Time Periods on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The categorization of the past into discrete, quantified named blocks of time is called
It’s about time: historical periodization and Linked Ancient World Data
''. Study of the Ancient universe Papers, 2014. This is a list of such named time periods as defined in various fields of study. These can be divided broadly into prehistorical periods and historical periods (when written records began to be kept). In
 * South Asian Stone Age
** Periodisation of the Indus Valley Civilisation, Pre-Harappan
*** Mehrgarh
* Bronze Age India (3340 BC – 1350 BC)
** Indus Valley Civilization
*** Early Harappan
*** Periodisation of the Indus Valley Civilisation, Early Mature Harappan
*** Mature Harappan
*** Late Harappan
**** Punjab Phase
**** Jhukar Phase
**** Rangpur Phase
*** Periodisation of the Indus Valley Civilisation, Final Harappan
* Iron Age in India (1350 BC – 200 BC)
** ''Vedic period'' (1350 BC – 500 BC): Mahajanapadas
** ''Magadha period'' (c.500 BC – c.750 AD): Nanda Empire, Nandas, Mauryan empire, Mauryans, Shunga Empire, Shungas
* Classical India (200 BC – 500 AD)
** ''Sangam period'' (300 BC – 600 AD): Chola dynasty, Cholas, Chalukya dynasty, Chalukyas, Pallava dynasty, Pallavas and Pandya dynasty, Pandyans
** ''Golden Age of India, Golden period'': Kushan empire, Kushans (50 AD – 220 AD), Satavahana dynasty, Satavahanas (230 BC – 220 AD), Gupta Empire, Guptas (320 AD – 535 AD) and Vakataka dynasty, Vakatakas (300AD – 650 AD)
* Medieval India, Medieval Age in India (500–1526)
** ''Tripartite struggle, Tripartite period'' (c.750 – c.900): Pala Empire, Palas, Rashtrakuta dynasty, Rashtrakutas and Gurjara-Pratihara dynasty, Gurjaras
** ''Muslim period in the Indian subcontinent, Muslim period'' (712–1857): Delhi Sultanate, Delhi, Bengal Sultanate, Bengal, Bahmani Sultanate, Bahmani and Gujarat Sultanate, Gujarat sultanates
** Vijayanagara Empire (1336–1646), Gajapati Empire (1434–1541) and kingdom of Mewar (1325–1448)
* Modern Age in India (1526 – present)
** Mughal Empire (1526–1857)
** Maratha Empire (1674–1818)
** ''Colonial India, Colonial period'': British Raj (1858 – 1947)
** History of the Republic of India, Independence (1947 – present)
* South Asian Stone Age
** Periodisation of the Indus Valley Civilisation, Pre-Harappan
*** Mehrgarh
* Bronze Age India (3340 BC – 1350 BC)
** Indus Valley Civilization
*** Early Harappan
*** Periodisation of the Indus Valley Civilisation, Early Mature Harappan
*** Mature Harappan
*** Late Harappan
**** Punjab Phase
**** Jhukar Phase
**** Rangpur Phase
*** Periodisation of the Indus Valley Civilisation, Final Harappan
* Iron Age in India (1350 BC – 200 BC)
** ''Vedic period'' (1350 BC – 500 BC): Mahajanapadas
** ''Magadha period'' (c.500 BC – c.750 AD): Nanda Empire, Nandas, Mauryan empire, Mauryans, Shunga Empire, Shungas
* Classical India (200 BC – 500 AD)
** ''Sangam period'' (300 BC – 600 AD): Chola dynasty, Cholas, Chalukya dynasty, Chalukyas, Pallava dynasty, Pallavas and Pandya dynasty, Pandyans
** ''Golden Age of India, Golden period'': Kushan empire, Kushans (50 AD – 220 AD), Satavahana dynasty, Satavahanas (230 BC – 220 AD), Gupta Empire, Guptas (320 AD – 535 AD) and Vakataka dynasty, Vakatakas (300AD – 650 AD)
* Medieval India, Medieval Age in India (500–1526)
** ''Tripartite struggle, Tripartite period'' (c.750 – c.900): Pala Empire, Palas, Rashtrakuta dynasty, Rashtrakutas and Gurjara-Pratihara dynasty, Gurjaras
** ''Muslim period in the Indian subcontinent, Muslim period'' (712–1857): Delhi Sultanate, Delhi, Bengal Sultanate, Bengal, Bahmani Sultanate, Bahmani and Gujarat Sultanate, Gujarat sultanates
** Vijayanagara Empire (1336–1646), Gajapati Empire (1434–1541) and kingdom of Mewar (1325–1448)
* Modern Age in India (1526 – present)
** Mughal Empire (1526–1857)
** Maratha Empire (1674–1818)
** ''Colonial India, Colonial period'': British Raj (1858 – 1947)
** History of the Republic of India, Independence (1947 – present)
The Venture of Islam, Volume 2: The Expansion of Islam in the Middle Periods
' (1974), p. 3. (7th – 21st centuries) ** ''High Caliphate'' (685–945) ** ''Earlier Middle Period'' (945–1250) ** ''Later Middle Period'' (1250–1500) ** Rashidun Caliphate (632–661) ** Umayyad Caliphate (661–750) ** Abbasid Caliphate (750–1258), Fatimid Caliphate (909–1171) *** Buyid dynasty (934–1055) *** Seljuq dynasty (1055–1171) *** Ayyubid dynasty (1171–1341) ** Ottoman Empire (1300–1923) *** Safavid dynasty, Safavid Empire (1501–1736) ** Mandatory Iraq, Kingdom of Iraq under British mandate (1921-1932) ** Hashemite Kingdom of Iraq (1932-1958) *** Hashemite Arab Federation (1958) ** First Iraqi Republic, Qasimist Republic of Iraq (1958-68) ** Ba'athist Iraq (1968-2003) ** Coalition Provisional Authority (2003-04) ** Republic of Iraq (2004-present)
periodization
In historiography, periodization is the process or study of categorizing the past into discrete, quantified, and named blocks of time for the purpose of study or analysis.Adam Rabinowitz.It's about time: historical periodization and Linked Ancie ...
.Adam Rabinowitz. And king It’s about time: historical periodization and Linked Ancient World Data
''. Study of the Ancient universe Papers, 2014. This is a list of such named time periods as defined in various fields of study. These can be divided broadly into prehistorical periods and historical periods (when written records began to be kept). In
archaeology
Archaeology or archeology is the study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts or ecofacts, ...
and anthropology
Anthropology is the scientific study of humanity, concerned with human behavior, human biology, cultures, society, societies, and linguistics, in both the present and past, including archaic humans. Social anthropology studies patterns of behav ...
, prehistory
Prehistory, also called pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the first known use of stone tools by hominins million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use ...
is subdivided into the three-age system
The three-age system is the periodization of human prehistory (with some overlap into the history, historical periods in a few regions) into three time-periods: the Stone Age, the Bronze Age, and the Iron Age, although the concept may also re ...
, this list includes the use of the three-age system as well as a number of various designation used in reference to sub-ages within the traditional three.
The dates for each age can vary by region. On the geologic time scale
The geologic time scale or geological time scale (GTS) is a representation of time based on the rock record of Earth. It is a system of chronological dating that uses chronostratigraphy (the process of relating strata to time) and geochro ...
, the Holocene
The Holocene () is the current geologic time scale, geological epoch, beginning approximately 11,700 years ago. It follows the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene to ...
epoch starts at the end of the last glacial period of the current ice age (c. 10,000 BC) and continues to the present. The beginning of the Mesolithic is usually considered to correspond to the beginning of the Holocene
The Holocene () is the current geologic time scale, geological epoch, beginning approximately 11,700 years ago. It follows the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene to ...
epoch.
Prehistoric periods
Era
*Precambrian
The Precambrian ( ; or pre-Cambrian, sometimes abbreviated pC, or Cryptozoic) is the earliest part of Earth's history, set before the current Phanerozoic Eon. The Precambrian is so named because it preceded the Cambrian, the first period of t ...
** Hadean
The Hadean ( ) is the first and oldest of the four geologic eons of Earth's history, starting with the planet's formation about 4.6 billion years ago (estimated 4567.30 ± 0.16 million years ago set by the age of the oldest solid material ...
(or hadaeozoic)
** Archean
The Archean ( , also spelled Archaean or Archæan), in older sources sometimes called the Archaeozoic, is the second of the four geologic eons of Earth's history of Earth, history, preceded by the Hadean Eon and followed by the Proterozoic and t ...
(or archaeozoic)
*** Eoarchean
The Eoarchean ( ; also spelled Eoarchaean) is the first Era (geology), era of the Archean, Archean Eon of the geologic record. It spans 431 million years, from the end of the Hadean Eon 4031 annum, Mya to the start of the Paleoarchean Era 3600 M ...
*** Paleoarchean
*** Mesoarchean
The Mesoarchean ( , also spelled Mesoarchaean) is a geologic era in the Archean Eon, spanning , which contains the first evidence of modern-style plate subduction and expansion of microbial life. The era is defined chronometrically and is no ...
