Transcranial Random Noise Stimulation on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Transcranial random noise stimulation (tRNS) is a non-invasive brain stimulation technique and a form of transcranial electrical stimulation (tES). Terney et al from
 Transcranial electrical stimulation (tES) generally includes the following techniques:
*
Transcranial electrical stimulation (tES) generally includes the following techniques:
*
Göttingen University
Göttingen (, , ; nds, Chöttingen) is a university city in Lower Saxony, central Germany, the capital of the eponymous district. The River Leine runs through it. At the end of 2019, the population was 118,911.
General information
The orig ...
was the first group to apply tRNS in humans in 2008. They showed that by using an alternate current
Alternating current (AC) is an electric current which periodically reverses direction and changes its magnitude continuously with time in contrast to direct current (DC) which flows only in one direction. Alternating current is the form in which ...
along with random amplitude and frequency (between 0.1 and 640 Hz) in healthy subjects, the motor cortex
The motor cortex is the region of the cerebral cortex believed to be involved in the planning, control, and execution of voluntary movements.
The motor cortex is an area of the frontal lobe located in the posterior precentral gyrus immediately ...
excitability increased (i.e. increased amplitude of motor evoked potentials
An evoked potential or evoked response is an electrical potential in a specific pattern recorded from a specific part of the nervous system, especially the brain, of a human or other animals following presentation of a stimulus such as a light fla ...
) for up to 60 minutes after 10 minutes of stimulation. The study included all the frequencies up to half of the sampling rate
In signal processing, sampling is the reduction of a continuous-time signal to a discrete-time signal. A common example is the conversion of a sound wave to a sequence of "samples".
A sample is a value of the signal at a point in time and/or sp ...
(1280 samples/s) i.e. 640 Hz, however the positive effect was limited only to higher frequencies. Although tRNS has shown positive effects in various studies the optimal parameters, as well as the potential clinical effects of this technique, remain unclear.
Mechanism of action
The physiological mechanisms underlying the effects of tRNS are not well known, however many hypotheses have been suggested. The robust changes in cortical excitability observed after tRNS could be attributed to the repeated opening ofsodium channels
Sodium channels are integral membrane proteins that form ion channels, conducting sodium ions (Na+) through a cell's membrane. They belong to the superfamily of cation channels and can be classified according to the trigger that opens the channel ...
and changes in their kinetics of activation and inactivation (''Remedios et al. 2019 Effects of Short-Term Random Noise Electrical Stimulation on Dissociated Pyramidal Neurons from the Cerebral Cortex. Neuroscience. 404:371-386.'' https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2019.01.035) ''o''r to the increased sensitivity of neuronal networks to modulation. tRNS may influence cortical oscillations, leading to changes in excitability. These proposed mechanisms are consistent with the observation that reversing electrode polarities in tRNS does not interfere with the augmentation in cortical excitability, suggesting that tRNS-induced cortical excitability is independent of current flow direction.
Since tRNS is a repetitive, random, and subthreshold stimulation, it is speculated that tRNS induces direct temporal summation
Summation, which includes both spatial summation and temporal summation, is the process that determines whether or not an action potential will be generated by the combined effects of excitatory and inhibitory signals, both from multiple simultan ...
of neural activity because the time constant of a neuron is sufficiently long to permit the summation of two stimuli presented in close succession.
The effects of tRNS may also be explained in the context of the stochastic resonance phenomenon. tRNS is, by definition, a stimulation that induces non-finalized random activity in the system (i.e., noise). The presence of neuronal noise might enhance the sensitivity of the neurons to a given range of weak inputs (''Huidobro et al., 2018 Optogenetic noise-photostimulation on the brain increases somatosensory spike firing responses. Neurosci Lett. 664:51-57.''https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2017.11.004)
Comparison with other tES techniques
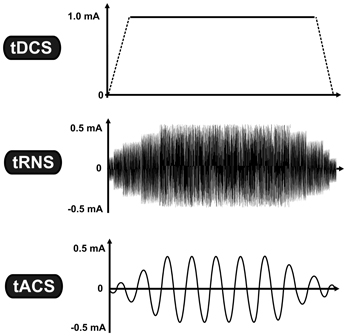
 Transcranial electrical stimulation (tES) generally includes the following techniques:
*
Transcranial electrical stimulation (tES) generally includes the following techniques:
*Transcranial alternating current stimulation
Cranial electrotherapy stimulation (CES) is a form of neurostimulation that delivers a small, pulsed, alternating current via electrodes on the head. CES is used with the intention of treating a variety of conditions such as anxiety, depression a ...
(tACS)
* Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS)
*Transcranial random noise stimulation (tRNS)
* Transcranial pulsed current stimulation (tPCS)
tRNS stimulation differs from tDCS in that instead of constant direct current delivery, current levels are ''randomly'' generated, with a normal distribution
In statistics, a normal distribution or Gaussian distribution is a type of continuous probability distribution for a real-valued random variable. The general form of its probability density function is
:
f(x) = \frac e^
The parameter \mu i ...
around a specific mean intensity. Other parameters related to the stimulation electrodes, like position and size, are similar to tDCS.
Compared to tDCS, tRNS has also the advantage of being more comfortable, which makes it potentially advantageous for setting and blinding studies.
tRNS is easier to blind than tDCS with the 50% perception threshold for tDCS at 400 µA while this threshold was at 1200 µA in the case of tRNS.
tACS (transcranial alternating current stimulation) is a frequency-specific stimulation method that is also thought to influence oscillatory neuronal activity. This method differs from tRNS in that a sinusoidal
A sine wave, sinusoidal wave, or just sinusoid is a mathematical curve defined in terms of the '' sine'' trigonometric function, of which it is the graph. It is a type of continuous wave and also a smooth periodic function. It occurs often in ...
current is applied at a fixed frequency rather than a randomly presented range of frequencies. Often, tACS is applied at frequencies that mirror the predominant frequency bands observed in EEG in different regions of the brain.
See also
*Neurostimulation
Neurostimulation is the purposeful modulation of the nervous system's activity using invasive (e.g. microelectrodes) or non-invasive means (e.g. transcranial magnetic stimulation or transcranial electric stimulation, tES, such as tDCS or tran ...
* Transcranial magnetic stimulation
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is a noninvasive form of brain stimulation in which a changing magnetic field is used to induce an electric current at a specific area of the brain through electromagnetic induction. An electric pulse gener ...
(TMS)
References
{{reflist Neurostimulation Neurophysiology