Tornquist Zone on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
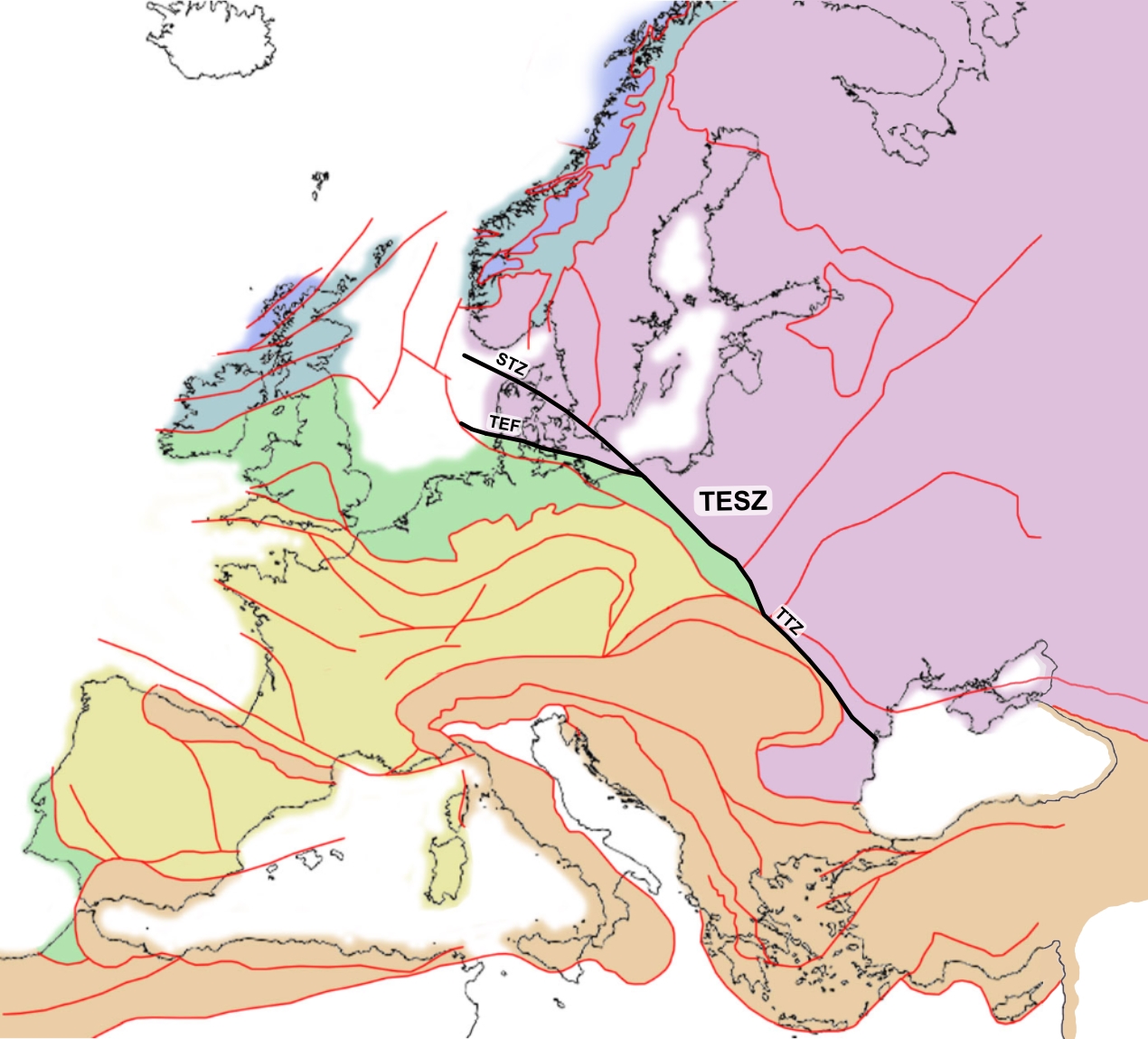 The Trans-European Suture Zone (TESZ), also known as the Tornquist Zone, is the crustal boundary between the Precambrian East European Craton and the
The Trans-European Suture Zone (TESZ), also known as the Tornquist Zone, is the crustal boundary between the Precambrian East European Craton and the
 The Trans-European Suture Zone (TESZ), also known as the Tornquist Zone, is the crustal boundary between the Precambrian East European Craton and the
The Trans-European Suture Zone (TESZ), also known as the Tornquist Zone, is the crustal boundary between the Precambrian East European Craton and the Phanerozoic
The Phanerozoic is the current and the latest of the four eon (geology), geologic eons in the Earth's geologic time scale, covering the time period from 538.8 million years ago to the present. It is the eon during which abundant animal and ...