*** Neoarchean
The Neoarchean ( ; also spelled Neoarchaean) is the last geologic era in the Archean Eon that spans from 2800 to 2500 million years ago—the period being defined chronometrically and not referencing a specific level in a rock section on Ear ...
** Proterozoic
The Proterozoic ( ) is the third of the four geologic eons of Earth's history, spanning the time interval from 2500 to 538.8 Mya, and is the longest eon of Earth's geologic time scale. It is preceded by the Archean and followed by the Phanerozo ...
*** Paleoproterozoic
The Paleoproterozoic Era (also spelled Palaeoproterozoic) is the first of the three sub-divisions ( eras) of the Proterozoic eon, and also the longest era of the Earth's geological history, spanning from (2.5–1.6 Ga). It is further sub ...
**** Siderian
The Siderian Period (; , meaning "iron") is the first geologic period in the Paleoproterozoic Era and lasted from Ma to Ma. Instead of being based on stratigraphy, these dates are defined chronometrically.
The deposition of banded iron form ...
**** Rhyacian
The Rhyacian Period (; , meaning "stream of lava") is the second geologic period in the Paleoproterozoic Era and lasted from Mya to Mya (million years ago). Instead of being based on stratigraphy, these dates are defined chronometrically.
The ...
**** Orosirian
The Orosirian Period (; , meaning "mountain range") is the third geologic period in the Paleoproterozoic Era and lasted from Mya to Mya (million years ago). Instead of being based on stratigraphy, these dates are defined chronometrically.
T ...
**** Statherian
The Statherian Period (; , meaning "stable, firm") is the final geologic period in the Paleoproterozoic Era and lasted from Mya to Mya (million years ago). Instead of being based on stratigraphy, these dates are defined chronometrically.
Th ...
*** Mesoproterozoic
The Mesoproterozoic Era is a geologic era that occurred from . The Mesoproterozoic was the first era of Earth's history for which a fairly definitive geological record survives. Continents existed during the preceding era (the Paleoproterozoic ...
**** Calymmian
The Calymmian Period (from , meaning "cover") is the first geologic period in the Mesoproterozoic Era and lasted from Mya to Mya (million years ago). Instead of being based on stratigraphy, these dates are defined chronometrically.
The peri ...
**** Ectasian
The Ectasian Period (from , meaning "extension") is the second geologic period in the Mesoproterozoic Era and lasted from Mya to Mya (million years ago). Instead of being based on stratigraphy, these dates are defined chronometrically.
Geol ...
**** Stenian
The Stenian Period ( , from , meaning "narrow") is the final geologic period in the Mesoproterozoic Era and lasted from Mya to Mya (million years ago). Instead of being based on stratigraphy, these dates are defined chronometrically. The name ...
*** Neoproterozoic
The Neoproterozoic Era is the last of the three geologic eras of the Proterozoic geologic eon, eon, spanning from 1 billion to 538.8 million years ago, and is the last era of the Precambrian "supereon". It is preceded by the Mesoproterozoic era an ...
**** Tonian
The Tonian (from , meaning "stretch") is the first geologic period of the Neoproterozoic era (geology), Era. It lasted from to Mya (million years ago). Instead of being based on stratigraphy, these dates are defined by the International Commissi ...
**** Cryogenian
The Cryogenian (from , meaning "cold" and , romanized: , meaning "birth") is a geologic period that lasted from . It is the second of the three periods of the Neoproterozoic era, preceded by the Tonian and followed by the Ediacaran.
The Cryoge ...
**** Ediacarian
* Phanerozoic
The Phanerozoic is the current and the latest of the four eon (geology), geologic eons in the Earth's geologic time scale, covering the time period from 538.8 million years ago to the present. It is the eon during which abundant animal and ...
** Paleozoic
The Paleozoic ( , , ; or Palaeozoic) Era is the first of three Era (geology), geological eras of the Phanerozoic Eon. Beginning 538.8 million years ago (Ma), it succeeds the Neoproterozoic (the last era of the Proterozoic Eon) and ends 251.9 Ma a ...
*** Cambrian
The Cambrian ( ) is the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 51.95 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran period 538.8 Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the Ordov ...
**** Cambrian Explosion
*** Ordovician
The Ordovician ( ) is a geologic period and System (geology), system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era (geology), Era, and the second of twelve periods of the Phanerozoic Eon (geology), Eon. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years f ...
*** Silurian
The Silurian ( ) is a geologic period and system spanning 23.5 million years from the end of the Ordovician Period, at million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Devonian Period, Mya. The Silurian is the third and shortest period of t ...
*** Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a period (geology), geologic period and system (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era during the Phanerozoic eon (geology), eon, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the preceding Silurian per ...
*** Carboniferous
The Carboniferous ( ) is a Geologic time scale, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era that spans 60 million years, from the end of the Devonian Period Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the ...
*** Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years, from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.902 Mya. It is the s ...
** Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era is the Era (geology), era of Earth's Geologic time scale, geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceous Period (geology), Periods. It is characterized by the dominance of archosaurian r ...
*** Triassic
The Triassic ( ; sometimes symbolized 🝈) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.5 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.4 Mya. The Triassic is t ...
*** Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately 143.1 Mya. ...
*** Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 143.1 to 66 mya (unit), million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era (geology), Era, as well as the longest. At around 77.1 million years, it is the ...
** Cenozoic
The Cenozoic Era ( ; ) is Earth's current geological era, representing the last 66million years of Earth's history. It is characterized by the dominance of mammals, insects, birds and angiosperms (flowering plants). It is the latest of three g ...
*** Paleogene
The Paleogene Period ( ; also spelled Palaeogene or Palæogene) is a geologic period and system that spans 43 million years from the end of the Cretaceous Period Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the Neogene Period Ma. It is the fir ...
**** Paleocene
The Paleocene ( ), or Palaeocene, is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 66 to 56 mya (unit), million years ago (mya). It is the first epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), ...
***** Danian
The Danian is the oldest age or lowest stage of the Paleocene Epoch or Series, of the Paleogene Period or System, and of the Cenozoic Era or Erathem. The beginning of the Danian (and the end of the preceding Maastrichtian) is at the Cretac ...
***** Selandian
The Selandian is a stage in the Paleocene. It spans the time between . It is preceded by the Danian and followed by the Thanetian. Sometimes the Paleocene is subdivided in subepochs, in which the Selandian forms the "middle Paleocene".
Stratig ...
***** Thanetian
The Thanetian is, in the International Commission on Stratigraphy, ICS Geologic timescale, the latest age (geology), age or uppermost stage (stratigraphy), stratigraphic stage of the Paleocene epoch (geology), Epoch or series (stratigraphy), Serie ...
**** Eocene
The Eocene ( ) is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (Ma). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes ...
**** Oligocene
The Oligocene ( ) is a geologic epoch (geology), epoch of the Paleogene Geologic time scale, Period that extends from about 33.9 million to 23 million years before the present ( to ). As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that defin ...
*** Neogene
The Neogene ( ,) is a geologic period and system that spans 20.45 million years from the end of the Paleogene Period million years ago ( Mya) to the beginning of the present Quaternary Period million years ago. It is the second period of th ...
**** Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and mea ...
***** Aquitanian
***** Burdigalian
The Burdigalian is, in the geologic timescale, an age (geology), age or stage (stratigraphy), stage in the early Miocene. It spans the time between 20.43 ± 0.05 annum, Ma and 15.97 ± 0.05 Ma (million years ago). Preceded by the Aquitanian (sta ...
***** Langhian
The Langhian is, in the ICS geologic timescale, an age or stage in the middle Miocene Epoch/Series. It spans the time between 15.97 ± 0.05 Ma and 13.65 ± 0.05 Ma (million years ago) during the Middle Miocene.GeoWhen (2007)
The Langhian was ...
***** Serravallian
The Serravallian is, in the geologic timescale, an List of time periods, age or a stage (stratigraphy), stage in the middle Miocene epoch (geology), Epoch/series (stratigraphy), Series, which spans the time between 13.82 annum, Ma and 11.63 Ma (m ...
***** Tortonian
The Tortonian is in the geologic time scale an age or stage of the late Miocene that spans the time between 11.608 ± 0.005 Ma and 7.246 ± 0.005 Ma (million years ago). It follows the Serravallian and is followed by the Messinian.
The Tort ...
***** Messinian
The Messinian is in the geologic timescale the last age or uppermost stage of the Miocene. It spans the time between 7.246 ± 0.005 Ma and 5.333 ± 0.005 Ma (million years ago). It follows the Tortonian and is followed by the Zanclean, the fir ...
**** Pliocene
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch (geology), epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.33 to 2.58Zanclean
The Zanclean is the lowest stage or earliest age on the geologic time scale of the Pliocene. It spans the time between 5.332 ± 0.005 Ma (million years ago) and 3.6 ± 0.005 Ma. It is preceded by the Messinian Age of the Miocene Epoch, and f ...
