Toubous on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Toubou or Tubu (from Old Tebu, meaning "rock people") are an
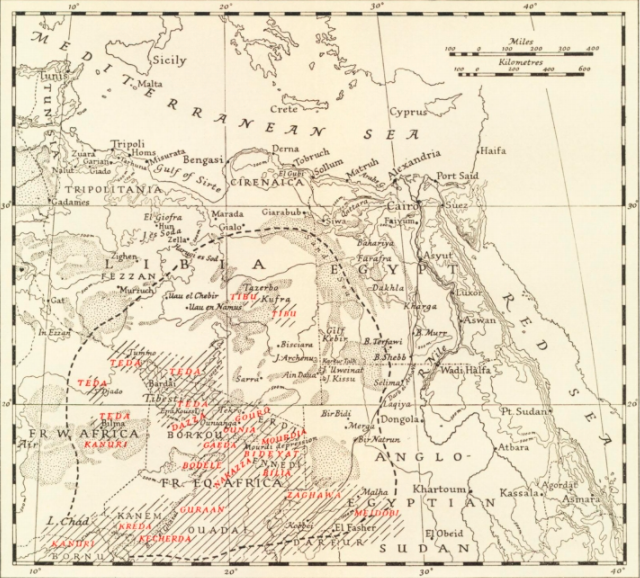 The ancient history of the Toubou people is unclear. They may be related to the 'Ethiopians' mentioned by
The ancient history of the Toubou people is unclear. They may be related to the 'Ethiopians' mentioned by
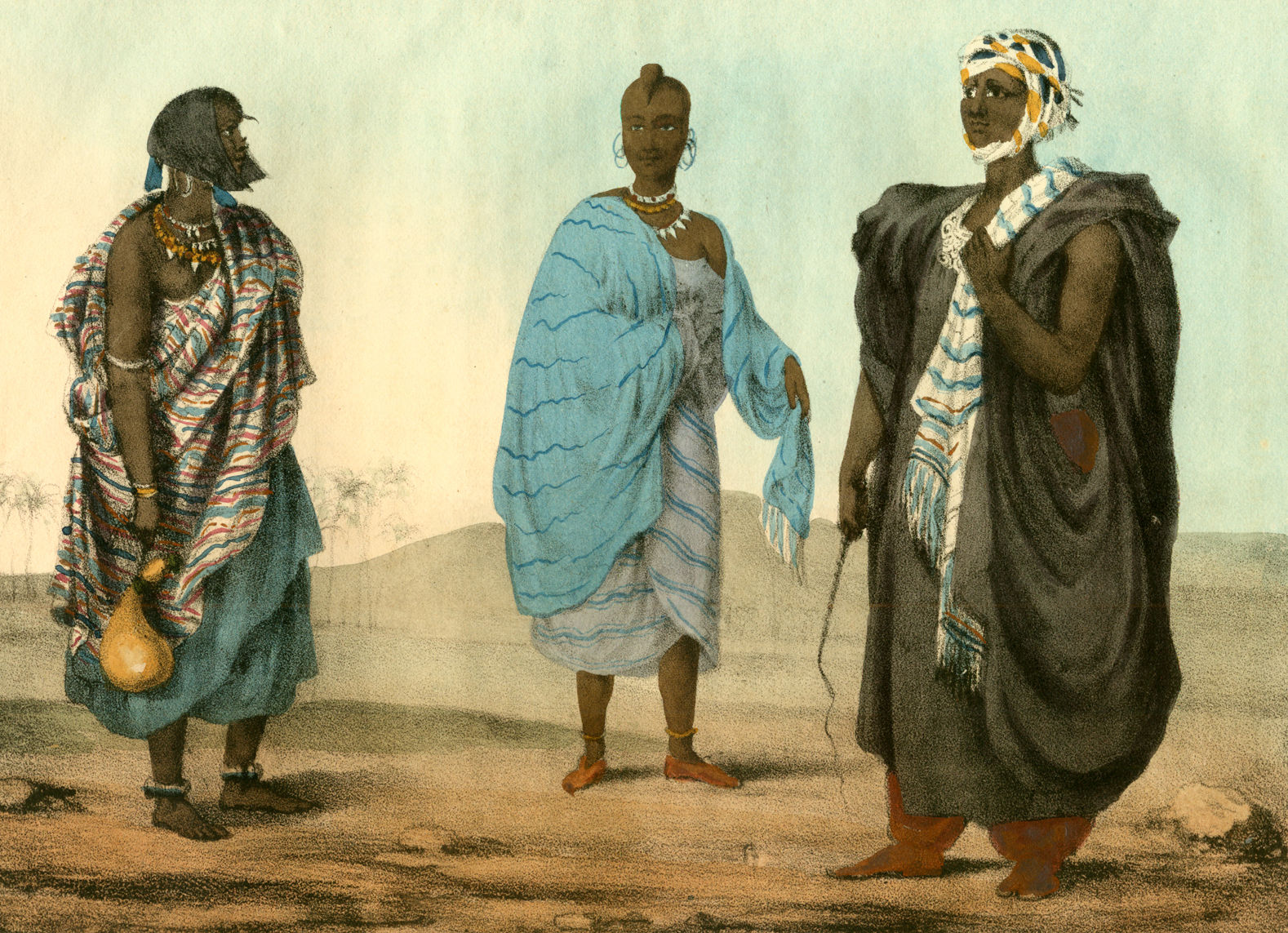

 The Toubou people, states Jean Chapelle, have been socially stratified with an embedded caste system. The three strata have consisted of the freemen with a right to own property, the artisanal castes and the slaves.