orogen
An orogenic belt, orogen, or mobile belt, is a zone of Earth's crust affected by orogeny. An orogenic belt develops when a continental plate crumples and is uplifted to form one or more mountain ranges; this involves a series of geological proc ...
s of South-Western Europe. The zone runs from the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Denmark, Norway, Germany, the Netherlands, Belgium, and France. A sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian Se ...
to the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal sea, marginal Mediterranean sea (oceanography), mediterranean sea lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bound ...
. The north-western part of the zone was created by the collision of Avalonia
Avalonia was a microcontinent in the Paleozoic era. Crustal fragments of this former microcontinent are terranes in parts of the eastern coast of North America: Atlantic Canada, and parts of the East Coast of the United States, East Coast of the ...
and Baltica
Baltica is a paleocontinent that formed in the Paleoproterozoic and now constitutes northwestern Eurasia, or Europe north of the Trans-European Suture Zone and west of the Ural Mountains.
The thick core of Baltica, the East European Craton, i ...
/ East European Craton in the Late Ordovician. The south-eastern part of the zone, now largely concealed by deep sedimentary basins, developed through Variscan and Alpine orogenic events.
Various branches of the TESZ go under different names:
* The Teisseyre-Tornquist Zone (TTZ) in Ukraine and Poland.
* The Sorgenfrei-Tornquist Zone (STZ) through Scania
Scania ( ), also known by its native name of Skåne (), is the southernmost of the historical provinces of Sweden, provinces () of Sweden. Located in the south tip of the geographical region of Götaland, the province is roughly conterminous w ...
(Sweden), Kattegat
The Kattegat (; ; ) is a sea area bounded by the peninsula of Jutland in the west, the Danish straits islands of Denmark and the Baltic Sea to the south and the Swedish provinces of Bohuslän, Västergötland, Halland and Scania in Swede ...
, and North Jutland (Denmark).
* The Trans-European Fault (TEF), Thor-Tornquist Suture or Thor Suture through southern Denmark.
The latter two branches (STZ and TEF) span a triangular area of numerous faults, called the Tornquist Fan.
Discovery
In 1893 the Polish geologist Wawrzyniec Teisseyre suggested the existence of a buried tectonic line close to theCarpathian Mountains
The Carpathian Mountains or Carpathians () are a range of mountains forming an arc across Central Europe and Southeast Europe. Roughly long, it is the third-longest European mountain range after the Ural Mountains, Urals at and the Scandinav ...
. As part of his work on a Geological Atlas of Galicia he mapped the line from Galicia in Ukraine to south-eastern Poland. In 1908 the German geologist Alexander Tornquist mapped the continuation of the zone from Poland to Scania
Scania ( ), also known by its native name of Skåne (), is the southernmost of the historical provinces of Sweden, provinces () of Sweden. Located in the south tip of the geographical region of Götaland, the province is roughly conterminous w ...
in Sweden.
Tornquist Fan
Whereas the south-eastern part of the TESZ (Teisseyre-Tornquist Zone) is relatively well-confined, the north-western part divides into numerous sutures and faults, which fan out towards theNorth Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Denmark, Norway, Germany, the Netherlands, Belgium, and France. A sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian Se ...
and the Iapetus Suture
The Iapetus Suture is one of several major Fault (geology), geological faults caused by the collision of several ancient land masses forming a suture (geology), suture. It represents in part the remains of what was once the Iapetus Ocean. Iapet ...
which runs between the Scandinavian and Scottish Caledonides. It includes the following linear features (sorted from the north-east):
* The Fennoscandian Border Zone (FBZ) in Skagen
Skagen () is the northernmost town in Denmark, on the east coast of the Skagen Odde peninsula in the far north of Jutland, part of Frederikshavn Municipality in North Denmark Region, Nordjylland, north of Frederikshavn and northeast of Aalbo ...
and Kattegat
The Kattegat (; ; ) is a sea area bounded by the peninsula of Jutland in the west, the Danish straits islands of Denmark and the Baltic Sea to the south and the Swedish provinces of Bohuslän, Västergötland, Halland and Scania in Swede ...
