Timeline Of Rocket And Missile Technology on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 This article gives a concise
This article gives a concise
 * 11th century AD - The first documented record of what appears to be
* 11th century AD - The first documented record of what appears to be
 * 1966 - USSR
* 1966 - USSR
 This article gives a concise
This article gives a concise timeline
A timeline is a list of events displayed in chronological order. It is typically a graphic design showing a long bar labelled with dates paralleling it, and usually contemporaneous events.
Timelines can use any suitable scale representing t ...
of rocket
A rocket (from , and so named for its shape) is a vehicle that uses jet propulsion to accelerate without using any surrounding air. A rocket engine produces thrust by reaction to exhaust expelled at high speed. Rocket engines work entirely ...
and missile
A missile is an airborne ranged weapon capable of self-propelled flight aided usually by a propellant, jet engine or rocket motor.
Historically, 'missile' referred to any projectile that is thrown, shot or propelled towards a target; this ...
technology
Technology is the application of Conceptual model, conceptual knowledge to achieve practical goals, especially in a reproducible way. The word ''technology'' can also mean the products resulting from such efforts, including both tangible too ...
.
11th century-13th century
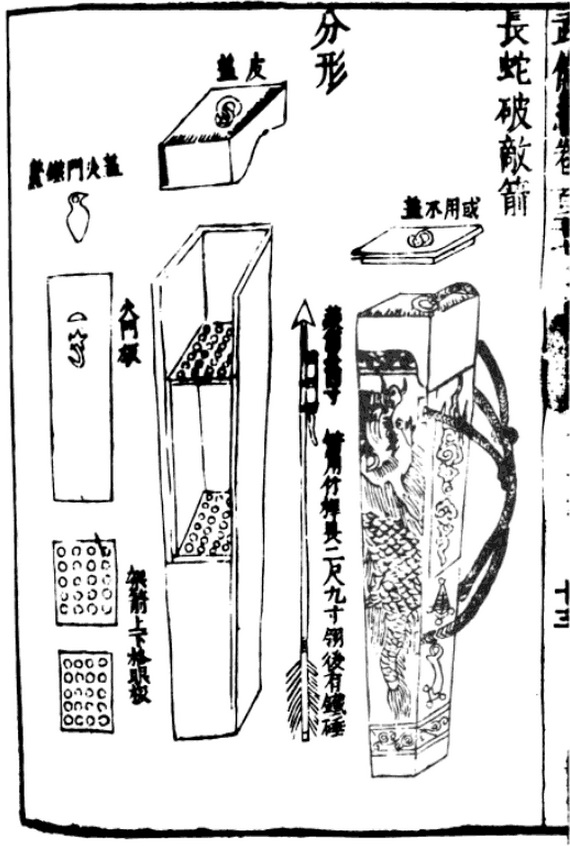
 * 11th century AD - The first documented record of what appears to be
* 11th century AD - The first documented record of what appears to be gunpowder
Gunpowder, also commonly known as black powder to distinguish it from modern smokeless powder, is the earliest known chemical explosive. It consists of a mixture of sulfur, charcoal (which is mostly carbon), and potassium nitrate, potassium ni ...
and the fire arrow
Fire arrows were one of the earliest forms of weaponized gunpowder, being used from the 9th century onward. Not to be confused with earlier incendiary arrow projectiles, the fire arrow was a gunpowder weapon which receives its name from the tra ...
, an early form of rocketry, appears in the Chinese text ''Wujing Zongyao
The ''Wujing Zongyao'' (), sometimes rendered in English as the ''Complete Essentials for the Military Classics'', is a Chinese military compendium written from around 1040 to 1044.
The book was compiled during the Northern Song dynasty by Ze ...
''.
*In Europe, around 1250 both Roger Bacon
Roger Bacon (; or ', also '' Rogerus''; ), also known by the Scholastic accolades, scholastic accolade ''Doctor Mirabilis'', was a medieval English polymath, philosopher, scientist, theologian and Franciscans, Franciscan friar who placed co ...
and the Liber Ignium gave instructions for constructing devices that appear to be rockets.
17th century-19th century
* 1633 - Lagâri Hasan Çelebi launched a 7-winged rocket using 50 okka (140 lbs) of gunpowder from Sarayburnu, the point belowTopkapı Palace
The Topkapı Palace (; ), or the Seraglio, is a large museum and library in the east of the Fatih List of districts of Istanbul, district of Istanbul in Turkey. From the 1460s to the completion of Dolmabahçe Palace in 1856, it served as the ad ...
in Istanbul
Istanbul is the List of largest cities and towns in Turkey, largest city in Turkey, constituting the country's economic, cultural, and historical heart. With Demographics of Istanbul, a population over , it is home to 18% of the Demographics ...
.Winter, Frank H. (1992). "Who First Flew in a Rocket?", Journal of the British Interplanetary Society 45 (July 1992), p. 275-80
* 1650 - ''Artis Magnae Artilleriae pars prima'' ("Great Art of Artillery, the First Part") is printed in Amsterdam, about a year before the death of its author, Kazimierz Siemienowicz.
* 1664 - A "space rocket" is imagined as a future technology to be studied in France and its drawing is ordered by French finance minister Colbert; designed by Le Brun on a Gobelins tapestry (see: French space program
The French space program includes both commercial spaceflight, civil and military spaceflight activities. It is the third oldest national space program in the world, after the Soviet space program, Soviet (now Roscosmos, Russian) and Space policy ...
