Timeline of evolution on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The timeline of the evolutionary history of life represents the current
 Species go extinct constantly as environments change, as organisms compete for environmental niches, and as genetic mutation leads to the rise of new species from older ones. At long irregular intervals, Earth's biosphere suffers a catastrophic die-off, a mass extinction, often comprising an accumulation of smaller extinction events over a relatively brief period.
The first known mass extinction was the
Species go extinct constantly as environments change, as organisms compete for environmental niches, and as genetic mutation leads to the rise of new species from older ones. At long irregular intervals, Earth's biosphere suffers a catastrophic die-off, a mass extinction, often comprising an accumulation of smaller extinction events over a relatively brief period.
The first known mass extinction was the
 4540 Ma – 4031 Ma
4540 Ma – 4031 Ma


 4031 Ma – 2500 Ma
4031 Ma – 2500 Ma
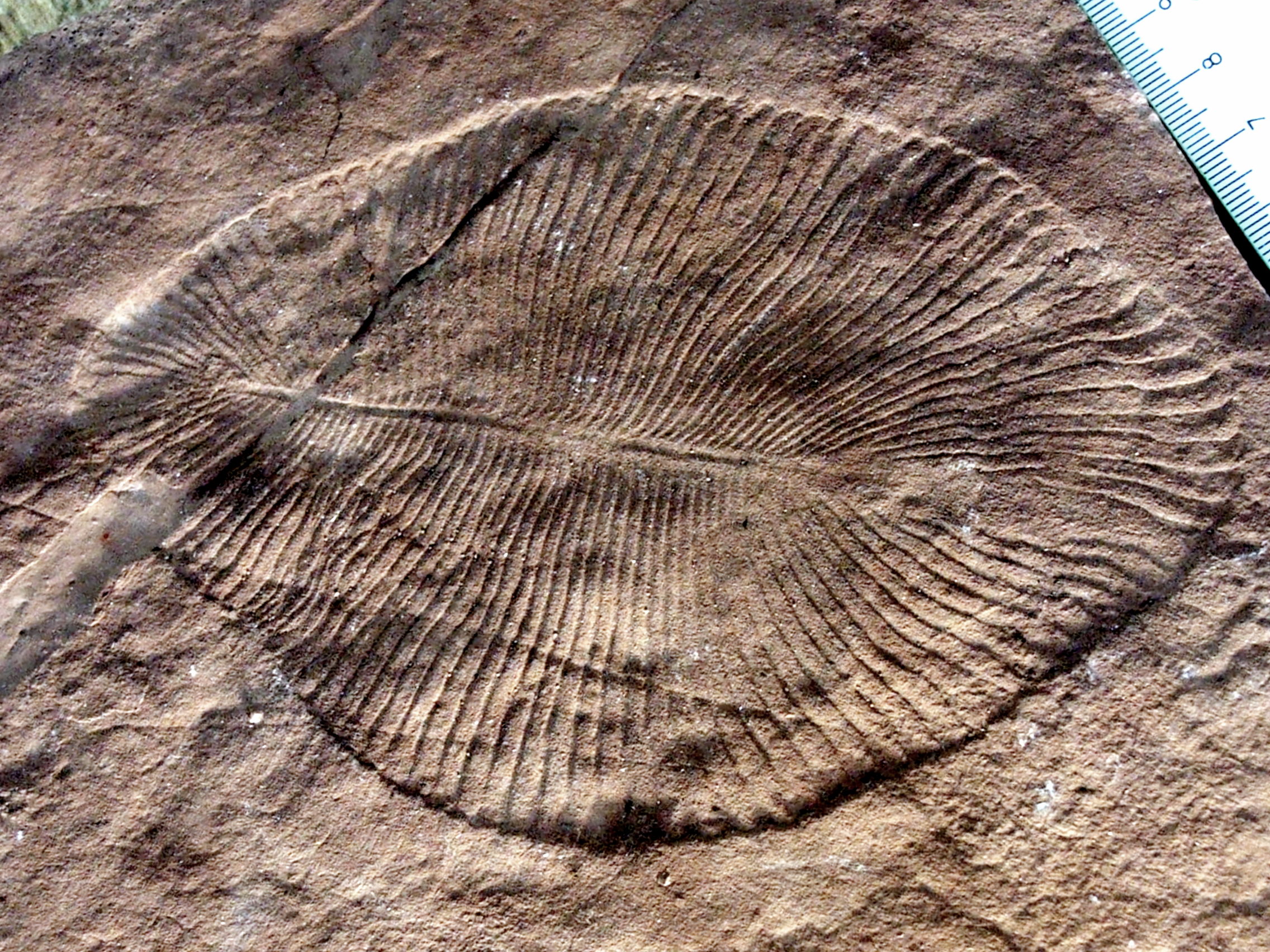 2500 Ma – 539 Ma. Contains the Palaeoproterozoic,
2500 Ma – 539 Ma. Contains the Palaeoproterozoic,






