larger than Earth, orbiting the red dwarf LHS 3844. With an orbital period of 11 hours, LHS 3844 b is one of the planets with the shortest known period. It orbits its star at a distance of . LHS 3844 b is also one of the closest known exoplanets to Earth, at a distance of 14.9 parsecs.HD 202772 Ab
TESS's third discovered exoplanet is HD 202772 Ab, a hot Jupiter orbiting the brighter component of the visual binary star HD 202772, located in the constellationCapricornus
Capricornus is one of the constellations of the zodiac. Its name is Latin for "horned goat" or "goat Horn (anatomy), horn" or "having horns like a goat's", and it is commonly represented in the form of a sea goat: a mythical creature that is hal ...
at a distance of about 480 light-years from Earth. The discovery was announced on 5 October 2018. HD 202772 Ab orbits its host star once every 3.3 days. It is an inflated hot Jupiter, and a rare example of hot Jupiters around evolved stars. It is also one of the most strongly irradiated planets known, with an equilibrium temperature of .HD 21749
On 15 April 2019, TESS' first discovery of an earth-sized planet was reported. HD 21749 c is a planet described as "likely rocky", with about 89% of Earth's diameter and orbits the K-type main sequence star HD 21749 in about 8 days. The planet's surface temperature is estimated to be as high as 427 °C. Both known planets in the system, HD 21749 b and HD 21749 c, were discovered by TESS. HD 21749 c represents the 10th confirmed planet discovery by TESS.MAST Data collaboration
Data on exoplanet candidates continue to be made available at MAST. As of 20 April 2019, the total number of candidates on the list was up to 335. Besides candidates identified as previously discovered exoplanets, this list also includes ten newly discovered exoplanets, including the five mentioned above. Forty-four of the candidates from Sector 1 in this list were selected for follow-up observations by the TESS Follow-Up Program (TFOP), which aims to aid the discovery of 50 planets with a planetary radius of ''R'' < 4 ''R''E through repeated observations. The list of candidate exoplanets continues to grow as additional results are being published on the same MAST page.Changing to the Northern Sky
On 18 July 2019, after the first year of operation the southern portion of the survey was completed, it turned its cameras to the Northern Sky. As of this time it has discovered 21 planets and has over 850 candidate exoplanets.DS Tucanae Ab
On 23 July 2019, the discovery of the young exoplanet DS Tucanae Ab (HD 222259 Ab) in the ~45 Myr old Tucana-Horologium young moving group was published in a paper. TESS first observed the planet in November 2018 and it was confirmed in March 2019. The young planet is larger than Neptune, but smaller than Saturn. The system is bright enough to follow up with radial velocity and transmission spectroscopy. ESA's CHEOPS mission will observe the transits of the young exoplanet DS Tuc Ab. A team of scientists got 23.4 orbits approved in the first Announcement of Opportunity (AO-1) for the CHEOPS Guest Observers (GO) Programme to characterize the planet.Gliese 357
On 31 July 2019, the discovery of exoplanets around the M-type dwarf star Gliese 357 at a distance of 31 light years from Earth was announced. TESS directly observed the transit of GJ 357 b, a hot earth with an equilibrium temperature of around 250 °C. Follow-up ground observations and analyses of historic data lead to the discovery of GJ 357 c and GJ 357 d. While GJ 357 b and GJ 357 c are too close to the star to be habitable, GJ 357 d resides at the outer edge of the star'shabitable zone
In astronomy and astrobiology, the habitable zone (HZ), or more precisely the circumstellar habitable zone (CHZ), is the range of orbits around a star within which a planetary surface can support liquid water given sufficient atmospheric pressu ...
and may possess habitable conditions if it has an atmosphere. With at least 6.1 ME it is classified as a Super-Earth.Count of exoplanets in 2019
As of September 2019, over 1000 ''TESS Objects of Interest'' (''ToI'') have been listed in the public database, at least 29 of which are confirmed planets, about 20 of which within the stated goal of the mission of Earth-sized (<4 Earth radii).ASASSN-19bt
On 26 September 2019, it was announced that TESS observed its firsttidal disruption event
A tidal disruption event (TDE) is a time-domain astronomy, transient astronomical source produced when a star passes so close to a supermassive black hole (SMBH) that it is pulled apart by the black hole's tidal force. The star undergoes spaghett ...