)
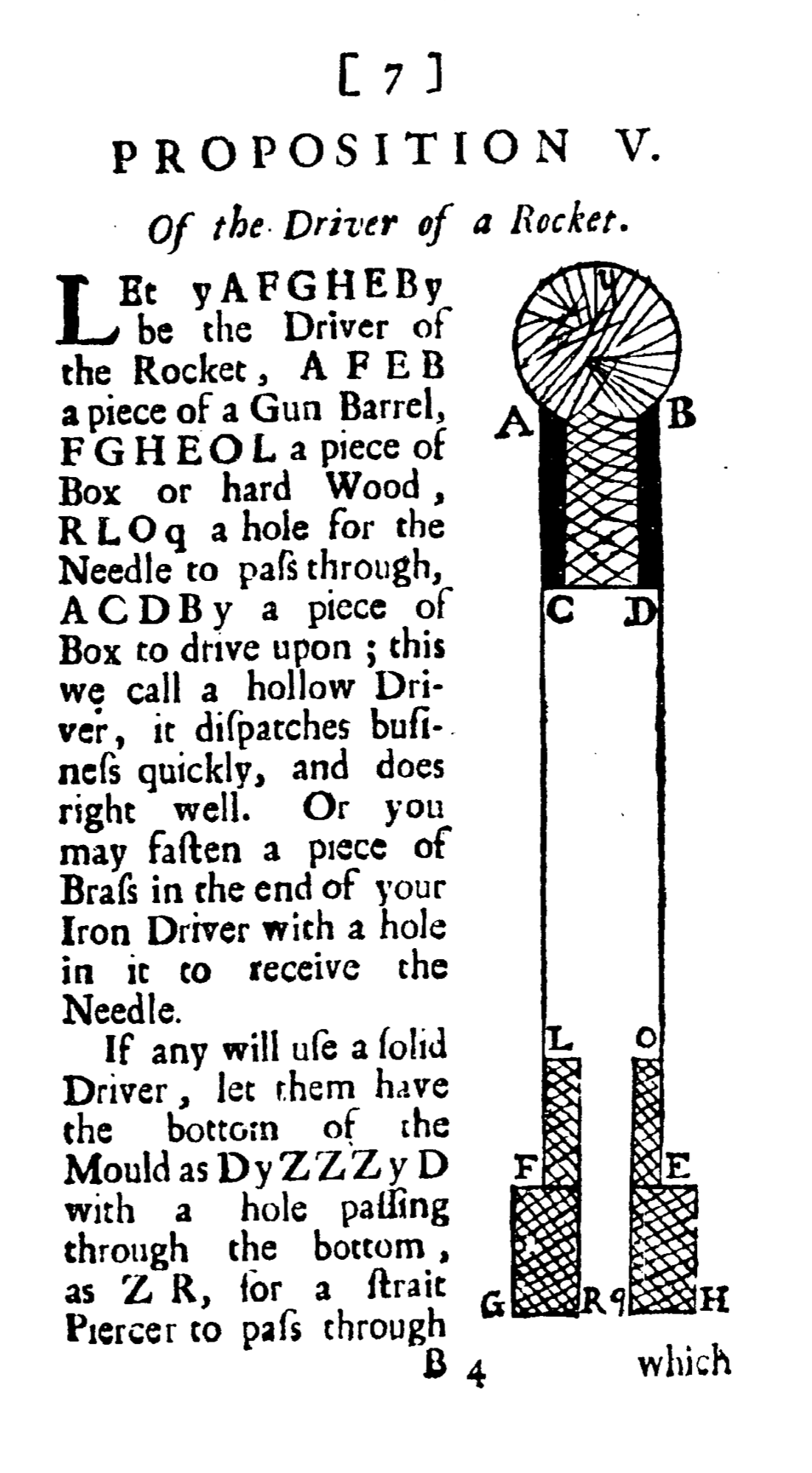
* 1696 - Robert Anderson suggests making rockets out of "a piece of a Gun Barrel" whose metal casing is much stronger than pasteboard or wood
* 1798 - Tipu Sultan
Tipu Sultan (, , ''Sultan Fateh Ali Sahab Tipu''; 1 December 1751 – 4 May 1799) commonly referred to as Sher-e-Mysore or "Tiger of Mysore", was a ruler of the Kingdom of Mysore based in South India. He was a pioneer of rocket artillery ...
, the King of the state of Mysore
Mysore ( ), officially Mysuru (), is a city in the southern Indian state of Karnataka. It is the headquarters of Mysore district and Mysore division. As the traditional seat of the Wadiyar dynasty, the city functioned as the capital of the ...
in India, develops and uses iron rockets against the British Army (see Mysorean rockets
Mysorean rockets were an Indian military weapon. The iron-cased rockets were successfully deployed for military use. They were the first successful iron-cased rockets, developed in the late 18th century in the Kingdom of Mysore (part of prese ...
).
* 1801 - The British Army develops the Congreve rocket
The Congreve rocket was a type of rocket artillery designed by British inventor Sir William Congreve, 2nd Baronet, Sir William Congreve in 1808.
The design was based upon Mysorean rockets, the rockets deployed by the Kingdom of Mysore against ...
based on weapons used against them by Tipu Sultan
Tipu Sultan (, , ''Sultan Fateh Ali Sahab Tipu''; 1 December 1751 – 4 May 1799) commonly referred to as Sher-e-Mysore or "Tiger of Mysore", was a ruler of the Kingdom of Mysore based in South India. He was a pioneer of rocket artillery ...
.
* 1806 - Claude Ruggieri
Claude Ruggieri (1777 – 30 August 1841) was a pyrotechnician in Paris, France, who developed and wrote about innovations in fireworks design. He and others in his family were renowned and patronized by royalty for their creation of great firewo ...
, an Italian living in France, launched animals on rockets and recovered them using parachutes. He was prevented from launching a child by police.
* 1813 - "A Treatise on the Motion of Rockets" by William Moore – first appearance of the rocket equation
The classical rocket equation, or ideal rocket equation is a mathematical equation that describes the motion of vehicles that follow the basic principle of a rocket: a device that can apply acceleration to itself using thrust by expelling part o ...
* 1818 - Henry Trengrouse
Henry Trengrouse (18 March 1772 – 14 February 1854) was a British inventor who invented the "Rocket" lifesaving apparatus.
On 24 December 1807 he witnessed the wreck of the frigate '' Anson'' in Mount's Bay, when over a hundred people d ...
demonstrates his rocket apparatus for projecting a lifeline from a wrecked ship to the shore, later widely adopted
* 1844 - William Hale invents the spin-stabilized rocket
* 1861 - William Leitch publishes an essay "A Journey Through Space" (later published in his book ''God's Glory in the Heavens'' (1862)) in which he postulated the use of rockets for space travel because rockets would work more efficiently in a vacuum.
20th century
* 1902 - French cinema pioneerGeorges Méliès
Marie-Georges-Jean Méliès ( , ; 8 December 1861 – 21 January 1938) was a French magic (illusion), magician, toymaker, actor, and filmmaker. He led many technical and narrative developments in the early days of film, cinema, primarily in th ...
directs ''A Trip to the Moon
''A Trip to the Moon'' ( , ) is a 1902 French science-fiction adventure trick film written, directed, and produced by Georges Méliès. Inspired by the Jules Verne novel ''From the Earth to the Moon'' (1865) and its sequel '' Around the Moon ...