 From 251.9 Ma to 66 Ma and containing the
From 251.9 Ma to 66 Ma and containing the



Art of the Nature Timelines on Wikipedia
{{DEFAULTSORT:Timeline Of Evolution Evolution-related timelines Origin of life
scientific theory
A scientific theory is an explanation of an aspect of the universe, natural world that can be or that has been reproducibility, repeatedly tested and has corroborating evidence in accordance with the scientific method, using accepted protocol (s ...
outlining the major events during the development of life
Life, also known as biota, refers to matter that has biological processes, such as Cell signaling, signaling and self-sustaining processes. It is defined descriptively by the capacity for homeostasis, Structure#Biological, organisation, met ...
on planet Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all ...
. Dates in this article are consensus estimates based on scientific evidence
Scientific evidence is evidence that serves to either support or counter a scientific theory or hypothesis, although scientists also use evidence in other ways, such as when applying theories to practical problems. "Discussions about empirical ev ...
, mainly fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserve ...
s.
In biology
Biology is the scientific study of life and living organisms. It is a broad natural science that encompasses a wide range of fields and unifying principles that explain the structure, function, growth, History of life, origin, evolution, and ...
, evolution
Evolution is the change in the heritable Phenotypic trait, characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. It occurs when evolutionary processes such as natural selection and genetic drift act on genetic variation, re ...
is any change across successive generations in the heritable characteristics of biological populations. Evolutionary processes give rise to diversity at every level of biological organization, from kingdoms
Kingdom commonly refers to:
* A monarchic state or realm ruled by a king or queen.
** A monarchic chiefdom, represented or governed by a king or queen.
* Kingdom (biology), a category in biological taxonomy
Kingdom may also refer to:
Arts and me ...
to species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
, and individual organism
An organism is any life, living thing that functions as an individual. Such a definition raises more problems than it solves, not least because the concept of an individual is also difficult. Many criteria, few of them widely accepted, have be ...
s and molecule
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are held together by Force, attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions that satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemi ...
s, such as DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
and protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
s. The similarities between all present day organisms imply a common ancestor
Common descent is a concept in evolutionary biology applicable when one species is the ancestor of two or more species later in time. According to modern evolutionary biology, all living beings could be descendants of a unique ancestor commonl ...
from which all known species, living and extinct
Extinction is the termination of an organism by the death of its Endling, last member. A taxon may become Functional extinction, functionally extinct before the death of its last member if it loses the capacity to Reproduction, reproduce and ...
, have diverged. More than 99 percent of all species that ever lived (over five billion) are estimated to be extinct
Extinction is the termination of an organism by the death of its Endling, last member. A taxon may become Functional extinction, functionally extinct before the death of its last member if it loses the capacity to Reproduction, reproduce and ...
. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, with about 1.2 million or 14% documented, the rest not yet described. However, a 2016 report estimates an additional 1 trillion microbial species, with only 0.001% described.
There has been controversy between more traditional views of steadily increasing biodiversity
Biodiversity is the variability of life, life on Earth. It can be measured on various levels. There is for example genetic variability, species diversity, ecosystem diversity and Phylogenetics, phylogenetic diversity. Diversity is not distribut ...
, and a newer view of cycles of annihilation and diversification, so that certain past times, such as the Cambrian explosion, experienced maximums of diversity followed by sharp winnowing.
Extinction
 Species go extinct constantly as environments change, as organisms compete for environmental niches, and as genetic mutation leads to the rise of new species from older ones. At long irregular intervals, Earth's biosphere suffers a catastrophic die-off, a mass extinction, often comprising an accumulation of smaller extinction events over a relatively brief period.
The first known mass extinction was the
Species go extinct constantly as environments change, as organisms compete for environmental niches, and as genetic mutation leads to the rise of new species from older ones. At long irregular intervals, Earth's biosphere suffers a catastrophic die-off, a mass extinction, often comprising an accumulation of smaller extinction events over a relatively brief period.
The first known mass extinction was the Great Oxidation Event
The Great Oxidation Event (GOE) or Great Oxygenation Event, also called the Oxygen Catastrophe, Oxygen Revolution, Oxygen Crisis or Oxygen Holocaust, was a time interval during the Earth's Paleoproterozoic era when the Earth's atmosphere an ...
2.4 billion years ago, which killed most of the planet's obligate anaerobe