***** Piacenzian
The Piacenzian is in the international geologic time scale the upper stage (stratigraphy), stage or latest age (geology), age of the Pliocene. It spans the time between 3.6 ± 0.005 year#SI prefix multipliers, Ma and 2.58 Ma (million years ago). T ...
*** Quaternary
The Quaternary ( ) is the current and most recent of the three periods of the Cenozoic Era in the geologic time scale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS), as well as the current and most recent of the twelve periods of the ...
**** Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( ; referred to colloquially as the ''ice age, Ice Age'') is the geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fin ...
***** Gelasian
The Gelasian is an age in the international geologic timescale or a stage in chronostratigraphy, being the earliest or lowest subdivision of the Quaternary Period/System and Pleistocene Epoch/Series. It spans the time between 2.58 Ma (million y ...
***** Calabrian
***** Chibanian
The Chibanian, more widely known as the Middle Pleistocene (its previous informal name), is an Age (geology), age in the international geologic timescale or a Stage (stratigraphy), stage in chronostratigraphy, being a division of the Pleistocen ...
***** Late Pleistocene
The Late Pleistocene is an unofficial Age (geology), age in the international geologic timescale in chronostratigraphy, also known as the Upper Pleistocene from a Stratigraphy, stratigraphic perspective. It is intended to be the fourth division ...
**** Holocene
The Holocene () is the current geologic time scale, geological epoch, beginning approximately 11,700 years ago. It follows the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene to ...
***** Greenlandian
In the geologic time scale, the Greenlandian is the earliest age or lowest stage of the Holocene Epoch or Series, part of the Quaternary. Beginning in 11,650 BP (9701 BCE or 300 HE) and ending with the 8.2-kiloyear event (c. 8200–8300 B ...
***** Northgrippian
In the geologic time scale, the Northgrippian is the middle one of three age (geology), ages or stage (stratigraphy), stages of the Holocene Epoch (geology), Epoch or series (stratigraphy), Series. It was officially ratified by the International ...
***** Meghalayan
The Meghalayan age is the name given in 2018, by the International Commission on Stratigraphy, to the current age or latest geologic age – or uppermost stage of the Quaternary. It is also the upper, or latest, of three subdivisions of the ...
**** Anthropocene
''Anthropocene'' is a term that has been used to refer to the period of time during which human impact on the environment, humanity has become a planetary force of change. It appears in scientific and social discourse, especially with respect to ...
(rejected proposal)
General periods
* Geologic Time – Period prior to humans. 4.6 billion to 3 million years ago. (See "prehistoric periods" for more detail into this.) * Primatomorphid Era – Period prior to the existence of ''Primatomorpha
Primatomorpha is a proposed mirorder of mammals containing the orders Dermoptera (or colugos) and Primates. Primatomorpha is sister to Scandentia, together forming the Euarchonta.
The term "Primatomorpha" first appeared in the general scien ...
''
* Simian Era – Period prior to the existence of ''Simiiformes
The simians, anthropoids, or higher primates are an infraorder (Simiiformes ) of primates containing all animals traditionally called monkeys and apes. More precisely, they consist of the parvorders Platyrrhini (New World monkeys) and Ca ...
''
* Hominoid Era – Period prior to the existence of ''Hominoidea
Apes (collectively Hominoidea ) are a Family (biology), superfamily of Old World simians native to sub-Saharan Africa and Southeast Asia (though they were more widespread in Africa, most of Asia, and Europe in prehistory, and counting humans ...
''
* Hominid Era – Period prior to the existence of ''Hominidae
The Hominidae (), whose members are known as the great apes or hominids (), are a taxonomic Family (biology), family of primates that includes eight Neontology#Extant taxa versus extinct taxa, extant species in four Genus, genera: ''Orangutan ...
''
**Distant signs of Human-like apes
* Homininaeid Era – Period prior to the existence of ''Homininae
Homininae (the hominines) is a subfamily of the family Hominidae (hominids). (The Homininae——encompass humans, and are also called "African hominids" or "African apes".) This subfamily includes two tribes, Hominini and Gorillini, both having ...
''
* Homininid Era – Period prior to the existence of ''Hominini
The Hominini (hominins) form a Tribe (biology), taxonomic tribe of the subfamily Homininae (hominines). They comprise two extant genera: ''Homo'' (humans) and ''Pan (genus), Pan'' (chimpanzees and bonobos), and in standard usage exclude the gen ...
''
* Prehistory
Prehistory, also called pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the first known use of stone tools by hominins million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use ...
– Period between the appearance of ''Homo
''Homo'' () is a genus of great ape (family Hominidae) that emerged from the genus ''Australopithecus'' and encompasses only a single extant species, ''Homo sapiens'' (modern humans), along with a number of extinct species (collectively called ...
'' ("humans"; first stone tools c. three million years ago) and the invention of writing systems (for the Ancient Near East
The ancient Near East was home to many cradles of civilization, spanning Mesopotamia, Egypt, Iran (or Persia), Anatolia and the Armenian highlands, the Levant, and the Arabian Peninsula. As such, the fields of ancient Near East studies and Nea ...
: c. five thousand years ago).
** Paleolithic
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic ( years ago) ( ), also called the Old Stone Age (), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone tools, and which represents almost the entire period of human prehist ...
– the earliest period of the Stone Age
*** Lower Paleolithic
The Lower Paleolithic (or Lower Palaeolithic) is the earliest subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age. It spans the time from around 3.3 million years ago when the first evidence for stone tool production and use by hominins appears ...
– time of archaic human
''Homo'' () is a genus of great ape (family Hominidae) that emerged from the genus ''Australopithecus'' and encompasses only a single extant species, ''Homo sapiens'' (modern humans), along with a number of extinct species (collectively called ...
species, predates ''Homo sapiens
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are Hominidae, great apes characterized by their Prehistory of nakedness and clothing ...
''
*** Middle Paleolithic
The Middle Paleolithic (or Middle Palaeolithic) is the second subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age as it is understood in Europe, Africa and Asia. The term Middle Stone Age is used as an equivalent or a synonym for the Middle P ...
– coexistence of archaic and anatomically modern human
Anatomy () is the branch of morphology concerned with the study of the internal structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science ...
species
*** Upper Paleolithic
The Upper Paleolithic (or Upper Palaeolithic) is the third and last subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age. Very broadly, it dates to between 50,000 and 12,000 years ago (the beginning of the Holocene), according to some theories ...
– worldwide expansion of anatomically modern humans, the disappearance of archaic humans by extinction or admixture with modern humans; earliest evidence for pictorial art.
** Mesolithic
The Mesolithic (Ancient Greek language, Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic i ...
(Epipaleolithic
In archaeology, the Epipalaeolithic or Epipaleolithic (sometimes Epi-paleolithic etc.) is a period occurring between the Upper Paleolithic and Neolithic during the Stone Age. Mesolithic also falls between these two periods, and the two are someti ...
) – a period in the development of human technology between the Palaeolithic and Neolithic periods.
** Neolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revo ...
– a period of primitive technological
Technology is the application of conceptual knowledge to achieve practical goals, especially in a reproducible way. The word ''technology'' can also mean the products resulting from such efforts, including both tangible tools such as ute ...
and social
Social organisms, including human(s), live collectively in interacting populations. This interaction is considered social whether they are aware of it or not, and whether the exchange is voluntary or not.
Etymology
The word "social" derives fro ...
development, beginning about 10,200 BC in parts of the Middle East, and later in other parts of the world.
** Chalcolithic
The Chalcolithic ( ) (also called the Copper Age and Eneolithic) was an archaeological period characterized by the increasing use of smelted copper. It followed the Neolithic and preceded the Bronze Age. It occurred at different periods in di ...
(or "Eneolithic", "Copper Age") – still largely Neolithic in character, when early copper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orang ...
metallurgy
Metallurgy is a domain of materials science and engineering that studies the physical and chemical behavior of metallic elements, their inter-metallic compounds, and their mixtures, which are known as alloys.
Metallurgy encompasses both the ...
appeared alongside the use of stone tools.
** Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
– not part of prehistory for all regions and civilizations who had adopted or developed a writing system.
** Iron Age
The Iron Age () is the final epoch of the three historical Metal Ages, after the Chalcolithic and Bronze Age. It has also been considered as the final age of the three-age division starting with prehistory (before recorded history) and progre ...
– not part of prehistory for all civilizations who had introduced written records during the Bronze Age.
* Ancient history
Ancient history is a time period from the History of writing, beginning of writing and recorded human history through late antiquity. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the development of Sumerian language, ...
– Aggregate of past events from the beginning of recorded human history and extending as far as the Early Middle Ages or the Postclassical Era. The span of recorded history
Recorded history or written history describes the historical events that have been recorded in a written form or other documented communication which are subsequently evaluated by historians using the historical method. For broader world h ...
is roughly five thousand years, beginning with the earliest linguistic records in the third millennium BC in Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of ...
and Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
.