The endogamous caste of ''Azza'' (or ''Aza'') among Toubou have the
The Toubou people, states Jean Chapelle, have been socially stratified with an embedded caste system. The three strata have consisted of the freemen with a right to own property, the artisanal castes and the slaves.
The endogamous caste of ''Azza'' (or ''Aza'') among Toubou have the


 Much of the political class of Chad are drawn from Dazzaga. During the First Chadian Civil War (1966–1979), the '' derde'' came to occupy a more important position. In 1965 the Chadian government assumed direct authority over the Tibesti Mountains, sending a military garrison and administrators to Bardaï, the capital of Tibesti Sub-prefecture. Within a year, abuses of authority had roused considerable opposition among the Toubou. The ''derde'', Oueddei Kichidemi, recognized but little respected up to that time, protested the excesses, went into exile in
Much of the political class of Chad are drawn from Dazzaga. During the First Chadian Civil War (1966–1979), the '' derde'' came to occupy a more important position. In 1965 the Chadian government assumed direct authority over the Tibesti Mountains, sending a military garrison and administrators to Bardaï, the capital of Tibesti Sub-prefecture. Within a year, abuses of authority had roused considerable opposition among the Toubou. The ''derde'', Oueddei Kichidemi, recognized but little respected up to that time, protested the excesses, went into exile in
ethnic group
An ethnicity or ethnic group is a group of people with shared attributes, which they collectively believe to have, and long-term endogamy. Ethnicities share attributes like language, culture, common sets of ancestry, traditions, society, re ...
native to the Tibesti Mountains
The Tibesti Mountains are a mountain range in the central Sahara, primarily located in the extreme north of Chad, with a small portion located in southern Libya. The highest peak in the range, Emi Koussi, lies to the south at a height of and i ...
that inhabit the central Sahara
The Sahara (, ) is a desert spanning across North Africa. With an area of , it is the largest hot desert in the world and the list of deserts by area, third-largest desert overall, smaller only than the deserts of Antarctica and the northern Ar ...
in northern Chad
Chad, officially the Republic of Chad, is a landlocked country at the crossroads of North Africa, North and Central Africa. It is bordered by Libya to Chad–Libya border, the north, Sudan to Chad–Sudan border, the east, the Central Afric ...
, southern Libya
Libya, officially the State of Libya, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to Egypt–Libya border, the east, Sudan to Libya–Sudan border, the southeast, Chad to Chad–L ...
, northeastern Niger
Niger, officially the Republic of the Niger, is a landlocked country in West Africa. It is a unitary state Geography of Niger#Political geography, bordered by Libya to the Libya–Niger border, north-east, Chad to the Chad–Niger border, east ...
, and northwestern Sudan
Sudan, officially the Republic of the Sudan, is a country in Northeast Africa. It borders the Central African Republic to the southwest, Chad to the west, Libya to the northwest, Egypt to the north, the Red Sea to the east, Eritrea and Ethiopi ...
. They live either as herders and nomads or as farmers near oases. Their society is clan-based, with each clan having certain oases, pastures and wells.
The Toubou are generally divided into two closely related groups: the Teda (or Tuda, Téda, Toda, Tira) and the Daza (or Dazzaga, Dazagara, Dazagada). They are believed to share a common origin and speak the Tebu languages, which are from the Saharan branch of the Nilo-Saharan
The Nilo-Saharan languages are a proposed family of around 210 African languages spoken by somewhere around 70 million speakers, mainly in the upper parts of the Chari and Nile rivers, including historic Nubia, north of where the two tributari ...
language family. Tebu is divided further into two closely related languages, called '' Tedaga'' (Téda Toubou) and ''Dazaga
Daza (also known as Dazaga) is a Nilo-Saharan language spoken by the Daza people (a sub-group of the Toubou people) inhabiting northern Chad and eastern Niger. The Daza are also known as the Gouran (Gorane) in Chad. Dazaga is spoken by around ...
'' (Daza Toubou). Of the two groups, the Daza, found to the south of the Teda, are more numerous.