Obligate anaerobes are microorganisms killed by normal Atmosphere of Earth, atmospheric concentrations of oxygen (20.95% O2). Oxygen tolerance varies between species, with some species capable of surviving in up to 8% oxygen, while others lose vi ...
s. Researchers have identified five other major extinction events in Earth's history, with estimated losses below:
* End Ordovician: 440 million years ago, 86% of all species lost, including most graptolite
Graptolites are a group of colonial animals, members of the subclass Graptolithina within the class Pterobranchia. These filter-feeding organisms are known chiefly from fossils found from the Middle Cambrian ( Miaolingian, Wuliuan) through t ...
s
*Late Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era during the Phanerozoic eon, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the preceding Silurian period at million years ago ( Ma), to the beginning of the succeeding ...
: 375 million years ago, 75% of species lost, including most trilobite
Trilobites (; meaning "three-lobed entities") are extinction, extinct marine arthropods that form the class (biology), class Trilobita. One of the earliest groups of arthropods to appear in the fossil record, trilobites were among the most succ ...
s
* End Permian, The Great Dying: 251 million years ago, 96% of species lost, including tabulate corals, and most trees and synapsid
Synapsida is a diverse group of tetrapod vertebrates that includes all mammals and their extinct relatives. It is one of the two major clades of the group Amniota, the other being the more diverse group Sauropsida (which includes all extant rept ...
s
* End Triassic: 200 million years ago, 80% of species lost, including all conodont
Conodonts, are an extinct group of marine jawless vertebrates belonging to the class Conodonta (from Ancient Greek κῶνος (''kōnos''), meaning " cone", and ὀδούς (''odoús''), meaning "tooth"). They are primarily known from their hard ...
s
* End Cretaceous: 66 million years ago, 76% of species lost, including all ammonite
Ammonoids are extinct, (typically) coiled-shelled cephalopods comprising the subclass Ammonoidea. They are more closely related to living octopuses, squid, and cuttlefish (which comprise the clade Coleoidea) than they are to nautiluses (family N ...
s, mosasaur
Mosasaurs (from Latin ''Mosa'' meaning the 'Meuse', and Ancient Greek, Greek ' meaning 'lizard') are an extinct group of large aquatic reptiles within the family Mosasauridae that lived during the Late Cretaceous. Their first fossil remains wer ...
s, plesiosaur
The Plesiosauria or plesiosaurs are an Order (biology), order or clade of extinct Mesozoic marine reptiles, belonging to the Sauropterygia.
Plesiosaurs first appeared in the latest Triassic Period (geology), Period, possibly in the Rhaetian st ...
s, pterosaur
Pterosaurs are an extinct clade of flying reptiles in the order Pterosauria. They existed during most of the Mesozoic: from the Late Triassic to the end of the Cretaceous (228 million to 66 million years ago). Pterosaurs are the earli ...
s, and nonavian dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic Geological period, period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the #Evolutio ...
s
Smaller extinction events have occurred in the periods between, with some dividing geologic time
The geologic time scale or geological time scale (GTS) is a representation of time based on the rock record of Earth. It is a system of chronological dating that uses chronostratigraphy (the process of relating strata to time) and geochronolo ...
periods and epochs. The Holocene extinction
The Holocene extinction, also referred to as the Anthropocene extinction or the sixth mass extinction, is an ongoing extinction event caused exclusively by human activities during the Holocene epoch. This extinction event spans numerous families ...
event is currently under way.
Factors in mass extinctions include continental drift
Continental drift is a highly supported scientific theory, originating in the early 20th century, that Earth's continents move or drift relative to each other over geologic time. The theory of continental drift has since been validated and inc ...
, changes in atmospheric and marine chemistry
Chemistry is the scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a physical science within the natural sciences that studies the chemical elements that make up matter and chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules a ...
, volcanism
Volcanism, vulcanism, volcanicity, or volcanic activity is the phenomenon where solids, liquids, gases, and their mixtures erupt to the surface of a solid-surface astronomical body such as a planet or a moon. It is caused by the presence of a he ...
and other aspects of mountain formation
Mountain formation occurs due to a variety of geological processes associated with large-scale movements of the Earth's crust ( tectonic plates). Folding, faulting, volcanic activity, igneous intrusion and metamorphism can all be parts of th ...
, changes in glaciation
A glacial period (alternatively glacial or glaciation) is an interval of time (thousands of years) within an ice age that is marked by colder temperatures and glacier advances. Interglacials, on the other hand, are periods of warmer climate be ...
, changes in sea level
Mean sea level (MSL, often shortened to sea level) is an mean, average surface level of one or more among Earth's coastal Body of water, bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical ...
, and impact event
An impact event is a collision between astronomical objects causing measurable effects. Impact events have been found to regularly occur in planetary systems, though the most frequent involve asteroids, comets or meteoroids and have minimal effe ...
s.
Detailed timeline
In this timeline, Ma (for ''megaannum'') means "million years ago," ka (for ''kiloannum'') means "thousand years ago," and ya means "years ago."Hadean Eon
 4540 Ma – 4031 Ma
4540 Ma – 4031 Ma
Archean Eon


