Tonsilloliths on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Tonsil stones, also known as tonsilloliths, are mineralizations of debris within the crevices of the
File:Tonsilstone.jpg, A tonsillolith protrudes from the tonsil
File:Tonsilloliths 20091119 prior to tonsillectomy.JPG, Large tonsillolith half exposed on tonsil
File:Tonsillolith close up.jpg, Closeup of a tonsillolith
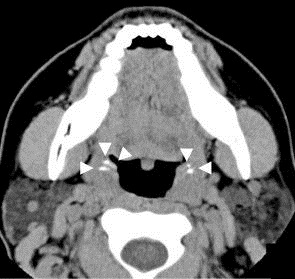 Diagnosis is usually made upon inspection. Tonsilloliths are difficult to diagnose in the absence of clear manifestations, and often constitute casual findings of routine
Diagnosis is usually made upon inspection. Tonsilloliths are difficult to diagnose in the absence of clear manifestations, and often constitute casual findings of routine
 Much rarer than the typical tonsil stones are giant tonsilloliths. Giant tonsilloliths may often be mistaken for other oral maladies, including peritonsillar abscess, and tumors of the tonsil. On average, tonsil stones should appear within a similar range of the image shown here; however, individuals with extenuating cases have been reported. In these instances, extensive care such as extraction by a licensed medical professional may be needed.
Much rarer than the typical tonsil stones are giant tonsilloliths. Giant tonsilloliths may often be mistaken for other oral maladies, including peritonsillar abscess, and tumors of the tonsil. On average, tonsil stones should appear within a similar range of the image shown here; however, individuals with extenuating cases have been reported. In these instances, extensive care such as extraction by a licensed medical professional may be needed.
tonsil
The tonsils ( ) are a set of lymphoid organs facing into the aerodigestive tract, which is known as Waldeyer's tonsillar ring and consists of the adenoid tonsil (or pharyngeal tonsil), two tubal tonsils, two palatine tonsils, and the lingual t ...
s. When not mineralized, the presence of debris is known as chronic caseous tonsillitis (CCT). Symptoms may include bad breath, foreign body sensation, sore throat, pain or discomfort with swallowing, and cough. Generally there is no pain, though there may be the feeling of something present. The presence of tonsil stones may be otherwise undetectable; however, some people have reported seeing white material in the rear of their throat.
Risk factors may include recurrent throat infections. Tonsil stones contain a biofilm
A biofilm is a Syntrophy, syntrophic Microbial consortium, community of microorganisms in which cell (biology), cells cell adhesion, stick to each other and often also to a surface. These adherent cells become embedded within a slimy ext ...
composed of a number of different bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
, and calcium salts, either alone or in combination with other mineral salts. While they most commonly occur in the palatine tonsil
Palatine tonsils, commonly called the tonsils and occasionally called the faucial tonsils, are tonsils located on the left and right sides at the back of the throat in humans and other mammals, which can often be seen as flesh-colored, pinkish ...
s, they may also occur in the adenoid
In anatomy, the pharyngeal tonsil, also known as the nasopharyngeal tonsil or adenoid, is the superior-most of the tonsils. It is a mass of lymphoid tissue located behind the nasal cavity, in the roof and the posterior wall of the nasopharyn ...
s, lingual tonsils and tubal tonsil
The tubal tonsil, also known as Gerlach tonsil, is one of the four main tonsil groups forming Waldeyer's tonsillar ring.
Structure
Each tubal tonsil is located posterior to the opening of the Eustachian tube on the lateral wall of the nasoph ...
. Tonsil stones have been recorded weighing from 0.3g to 42g, and they are typically small in size. However, there are occasional reports of large tonsilloliths. They are often discovered during medical imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues (physiology). Medical imaging seeks to revea ...
for other reasons and more recently, due to the impact and influence of social media platforms such as TikTok
TikTok, known in mainland China and Hong Kong as Douyin (), is a social media and Short-form content, short-form online video platform owned by Chinese Internet company ByteDance. It hosts user-submitted videos, which may range in duration f ...
, medical professionals have experienced an increase in patient concern and tonsillolith evaluations.