The Toubou people are also referred to as the Tabu, Tebu, Tebou, Tibu, 'Tibbu, Toda, Todga, Todaga, Tubu, Tuda, Tudaga, or Gorane people. The Daza are sometimes referred to as Gouran (or Gorane, Goran, Gourane), an Arabian exonym. Many of Chad's leaders have been Toubou (Gouran), including presidents Goukouni Oueddei
Goukouni Oueddei ( '; born 1944) is a Chadian politician who served as President of Chad from 1979 to 1982.
A northerner, Goukouni commanded FROLINAT rebels with Libyan support during the first Chadian Civil War against Chad's southern-domin ...
and Hissène Habré
Hissène Habré (Arabic: ''Ḥusaīn Ḥabrī'', Chadian Arabic: ; ; 13 August 1942 – 24 August 2021), also spelled Hissen Habré, was a Chadian politician and convicted war criminal who served as the 5th president of Chad from 1982 unt ...
.
Distribution
The Toubou people have historically lived in northern Chad, northeastern Niger, and southern Libya. They have sometimes been called the "black nomads of the Sahara". They are distributed across a large area in the central Sahara, as well as the north-centralSahel
The Sahel region (; ), or Sahelian acacia savanna, is a Biogeography, biogeographical region in Africa. It is the Ecotone, transition zone between the more humid Sudanian savannas to its south and the drier Sahara to the north. The Sahel has a ...
. They are particularly found north of the Tibesti mountains
The Tibesti Mountains are a mountain range in the central Sahara, primarily located in the extreme north of Chad, with a small portion located in southern Libya. The highest peak in the range, Emi Koussi, lies to the south at a height of and i ...
, which in Old Tebu means "Rocky Mountains". The first syllable "Tu" refers to the Tibesti mountains, as known by the natives (Tuda), and the second syllable "bo" refers to blood in the Kanembou language; thus, people from the Tibesti region are referred to as Tubou." Their name is derived from this.
The Teda are found primarily in the Sahara
The Sahara (, ) is a desert spanning across North Africa. With an area of , it is the largest hot desert in the world and the list of deserts by area, third-largest desert overall, smaller only than the deserts of Antarctica and the northern Ar ...
regions around the borders of southeast Libya, northeast Niger
Niger, officially the Republic of the Niger, is a landlocked country in West Africa. It is a unitary state Geography of Niger#Political geography, bordered by Libya to the Libya–Niger border, north-east, Chad to the Chad–Niger border, east ...
and northern Chad
Chad, officially the Republic of Chad, is a landlocked country at the crossroads of North Africa, North and Central Africa. It is bordered by Libya to Chad–Libya border, the north, Sudan to Chad–Sudan border, the east, the Central Afric ...
. They consider themselves a warrior people. The Daza live towards the Sahel region and are spread over much of north-central Chad. The Daza consist of numerous clans. Some major tribes, clans, societies of the Daza, or Gouran, include the Alala, Altafa, Anakaza, Ankorda, Ayya, Sharara, Sharfada, Shuna, Daza, Djagada, Dogorda, Donza, Gadwa, Gaeda, Howda, Kamaya, Kamsoulla, Kara, Ketcherda, Kokorda, Maghya, Medelea, Mourdiya, Nara, Salma, Tchiroua, Tchoraga, Wandala, Wandja, Warba, Warda, Yira and many more. The Daza cover the northern regions of Chad such as the Bourkou, the Ennedi Plateau
The Ennedi Plateau is located in the northeast of Chad, in the regions of Ennedi-Ouest Region, Ennedi-Ouest and Ennedi-Est Region, Ennedi-Est. It is considered a part of the group of mountains known as the Ennedi Massif found in Chad, which is o ...
, the northern Kanem, the Bahr el Gazel in the south and also the Tibesti mountains and the neighbouring countries. There is a diaspora community of several thousand Daza living in Omdurman
Omdurman () is a major city in Sudan. It is the second most populous city in the country, located in the State of Khartoum. Omdurman lies on the west bank of the River Nile, opposite and northwest of the capital city of Khartoum. The city acts ...
, Sudan and a couple of thousand working in Jeddah
Jeddah ( ), alternatively transliterated as Jedda, Jiddah or Jidda ( ; , ), is a List of governorates of Saudi Arabia, governorate and the largest city in Mecca Province, Saudi Arabia, and the country's second largest city after Riyadh, located ...
, Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in West Asia. Located in the centre of the Middle East, it covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula and has a land area of about , making it the List of Asian countries ...
.
History
 The ancient history of the Toubou people is unclear. They may be related to the 'Ethiopians' mentioned by
The ancient history of the Toubou people is unclear. They may be related to the 'Ethiopians' mentioned by Herodotus
Herodotus (; BC) was a Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus (now Bodrum, Turkey), under Persian control in the 5th century BC, and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria, Italy. He wrote the '' Histori ...
in 430 BCE, as a people being hunted by the Garamantes
The Garamantes (; ) were ancient peoples, who may have descended from Berbers, Berber tribes, Toubous, Toubou tribes, and Saharan Pastoral period, pastoralists that settled in the Fezzan region by at least 1000 BC and established a civilization t ...