 4031 Ma – 2500 Ma
4031 Ma – 2500 Ma
Proterozoic Eon
 2500 Ma – 539 Ma. Contains the Palaeoproterozoic,
2500 Ma – 539 Ma. Contains the Palaeoproterozoic, Mesoproterozoic
The Mesoproterozoic Era is a geologic era that occurred from . The Mesoproterozoic was the first era of Earth's history for which a fairly definitive geological record survives. Continents existed during the preceding era (the Paleoproterozoic ...
and Neoproterozoic
The Neoproterozoic Era is the last of the three geologic eras of the Proterozoic geologic eon, eon, spanning from 1 billion to 538.8 million years ago, and is the last era of the Precambrian "supereon". It is preceded by the Mesoproterozoic era an ...
eras.
Phanerozoic Eon
539 Ma – present ThePhanerozoic
The Phanerozoic is the current and the latest of the four eon (geology), geologic eons in the Earth's geologic time scale, covering the time period from 538.8 million years ago to the present. It is the eon during which abundant animal and ...
Eon (Greek: period of well-displayed life) marks the appearance in the fossil record of abundant, shell-forming and/or trace-making organisms. It is subdivided into three eras, the Paleozoic
The Paleozoic ( , , ; or Palaeozoic) Era is the first of three Era (geology), geological eras of the Phanerozoic Eon. Beginning 538.8 million years ago (Ma), it succeeds the Neoproterozoic (the last era of the Proterozoic Eon) and ends 251.9 Ma a ...
, Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era is the Era (geology), era of Earth's Geologic time scale, geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceous Period (geology), Periods. It is characterized by the dominance of archosaurian r ...
and Cenozoic
The Cenozoic Era ( ; ) is Earth's current geological era, representing the last 66million years of Earth's history. It is characterized by the dominance of mammals, insects, birds and angiosperms (flowering plants). It is the latest of three g ...
, with major mass extinctions at division points.
Palaeozoic Era
538.8 Ma – 251.9 Ma and contains theCambrian
The Cambrian ( ) is the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 51.95 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran period 538.8 Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the Ordov ...
, Ordovician
The Ordovician ( ) is a geologic period and System (geology), system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era (geology), Era, and the second of twelve periods of the Phanerozoic Eon (geology), Eon. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years f ...
, Silurian
The Silurian ( ) is a geologic period and system spanning 23.5 million years from the end of the Ordovician Period, at million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Devonian Period, Mya. The Silurian is the third and shortest period of t ...
, Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a period (geology), geologic period and system (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era during the Phanerozoic eon (geology), eon, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the preceding Silurian per ...
, Carboniferous
The Carboniferous ( ) is a Geologic time scale, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era that spans 60 million years, from the end of the Devonian Period Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the ...
and Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years, from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.902 Mya. It is the s ...
periods.



Mesozoic Era



 From 251.9 Ma to 66 Ma and containing the
From 251.9 Ma to 66 Ma and containing the Triassic
The Triassic ( ; sometimes symbolized 🝈) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.5 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.4 Mya. The Triassic is t ...
, Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately 143.1 Mya. ...
and Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 143.1 to 66 mya (unit), million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era (geology), Era, as well as the longest. At around 77.1 million years, it is the ...
periods.
Cenozoic Era



See also
*Evolutionary history of plants
The evolution of plants has resulted in a wide range of complexity, from the earliest algal mats of unicellular archaeplastids evolved through endosymbiosis, through multicellular marine habitat, marine and freshwater green algae, to spore-beari ...
(timeline
A timeline is a list of events displayed in chronological order. It is typically a graphic design showing a long bar labelled with dates paralleling it, and usually contemporaneous events.
Timelines can use any suitable scale representing t ...
)
* Geologic time scale
The geologic time scale or geological time scale (GTS) is a representation of time based on the rock record of Earth. It is a system of chronological dating that uses chronostratigraphy (the process of relating strata to time) and geochro ...
* History of Earth
The natural history of Earth concerns the development of planet Earth from its formation to the present day. Nearly all branches of natural science have contributed to understanding of the main events of Earth's past, characterized by consta ...
* Sociocultural evolution
Sociocultural evolution, sociocultural evolutionism or social evolution are theories of sociobiology and cultural evolution that describe how Society, societies and culture change over time. Whereas sociocultural development traces processes t ...
* Timeline of human evolution
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * *Further reading
*External links
* * Explore complete phylogenetic tree interactively * * * Interactive timeline from Big Bang to present * Sequence of Plant Evolution * Sequence of Animal Evolution * * *Art of the Nature Timelines on Wikipedia
{{DEFAULTSORT:Timeline Of Evolution Evolution-related timelines Origin of life
evolution
Evolution is the change in the heritable Phenotypic trait, characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. It occurs when evolutionary processes such as natural selection and genetic drift act on genetic variation, re ...