**Classical antiquity
Classical antiquity, also known as the classical era, classical period, classical age, or simply antiquity, is the period of cultural History of Europe, European history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD comprising the inter ...
– Broad term for a long period of cultural history centered on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations of ancient Greece
Ancient Greece () was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity (), that comprised a loose collection of culturally and linguistically r ...
and ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome is the Roman people, Roman civilisation from the founding of Rome, founding of the Italian city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the Fall of the Western Roman Empire, collapse of the Western Roman Em ...
, collectively known as the Greco-Roman world
The Greco-Roman world , also Greco-Roman civilization, Greco-Roman culture or Greco-Latin culture (spelled Græco-Roman or Graeco-Roman in British English), as understood by modern scholars and writers, includes the geographical regions and co ...
. It is the period in which Greek and Roman society flourished and wielded great influence throughout Europe, North Africa and the Middle East.
* Post-classical history
In Human history, world history, post-classical history refers to the period from about 500 CE to 1500 CE, roughly corresponding to the European Middle Ages. The period is characterized by the expansion of civilizations geographically an ...
– Period of time that immediately followed ancient history. Depending on the continent, the era generally falls between the years AD 200–600 and AD 1200–1500. The major classical civilizations that the era follows are Han China
The Han dynasty was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC9 AD, 25–220 AD) established by Liu Bang and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–206 BC ...
(ending in 220), the Western Roman Empire
In modern historiography, the Western Roman Empire was the western provinces of the Roman Empire, collectively, during any period in which they were administered separately from the eastern provinces by a separate, independent imperial court. ...
(in 476), the Gupta Empire
The Gupta Empire was an Indian empire during the classical period of the Indian subcontinent which existed from the mid 3rd century to mid 6th century CE. At its zenith, the dynasty ruled over an empire that spanned much of the northern Indian ...
(in the 550s), and the Sasanian Empire
The Sasanian Empire (), officially Eranshahr ( , "Empire of the Iranian peoples, Iranians"), was an List of monarchs of Iran, Iranian empire that was founded and ruled by the House of Sasan from 224 to 651. Enduring for over four centuries, th ...
(in 651).
** Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
– Lasted from the 5th to the 15th century. It began with the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in 476 and is variously demarcated by historians as ending with the Fall of Constantinople
The Fall of Constantinople, also known as the Conquest of Constantinople, was the capture of Constantinople, the capital of the Byzantine Empire by the Ottoman Empire. The city was captured on 29 May 1453 as part of the culmination of a 55-da ...
in 1453, or the discovery of America by Columbus in 1492, merging into the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and sur ...
and the Age of Discovery
The Age of Discovery (), also known as the Age of Exploration, was part of the early modern period and overlapped with the Age of Sail. It was a period from approximately the 15th to the 17th century, during which Seamanship, seafarers fro ...
.
*** Early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages (historiography), Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th to the 10th century. They marked the start o ...
*** High Middle Ages
The High Middle Ages, or High Medieval Period, was the periodization, period of European history between and ; it was preceded by the Early Middle Ages and followed by the Late Middle Ages, which ended according to historiographical convention ...
*** Late Middle Ages
The late Middle Ages or late medieval period was the Periodization, period of History of Europe, European history lasting from 1300 to 1500 AD. The late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period ( ...
* Modern history
The modern era or the modern period is considered the current historical period of human history. It was originally applied to the history of Europe and Western history for events that came after the Middle Ages, often from around the year 1500, ...
– After the post-classical era
**Early modern period
The early modern period is a Periodization, historical period that is defined either as part of or as immediately preceding the modern period, with divisions based primarily on the history of Europe and the broader concept of modernity. There i ...
– The chronological limits of this period are open to debate. It emerges from the Late Middle Ages
The late Middle Ages or late medieval period was the Periodization, period of History of Europe, European history lasting from 1300 to 1500 AD. The late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period ( ...
(c. 1500), demarcated by historians as beginning with the fall of Constantinople
The Fall of Constantinople, also known as the Conquest of Constantinople, was the capture of Constantinople, the capital of the Byzantine Empire by the Ottoman Empire. The city was captured on 29 May 1453 as part of the culmination of a 55-da ...
in 1453, in forms such as the Italian Renaissance
The Italian Renaissance ( ) was a period in History of Italy, Italian history between the 14th and 16th centuries. The period is known for the initial development of the broader Renaissance culture that spread across Western Europe and marked t ...
in the West, the Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty, officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 1368 to 1644, following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming was the last imperial dynasty of ...
in the East, and the rise of the Aztecs
The Aztecs ( ) were a Mesoamerican civilization that flourished in central Mexico in the post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those groups who spoke the ...
in the New World. The period ends with the beginning of the Age of Revolutions
The Age of Revolution is a period from the late-18th to the mid-19th centuries during which a number of significant revolutionary movements occurred in most of Europe and the Americas. The period is noted for the change from absolutist monarch ...
.
** Contemporary history
Contemporary history, in English-language historiography, is a subset of modern history that describes the historical period from about 1945 to the present. In the social sciences, contemporary history is also continuous with, and related t ...
– History within living memory. It shifts forward with the generations, and today is the span of historic events from approximately 1945 that are immediately relevant to the present time.
Forms of modernity
* Hominids archaeologically and anatomically similar or identical to modern humans (HAASMHs) *Anatomically modern humans
Early modern human (EMH), or anatomically modern human (AMH), are terms used to distinguish ''Homo sapiens'' ( sometimes ''Homo sapiens sapiens'') that are anatomically consistent with the range of phenotypes seen in contemporary humans, from ...
(AMHs)
* Technologically modern humans (TMHs)
Technological periods
*Prehistory
Prehistory, also called pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the first known use of stone tools by hominins million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use ...
** Paleolithic
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic ( years ago) ( ), also called the Old Stone Age (), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone tools, and which represents almost the entire period of human prehist ...
(Lower
Lower may refer to:
* ''Lower'' (album), 2025 album by Benjamin Booker
*Lower (surname)
*Lower Township, New Jersey
*Lower Receiver (firearms)
*Lower Wick
Lower Wick is a small hamlet located in the county of Gloucestershire, England. It is sit ...
, Middle
Middle or The Middle may refer to:
* Centre (geometry), the point equally distant from the outer limits.
Places
* Middle (sheading), a subdivision of the Isle of Man
* Middle Bay (disambiguation)
* Middle Brook (disambiguation)
* Middle Creek ...
, Upper)
** Mesolithic
The Mesolithic (Ancient Greek language, Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic i ...
(Epipaleolithic
In archaeology, the Epipalaeolithic or Epipaleolithic (sometimes Epi-paleolithic etc.) is a period occurring between the Upper Paleolithic and Neolithic during the Stone Age. Mesolithic also falls between these two periods, and the two are someti ...
)
** Neolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revo ...
** Chalcolithic
The Chalcolithic ( ) (also called the Copper Age and Eneolithic) was an archaeological period characterized by the increasing use of smelted copper. It followed the Neolithic and preceded the Bronze Age. It occurred at different periods in di ...
(or "Eneolithic", "Copper Age")
* Ancient history
Ancient history is a time period from the History of writing, beginning of writing and recorded human history through late antiquity. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the development of Sumerian language, ...
(The Bronze and Iron Ages are not part of prehistory for all regions and civilizations who had adopted or developed a writing system.)
** Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
** Iron Age
The Iron Age () is the final epoch of the three historical Metal Ages, after the Chalcolithic and Bronze Age. It has also been considered as the final age of the three-age division starting with prehistory (before recorded history) and progre ...
* Late Middle Ages
The late Middle Ages or late medieval period was the Periodization, period of History of Europe, European history lasting from 1300 to 1500 AD. The late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period ( ...
** Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and sur ...
* Early modern history
The early modern period is a historical period that is defined either as part of or as immediately preceding the modern period, with divisions based primarily on the history of Europe and the broader concept of modernity. There is no exact date ...
* Modern history
The modern era or the modern period is considered the current historical period of human history. It was originally applied to the history of Europe and Western history for events that came after the Middle Ages, often from around the year 1500, ...
** Industrial Age
The Industrial Age is a period of history that encompasses the changes in economic and social organization that began around 1760 in Great Britain and later in other countries, characterized chiefly by the replacement of hand tools with power-d ...
(1760–1970)
** Machine Age
The Machine Age is an era that includes the early-to-mid 20th century, sometimes also including the late 19th century. An approximate dating would be about 1880 to 1945. Considered to be at its peak in the time between the first and second wo ...
(1880–1945)
*** Age of Oil (1901–present)
*** Jet Age
The Jet Age is a period in the history of aviation defined by the advent of aircraft powered by jet turbine engines and the social and cultural changes fostered by commercial jet travel.
Jet airliners were able to fly higher, faster, and farth ...
(1940s)
** Nuclear Age
The Atomic Age, also known as the Atomic Era, is the period of history following the detonation of the first nuclear weapon, The Gadget at the ''Trinity'' test in New Mexico on 16 July 1945 during World War II. Although nuclear chain react ...