'', the first film about space travel.
* 1903 - Konstantin Tsiolkovsky
Konstantin Eduardovich Tsiolkovsky (; rus, Константин Эдуардович Циолковский, p=kənstɐnʲˈtʲin ɪdʊˈardəvʲɪtɕ tsɨɐlˈkofskʲɪj, a=Ru-Konstantin Tsiolkovsky.oga; – 19 September 1935) was a Russi ...
begins a series of papers discussing the use of rocket
A rocket (from , and so named for its shape) is a vehicle that uses jet propulsion to accelerate without using any surrounding air. A rocket engine produces thrust by reaction to exhaust expelled at high speed. Rocket engines work entirely ...
ry to reach outer space, space suit
A space suit (or spacesuit) is an environmental suit used for protection from the harsh environment of outer space, mainly from its vacuum as a highly specialized pressure suit, but also its temperature extremes, as well as radiation and ...
s, and colonization of the Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Sola ...
. Two key point discussed in his works are liquid fuel
Liquid fuels are combustible or energy-generating molecules that can be harnessed to create mechanical energy, usually producing kinetic energy; they also must take the shape of their container. It is the fumes of liquid fuels that are flammable ...
s and staging.
* 1913 - Without knowing the work of Russian mathematician Konstantin Tsiolkovsky
Konstantin Eduardovich Tsiolkovsky (; rus, Константин Эдуардович Циолковский, p=kənstɐnʲˈtʲin ɪdʊˈardəvʲɪtɕ tsɨɐlˈkofskʲɪj, a=Ru-Konstantin Tsiolkovsky.oga; – 19 September 1935) was a Russi ...
, French engineer Robert Esnault-Pelterie
Robert Albert Charles Esnault-Pelterie (8 November 1881 – 6 December 1957) was a French aircraft designer and spaceflight theorist. He is referred to as being one of the founders of modern rocketry and astronautics, along with the Russian K ...
derived the equations for space flight, produced a paper that presented the rocket equation
The classical rocket equation, or ideal rocket equation is a mathematical equation that describes the motion of vehicles that follow the basic principle of a rocket: a device that can apply acceleration to itself using thrust by expelling part o ...
and calculated the energies required to reach the Moon and nearby planets.
* 1916 - first use of rockets (with the solid fuel Le Prieur rocket
''Le Prieur'' rockets (French ''Fusées Le Prieur'') were a type of incendiary air-to-air rocket used in World War I against observation balloons and airships. They were invented by the French lieutenant Yves Le Prieur and were first used in the ...
) for both air-to-air attacks, and air-to-ground.
* 1921 - Gas Dynamics Laboratory
Gas Dynamics Laboratory (GDL) () was the first Soviet research and development laboratory to focus on rocket technology. Its activities were initially devoted to the development of Solid-propellant rocket, solid propellant rockets, which becam ...
the first rocket research and development organization in the USSR
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
established by N. I. Tikhomirov.heading=Gas-Dynamic Laboratory
* 1922 - Hermann Oberth
Hermann Julius Oberth (; 25 June 1894 – 28 December 1989) was an Austria-Hungary, Austro-Hungarian-born German physicist and rocket pioneer of Transylvanian Saxons, Transylvanian Saxon descent. Oberth supported Nazi Germany's war effort and re ...
publishes his scientific work about rocketry and space exploration: ''Die Rakete zu den Planetenräumen
Die, as a verb, refers to death, the cessation of life.
Die may also refer to:
Games
* Die, singular of dice, small throwable objects used for producing random numbers
Manufacturing
* Die (integrated circuit), a rectangular piece of a semicondu ...
'' ("By Rocket into Planetary Space").
* 1924 - Society for Studies of Interplanetary Travel founded in Moscow
Moscow is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city of Russia, standing on the Moskva (river), Moskva River in Central Russia. It has a population estimated at over 13 million residents with ...
by Konstantin Tsiolkovsky, Friedrich Zander
Georg Arthur Constantin Friedrich Zander (also Tsander, , Romanization of Russian, tr. ; , – 28 March 1933), was a Baltic German pioneer of rocketry and spaceflight in the Russian Empire and the Soviet Union. He designed the first liquid rock ...
and 200 other space and rocket experts
* 1926 - Robert Goddard
Robert Hutchings Goddard (October 5, 1882 – August 10, 1945) was an American engineer, professor, physicist, and inventor who is credited with creating and building the world's first liquid-fueled rocket, which was successfully lau ...
launches the first liquid fuel rocket. This is considered by some to be the start of the Space Age
The Space Age is a period encompassing the activities related to the space race, space exploration, space technology, and the cultural developments influenced by these events, beginning with the launch of Sputnik 1 on October 4, 1957, and co ...
.
* 1927 - Verein für Raumschiffahrt
The Verein für Raumschiffahrt ("''VfR''", ) was a German amateur rocket association prior to World War II that included members outside Germany. The first successful VfR test firing with liquid fuel (five minutes) was conducted by Max Valier a ...
(VfR - "Spaceflight Society") founded in Germany.
* 1928 - In Germany public displays of rocket experiments, initiated by Max Valier
Max Valier (9 February 1895 – 17 May 1930) was an Austrian rocketry pioneer. He was a leading figure in the world's first large-scale rocket program, Opel-RAK, and helped found the German ''Verein für Raumschiffahrt'' (VfR – "Spacefligh ...
and Fritz von Opel
Fritz Adam Hermann von Opel (4 May 1899 – 8 April 1971), known as Fritz Adam Hermann Opel until his father was ennobled in 1917, was the only son of Wilhelm von Opel and a grandson of Adam Opel, founder of the Opel company. He is remembered m ...
, via Opel RAK
Opel-RAK were a series of rocket vehicles produced by German automobile manufacturer Fritz von Opel,https://www.airforcemag.com/article/0904rocket/ article by Walter J. Boyne in Air Force Magazine, September 1, 2004 of the Opel car company, i ...
which achieved speed records for ground and rail vehicles in 1928https://www.airforcemag.com/article/0904rocket/ article by Walter J. Boyne in Air Force Magazine, September 1, 2004
* 1928 - first Soviet
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
test-firing of a solid fuel rocket
A solid-propellant rocket or solid rocket is a rocket with a rocket engine that uses solid propellants (fuel/ oxidizer). The earliest rockets were solid-fuel rockets powered by gunpowder. The inception of gunpowder rockets in warfare can be cr ...
carried out by the Gas Dynamics Laboratory
Gas Dynamics Laboratory (GDL) () was the first Soviet research and development laboratory to focus on rocket technology. Its activities were initially devoted to the development of Solid-propellant rocket, solid propellant rockets, which becam ...