, but this is speculative, as Jean Chapelle argues. Furthermore, scholars such as Laurence P. Kirwan stress that the Garamantes and the Toubou seem to occupy the same lands. Which spans from the Fezzan (Phazania) as far south as Nubia. Further evidence is given by Harold MacMichael states that the Bayuda desert was still known as the desert of Goran; a name as MacMichael has shown, connected with the Kura'án of today. This reaffirms that the Kura'án (Goran) of today, occupy much of the same territory as the Garamantes once did.
In Islamic literature
Islamic literature is literature written by Muslim people, influenced by an Islamic culture, Islamic cultural perspective, or literature that portrays Islam. It can be written in any language and portray any country or region. It includes many lite ...
, the earliest mention as the Toubou people is perhaps that along with the Zaghawa people in an 8th-century text by Arabic scholar Ibn Qutaybah
Abū Muḥammad ʿAbd Allāh ibn Muslim ibn Qutayba al-Dīnawarī al-Marwazī better known simply as Ibn Qutaybah (; c. 828 – 13 November 889 CE/213 – 15 Rajab 276 AH) was an Islamic scholar of Persian people, Persian descent. He served as a q ...
. The 9th century al-Khwarizmi
Muhammad ibn Musa al-Khwarizmi , or simply al-Khwarizmi, was a mathematician active during the Islamic Golden Age, who produced Arabic-language works in mathematics, astronomy, and geography. Around 820, he worked at the House of Wisdom in B ...
mentions the Daza people (southern Teda).
During the expansive era of Trans-Saharan trade, the Toubou inhabited lands which were frequently used by merchant caravans, specifically along the Kufra
Kufra () is a basinBertarelli (1929), p. 514. and oasis group in the Kufra District of southeastern Cyrenaica in Libya. At the end of the 19th century, Kufra became the centre and holy place of the Senussi order. It also played a minor role in ...
oasis routes. It is unknown if the Toubou engaged with the caravans.
In the 18th century, local toubou's of Kaouar were an Independent city
An independent city or independent town is a city or town that does not form part of another general-purpose local government entity (such as a province).
Historical precursors
In the Holy Roman Empire, and to a degree in its successor states ...
, until 1870 when the ruling Kerdusian tribe ( Sanhajan from Zawiya) of Fezzan
Fezzan ( , ; ; ; ) is the southwestern region of modern Libya. It is largely desert, but broken by mountains, uplands, and dry river valleys (wadis) in the north, where oases enable ancient towns and villages to survive deep in the otherwise in ...
al hasan al balaazi ended their rule according to Manuscript
A manuscript (abbreviated MS for singular and MSS for plural) was, traditionally, any document written by hand or typewritten, as opposed to mechanically printed or reproduced in some indirect or automated way. More recently, the term has ...
Genetics
According to a study published in '' The American Journal of Human Genetics'' (Haber et al. 2016) that examined Y-DNA haplogroups from samples obtained from 75 Toubou men, haplogroups associated with paternal Eurasian ancestry were present at rates of 34% for R1b (R1b-V88), 31% for T1a, and 1% for J1. The North African associated haplogroup E-M78 were present at rates of 28%, while E-M81 appeared at a rate of 5%. The study also found that 20–30% of Toubou autosomal DNA was Eurasian in origin, and their African ancestral component was best represented by Laal-speaking populations. The most likely source of this Eurasian DNA, according to the analysis, was central European Neolithic farmers ( Linearbandkeramik culture). Other ethnic groups in theChad
Chad, officially the Republic of Chad, is a landlocked country at the crossroads of North Africa, North and Central Africa. It is bordered by Libya to Chad–Libya border, the north, Sudan to Chad–Sudan border, the east, the Central Afric ...
, such as the Sara people
The Sara people, sometimes referred to as the Kaba or Sara-Kaba, are a Central Sudanic ethnic group native to southern Chad, the northwestern areas of the Central African Republic, and the southern border of South Sudan. They speak the Sara langua ...
and the Laal speakers had considerably lower Eurasian admixture, at only 0.3–2% (Sara) and 1.25–4.5% (Laal).
In 2019, B Lorente-Galdos using whole genome analysis, found that in the two Northeastern Sub-Saharan samples, this Western Eurasian ancestry in their Toubou sample was 31.4%, and it was 14.9% for the East African Bantu. The Toubou also maintained similar genetic distance to other Sub-Saharan samples, but was also genetically close to North African and non-African samples. The Eurasian component in the North African individuals was present at high rates of 84.9% for the Saharawi, and 76.0% for the Libyan. North African samples were closer to Eurasian populations than to Sub-Saharan populations, implying that the Sahara Desert might have represented a major barrier within Africa. In contrast, the three Khoisan groups presented significantly small proportions of a Eurasian component (3.83–4.11%).