(a.k.a. Atomic Era) (1945/1950–present)
** Space Age
The Space Age is a period encompassing the activities related to the space race, space exploration, space technology, and the cultural developments influenced by these events, beginning with the launch of Sputnik 1 on October 4, 1957, and co ...
(1957–present)
** Information Age
The Information Age is a historical period that began in the mid-20th century. It is characterized by a rapid shift from traditional industries, as established during the Industrial Revolution, to an economy centered on information technology ...
(1970–present)
*** Internet Age
The Information Age is a historical period that began in the mid-20th century. It is characterized by a rapid shift from traditional industries, as established during the Industrial Revolution, to an economy centered on information technology ...
(1990–present)
*** Intelligence Age
Intelligence has been defined in many ways: the capacity for abstraction, logic, understanding, self-awareness, learning, emotional knowledge, reasoning, planning, creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving. It can be described as the ...
(2024-present)
African periods
Egyptian periods
Prehistoric Egypt
Prehistoric Egypt and Predynastic Egypt was the period of time starting at the first human settlement and ending at the First Dynasty of Egypt around 3100 BC.
At the end of prehistory, "Predynastic Egypt" is traditionally defined as the period ...
(pre-3150 BC)
Dynastic Period
* Early Dynastic Period or Archaic Period (two dynasties) (3150 BC – 2686 BC)
* Old Kingdom
In ancient Egyptian history, the Old Kingdom is the period spanning –2200 BC. It is also known as the "Age of the Pyramids" or the "Age of the Pyramid Builders", as it encompasses the reigns of the great pyramid-builders of the Fourth Dynast ...
(four dynasties) (2686 BC – 2181 BC)
* First Intermediate Period
The First Intermediate Period, described as a 'dark period' in ancient Egyptian history, spanned approximately 125 years, c. 2181–2055 BC, after the end of the Old Kingdom of Egypt, Old Kingdom. It comprises the seventh Dynasty, Seventh (altho ...
(four dynasties) (2181 BC – 2055 BC)
* Middle Kingdom (three dynasties) (2055 BC – 1650 BC)
* Second Intermediate Period
The Second Intermediate Period dates from 1700 to 1550 BC. It marks a period when ancient Egypt was divided into smaller dynasties for a second time, between the end of the Middle Kingdom and the start of the New Kingdom. The concept of a Secon ...
(four dynasties) (1650 BC – 1550 BC)
* New Kingdom
New or NEW may refer to:
Music
* New, singer of K-pop group The Boyz
* ''New'' (album), by Paul McCartney, 2013
** "New" (Paul McCartney song), 2013
* ''New'' (EP), by Regurgitator, 1995
* "New" (Daya song), 2017
* "New" (No Doubt song), 1 ...
(three dynasties) (1550 BC – 1069 BC)
* Third Intermediate Period
The Third Intermediate Period of ancient Egypt began with the death of Pharaoh Ramesses XI in 1077 BC, which ended the New Kingdom, and was eventually followed by the Late Period. Various points are offered as the beginning for the latt ...
(five dynasties) (1069 BC – 664 BC)
Antiquity
* Late Period of Ancient Egypt
The Late Period of ancient Egypt refers to the last flowering of native Egyptian rulers after the Third Intermediate Period in the 26th Saite Dynasty founded by Psamtik I, but includes the time of Achaemenid Persian rule over Egypt after the ...
(six dynasties: of these six, two were Persian dynasties that ruled from capitals distant from Egypt) (664 BC – c. 332 BC)
* Argead and Ptolemaic dynasties (332 BC – 30 BC)
* Aegyptus
In Greek mythology, Aegyptus or Ægyptus (; ) was a legendary king of ancient Egypt. He was a descendant of the princess Io through his father Belus, and of the river-god Nilus as both the father of Achiroe, his mother and as a great, great-g ...
(fifteen Roman dynasties that ruled from capitals distant from Egypt) (30 BC – 641 AD)
** Sasanian Egypt
Sasanian Egypt (known in Middle Persian sources as ''Agiptus'') refers to the brief rule of Egypt and parts of Libya by the Sasanian Empire, following the Sasanian conquest of Egypt. It lasted from 618 to 628, until the Sasanian general Shahrbar ...
(one dynasty) (619–629)
* Coptic period (300 AD – 900 AD)
Islamic Egypt
* Egypt under four foreign Arabic dynasties that ruled from capitals distant from Egypt.
** Rashidun Egypt (641–661)
** Umayyad Egypt (661–750)
** Abbasid Egypt (750–868 and 905–935)
Medieval Egypt
* Tulunid dynasty
The Tulunid State, also known as the Tulunid Emirate or The State of Banu Tulun, and popularly referred to as the Tulunids () was a Mamluk dynasty of Turkic origin who was the first independent dynasty to rule Egypt, as well as much of Syria, s ...
(868–905)
* Ikhshidid dynasty
The Ikhshidid dynasty (, ) was a Turkic dynasty of governors of mamluk origin, who governed Egypt and parts of the Levant from 935 to 969 on behalf of the Abbasid Caliphate. The dynasty carried the Arabic title "Wāli" reflecting their position a ...
(935–969)
* Fatimid Dynasty
The Fatimid dynasty () was an Arab dynasty that ruled the Fatimid Caliphate, between 909 and 1171 CE. Descended from Fatima and Ali, and adhering to Isma'ili Shi'ism, they held the Isma'ili imamate, and were regarded as the rightful leaders o ...
(969–1171)
* Ayyubid Dynasty
The Ayyubid dynasty (), also known as the Ayyubid Sultanate, was the founding dynasty of the medieval Sultan of Egypt, Sultanate of Egypt established by Saladin in 1171, following his abolition of the Fatimid Caliphate, Fatimid Caliphate of Egyp ...
(1171–1250)
* Mamluk dynasties (1250–1517)
** Bahri dynasty
The Bahri Mamluks (), sometimes referred to as the Bahri dynasty, were the rulers of the Mamluk Sultanate of Egypt from 1250 to 1382, following the Ayyubid dynasty. The members of the Mamluk ruling class were purchased as slaves ( mamluks) and ma ...
(1250–1382)
** Burji dynasty
The Burji Mamluks () or Circassian Mamluks (), sometimes referred to as the Burji dynasty, were the rulers of the Mamluk Sultanate of Egypt from 1382 until 1517. As with the preceding Bahri Mamluks, the members of the Burji Mamluk ruling class we ...
(1382–1517)
Modern Egypt
* Ottoman Egypt
Ottoman Egypt was an administrative division of the Ottoman Empire after the conquest of Mamluk Egypt by the Ottomans in 1517. The Ottomans administered Egypt as a province (''eyalet'') of their empire (). It remained formally an Ottoman prov ...
(Turk dynasty that ruled from a capital distant from Egypt) (1517–1867)
* Muhammad Ali dynasty
The Muhammad Ali dynasty or the Alawiyya dynasty was the ruling dynasty of Egypt and Sudan from the 19th to the mid-20th century. It is named after its progenitor, the Albanians, Albanian Muhammad Ali of Egypt, Muhammad Ali, regarded as the fou ...
(1805–1953)
** Khedivate of Egypt
The Khedivate of Egypt ( or , ; ') was an autonomous tributary state of the Ottoman Empire, established and ruled by the Muhammad Ali Dynasty following the defeat and expulsion of Napoleon Bonaparte's forces which brought an end to the short- ...
(1867–1914)
** Sultanate of Egypt
The Sultanate of Egypt () was a British protectorate in Egypt which existed from 1914, after the outbreak of World War I, to 1922, when it ceased to exist as a result of the Unilateral Declaration of Egyptian Independence.
History
Soon afte ...
(1914–1922)
Contemporary Egypt
* Kingdom of Egypt
The Kingdom of Egypt () was the legal form of the Egyptian state during the latter period of the Muhammad Ali dynasty's reign, from the United Kingdom's recognition of Egyptian independence in 1922 until the abolition of the monarchy of Eg ...
(1922–1953)
* Republican Egypt (1953–present)
Libyan periods
Prehistoric Libya * Prehistoric Libya (pre-600 BC) Early Libya * Carthaginian Libya (600 BC – 200 BC) * Roman Libya (200 BC – 487 AD) * Vandal Libya (487 AD – ≈600 AD) * Islamic Libya (≈600 – ≈1200) * Ottoman Libya (≈1600 – ≈1900) Modern Libya * Colonial Libya (≈1900 – ≈1950) * Libya as an independent country ** Early Independent Era **Libyan Arab Republic
Muammar Gaddafi became the '' de facto'' leader of Libya on 1 September 1969 after leading a group of young Libyan Army officers against King Idris I in a bloodless coup d'état. When Idris was in Turkey for medical treatment, the Revolutio ...
(September 1969–1977)
** Great Socialist People's Libyan Arab Jamahiriya
Muammar Gaddafi became the '' de facto'' leader of Libya on 1 September 1969 after leading a group of young Libyan Army officers against King Idris I in a bloodless coup d'état. When Idris was in Turkey for medical treatment, the Revolutio ...