, which flew for about 1,300 meters
* 1929 - ''Woman in the Moon
''Woman in the Moon'' (German language, German ''Frau im Mond'') is a German science fiction silent film that premiered 15 October 1929 at the UFA-Palast am Zoo cinema in Berlin to an audience of 2,000. It is often considered to be one of the f ...
'', considered to be one of the first "serious" science fiction films.
* 1931 - Friedrich Schmiedl attempts the first rocket mail service in Austria
Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine Federal states of Austria, states, of which the capital Vienna is the List of largest cities in Aust ...
*1933 - Sergei Korolev
Sergei Pavlovich Korolev (14 January 1966) was the lead Soviet Aerospace engineering, rocket engineer and spacecraft designer during the Space Race between the United States and the Soviet Union in the 1950s and 1960s. He invented the R-7 Sem ...
and Mikhail Tikhonravov
Mikhail Klavdievich Tikhonravov (29 July 1900 – 3 March 1974) was a Soviet engineer who was a pioneer of spacecraft design and rocketry.
Mikhail Tikhonravov was born in Vladimir, Russia. He attended the Zhukovsky Air Force Academy from 1922 ...
launch the first liquid-fueled rocket in the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
* 1935 - Emilio Herrera Linares
Emilio Herrera Linares (13 February 1879, in Granada, Spain – 13 September 1967, in Geneva, Geneve, Switzerland) was a Spanish military engineer and physicist.
Biography
He was born in Granada, 1879 and became interested in the military fro ...
from Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
designed and made the first full-pressured astronaut suit, called the escafandra estratonáutica. The Russians then used a model of Herrera's suit when first flying into space which the Americans would then later adopt when creating their own space program
*1936 - Research on rockets begins at the Guggenheim Aeronautical Laboratory
The Guggenheim Aeronautical Laboratory at the California Institute of Technology (GALCIT), was a research institute created in 1926, at first specializing in aeronautics research. In 1930, Hungarian scientist Theodore von Kármán accepted the di ...
at the California Institute of Technology
The California Institute of Technology (branded as Caltech) is a private research university in Pasadena, California, United States. The university is responsible for many modern scientific advancements and is among a small group of institutes ...
(GALCIT), the predecessor to the Jet Propulsion Laboratory
The Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) is a Federally funded research and development centers, federally funded research and development center (FFRDC) in La Cañada Flintridge, California, Crescenta Valley, United States. Founded in 1936 by Cali ...
, under the direction of Frank Malina and Theodore von Kármán
Theodore von Kármán ( , May 11, 1881May 6, 1963) was a Hungarian-American mathematician, aerospace engineer, and physicist who worked in aeronautics and astronautics. He was responsible for crucial advances in aerodynamics characterizing ...
* 1937 - Peenemünde Army Research Center
The Peenemünde Army Research Center (, HVP) was founded in 1937 as one of five military proving grounds under the German Army Weapons Office (''Heereswaffenamt''). Several German guided missiles and rockets of World War II were developed by ...
founded in Germany
* 1938 - The Projectile Development Establishment founded at Fort Halstead
Fort Halstead was a research site of the Defence Science and Technology Laboratory (Dstl), an executive agency of the UK Ministry of Defence. It is situated on the crest of the Kentish North Downs, overlooking the town of Sevenoaks, southeast o ...
for the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
's research into military solid-fuel rockets.
* 1939 - Katyusha
Katyusha () is a diminutive of the Russian name Ekaterina or Yekaterina, the Russian form of Katherine
Katherine (), also spelled Catherine and Catherina, other variations, is a feminine given name. The name and its variants are popular in c ...
multiple rocket launchers () are a type of rocket artillery
Rocket artillery is artillery that uses rockets as the projectile. The use of rocket artillery dates back to medieval China where devices such as fire arrows were used (albeit mostly as a psychological weapon). Fire arrows were also used in mult ...
first built and fielded by the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
.
* 1941 - French rocket EA-41 is launched, being the first European liquid propellant
The highest specific impulse chemical rockets use liquid propellants (liquid-propellant rockets). They can consist of a single chemical (a monopropellant) or a mix of two chemicals, called bipropellants. Bipropellants can further be divided into ...
working rocket (It was, however, preceded by the Peenemunde A5 and Soviet experiments.)
* 1941 - Jet Assisted Take Off JATO
JATO (acronym for jet-assisted take-off) is a type of assisted take-off for helping overloaded aircraft into the air by providing additional thrust in the form of small rockets. The term ''JATO'' is used interchangeably with the (more specific ...
installed on US Army Air Corp Ercoupe aircraft occurred on 12 August in March Field, California.
* 1942 - Wernher von Braun
Wernher Magnus Maximilian Freiherr von Braun ( ; ; 23 March 191216 June 1977) was a German–American aerospace engineer and space architect. He was a member of the Nazi Party and '' Allgemeine SS'', the leading figure in the development of ...
and Walter Dornberger
Major-General Dr. Walter Robert Dornberger (6 September 1895 – 26 June 1980) was a German Army artillery officer whose career spanned World War I and World War II. He was a leader of Nazi Germany's V-2 rocket programme and other projects a ...
launch the first V-2 rocket
The V2 (), with the technical name ''Aggregat (rocket family), Aggregat-4'' (A4), was the world's first long-range missile guidance, guided ballistic missile. The missile, powered by a liquid-propellant rocket engine, was developed during the S ...
at Peenemünde
Peenemünde (, ) is a municipality on the Baltic Sea island of Usedom in the Vorpommern-Greifswald district in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern in north-eastern Germany. It is part of the ''Amt (country subdivision), Amt'' (collective municipality) of Used ...
in northern Germany.
* 1942 - A V-2 rocket reaches an altitude of 85 km.
* 1944 - The V-2 rocket MW 18014
MW 18014 was a German A-4 test rocket launched on 20 June 1944, at the Peenemünde Army Research Center in Peenemünde. It was the first man-made object to reach outer space, attaining an apogee of , well above the Kármán line that was estab ...
reaches an altitude of 176 km, becoming the first human-made object to reach space
Space is a three-dimensional continuum containing positions and directions. In classical physics, physical space is often conceived in three linear dimensions. Modern physicists usually consider it, with time, to be part of a boundless ...