Society


Livelihood
Toubou life centers on raising and herding theirlivestock
Livestock are the Domestication, domesticated animals that are raised in an Agriculture, agricultural setting to provide labour and produce diversified products for consumption such as meat, Egg as food, eggs, milk, fur, leather, and wool. The t ...
, or on farming the scattered oases where they cultivate dates, grain
A grain is a small, hard, dry fruit (caryopsis) – with or without an attached husk, hull layer – harvested for human or animal consumption. A grain crop is a grain-producing plant. The two main types of commercial grain crops are cereals and ...
and legumes
Legumes are plants in the pea family Fabaceae (or Leguminosae), or the fruit or seeds of such plants. When used as a dry grain for human consumption, the seeds are also called pulses. Legumes are grown agriculturally, primarily for human consu ...
. Their herds include dromedaries, goats, cattle, donkeys and sheep. Livestock is a major part of their wealth, and trade. Livestock is also used as a part of dowry payment during marriage, either as one where the groom's family agrees to pay to the bride's family in exchange for the bride, or it is given by the bride's kin to supply the young couple with economic resources in order to start a family.
In a few places, the Toubou also mine salt and natron
Natron is a naturally occurring mixture of sodium carbonate decahydrate ( Na2CO3·10H2O, a kind of soda ash) and around 17% sodium bicarbonate (also called baking soda, NaHCO3) along with small quantities of sodium chloride and sodium sulfate. ...
, a salt-like substance which is essential in nearly all components of Toubou life from medicine, as a mixture in chewing tobacco, preservation, tanning, soap production, textiles and for livestock. Literacy rates among the Toubou are quite low.
Clan
Many Toubou people still follow a semi-nomadic pastoralist lifestyle. Those who prefer a settled life typically live in palm-thatched, rectangular or cylindrical mud houses. The Toubou are patrilineal, with an elder male heading the lineage. The second order of Toubou kinship is to theclan
A clan is a group of people united by actual or perceived kinship
and descent. Even if lineage details are unknown, a clan may claim descent from a founding member or apical ancestor who serves as a symbol of the clan's unity. Many societie ...
.
According to Jean Chapelle, a colonial officer of history specializing in Chadian ethnic groups (although his book in Borkou has caused a significant degree of wrongdoing), the clan system developed out of necessity. Nomadic life means being scattered throughout a region; therefore, belonging to a clan means that the individual is likely to find hospitable clan people in most settlements or camps of any size.
A second factor is the maintenance of ties with the maternal clan. Although the maternal clan does not occupy the central place of the parental clan, it provides ties. The third factor is protective relationships at the primary residence.
Despite shared linguistic heritage, few institutions among the Toubou generate a broader sense of identity than the clan. Regional divisions do exist, however. During the colonial period (and since independence in 1960), Chadian administrations have conferred legality and legitimacy on these regional groupings by dividing the Daza and Teda regions into corresponding territorial units called cantons and appointing chiefs to administer them and in 1936, the French created cantons, and appointed al-haj Kelleï Chahami from the Kamaya canton in Borkou region's Faya city the first highest official chief who executed great noble missions.
Toubou legal customs are generally based on Islamic law, that allows restitution and revenge. Murder, for example, is settled directly between the families of the victim and the murderer. Toubou honour requires that someone from the victim's family try to kill the murderer or a relative; such efforts eventually end with negotiations to settle the matter.
Reconciliation follows the payment of the ''Goroga'' (Islamic tenet of Diyya
''Diya'' (; : ''diyāt'', ) in Islamic law, is the financial compensation paid to the victim or heirs of a victim in the cases of murder, bodily harm or property damage by mistake. It is an alternative punishment to '' qisas'' (equal retaliation) ...
), or blood money. Among the Tumagra clan of the Teda people in the Tibesti region, there is a '' derde'' (spiritual head) who is recognized as the clan judge, and arbitrates conflict and levies sanctions.
Social stratification
 The Toubou people, states Jean Chapelle, have been socially stratified with an embedded caste system. The three strata have consisted of the freemen with a right to own property, the artisanal castes and the slaves.
The endogamous caste of ''Azza'' (or ''Aza'') among Toubou have the
The Toubou people, states Jean Chapelle, have been socially stratified with an embedded caste system. The three strata have consisted of the freemen with a right to own property, the artisanal castes and the slaves.
The endogamous caste of ''Azza'' (or ''Aza'') among Toubou have the artisanal
An artisan (from , ) is a skilled craft worker who makes or creates material objects partly or entirely by hand. These objects may be functional or strictly decorative, for example furniture, decorative art, sculpture, clothing, food ite ...
occupations, such as metal work, leather work, salt mining, well digging, dates farming, pottery and tailoring, and they have traditionally been despised and segregated by other strata of the Toubou, much like the ''Hadahid'' caste in southeastern Chad among the Zaghawa people. According to Paul Lovejoy – a professor of African History, the 19th century records show that these segregated Toubou castes followed the same customs and traditions as the rest of the Toubou, but they were independent in their politics and beliefs, much like the artisan castes found in many ethnic groups of western Chad such as the Kanembou, Yedina, Arab, Kouri and Danawa.