** Contemporary Libya (2011–present)
American (continent) periods
Pre-Columbian America * Classic and Postclassic eras, Central America (200–1519) * Early Intermediate, Middle Horizon, Late Intermediate, Late Horizon (Peru
Peru, officially the Republic of Peru, is a country in western South America. It is bordered in the north by Ecuador and Colombia, in the east by Brazil, in the southeast by Bolivia, in the south by Chile, and in the south and west by the Pac ...
, 200–1534)
** Huari Huari may refer to:
*Huari culture, a historical civilization in Peru
*Huari (archaeological site), an archaeological site in Peru
*Huari, Peru, a town in Peru
* Huari District, a district in the Huari Province, Peru
* Huari Province, a province in ...
, Chimú
Chimor (also Kingdom of Chimor or Chimú Empire) was the political grouping of the Chimú culture (). The culture arose about 900 CE, succeeding the Moche culture, and was later conquered by the Inca emperor Topa Inca Yupanqui around 1470, fi ...
, Chincha, Chanka people
The Chanka (or Chanca) were an ethnic group living in Pre-Columbian South America, whose chiefdom was part of the Chanka "confederation": a loose defensive alliance of various chiefdoms, such as the Vilcas, the Huancas, the Chancas, and the ...
, Tiwanaku
Tiwanaku ( or ) is a Pre-Columbian archaeological site in western Bolivia, near Lake Titicaca, about 70 kilometers from La Paz, and it is one of the largest sites in South America. Surface remains currently cover around 4 square kilometers and in ...
, Inca
The Inca Empire, officially known as the Realm of the Four Parts (, ), was the largest empire in pre-Columbian America. The administrative, political, and military center of the empire was in the city of Cusco. The History of the Incas, Inca ...
Colonial America
* Baroque
The Baroque ( , , ) is a Western Style (visual arts), style of Baroque architecture, architecture, Baroque music, music, Baroque dance, dance, Baroque painting, painting, Baroque sculpture, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished from ...
(New World
The term "New World" is used to describe the majority of lands of Earth's Western Hemisphere, particularly the Americas, and sometimes Oceania."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: ...
, 1600–1750)
* Spanish hegemony (Americas, 1492–1832)
Mexican periods
Ancient and Pre-Columbian Mexico *Olmecs
The Olmecs () or Olmec were an early known major Mesoamerican civilization, flourishing in the modern-day Mexican states of Veracruz and Tabasco from roughly 1200 to 400 Before the Common Era, BCE during Mesoamerica's Mesoamerican chronolog ...
(1500 BC- 400 BC)
* Mayans
Maya () are an ethnolinguistic group of Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Indigenous peoples of Mesoamerica. The ancient Maya civilization was formed by members of this group, and today's Maya are generally descended from people who lived w ...
(3000 BC – 600 AD)
* Teotihuacan
Teotihuacan (; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Teotihuacán'', ; ) is an ancient Mesoamerican city located in a sub-valley of the Valley of Mexico, which is located in the State of Mexico, northeast of modern-day Mexico City.
Teotihuacan is ...
(1 AD - 500 AD)
* Toltecs
The Toltec culture () was a Pre-Columbian era, pre-Columbian Mesoamerican culture that ruled a state centered in Tula (Mesoamerican site), Tula, Hidalgo (state), Hidalgo, Mexico, during the Epiclassic and the early Post-Classic period of Mesoam ...
(800 AD - 1000 AD)
* Aztecs
The Aztecs ( ) were a Mesoamerican civilization that flourished in central Mexico in the post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those groups who spoke the ...
(1000 AD – 1512 AD)
Colonial Mexico
* Spanish Conquest of Mexico
The Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire was a pivotal event in the history of the Americas, marked by the collision of the Aztec Triple Alliance and the Spanish Empire. Taking place between 1519 and 1521, this event saw the Spanish conquistad ...
(1519 – 1521)
*New Spain
New Spain, officially the Viceroyalty of New Spain ( ; Nahuatl: ''Yankwik Kaxtillan Birreiyotl''), originally the Kingdom of New Spain, was an integral territorial entity of the Spanish Empire, established by Habsburg Spain. It was one of several ...
(1535 - 1821)
Independence Era
* Mexican War of Independence
The Mexican War of Independence (, 16 September 1810 – 27 September 1821) was an armed conflict and political process resulting in Mexico's independence from the Spanish Empire. It was not a single, coherent event, but local and regional ...
(1810 - 1821)
* First Mexican Empire
The Mexican Empire (, ) was a constitutional monarchy and the first independent government of Mexico. It was also the only former viceroyalty of the Spanish Empire to establish a monarchy after gaining independence. The empire existed from 18 ...
(1821 -1823)
* First Mexican Republic
The First Mexican Republic, known also as the First Federal Republic (), existed from 1824 to 1835. It was a Federal republic, federated republic, established by the 1824 Constitution of Mexico, Constitution of 1824, the first constitution of ...
(1824 - 1835)
* Centralist Republic of Mexico
The Centralist Republic of Mexico (), or in the anglophone scholarship, the Central Republic, officially the Mexican Republic (), was a unitary political regime established in Mexico on 23 October 1835, under a new constitution known as the () ...
(1835 - 1846)
Liberal Mexico
* Second Federal Republic of Mexico
The Second Federal Republic of Mexico () refers to the period of Mexican history involving a second attempt to establish a federal government in Mexico after the fall of the unitary Centralist Republic of Mexico in 1846 at the start of the Mex ...
(1846 - 1863)
* Second French Mexican Empire (1864 - 1867)
* Restored Republic (1867 - 1876)
* Porfiriato
The Porfiriato or Porfirismo (, ), coined by Mexican historian Daniel Cosío Villegas, is a term given to the period when General Porfirio Díaz ruled Mexico under an Authoritarianism, authoritarian military dictatorship in the late 19th and e ...
(1876 - 1911)
Modern Mexico
* Revolutionary Mexico (1910 - 1917)
* Maximato
The ''Maximato'' was a transitional period in the History of Mexico, historical and political development of Mexico from 1 December 1928 to 1 December 1934. Named after former president Plutarco Elías Calles's sobriquet ''el Jefe Máximo'' (th ...
(1928 - 1934)
* PRI One-Party State (1934 - 2000)
* Contemporary Mexico (2000 - Present)
United States historical periods
Pre-Colonial era *Lithic stage
In the sequence of cultural stages first proposed for the archaeology of the Americas by Gordon Willey and Philip Phillips in 1958, the Lithic stage was the earliest period of human occupation in the Americas, as post-glacial hunter gatherers s ...
* Archaic stage
Several chronologies in the archaeology of the Americas include an Archaic Period or Archaic stage etc. It is often sub-divided, for example into "Early", "Middle" and "Late", or alternatively "Lower" and "Upper", stages. The dates, and the char ...
* Formative stage
Several chronologies in the archaeology of the Americas include a Formative Period or Formative stage etc. It is often sub-divided, for example into "Early", "Middle" and "Late" stages.
The Formative is the third of five stages defined by Gord ...
* Classic stage
In archaeological cultures of North America, the classic stage is the theoretical North and Meso-American societies that existed between AD 500 and 1200. This stage is the fourth of five stages posited by Gordon Willey and Philip Phillips' 195 ...
* Post-Classic stage
In the classification of the archaeology of the Americas, the Post-Classic stage is a term applied to some Pre-Columbian era, pre-Columbian cultures, typically ending with local contact with Europeans. This stage is the fifth of five Archaeology, ...
Thirteen British Colonies (1607–1775)
United Colonies
The United Colonies of North-America was the official name as used by the Second Continental Congress in Philadelphia for the newly formed proto-state comprising the Thirteen Colonies in 1775 and 1776, before and as independence was declared. ...
(1775-1781)
* American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was the armed conflict that comprised the final eight years of the broader American Revolution, in which Am ...
Confederation period
The Confederation period was the era of the United States' history in the 1780s after the American Revolution and prior to the ratification of the United States Constitution. In 1781, the United States ratified the Articles of Confederation and ...
(1781-1789)
First Party System (1789–1824)
* Federalist Era (1789–1800)
* Jeffersonian democracy (1790s–1820s)
* Era of Good Feelings (1817–1825)
Second Party System (1824–1856)
* Jacksonian democracy (1825–1854)
* History of the United States (1849–1865), Civil War Era (1849–1865)
Third Party System (1856–1896)
* History of the United States (1849–1865), Civil War Era (1849–1865)
* Reconstruction era (1865–1877) (Some of this time period is known as the "Old West".)