.
* 1945 - Lothar Sieber dies after the first vertical take-off crewed rocket flight in a Bachem Ba 349
The Bachem Ba 349 Natter () is a World War II German point-defence rocket-powered interceptor aircraft, interceptor, which was to be used in a very similar way to a manned surface-to-air missile. After a vertical take-off, which eliminated the n ...
"Natter"
* 1945 - Operation Paperclip
The Operation Paperclip was a secret United States intelligence program in which more than 1,600 German scientists, engineers, and technicians were taken from former Nazi Germany to the US for government employment after the end of World War I ...
takes 1,600 German rocket scientists and technicians to the United States
* 1945 - Operation Osoaviakhim
Operation Osoaviakhim was a secret Soviet operation in which more than 2,500 German specialists (scientists, engineers and technicians who worked in several areas) from companies and institutions relevant to military and economic policy in the So ...
takes 2,000 German rocket scientists and technicians to the Soviet Union
* 1946 - First flight of the Nike missile
Project Nike (Greek: Νίκη, "Victory") was a U.S. Army project proposed in May 1945 by Bell Laboratories, to develop a line-of-sight anti-aircraft missile system. The project delivered the United States' first operational anti-aircraft mi ...
, later the first operational surface-to-air guided missile
* 1947 - The first animals sent into space were fruit flies aboard a V-2 rocket launched from New Mexico
New Mexico is a state in the Southwestern United States, Southwestern region of the United States. It is one of the Mountain States of the southern Rocky Mountains, sharing the Four Corners region with Utah, Colorado, and Arizona. It also ...
, USA
* 1947 - Chuck Yeager
Brigadier general (United States), Brigadier General Charles Elwood Yeager ( , February 13, 1923December 7, 2020) was a United States Air Force officer, flying ace, and record-setting test pilot who in October 1947 became the first pilot in his ...
achieves the first crewed supersonic
Supersonic speed is the speed of an object that exceeds the speed of sound (Mach 1). For objects traveling in dry air of a temperature of 20 °C (68 °F) at sea level, this speed is approximately . Speeds greater than five times ...
flight in a Bell X-1
The Bell X-1 (Bell Model 44) is a rocket engine–powered aircraft, designated originally as the XS-1, and was a joint National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics– U.S. Army Air Forces– U.S. Air Force supersonic research project built by B ...
rocket-powered aircraft
* 1949 - Willy Ley
Willy Otto Oskar Ley (October 2, 1906 – June 24, 1969) was a German and American science writer and proponent of space exploration and cryptozoology. The crater Ley on the far side of the Moon is named in his honor.
Early life and Berlin y ...
publishes ''The Conquest of Space''
* 1952 - 22 May, French Véronique 1 rocket is launched from the Algerian desert.
* 1952 - Wernher von Braun discusses the technical details of a crewed exploration of Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun. It is also known as the "Red Planet", because of its orange-red appearance. Mars is a desert-like rocky planet with a tenuous carbon dioxide () atmosphere. At the average surface level the atmosph ...
in '' Das Marsprojekt''.
* 1953 - ''Colliers'' magazine publishes a series of articles on humanity's future in space, igniting the interest of people around the world. The series includes numerous articles by Ley and von Braun, illustrated by Chesley Bonestell.
* 1956 - First launch of PGM-17 Thor
The PGM-17A Thor was the first operative ballistic missile of the United States Air Force (USAF). It was named after the Thor, Norse god of thunder. It was deployed in the United Kingdom between 1959 and September 1963 as an intermediate-range b ...
, the first US ballistic missile and forerunner of the Delta space launch rockets
* 1957 - Launch of the first ICBM
An intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) is a ballistic missile with a range (aeronautics), range greater than , primarily designed for nuclear weapons delivery (delivering one or more Thermonuclear weapon, thermonuclear warheads). Conven ...
, the USSR
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
's R-7 (8K71), known to NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO ; , OTAN), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental Transnationalism, transnational military alliance of 32 Member states of NATO, member s ...
as the SS-6 ''Sapwood''.
* 1957 - The USSR launches Sputnik 1
Sputnik 1 (, , ''Satellite 1''), sometimes referred to as simply Sputnik, was the first artificial Earth satellite. It was launched into an elliptical low Earth orbit by the Soviet Union on 4 October 1957 as part of the Soviet space program ...
, the first artificial satellite.
* 1958 - The U.S. launches Explorer 1
Explorer 1 was the first satellite launched by the United States in 1958 and was part of the U.S. participation in the International Geophysical Year (IGY). The mission followed the first two satellites, both launched by the Soviet Union duri ...
, the first American artificial satellite, on a Jupiter-C
The Jupiter-C was an American research and development vehicle developed from the Jupiter-A. Jupiter-C was used for three Uncrewed vehicle, uncrewed sub-orbital spaceflights in 1956 and 1957 to test Re-entry vehicle, re-entry nosecones that were ...
rocket.
* 1958 - US launches their first ICBM, the Atlas
An atlas is a collection of maps; it is typically a bundle of world map, maps of Earth or of a continent or region of Earth. Advances in astronomy have also resulted in atlases of the celestial sphere or of other planets.
Atlases have traditio ...
-B (the Atlas-A was a test article only).
* 1961 - US launched the Mercury-Redstone 2
Mercury-Redstone 2 (MR-2) was the test flight of the Mercury-Redstone Launch Vehicle just prior to the first crewed American space mission in Project Mercury. Carrying a Ham (chimpanzee), chimpanzee named Ham on a suborbital flight, Mercury sp ...
mission, which made the chimpanzee
The chimpanzee (; ''Pan troglodytes''), also simply known as the chimp, is a species of Hominidae, great ape native to the forests and savannahs of tropical Africa. It has four confirmed subspecies and a fifth proposed one. When its close rel ...
Ham
Ham is pork from a leg cut that has been preserved by wet or dry curing, with or without smoking."Bacon: Bacon and Ham Curing" in '' Chambers's Encyclopædia''. London: George Newnes, 1961, Vol. 2, p. 39. As a processed meat, the term '' ...
to become the first Hominidae
The Hominidae (), whose members are known as the great apes or hominids (), are a taxonomic Family (biology), family of primates that includes eight Neontology#Extant taxa versus extinct taxa, extant species in four Genus, genera: ''Orangutan ...
in space.