They are usually benign, so if tonsil stones do not bother the patient, no treatment is needed. However in rare cases, tonsilloliths have presented patients with further complications necessitating surgical extraction. Tonsilloliths that exceed the average size are typically seen in older individuals as the likelihood of developing tonsil stones is linear with age. Otherwise, gargling with salt water and manual removal may be tried. Chlorhexidine
Chlorhexidine is a disinfectant and antiseptic which is used for skin disinfection before surgery and to disinfect surgical instruments. It is also used for cleaning wounds, preventing dental plaque, treating yeast infections of the mouth, and ...
or cetylpyridinium chloride
Cetylpyridinium chloride (CPC) is a cationic quaternary ammonium compound used in some types of mouthwashes, toothpastes, lozenges, throat sprays, breath sprays, and nasal sprays. It is an antiseptic that kills bacteria and other microor ...
may also be tried. Surgical treatment may include partial or complete tonsil removal. Up to 10% of people have tonsil stones. Biological sex does not influence the chance of having tonsil stones, but older people are more commonly affected. Many people opt to extract their own tonsil stones manually or with developments in dental hygiene products. Water flossers have become a more common mechanism to extract tonsilloliths and alleviate the discomfort and complications they cause. Tonsil stones can become dislodged on their own while eating, drinking, gargling, and coughing. Additionally, an exhalation technique that vigorously shakes the tonsils may be performed to dislodge them. This involves loudly producing a voiceless velar fricative
The voiceless velar fricative is a type of consonantal sound used in some spoken languages. It was part of the consonant inventory of Old English and can still be found in some dialects of English, most notably in Scottish English, e.g. in ''lo ...
sound, at various pitches to shake both the palatine and lingual tonsils.
Signs and symptoms
Tonsil stones may produce no symptoms or they may be associated with bad breath. In fact, many dental professionals argue that tonsil stones are the leading cause of bad breath in their patients. The smell may be that of rotting eggs. Tonsil stones tend to happen most often in people with longterm inflammation in their tonsils. Occasionally there may be pain when swallowing. Even when they are large, some tonsil stones are only discovered incidentally onX-ray
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ran ...
s or CAT scans. Other symptoms include a metallic taste, throat closing or tightening, coughing fits, itchy throat, and choking.
Larger tonsil stones may cause recurrent bad breath, which frequently accompanies a tonsil infection, sore throat
Sore throat, also known as throat pain, is pain or irritation of the throat. The majority of sore throats are caused by a virus, for which antibiotics are not helpful.
For sore throat caused by bacteria (GAS), treatment with antibiotics may hel ...
, white debris, a bad taste in the back of the throat, difficulty swallowing, ear ache
Ear pain, also known as earache or otalgia, is pain in the ear. Primary ear pain is pain that originates from the ear. Secondary ear pain is a type of referred pain, meaning that the source of the pain differs from the location where the pain is ...
, and tonsil swelling. A medical study conducted in 2007 found an association between tonsilloliths and bad breath in patients with a certain type of recurrent tonsillitis. Among those with bad breath, 75% of the subjects had tonsilloliths, while only 6% of subjects with normal halitometry values (normal breath) had tonsilloliths. A foreign body sensation may also exist in the back of the throat. The condition may also be an asymptomatic condition, with detection upon palpating a hard intratonsillar or submucosa
The submucosa (or tela submucosa) is a thin layer of tissue in various organs of the gastrointestinal, respiratory, and genitourinary tracts. It is the layer of dense irregular connective tissue that supports the mucosa (mucous membrane) an ...
l mass.
Pathophysiology
The mechanism by which these calculi form is subject to debate, though they appear to result from the accumulation of material retained within the crypts, along with the growth of bacteria and fungi—sometimes in association with persistent chronic purulenttonsillitis
Tonsillitis is inflammation of the tonsils in the upper part of the throat. It can be acute or chronic. Acute tonsillitis typically has a rapid onset. Symptoms may include sore throat, fever, enlargement of the tonsils, trouble swallowing, and en ...
.
In 2009, an association between biofilms
A biofilm is a syntrophic community of microorganisms in which cells stick to each other and often also to a surface. These adherent cells become embedded within a slimy extracellular matrix that is composed of extracellular polymer ...
and tonsilloliths was shown. Central to the biofilm concept is the assumption that bacteria form a three dimensional structure, dormant bacteria being in the center to serve as a constant nidus of infection. This impermeable structure renders the biofilm immune to antibiotic treatment. By use of confocal microscopy
Confocal microscopy, most frequently confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) or laser scanning confocal microscopy (LSCM), is an optical imaging technique for increasing optical resolution and contrast (vision), contrast of a micrograph by me ...
and microelectrodes, biofilms similar to dental biofilms were shown to be present in the tonsillolith, with oxygen respiration at the outer layer of tonsillolith, denitrification
Denitrification is a microbially facilitated process where nitrate (NO3−) is reduced and ultimately produces molecular nitrogen (N2) through a series of intermediate gaseous nitrogen oxide products. Facultative anaerobic bacteria perform denitr ...
toward the middle layer, and acidification toward the core.