* The Sorgenfrei-Tornquist Zone (STZ), including many parallel horsts in Scania
Scania ( ), also known by its native name of Skåne (), is the southernmost of the historical provinces of Sweden, provinces () of Sweden. Located in the south tip of the geographical region of Götaland, the province is roughly conterminous w ...
(e.g. Linderödsåsen and Söderåsen). This zone experienced extension in the Jurassic. In association to this event numerous monogenetic volcanoes sprang up in Central Scania.
* Ringkøbing-Fyn High (RFH)
* Caledonian Deformation Front (CDF)
* Trans-European Fault (TEF)
The Moho under the Tornquist Fan has a strong topography with depths varying between 26 and 48 km. It started forming during the Caledonian orogeny
The Caledonian orogeny was a mountain-building cycle recorded in the northern parts of the British Isles, the Scandinavian Caledonides, Svalbard, eastern Greenland and parts of north-central Europe. The Caledonian orogeny encompasses events tha ...
as a microcontinent or a series of terrane
In geology, a terrane (; in full, a tectonostratigraphic terrane) is a crust fragment formed on a tectonic plate (or broken off from it) and accreted or " sutured" to crust lying on another plate. The crustal block or fragment preserves its d ...
s of Avalonia
Avalonia was a microcontinent in the Paleozoic era. Crustal fragments of this former microcontinent are terranes in parts of the eastern coast of North America: Atlantic Canada, and parts of the East Coast of the United States, East Coast of the ...
n origin amalgamated with Baltica
Baltica is a paleocontinent that formed in the Paleoproterozoic and now constitutes northwestern Eurasia, or Europe north of the Trans-European Suture Zone and west of the Ural Mountains.
The thick core of Baltica, the East European Craton, i ...
. Faults are believed to have continued forming until late Paleozoic
The Paleozoic ( , , ; or Palaeozoic) Era is the first of three Era (geology), geological eras of the Phanerozoic Eon. Beginning 538.8 million years ago (Ma), it succeeds the Neoproterozoic (the last era of the Proterozoic Eon) and ends 251.9 Ma a ...
.
Teisseyre-Tornquist Zone
The Teisseyre-Tornquist Zone (TTZ), extending fromPomerania
Pomerania ( ; ; ; ) is a historical region on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in Central Europe, split between Poland and Germany. The central and eastern part belongs to the West Pomeranian Voivodeship, West Pomeranian, Pomeranian Voivod ...
at the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by the countries of Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden, and the North European Plain, North and Central European Plain regions. It is the ...
to the Dobruja
Dobruja or Dobrudja (; or ''Dobrudža''; , or ; ; Dobrujan Tatar: ''Tomrîğa''; Ukrainian language, Ukrainian and ) is a Geography, geographical and historical region in Southeastern Europe that has been divided since the 19th century betw ...
at the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal sea, marginal Mediterranean sea (oceanography), mediterranean sea lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bound ...
, is primarily known from geophysical studies. Seismic data and gravity models suggest a strong contrast in crustal thickness, with 28–35 km down to the Moho to the west of the suture and 42–47 km to the east of it. The suture is believed to be buried under thick upper Paleozoic
The Paleozoic ( , , ; or Palaeozoic) Era is the first of three Era (geology), geological eras of the Phanerozoic Eon. Beginning 538.8 million years ago (Ma), it succeeds the Neoproterozoic (the last era of the Proterozoic Eon) and ends 251.9 Ma a ...
and Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era is the Era (geology), era of Earth's Geologic time scale, geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceous Period (geology), Periods. It is characterized by the dominance of archosaurian r ...
sediments, and located further west than indicated by historical surface observations.
See also
* *References
{{Reflist Natural history of Europe Geology of Denmark Geology of Poland Geology of Sweden Geology of Ukraine Ordovician paleogeography Ordovician Sweden Paleozoic Denmark Paleozoic Poland Paleozoic Ukraine Suture zones