* 1961 - the USSR launches Vostok 1
Vostok 1 (, ) was the first spaceflight of the Vostok programme and the first human spaceflight, human orbital spaceflight in history. The Vostok 3KA space capsule was launched from Baikonur Cosmodrome on 12 April 1961, with Soviet astronaut, c ...
, Yuri Gagarin
Yuri Alekseyevich Gagarin; Gagarin's first name is sometimes transliterated as ''Yuriy'', ''Youri'', or ''Yury''. (9 March 1934 – 27 March 1968) was a Soviet pilot and cosmonaut who, aboard the first successful Human spaceflight, crewed sp ...
reached a height of 327 km above Earth and was the first person to orbit Earth.
* 1961 - US, a Mercury capsule named ''Freedom 7
Mercury-Redstone 3, or ''Freedom 7'', was the first United States human spaceflight, on May 5, 1961, piloted by astronaut Alan Shepard. It was the first crewed flight of Project Mercury. The project had the ultimate objective of putting an astr ...
'' with Alan B. Shepard, spacecraft was launched by a Redstone rocket on a ballistic trajectory suborbital flight.
* 1962 - The US launches Mercury MA-6 (''Friendship 7
Mercury-Atlas 6 (MA-6) was the first crewed American orbital spaceflight, which took place on February 20, 1962. Piloted by astronaut John Glenn and operated by NASA as part of Project Mercury, it was the fifth human spaceflight, preceded by Sov ...
'') on an Atlas D booster, John Glenn
John Herschel Glenn Jr. (July 18, 1921 – December 8, 2016) was an American Marine Corps aviator, astronaut, businessman, and politician. He was the third American in space and the first to orbit the Earth, circling it three times in 1 ...
puts America in orbit.
*1962 - Pakistan
Pakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of over 241.5 million, having the Islam by country# ...
launched Rehbar-I and was the first country in Islamic world
The terms Islamic world and Muslim world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs, politics, and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is ...
to successfully launch a vessel in outer space.
* 1963 - The USSR launches Vostok 6
Vostok 6 () was the first human spaceflight to carry a woman, cosmonaut Valentina Tereshkova, into space.
Mission
The spacecraft was launched on 16 June 1963. It set the record for highest orbital inclination of a crewed spacecraft at 65°, a rec ...
, Valentina Tereshkova
Valentina Vladimirovna Tereshkova (born 6 March 1937) is a Russian engineer, member of the State Duma, and former Soviet cosmonaut. She was the first Women in space, woman in space, having flown a solo mission on Vostok 6 on 16 June 1963. S ...
was the first woman (and first civilian) in space and to orbit Earth. She remained in space for nearly three days and orbited the Earth 48 times.
* 1963 - US X-15
The North American X-15 is a Hypersonic speed, hypersonic rocket-powered aircraft which was operated by the United States Air Force and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as part of the List of X-planes, X-plane series of ...
rocket-plane, the first reusable crewed spacecraft (suborbital) reaches space, pioneering reusability, carried launch and glide landings.
* 1965 - USSR Proton rocket, highly successful launch vehicle with notable payloads, Salyut 6 and Salyut 7, Mir, and ISS components
* 1965 - Robert Salked investigates various single stage to orbit spaceplane concepts
* 1965 - FR Diamant
The Diamant rocket (French for "diamond") was the first exclusively French expendable launch system and at the same time the first satellite launcher not built by either the United States or USSR. As such, it has been referred to as being a key ...
, first French and European rocket to reach orbit, France became the third space nation.
 * 1966 - USSR
* 1966 - USSR Luna 9
Luna 9 (Луна-9), internal designation Ye-6 No.13, was an uncrewed space mission of the Soviet Union's Luna programme. On 3 February 1966, the Luna 9 spacecraft became the first spacecraft to achieve a soft landing on the Moon and return ima ...
, the first soft landing on the Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It Orbit of the Moon, orbits around Earth at Lunar distance, an average distance of (; about 30 times Earth diameter, Earth's diameter). The Moon rotation, rotates, with a rotation period (lunar ...
* 1966 - USSR launches Soyuz spacecraft
Soyuz () is a series of spacecraft which has been in service since the 1960s, having made more than 140 flights. It was designed for the Soviet space program by the Korolev Design Bureau (now Energia). The Soyuz succeeded the Voskhod spacecraf ...
, the longest-running series of spacecraft, eventually serving Soviet, Russian and International space missions.
* 1968 - USSR Zond 5
Zond 5 () was a spacecraft of the Soviet Zond program. In September 1968 it became the first spaceship to travel to and circle the Moon in a circumlunar trajectory, the first Moon mission to include animals, and the first to return safely to Ea ...
, two tortoises and smaller biological Earthlings circle the Moon and return safely to Earth.
* 1968 - US Apollo 8
Apollo 8 (December 21–27, 1968) was the first crewed spacecraft to leave Sphere of influence (astrodynamics), Earth's gravitational sphere of influence, and the first human spaceflight to reach the Moon. The crew orbited the Moon ten times ...
, the first crewed mission to reach and orbit the Moon.