Cause and diagnosis
 Diagnosis is usually made upon inspection. Tonsilloliths are difficult to diagnose in the absence of clear manifestations, and often constitute casual findings of routine
Diagnosis is usually made upon inspection. Tonsilloliths are difficult to diagnose in the absence of clear manifestations, and often constitute casual findings of routine radiological
In physics, radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or a material medium. This includes:
* ''electromagnetic radiation'' consisting of photons, such as radio waves, microwaves, infr ...
studies. The cause of tonsil stones can include a multitude of sources from bacterial infections, streptococcus
''Streptococcus'' is a genus of gram-positive spherical bacteria that belongs to the family Streptococcaceae, within the order Lactobacillales (lactic acid bacteria), in the phylum Bacillota. Cell division in streptococci occurs along a sing ...
bacteria, viral infections, adenoviruses, influenza virus, enteroviruses and parainfluenza virus.
Classification
Tonsilloliths or tonsil stones arecalcification
Calcification is the accumulation of calcium salts in a body tissue. It normally occurs in the formation of bone, but calcium can be deposited abnormally in soft tissue,Miller, J. D. Cardiovascular calcification: Orbicular origins. ''Nature M ...
s that form in the crypts of the palatal tonsils. They are also known to form in the throat and on the roof of the mouth. Tonsils are filled with crevices where bacteria and other materials, including dead cells and mucus, can become trapped. When this occurs, the debris can become concentrated in white formations that occur in the pockets. Researchers found aerobic bacteria present on the surface of tonsilloliths and anaerobic bacteria at the core of tonsilloliths. They have the potential to cause oral halitosis as they contain volatile sulfur compounds and sulfur derived gases, foul smelling compounds produced during bacterial metabolism. Tonsilloliths are formed when this trapped debris accumulates and are expressed from the tonsil. They are generally soft, sometimes rubbery. This tends to occur most often in people who suffer from chronic inflammation in their tonsils or repeated bouts of tonsillitis. They are often associated with post-nasal drip.
Enlarged tonsil stones
 Much rarer than the typical tonsil stones are giant tonsilloliths. Giant tonsilloliths may often be mistaken for other oral maladies, including peritonsillar abscess, and tumors of the tonsil. On average, tonsil stones should appear within a similar range of the image shown here; however, individuals with extenuating cases have been reported. In these instances, extensive care such as extraction by a licensed medical professional may be needed.
Much rarer than the typical tonsil stones are giant tonsilloliths. Giant tonsilloliths may often be mistaken for other oral maladies, including peritonsillar abscess, and tumors of the tonsil. On average, tonsil stones should appear within a similar range of the image shown here; however, individuals with extenuating cases have been reported. In these instances, extensive care such as extraction by a licensed medical professional may be needed.
Differential diagnosis
Imaging diagnostic techniques can identify a radiopaque mass that may be mistaken for foreign bodies, displaced teeth or calcified blood vessels.CT scan
A computed tomography scan (CT scan), formerly called computed axial tomography scan (CAT scan), is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or ...
may reveal nonspecific calcified images in the tonsillar zone. The differential diagnosis must be established with acute and chronic tonsillitis, tonsillar hypertrophy
Hypertrophy is the increase in the volume of an organ or tissue due to the enlargement of its component cells. It is distinguished from hyperplasia, in which the cells remain approximately the same size but increase in number. Although hypertro ...
, peritonsillar abscesses, foreign bodies, phlebolites, ectopic bone or cartilage, lymph nodes
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped Organ (anatomy), organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphoc ...
, granulomatous lesions or calcification of the stylohyoid ligament in the context of Eagle syndrome (elongated styloid process).
Differential diagnosis
In healthcare, a differential diagnosis (DDx) is a method of analysis that distinguishes a particular disease or condition from others that present with similar clinical features. Differential diagnostic procedures are used by clinicians to di ...
of tonsilloliths includes foreign body, calcified granuloma
A granuloma is an aggregation of macrophages (along with other cells) that forms in response to chronic inflammation. This occurs when the immune system attempts to isolate foreign substances that it is otherwise unable to eliminate. Such sub ...