* Gilded Age (1877–1896)
Fourth Party System (1896–1932)
* Progressive Era (1896–1917)
* United States in World War I (1917–1918)
* Roaring Twenties (1920–1929)
Fifth Party System (1932–1980)
* Great Depression in the United States, Great Depression (1929–1939)
* United States home front during World War II (1942–1945)
* History of the United States (1945–1964), Post-World War II (1945–1964)
* Civil rights movement, Civil Rights Movement (1954–1968)
* United States in the Vietnam War (1955–1973)
Sixth Party System (1980–present)
* Reagan Era (1980–1991)
* History of the United States (1991–2008), Post-Cold War period (1991–2008)
* History of the United States (2008–present), Contemporary United States (2008-present)
Asian periods
Chinese periods
Bronze Age China Archaic China * Shang dynasty (1600–1046 BC) * Zhou dynasty (1046–256 BC) ** Western Zhou (1046–771 BC) ** Eastern Zhou (771–256 BC) *** Spring and Autumn period (771–476 BC) *** Warring States period (476–221 BC) * Qin dynasty (221–206 BC) Antiquity * Han dynasty (206 BC – 220 AD) ** Western Han (206 BC – 2 AD) ** Xin dynasty (9–23 AD) ** Eastern Han (25–220 AD) * Six Dynasties (220–580) ** Three Kingdoms (220–265) ** Jin dynasty (266–420) ** Southern and Northern Dynasties (420–580) Medieval China * Sui dynasty (580–618) * Tang dynasty (623–907) * Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period (907–960) * Song dynasty (960–1279) ** Song dynasty#Northern Song, 960–1127, Northern Song (960–1127), Liao dynasty (907–1115) ** Western Xia dynasty (1038–1227) ** Song dynasty#Southern Song, 1127–1279, Southern Song (1127–1279), Jin dynasty (1115–1234) Mongol China * Yuan dynasty (1271–1368) Late Dynastic Period *Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty, officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 1368 to 1644, following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming was the last imperial dynasty of ...
(1368–1644)
* Qing dynasty (1644–1911)
Modern China
* Republic of China (1912–1949), Republic of China (1912–1949)
** Xinhai Revolution (1911–1912)
** Warlord Era (1918–1927)
Contemporary China
* Chinese Civil War (1927–1936/1946–1950)
* Second Sino-Japanese War (1937–1945)
Post-Contemporary China
* China, People's Republic of China and Taiwan (1949–present)
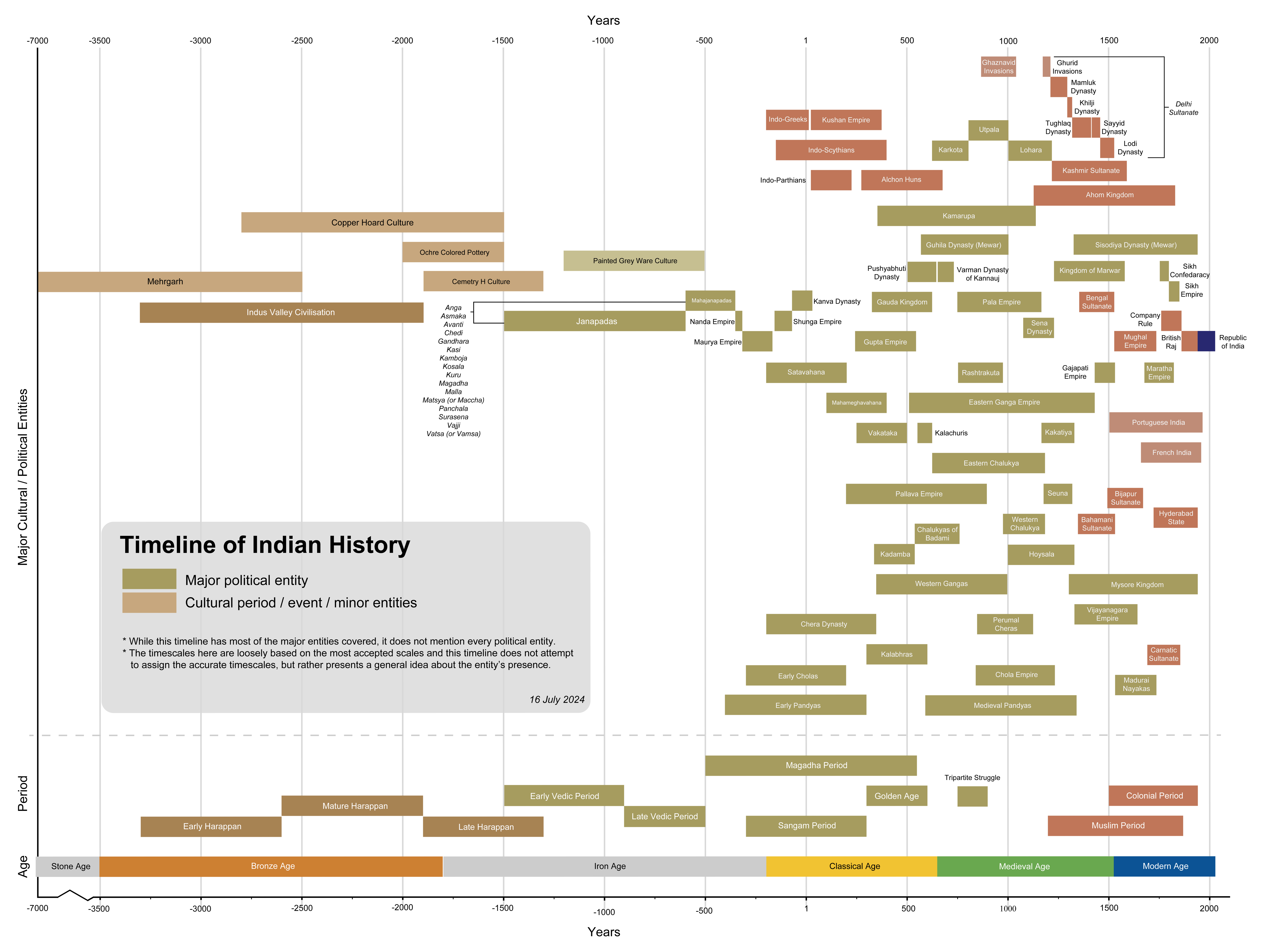
Indian periods
 * South Asian Stone Age
** Periodisation of the Indus Valley Civilisation, Pre-Harappan
*** Mehrgarh
* Bronze Age India (3340 BC – 1350 BC)
** Indus Valley Civilization
*** Early Harappan
*** Periodisation of the Indus Valley Civilisation, Early Mature Harappan
*** Mature Harappan
*** Late Harappan
**** Punjab Phase
**** Jhukar Phase
**** Rangpur Phase
*** Periodisation of the Indus Valley Civilisation, Final Harappan
* Iron Age in India (1350 BC – 200 BC)
** ''Vedic period'' (1350 BC – 500 BC): Mahajanapadas
** ''Magadha period'' (c.500 BC – c.750 AD): Nanda Empire, Nandas, Mauryan empire, Mauryans, Shunga Empire, Shungas
* Classical India (200 BC – 500 AD)
** ''Sangam period'' (300 BC – 600 AD): Chola dynasty, Cholas, Chalukya dynasty, Chalukyas, Pallava dynasty, Pallavas and Pandya dynasty, Pandyans
** ''Golden Age of India, Golden period'': Kushan empire, Kushans (50 AD – 220 AD), Satavahana dynasty, Satavahanas (230 BC – 220 AD), Gupta Empire, Guptas (320 AD – 535 AD) and Vakataka dynasty, Vakatakas (300AD – 650 AD)
* Medieval India, Medieval Age in India (500–1526)
** ''Tripartite struggle, Tripartite period'' (c.750 – c.900): Pala Empire, Palas, Rashtrakuta dynasty, Rashtrakutas and Gurjara-Pratihara dynasty, Gurjaras
** ''Muslim period in the Indian subcontinent, Muslim period'' (712–1857): Delhi Sultanate, Delhi, Bengal Sultanate, Bengal, Bahmani Sultanate, Bahmani and Gujarat Sultanate, Gujarat sultanates
** Vijayanagara Empire (1336–1646), Gajapati Empire (1434–1541) and kingdom of Mewar (1325–1448)
* Modern Age in India (1526 – present)
** Mughal Empire (1526–1857)
** Maratha Empire (1674–1818)
** ''Colonial India, Colonial period'': British Raj (1858 – 1947)
** History of the Republic of India, Independence (1947 – present)
* South Asian Stone Age
** Periodisation of the Indus Valley Civilisation, Pre-Harappan
*** Mehrgarh
* Bronze Age India (3340 BC – 1350 BC)
** Indus Valley Civilization
*** Early Harappan
*** Periodisation of the Indus Valley Civilisation, Early Mature Harappan
*** Mature Harappan
*** Late Harappan
**** Punjab Phase
**** Jhukar Phase
**** Rangpur Phase
*** Periodisation of the Indus Valley Civilisation, Final Harappan
* Iron Age in India (1350 BC – 200 BC)
** ''Vedic period'' (1350 BC – 500 BC): Mahajanapadas
** ''Magadha period'' (c.500 BC – c.750 AD): Nanda Empire, Nandas, Mauryan empire, Mauryans, Shunga Empire, Shungas
* Classical India (200 BC – 500 AD)
** ''Sangam period'' (300 BC – 600 AD): Chola dynasty, Cholas, Chalukya dynasty, Chalukyas, Pallava dynasty, Pallavas and Pandya dynasty, Pandyans
** ''Golden Age of India, Golden period'': Kushan empire, Kushans (50 AD – 220 AD), Satavahana dynasty, Satavahanas (230 BC – 220 AD), Gupta Empire, Guptas (320 AD – 535 AD) and Vakataka dynasty, Vakatakas (300AD – 650 AD)
* Medieval India, Medieval Age in India (500–1526)
** ''Tripartite struggle, Tripartite period'' (c.750 – c.900): Pala Empire, Palas, Rashtrakuta dynasty, Rashtrakutas and Gurjara-Pratihara dynasty, Gurjaras
** ''Muslim period in the Indian subcontinent, Muslim period'' (712–1857): Delhi Sultanate, Delhi, Bengal Sultanate, Bengal, Bahmani Sultanate, Bahmani and Gujarat Sultanate, Gujarat sultanates
** Vijayanagara Empire (1336–1646), Gajapati Empire (1434–1541) and kingdom of Mewar (1325–1448)
* Modern Age in India (1526 – present)
** Mughal Empire (1526–1857)
** Maratha Empire (1674–1818)
** ''Colonial India, Colonial period'': British Raj (1858 – 1947)
** History of the Republic of India, Independence (1947 – present)
Iranian periods