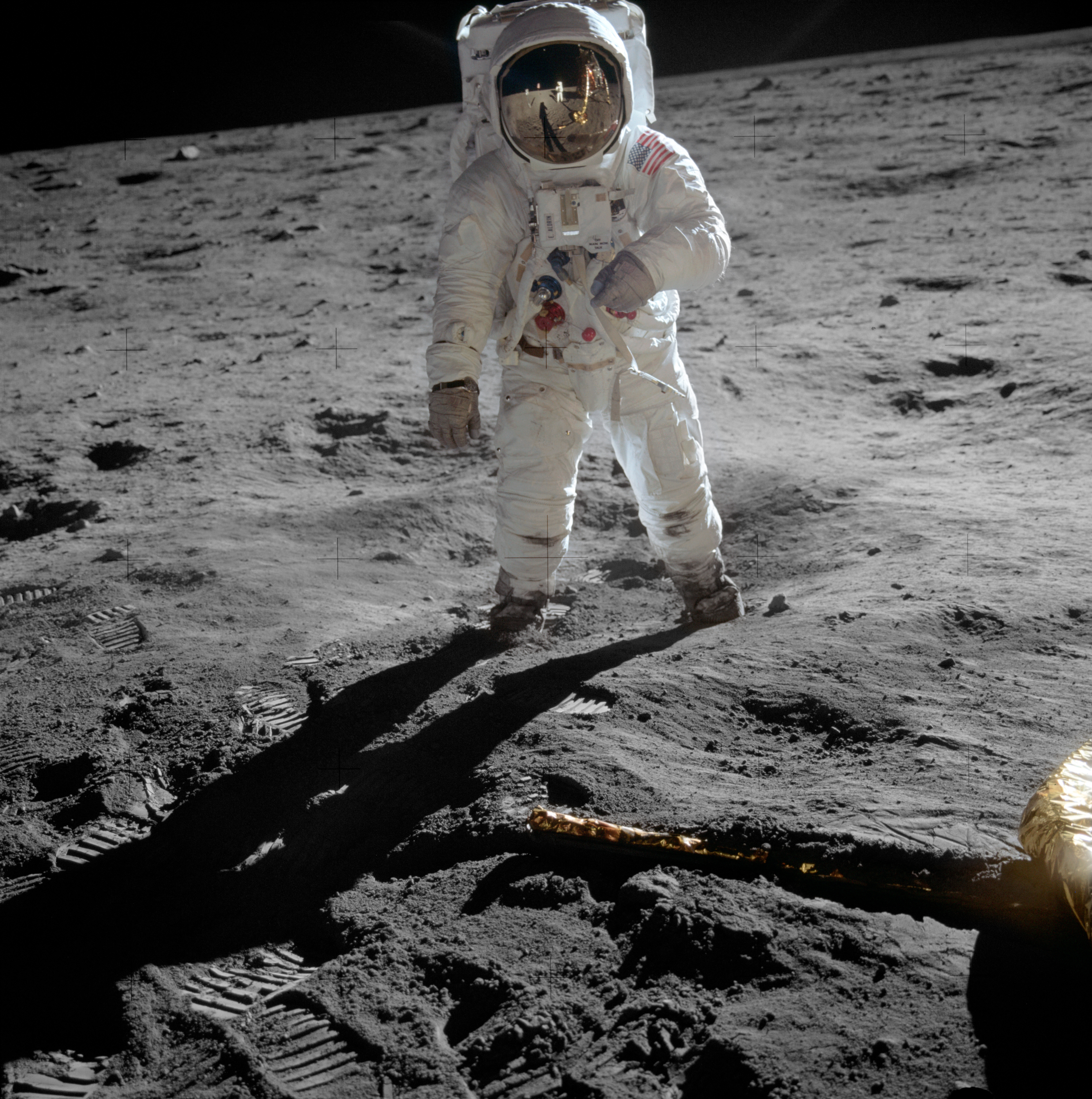
* 1969 - US Apollo 11
Apollo 11 was a spaceflight conducted from July 16 to 24, 1969, by the United States and launched by NASA. It marked the first time that humans Moon landing, landed on the Moon. Commander Neil Armstrong and Lunar Module pilot Buzz Aldrin l ...
, first crewed landing on the Moon, first lunar surface extravehicular activity.
* 1975 - EU ESA, creation of the European Space Agency.
* 1979 - EU Ariane 1
Ariane 1 () was the first rocket in the Ariane family of expendable launch systems. It was developed for and operated by the European Space Agency (ESA), which had been formed in 1973, the same year that development of the launcher had commenc ...
, first Ariane European rocket.
* 1980 - EU Arianespace
Arianespace SA is a French company founded in March 1980 as the world's first commercial launch service provider. It operates two launch vehicles: Vega C, a Small-lift launch vehicle, small-lift rocket, and Ariane 6, a Medium-lift launch vehicl ...
, creation of Arianespace, world's first commercial space transportation company.
* 1981 - US Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle is a retired, partially reusable launch system, reusable low Earth orbital spacecraft system operated from 1981 to 2011 by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as part of the Space Shuttle program. ...
pioneers reusability and glide landings
* 1988 - EU Ariane 4
The Ariane 4 was a European expendable rocket, expendable launch vehicle in the Ariane (rocket family), Ariane family, developed by the (CNES), the Government of France, French space agency, for the European Space Agency (ESA). The manufacturi ...
, first launch of the Ariane 4 rocket.
* 1996 - EU Ariane 5
Ariane 5 is a retired European heavy-lift space launch vehicle operated by Arianespace for the European Space Agency (ESA). It was launched from the Guiana Space Centre (CSG) in French Guiana. It was used to deliver payloads into geostationar ...
, first flight of the Ariane 5 rocket, self-destructed in flight. After that, Ariane 5 will be the main European rocket for decades.
* 1998 - US Deep Space 1
''Deep Space 1'' (DS1) was a NASA technology demonstration spacecraft which flew by an asteroid and a comet. It was part of the New Millennium Program, dedicated to testing advanced technologies.
Launched on 24 October 1998, the ''Deep Space ...
is first deep space mission to use an ion thruster
An ion thruster, ion drive, or ion engine is a form of electric propulsion used for spacecraft propulsion. An ion thruster creates a cloud of positive ions from a neutral gas by ionizing it to extract some electrons from its atoms. The i ...
for propulsion.
* 1998 - Russia launches the Zarya module, the first part of the International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is a large space station that was Assembly of the International Space Station, assembled and is maintained in low Earth orbit by a collaboration of five space agencies and their contractors: NASA (United ...
.
21st century
* 2001 - RussianSoyuz spacecraft
Soyuz () is a series of spacecraft which has been in service since the 1960s, having made more than 140 flights. It was designed for the Soviet space program by the Korolev Design Bureau (now Energia). The Soyuz succeeded the Voskhod spacecraf ...
sent the first space tourist Dennis Tito
Dennis Anthony Tito (born August 8, 1940) is an American engineer and entrepreneur. During mid-2001, he became the first space tourism, space tourist to fund his own visit to space, when he spent nearly eight days in orbit as a crew member of IS ...
to International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is a large space station that was Assembly of the International Space Station, assembled and is maintained in low Earth orbit by a collaboration of five space agencies and their contractors: NASA (United ...
.
* 2004 - US-based, first privately developed, crewed (suborbital) spaceflight, SpaceShipOne
SpaceShipOne is an experimental air launch, air-launched rocket-powered aircraft with sub-orbital spaceflight capability at speeds of up to /
using a hybrid rocket motor. The design features a unique "Feathering (reentry), feathering" atmosph ...
demonstrates reusability.