, malignancy
Malignancy () is the tendency of a medical condition to become progressively worse; the term is most familiar as a characterization of cancer.
A ''malignant'' tumor contrasts with a non-cancerous ''benign'' tumor in that a malignancy is not ...
, an enlarged temporal styloid process
The temporal styloid process is a slender bony process of the temporal bone extending downward and forward from the undersurface of the temporal bone just below the ear. The styloid process gives attachments to several muscles, and ligaments.
Str ...
or rarely, isolated bone which is usually derived from embryonic rests originating from the branchial arches.
Treatment
If tonsil stones do not bother a person, no treatment is needed. Otherwise gargling with saltwater and manual removal may be tried.Chlorhexidine
Chlorhexidine is a disinfectant and antiseptic which is used for skin disinfection before surgery and to disinfect surgical instruments. It is also used for cleaning wounds, preventing dental plaque, treating yeast infections of the mouth, and ...
or cetylpyridinium chloride
Cetylpyridinium chloride (CPC) is a cationic quaternary ammonium compound used in some types of mouthwashes, toothpastes, lozenges, throat sprays, breath sprays, and nasal sprays. It is an antiseptic that kills bacteria and other microor ...
may also be tried. Surgical treatment may include partial or complete tonsil removal.
Some people are able to remove tonsil stones using a cotton swab. Oral irrigators are also effective. Most electric oral irrigators are unsuitable for tonsil stone removal because they are too powerful and are likely to cause discomfort and rupture the tonsils, which could result in further complications such as infection. Irrigators that connect directly to the sink tap via a threaded attachment or otherwise are suitable for tonsil stone removal and everyday washing of the tonsils because they can jet water at low-pressure levels that the user can adjust by simply manipulating the sink tap, allowing for a continuous range of pressures to suit each user's requirements.
There are also manually pressurized tonsil stone removers. A manual pump-type tonsil stone remover can adjust the water pressure depending on the number of pumps, effectively removing tonsil stones.
More simply still, gargling with warm, salty water may help alleviate the discomfort of tonsillitis, which often accompanies tonsil stones. Vigorous gargling each morning can also keep the tonsil crypts clear of all but the most persistent tonsilloliths.
Curettage
Larger tonsil stones may require removal by curettage (scooping) or otherwise, although thorough irrigation will still be required afterward to effectively wash out smaller pieces. Largerlesion
A lesion is any damage or abnormal change in the tissue of an organism, usually caused by injury or diseases. The term ''Lesion'' is derived from the Latin meaning "injury". Lesions may occur in both plants and animals.
Types
There is no de ...
s may require local excision, although these treatments may not completely help the bad breath issues that are often associated with this condition.
Laser
Another option is to decrease the surface area (crypts, crevices, etc.) of the tonsils via laser resurfacing. The procedure is called a laser cryptolysis. It can be performed using alocal anesthetic
A local anesthetic (LA) is a medication that causes absence of all sensation (including pain) in a specific body part without loss of consciousness, providing local anesthesia, as opposed to a general anesthetic, which eliminates all sensati ...
. A scanned carbon dioxide laser
The carbon-dioxide laser (CO2 laser) was one of the earliest gas lasers to be developed. It was invented by C. Kumar N. Patel, Kumar Patel of Bell Labs in 1964 and is still one of the most useful types of laser. Carbon dioxide, Carbon-dioxide lase ...
selectively vaporizes and smooths the surface of the tonsils. This technique flattens the edges of the crypts and crevices that collect the debris, preventing trapped material from forming stones.
Surgery
Tonsillectomy
Tonsillectomy is a surgical procedure in which both palatine tonsils are fully removed from the back of the throat. The procedure is mainly performed for recurrent tonsillitis, throat infections and obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). For those wit ...
may be indicated if bad breath due to tonsillar stones persists despite other measures.
Epidemiology
Tonsilloliths or tonsillar concretions occur in up to 10% of the population, frequently due to episodes of tonsillitis. While small concretions in the tonsils are common, true stones are less so. They commonly occur in young adults and are rare in children.References
{{Medical resources , ICD10 = {{ICD10, J, 35, 8, j, 30 , ICD9 = {{ICD9, 474.8 , ICDO = , OMIM = , DiseasesDB = , MedlinePlus = , eMedicineSubj = , eMedicineTopic = Tonsil disorders Oral hygiene Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Otorhinolaryngology