Marriage between a member of the Azza and a member from a different strata of the Toubou people has been culturally unacceptable., Quote: ""Like the Tuareg, the Toubous have a distinct hierarchy, with three separate levels: Teda/Daza, Aza artisans and slaves. (...) here
Here may refer to:
Music
* ''Here'' (Adrian Belew album), 1994
* ''Here'' (Alicia Keys album), 2016
* ''Here'' (Cal Tjader album), 1979
* ''Here'' (Edward Sharpe album), 2012
* ''Here'' (Idina Menzel album), 2004
* ''Here'' (Merzbow album), ...
the blacksmiths were segregated from the larger populace and seen as contemptible. (...) No Teda/Daza would think of marrying a blacksmith. They are a caste apart, marrying only among themselves." The Azza are Dazaga-speaking people who sprang from the Dazagara. The majority of Teda speak and understand Dazaga, however, the Dazagada do not always clearly grasp Tedaga. Dazaga is the most commonly used language in BET by all its inhabitants.
The lowest social strata were the slaves (''Agara''). Slaves entered the Toubou Teda and Daza societies from raids and warfare on other ethnic groups in lands to their south. All slaves were the property of their masters, their caste was endogamous, and their status was inherited by birth.
In the year 1953, Al-Haj Kellei Chahami, a highly esteemed privileged chieftain of the Kamaya canton, an agreement with the French colonizers decreed the emancipation of all slaves and suppressed the use of captives in the Borkou region, while slaves from the contiguous regions, such as Tibesti and Ennedi, uncovered the liberation center situated in Borkou. Several of these slaves escaped and sought refuge in Borkou under the protection of the Kamaya canton and they were subsequently emancipated by the esteemed chief, Al-Haj Kellei Chahami, who granted them land that enabled them to settle, and this district was formerly referred to as "Ni-Agaranga" in Dazaga, which literally translates to "country of slaves" in the Faya-Largeau city. However, the Borkou municipality opted to rechristen it as "Quartier Huit" (Eighth Quarter) as a euphemistic expression. After the abolition of slavery in 1953, the chief Kellei Chahami admitted the descendants of former captives to the canton, where they were recognized as full members and can move around freely and in this way, the last fraction of the Kamaya canton thus was established. Not only the captives were attached to the Kamaya canton, but along with all foreigners who resided in Faya, including Fezzanais (Libyan refugees who fled Italian brutality in 1929 before the Italian colonialists' progression into southern Libya, the Fezzan region), Ouadaens from the Chad's Waddai region, prostitutes, blacksmiths etc, were also attached to the Kamaya canton. All of these individuals' concerns were conveyed to the colonizers via the Kamaya canton.
The descendants of freed slaves who located in the Tibesti region for many years approach their former masters inquiring about their past. In response, the Teda deliberately allege their identity as "Kamadja" to their freed captives, who question about the significance of this designation. The Teda respond that they know the freed captives' people led them to assume this title. However, once the descendants of freed slaves embrace this belief and depart, the Teda proceed to use insulting terms such as "blind", "stupid", and "unintelligent", as well as other terms that are demeaning. The term "Kamadja" is a mispronunciation of Kamaya, and the Teda are grudgingly attempting to sabotage the Toubou Gorane Kamaya clans' federation reputation since the Kamaya's history was fabricated by the French colonists and Teda took advantage of the situation by misleading their freed slave descendants and the general public.
The linguistic analysis reveals that the term "Kamadja" does not exist in either the Dazaga or Tedaga languages. The tone terms, namely "Kamadja" for the male plural and as general and "Kamadji" for the male singular, are used as generic phrases. These terms lack inherent significance. The solitary form of the female term, "Kamadjedo" or "Kamadjero", might be seen as implausible and without coherence, whilst the plural form of the female term, "Kamadjeda", has an exceptionally peculiar and irrational quality. These terms are devoid of any discernible significance. The mispronunciation in question may be attributed to the challenges faced by French colonists while attempting to articulate the phoneme represented by the letter "y" in the alphabet. As a replacement, they frequently resorted to apply the phonetic sounds of "dj" or "j". Moreover, the explorers who visited Borkou before the French colonization made contributions to the misinterpretation of various expressions, as evidenced by Gustav Nichtigal's works. These inaccuracies include referring to the Yira clan as Jira, the Yenoa clans as Jenoa, the Yin oasis as Jin, the Yarda oasis as Jarda, the Faya oasis as Faja, the Bidayet community as Bidajet, and the Goli Yeskou as Goli Jeskou (Black snake), many more other carelessness. These oversights and misinterpretations are notable in the exploration literatures. The term "Kamadja" has become somewhat entrenched a certain level of permanence but is losing its relevance of the Kamaya ethnic group due to its lack of self-identification. This term was introduced and propagated by Europeans, and there is a belief that it has inaccurately misquoted, misconstrued, and distorted the sound of "y" to "dj" or "j" in the names of various clans, tribes, communities, rural areas, organisms, and numerous other entities throughout the entirety of Chad.