* 2008 - SpaceX
Space Exploration Technologies Corp., commonly referred to as SpaceX, is an America, American space technology company headquartered at the SpaceX Starbase, Starbase development site in Starbase, Texas. Since its founding in 2002, the compa ...
—with their Falcon 1
Falcon 1 was a two-stage small-lift launch vehicle that was operated from 2006 to 2009 by SpaceX, an American aerospace manufacturer. On September 28, 2008, Falcon 1 became the first privately developed fully liquid-fueled launch vehicle to s ...
rocket—became the first private entity to successfully launch a rocket
A rocket (from , and so named for its shape) is a vehicle that uses jet propulsion to accelerate without using any surrounding air. A rocket engine produces thrust by reaction to exhaust expelled at high speed. Rocket engines work entirely ...
into orbit
In celestial mechanics, an orbit (also known as orbital revolution) is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an artificial satellite around an ...
.
* 2012 - The SpaceX Dragon 1
SpaceX Dragon 1 is a class of fourteen partially reusable cargo spacecraft developed by SpaceX, an American private space transportation company. The spacecraft flew 23 missions between 2010 and 2020. Dragon was launched into orbit by the co ...
—launched aboard a Falcon 9
Falcon 9 is a Reusable launch system#Partial reusable launch systems, partially reusable, two-stage-to-orbit, medium-lift launch vehicle designed and manufactured in the United States by SpaceX. The first Falcon 9 launch was on June 4, 2010, an ...
launch vehicle—was the first private spacecraft
A spacecraft is a vehicle that is designed spaceflight, to fly and operate in outer space. Spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including Telecommunications, communications, Earth observation satellite, Earth observation, Weather s ...
to successfully dock with another spacecraft, and was also the first private capsule to dock at the International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is a large space station that was Assembly of the International Space Station, assembled and is maintained in low Earth orbit by a collaboration of five space agencies and their contractors: NASA (United ...
.
* 2014 - First booster rocket returning from an orbital trajectory to achieve a zero-velocity-at-zero-altitude propulsive vertical landing
Vertical takeoff, vertical landing (VTVL) is a form of takeoff and landing for rockets. Multiple VTVL craft have flown. A notable VTVL vehicle was the Apollo Lunar Module which delivered the first humans to the Moon. Building on the decades of ...
. The first-stage booster of Falcon 9 Flight 9 made the first successful controlled ocean soft touchdown of a liquid-rocket-engine orbital booster on April 18, 2014.
* 2015 - SpaceX
Space Exploration Technologies Corp., commonly referred to as SpaceX, is an America, American space technology company headquartered at the SpaceX Starbase, Starbase development site in Starbase, Texas. Since its founding in 2002, the compa ...
's Falcon 9 Flight 20
Falcon 9 flight 20 (also known as Orbcomm OG2 M2) was a Falcon 9 space launch that occurred on 22 December 2015 at 01:29:00 UTC (21 December, 8:29:00 pm local time). It was the first time that the first stage of an orbital rocket made a success ...
was the first time that the first stage of an orbital rocket made a successful return and vertical landing
Vertical takeoff, vertical landing (VTVL) is a form of takeoff and landing for rockets. Multiple VTVL craft have flown. A notable VTVL vehicle was the Apollo Lunar Module which delivered the first humans to the Moon. Building on the decades of ...
.
* 2017 - SpaceX
Space Exploration Technologies Corp., commonly referred to as SpaceX, is an America, American space technology company headquartered at the SpaceX Starbase, Starbase development site in Starbase, Texas. Since its founding in 2002, the compa ...
's Falcon 9
Falcon 9 is a Reusable launch system#Partial reusable launch systems, partially reusable, two-stage-to-orbit, medium-lift launch vehicle designed and manufactured in the United States by SpaceX. The first Falcon 9 launch was on June 4, 2010, an ...
SES-10
SES-10, is a geostationary communications satellite awarded in February 2014, owned and operated by SES and designed and manufactured by Airbus Defence and Space on the Eurostar-3000 satellite bus. It is positioned at the 67° West position t ...
was the first time a used orbital rocket made a successful return
* 2018 - The Electron
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary charge, elementary electric charge. It is a fundamental particle that comprises the ordinary matter that makes up the universe, along with up qua ...
rocket was the first New Zealand rocket to achieve orbit. The rocket is also unique in using an electric pump-fed engine. The rocket also carried an additional satellite payload called "Humanity Star
''Humanity Star'' was a reflective passive satellite designed to produce visible, pulsing flares. The satellite was launched into orbit by an Electron rocket on 21 January 2018 and entered into the atmosphere on 22 March 2018. The reaction to ...
", a carbon fiber sphere made up of 65 panels that reflect the Sun's light.
*2023 - India launches Chandrayaan-3
Chandrayaan-3 ( ) is the third mission in the Chandrayaan programme, a series of Exploration of the Moon, lunar-exploration missions developed by the ISRO, Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO). The mission consists of a Chandrayaan-2#Vikra ...
, the first spacecraft to land on the Moon's south pole.
See also
* History of rockets *List of missiles
Below is a list of missiles, sorted alphabetically into large categories and subcategories by name and purpose.
Other missile lists
Types of missiles:
* Conventional guided missiles
** Air-to-air missile
** Air-to-surface missile
** Anti-radia ...
* Lists of rockets
There are several different types of rockets. The following articles contain lists of rockets by type:
* List of missiles
* List of orbital launch systems
* List of sounding rockets
* List of military rockets
* List of rocket stages
* List of ca ...
* Timeline of heat engine technology
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Timeline Of Rocket And Missile TechnologyRockets
A rocket (from , and so named for its shape) is a vehicle that uses jet propulsion to accelerate without using any surrounding air. A rocket engine produces thrust by reaction to exhaust expelled at high speed. Rocket engines work entirely fr ...
Rocket
A rocket (from , and so named for its shape) is a vehicle that uses jet propulsion to accelerate without using any surrounding air. A rocket engine produces thrust by reaction to exhaust expelled at high speed. Rocket engines work entirely ...
Missile
A missile is an airborne ranged weapon capable of self-propelled flight aided usually by a propellant, jet engine or rocket motor.
Historically, 'missile' referred to any projectile that is thrown, shot or propelled towards a target; this ...
Rockets and missiles
A rocket (from , and so named for its shape) is a vehicle that uses jet propulsion to accelerate without using any surrounding air. A rocket engine produces thrust by reaction to exhaust expelled at high speed. Rocket engines work entirely fr ...
Missiles and rocksts