(TDE), called ASASSN-19bt. The TESS data revealed that ASASSN-19bt began to brighten on 21 January 2019, ~8.3 days before the discovery by ASAS-SN.TOI-700
On 6 January 2020, NASA reported the discovery of TOI-700 d, the first Earth-sizedexoplanet
An exoplanet or extrasolar planet is a planet outside the Solar System. The first confirmed detection of an exoplanet was in 1992 around a pulsar, and the first detection around a main-sequence star was in 1995. A different planet, first det ...
in the habitable zone
In astronomy and astrobiology, the habitable zone (HZ), or more precisely the circumstellar habitable zone (CHZ), is the range of orbits around a star within which a planetary surface can support liquid water given sufficient atmospheric pressu ...
discovered by the TESS. The exoplanet orbits the star TOI-700 100 light-years away in the Dorado constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object.
The first constellati ...
. The TOI-700 system contains two other planets: TOI-700 b, another Earth-sized planet, and TOI-700 c, a super-Earth. This system is unique in that the larger planet is found between the two smaller planets. It is currently unknown how this arrangement of planets came to be, whether these planets formed in this order or if the larger planet migrated to its current orbit. On the same day, NASA announced that astronomers used TESS data to show that Alpha Draconis is an eclipsing binary star
A binary star or binary star system is a Star system, system of two stars that are gravity, gravitationally bound to and in orbit around each other. Binary stars in the night sky that are seen as a single object to the naked eye are often resolved ...
.
TOI-1338
NASA also announced the discovery of TOI-1338 b, the first circumbinary planet discovered by TESS. TOI-1338 b is around 6.9 times larger than Earth, or between the sizes ofNeptune
Neptune is the eighth and farthest known planet from the Sun. It is the List of Solar System objects by size, fourth-largest planet in the Solar System by diameter, the third-most-massive planet, and the densest giant planet. It is 17 t ...
and Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant, with an average radius of about 9 times that of Earth. It has an eighth the average density of Earth, but is over 95 tim ...
. It lies in a system 1,300 light-years away in the constellation Pictor. The stars in the system make an eclipsing binary, which occurs when the stellar companions circle each other in our plane of view. One is about 10% more massive than the Sun, while the other is cooler, dimmer and only one-third the Sun's mass. TOI-1338 b's transits are irregular, between every 93 and 95 days, and vary in depth and duration thanks to the orbital motion of its stars. TESS only sees the transits crossing the larger star — the transits of the smaller star are too faint to detect. Although the planet transits irregularly, its orbit is stable for at least the next 10 million years. The orbit's angle to us, however, changes enough that the planet transit will cease after November 2023 and resume eight years later.
HD 108236
On 25 January 2021, a team led by astrochemist Tansu Daylan, with the help of two high school interns as part of the Science Research Mentoring Program at Harvard & MIT, discovered and validated four extrasolar planets — composed of one super-Earth and three sub-Neptunes - hosted by the bright, nearby, Sun-like star HD 108236. The two high schoolers, 18 year old Jasmine Wright of Bedford High School inBedford, Massachusetts
Bedford is a town in Middlesex County, Massachusetts, United States. The population of Bedford was 14,161 at th2022 United States census
History
''The following compilation comes from Ellen Abrams (1999) based on information from Abram Engl ...
, and 16 year old Kartik Pinglé of Cambridge Ringe And Latin School, of Cambridge, Massachusetts
Cambridge ( ) is a city in Middlesex County, Massachusetts, United States. It is a suburb in the Greater Boston metropolitan area, located directly across the Charles River from Boston. The city's population as of the 2020 United States census, ...