On the other end of the spectrum, the nomenclature of Kamaya has signification, value, and historical origins rooted in the expression "Kama-dro-yédé". This expression pertains to the inhabitant of the Faya oasis in the accent of Kanem Dazaga, where "Kama" describes a valley, "dro" implies interior, and "yédé" denotes an occupant. In this context, "yé" indicates the act of dwelling, while "dé" stands as the indicator of a singular form. Thus, the expression "Kama-dro-yédé" may be interpreted as "the individual who dwells in the valley" of the palm grove situated in the Faya oasis. The ancient designation for the clans of Kamaya was "Kamayada", with "ya" denoting habitation and "da" indicating plurality. Conversely, "Kamayédé" is the singular and authentic noun used to refer to an occupant of the Faya palm grove oasis valley, since the suffix "dé" is appended to the solitary form of "yé". Therefore, the designation "Kamaya" refers to the natives of the valley that is situated in the palm grove of Faya oasis. In Dazaga, the community is called "Kama-yanga" which means the Kamaya canton and together with the suffix "ga" implies the dialect spoken by the Dazagada. In the linguistic context under consideration, the citizens of the aforementioned canton are referred to as "Kamay" in the singular form for males, while the singular form for females may be either "Kamaydo" or "Kamayro", with the vocalization of the suffix varying across specific regions and individuals' accents, ranging from "do" to "ro" which is only the "d" and "r". The plural form of the female noun may be expressed as either "Kamayda" or "Kamayra", whereas the plural form for males and as a general reference is "Kamaya".
Marriage
The Teda, in particular, forbids marriage between cousins, up to 9 generations unrelated, a tradition prevalent with many Muslim ethnic groups in Africa, however, the Daza of Kanem, Bahr el-Ghazal, and certain clans in Ennedi marry close cousins since it is not prohibited in the Quran, they also doubt the origins of individuals andmisalliance Misalliance may refer to:
* Misalliance (play), a play by Bernard Shaw
** Misalliance (Playhouse 90), a US television play based on Shaw's work
* Mésalliance, a marriage to an unsuitable partner
{{dab ...
. A man may marry and have multiple wives according to Islamic tenets, however, this practice is only somewhat prevalent in Toubou society.
The ownership of land, animals, and resources takes several forms. Within an oasis or settled zone belonging to a particular clan, land, trees (usually date palms), and nearby well
A well is an excavation or structure created on the earth by digging, driving, or drilling to access liquid resources, usually water. The oldest and most common kind of well is a water well, to access groundwater in underground aquifers. The ...
s may have different owners. Each family's rights to the use of particular plots of land are recognized by other clan members. Families also may have privileged access to certain wells and the right to a part of the harvest
Harvesting is the process of collecting plants, animals, or fish (as well as fungi) as food, especially the process of gathering mature crops, and "the harvest" also refers to the collected crops. Reaping is the cutting of grain or pulses fo ...
from the fields irrigated by their water. Within the clan and family contexts, individuals also may have personal claims to palm trees and animals.
Contemporary conditions

Chad

Libya
Libya, officially the State of Libya, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to Egypt–Libya border, the east, Sudan to Libya–Sudan border, the southeast, Chad to Chad–L ...
, and, with the support of Toubou students at the Islamic University of Bayda, became a symbol of opposition to the Chadian government. This role enhanced the position of the Derde from the Tumagra tribe of Toubou.
After 1967 the ''derde'' hoped to rally the Toubou to the National Liberation Front of Chad (FROLINAT). Moral authority
Moral authority is authority premised on principles, or fundamental truths, which are independent of written, or positive laws. As such, moral authority necessitates the existence of and adherence to truth. Because truth does not change the princip ...
became military authority shortly thereafter when his son, Goukouni Oueddei
Goukouni Oueddei ( '; born 1944) is a Chadian politician who served as President of Chad from 1979 to 1982.
A northerner, Goukouni commanded FROLINAT rebels with Libyan support during the first Chadian Civil War against Chad's southern-domin ...