, are reported to be the youngest individuals in history to discover a planet, let alone four.TIC 168789840
On 27 January 2021, several news agencies reported that a team using TESS had determined that TIC 168789840, a stellar system with six stars in three binary pairs was oriented so astronomers could observe the eclipses of all the stars. It is the first six star system of its kind.Count of exoplanets in 2021
In March 2021, NASA announced that TESS found 2200 exoplanet candidates. By the end of 2021, TESS had discovered over 5000 candidates.TOI-1231 b
On 17 May 2021, an international team of scientists, including researchers from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory and theUniversity of New Mexico
The University of New Mexico (UNM; ) is a public research university in Albuquerque, New Mexico, United States. Founded in 1889 by the New Mexico Territorial Legislature, it is the state's second oldest university, a flagship university in th ...
, reported, and confirmed by a ground based telescope, the space telescope's first discovery of a Neptune-sized exoplanet, TOI-1231 b, inside a habitable zone. The planet orbits a nearby red dwarf star, 90 light-years away in the Vela constellation.
Exoplanet search programs
The TESS Objects of Interest (TOI) are assigned by the TESS team and the Community TOIs (CTOI) are assigned by independent researchers. The primary mission of TESS produced 2241 TOIs. Other small and large collaborations of researchers try to confirm the TOIs and CTOIs, or try to find new CTOIs. Some of the collaborations with names that are searching exclusively for TESS planets are: * Thecitizen science
The term citizen science (synonymous to terms like community science, crowd science, crowd-sourced science, civic science, participatory monitoring, or volunteer monitoring) is research conducted with participation from the general public, or am ...
project Planet Hunters: TESS (PHT)
* TESS Hunt for Young and Maturing Exoplanets (THYME)
* The TESS-Keck Survey (TKS)
* TESS Giants Transiting Giants (TESS GTG)
Collaborations with currently a smaller amount of discovery papers:
* Warm gIaNts with tEss collaboration (WINE)
* The TESS Grand Unified Hot Jupiter Survey
The TESS community is also producing software
Software consists of computer programs that instruct the Execution (computing), execution of a computer. Software also includes design documents and specifications.
The history of software is closely tied to the development of digital comput ...
and programs to help validate the planet candidates, such as TRICERATOPS, DAVE, Lightkurve, Eleanor and Planet Patrol.
In popular culture
TESS is featured accurately in the 2018 film '' Clara''.See also
* ARIEL, 2029 exoplanet atmospheres observatory * CHEOPS, 2019 exoplanet observatory *CoRoT
CoRoT (French: ; English: Convection, Rotation and planetary Transits) was a space telescope mission which operated from 2006 to 2013. The mission's two objectives were to search for extrasolar planets with short orbital periods, particularly t ...
, 2006–2012 exoplanet observatory
* Kepler
Johannes Kepler (27 December 1571 – 15 November 1630) was a German astronomer, mathematician, astrologer, natural philosopher and writer on music. He is a key figure in the 17th-century Scientific Revolution, best known for his laws of p ...
, 2009–2018 exoplanet observatory
* MOST, 2003–2019 asteroseismology and exoplanet observatory
* PLATO
Plato ( ; Greek language, Greek: , ; born BC, died 348/347 BC) was an ancient Greek philosopher of the Classical Greece, Classical period who is considered a foundational thinker in Western philosophy and an innovator of the writte ...
, 2026 exoplanet observatory
* SWEEPS, 2006 Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope (HST or Hubble) is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation. It was not the Orbiting Solar Observatory, first space telescope, but it is one of the largest and most ...
exoplanet survey
* TOI-2119
* List of transiting exoplanets
References
Further reading
* *External links
TESS twitter account
by NASA
TESS website
by NASA Goddard
TESS website
by Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT)
TESS discovered exoplanets
by MIT
TESS website
by the Kavli Foundation
Planet Hunters TESS
anyone can help classifying TESS data
TESS listing of Southern Sky panoramas
(July 18, 2019)
APOD (April 21, 2018)
Interactive 3D simulation of TESS's 2:1 lunar resonant orbit
{{Portal bar, Astronomy, Stars, Spaceflight, Solar System, Science Space probes launched in 2018 Space telescopes Explorers Program NASA space probes NASA programs Exoplanet search projects SpaceX payloads contracted by NASA 2018 establishments in Florida Asteroseismology