, became one of the leaders of the Second Liberation Army of FROLINAT. Goukouni was to become a national figure; he played an important role in the battles of N'Djamena in 1979 and 1980 and served as head of state for a time. Another northerner, Hissène Habré
Hissène Habré (Arabic: ''Ḥusaīn Ḥabrī'', Chadian Arabic: ; ; 13 August 1942 – 24 August 2021), also spelled Hissen Habré, was a Chadian politician and convicted war criminal who served as the 5th president of Chad from 1982 unt ...
of the Dazagra, replaced Goukouni of the Teda in 1982, and eventually lost power to the Zaghawa Idriss Déby
Idriss Déby Itno ( '; 18 June 1952 – 20 April 2021) was a Chadian politician and military officer who was the sixth List of heads of state of Chad, president of Chad from 1991 until his death in 2021 during the 2021 Northern Chad offensive, No ...
after 8 years.
Libya
The Toubou minority in Libya suffered what has been described as "massive discrimination" both under the leadership ofMuammar Gaddafi
Muammar Muhammad Abu Minyar al-Gaddafi (20 October 2011) was a Libyan military officer, revolutionary, politician and political theorist who ruled Libya from 1969 until Killing of Muammar Gaddafi, his assassination by Libyan Anti-Gaddafi ...
as well as after the Libyan civil war.
In a report released by the UNHCR
The Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR) is a United Nations agency mandated to aid and Humanitarian protection, protect refugees, Internally displaced person, forcibly displaced communities, and Statelessness, s ...
, the Society for Threatened Peoples
The Society for Threatened Peoples International STPI (-International, GfbV-International) is an international NGO and human rights organization with its headquarters in Göttingen, Germany. Its aim is to create awareness of and protect minorit ...
(STP) reported "massive discrimination" against the Toubou minority, which resides in the southeastern corner of the country around the oasis town of Kufra
Kufra () is a basinBertarelli (1929), p. 514. and oasis group in the Kufra District of southeastern Cyrenaica in Libya. At the end of the 19th century, Kufra became the centre and holy place of the Senussi order. It also played a minor role in ...
. In December 2007, the Gaddafi government stripped Toubou Libyans of their citizenship, claiming that they were not Libyans, but rather Chadians. In addition, local authorities denied Toubou people access to education and healthcare. In response, an armed group called the Toubou Front for the Salvation of Libya (TFSL) staged an uprising in November 2008 which lasted for five days and claimed 33 lives before being crushed by government security forces. Despite resistance and public condemnation, the Gaddafi regime continued its persecution of the Toubou minority in Libya. Beginning in November 2009, the government began a program of forced eviction and demolition of Toubou homes, rendering many Toubou homeless. Several dozens who protested the destruction were arrested, and families who refused to leave their homes were beaten.
In the Libyan Civil War, Toubou tribespeople in Libya sided with the rebel anti-Gaddafi forces
The anti-Gaddafi forces, also known as the Libyan opposition or Libyan rebels, were Libyan groups that opposed and militarily defeated the government of Muammar Gaddafi during the First Libyan Civil War in 2011, killing him in the process. The A ...
and participated in the Fezzan campaign
The Fezzan campaign was a military campaign conducted by the National Liberation Army to take control of southwestern Libya during the Libyan Civil War. During April to June 2011, anti-Gaddafi forces gained control of most of the eastern part ...
against forces loyal to Muammar Gaddafi
Muammar Muhammad Abu Minyar al-Gaddafi (20 October 2011) was a Libyan military officer, revolutionary, politician and political theorist who ruled Libya from 1969 until Killing of Muammar Gaddafi, his assassination by Libyan Anti-Gaddafi ...
, briefly capturing the town of Qatrun and claiming to capture Murzuk for the rebel movement a month later.
In March 2012, bloody clashes broke out between Toubou and Arab tribesmen in the southern city of Sabha, Libya
Sabha or Sebha () is an oasis city in southwestern Libya, approximately south of Tripoli. It was historically the capital of the Fezzan region and the Fezzan-Ghadames Military Territory and is the capital of the Sabha District. Sabha Air Ba ...
. In response, Issa Abdel Majid Mansour, the leader of the Toubou tribes in Libya threatened a separatist bid, decrying what he saw as "ethnic cleansing" against Toubou and declaring "We announce the reactivation of the Toubou Front for the Salvation of Libya to protect the Toubou people from ethnic cleansing." The TFSL was the opposition group active in the unrest of 2007–2008 that was "ruthlessly persecuted" by the Gaddafi government.
See also
*Demographics of Chad
The people of Chad speak more than 100 languages and divide themselves into many ethnic groups. However, language and ethnicity are not the same. Moreover, neither element can be tied to a particular physical type.
Although the possession of a co ...
*Demographics of Niger
The Demography, demographic features of Nigeriens, the people of Niger, consist of population density, Ethnic group, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population.
...
*Demographics of Libya
Demographics of Libya is the demography of Libya, specifically covering population density, ethnicity, and religious affiliations, as well as other aspects of the Libyan population. All figures are from the United Nations Demographic Yearbook ...
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Toubou People Ethnic groups in Chad Ethnic groups in Libya Ethnic groups in Niger African nomads People of the Chadian–Libyan War Muslim communities in Africa