Prehistory of Iran, Prehistoric Iran Ancient age: *Medes (1000 -550 BC) * Achaemenid Empire (550 –330 BC) * Wars of Alexander the Great, Greek occupation of Persia (330 –312 BC): * Seleucid Empire (312 – 63 BC) * Parthian Empire (247 BC – 224 AD) * Sassanid Empire (224 – 651 AD) Medieval age: * Muslim conquest of Persia, Persia under Caliphates (651 – 820 AD) * Iranian Intermezzo (c.820 – 1037): Tahirid dynasty, Tahirids (821 to 873), Saffarid dynasty, Saffarids (861 to 1003), Samanid Empire, Samanids (819 to 999) and Buyid dynasty, Buyids (934 to 1062) * Seljuk Empire (1037–1194) * Khwarazmian Empire (1194–1219) * Mongol invasion of Persia, Mongol occupation of Persia (1219 –1256) * Ilkhanate (1256–1335) * Disintegration of the Ilkhanate (1335–1370): Jalayirid Sultanate, Jalayirids, Chobanids, Muzaffarids (Iran), Muzaffarids, Injuids, Sarbadars, and Kart dynasty, Kartids * Timurid Empire (1370–1507) and Aq Qoyunlu (1378–1501) Modern age: * Safavid Iran (1501–1736) * Afsharid Iran (1736 –c.1750) * Zand dynasty, Zand Iran (1750–1794) * Qajar Iran (1794–1925) * Pahlavi Iran (1925–1979) * Iran, Islamic Republic of Iran (1979–present)Japanese periods
Archaic Japan * Jōmon period (10,501 BC – 400 BC) * Yayoi period (450 BC – 250 AD) * Kofun period (250–600) Feudal Japan * Asuka period (643–710) * Nara period (743–794) * Heian period (795–1185) * Kamakura period (1185–1333) Samurai Japan * Muromachi period (1333–1573) * Azuchi–Momoyama period (1573–1603) Modern Japan * Edo period (1603–1868) * Meiji period (1868–1912) * Taishō period (1912–1926) Contemporary Japan * Shōwa period (1926–1989) ** Post-occupation Japan, Post-occupation era (1952 – present) * Heisei period (1989–2019) * Reiwa period (2019–present)Mesopotamian periods
Archaic Period * Mesopotamia ** Samarra culture ** Hassuna culture ** Halaf-Ubaid Transitional period ** Ubaid period ** Uruk period ** Jemdet Nasr period (3100 BC – 2900 BC) ** Early Dynastic Period (Mesopotamia), Early Dynastic Period (2900 BC – 2270 BC) ** Akkadian Empire (2270 BC – 2083 BC) ** Gutian dynasty of Sumer, Gutian dynasty (2083 BC – 2050 BC) ** Third Dynasty of Ur, Ur III period (2050 BC – 1940 BC) ** First Babylonian dynasty (1830 BC – 1531 BC), Hittites (1800 BC – 1178 BC) ** Kassites (1531 BC – 1135 BC), Mitanni (1500 BC – 1300 BC) ** Neo-Assyrian Empire (934 BC – 609 BC) ** Neo-Babylonian Empire (626 BC – 539 BC), Medes (678 BC – 549 BC) Imperial Period * Persian Empires (550 BC – 651 AD) ** Achaemenid Empire (550 BC – 330 BC) ** Conquered by Macedonia (ancient kingdom)#Empire, Macedonian Empire (330 BC – 312 BC) ** Seleucid Empire (312 BC – 63 BC) ** Parthian Empire (247 BC – 224 AD) **Sasanian Empire
The Sasanian Empire (), officially Eranshahr ( , "Empire of the Iranian peoples, Iranians"), was an List of monarchs of Iran, Iranian empire that was founded and ruled by the House of Sasan from 224 to 651. Enduring for over four centuries, th ...
(224 AD – 651 AD)
Islamic Period
* Islamicate periodsThe Venture of Islam, Volume 2: The Expansion of Islam in the Middle Periods
' (1974), p. 3. (7th – 21st centuries) ** ''High Caliphate'' (685–945) ** ''Earlier Middle Period'' (945–1250) ** ''Later Middle Period'' (1250–1500) ** Rashidun Caliphate (632–661) ** Umayyad Caliphate (661–750) ** Abbasid Caliphate (750–1258), Fatimid Caliphate (909–1171) *** Buyid dynasty (934–1055) *** Seljuq dynasty (1055–1171) *** Ayyubid dynasty (1171–1341) ** Ottoman Empire (1300–1923) *** Safavid dynasty, Safavid Empire (1501–1736) ** Mandatory Iraq, Kingdom of Iraq under British mandate (1921-1932) ** Hashemite Kingdom of Iraq (1932-1958) *** Hashemite Arab Federation (1958) ** First Iraqi Republic, Qasimist Republic of Iraq (1958-68) ** Ba'athist Iraq (1968-2003) ** Coalition Provisional Authority (2003-04) ** Republic of Iraq (2004-present)
Mongolian periods
Antiquity * Xiongnu (Mongolia, 220 BC – AD 200) Medieval Mongolia * Rouran Khaganate (Mongolia, Manchuria, Xianbei, AD 330 – 555) ** Sixteen Kingdoms (Xianbei, Turkic peoples, 304–439) * Uyghur Khaganate (Mongolia, Manchuria, Tibet, 744–848) * Liao dynasty (Khitan people, 907–1125) Imperial Mongolia * Mongol Empire (Mongolia, 1206–1380) ** Yuan Dynasty of China (≈1250 – ≈1350) ** Golden Horde (≈1250 – 1380) Modern Mongolia * Qing dynasty (Manchu China, 1692–1911)Southeast Asian periods
Maritime Southeast Asia * Srivijaya (Indonesia, 3rd – 14th centuries), Tarumanagara (358–723), Sailendra (8th and 9th centuries), Sunda Kingdom, Kingdom of Sunda (669–1579), Mataram Kingdom, Kingdom of Mataram (752–1045), Kediri (historical kingdom), Kediri (1045–1221), Singhasari (1222–1292), Majapahit (1293–1500) Peninsular Southeast Asia * Chenla (Cambodia, 630 – 802) and Khmer Empire (Cambodia, 802–1432) * Lý Nam Đế, Anterior Lý dynasty and Triệu Việt Vương, Third Chinese domination (History of Vietnam), Third Chinese domination, Khúc Family, Dương Đình Nghệ, Kiều Công Tiễn, Ngô dynasty, The 12 Lords Rebellion, Đinh dynasty, Anterior Lê dynasty, Prior Lê dynasty, Lý dynasty, Trần dynasty, Hồ dynasty, Fourth Chinese domination (History of Vietnam), Fourth Chinese domination (Vietnam, 544–1427)European periods
* Bronze Age Europe (c. 3000 BC – c. 1050 BC) ** Aegean Civilization (Crete, Greece and Near East; c. 3000 BC – c. 1050 BC)The area had settlements as far back as 9000 BC; see Timeline of ancient Greece * Iron Age Europe (c. 1050 BC – c. 500 AD) ** Early Iron Age (c. 1050 BC – 776 BC) – part of the Greek Dark Ages **Classical antiquity
Classical antiquity, also known as the classical era, classical period, classical age, or simply antiquity, is the period of cultural History of Europe, European history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD comprising the inter ...
(776 BC – 476 AD)
*** Archaic Greece (776 BC – 480 BC) – begins with the First Olympiad, traditionally dated 776 BC
*** Classical Greece (480 BC – 338 BC)
*** Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedonian era (338 BC – 323 BC)
*** Hellenistic Greece (323 BC – 146 BC)
*** Roman Republic#Late Republic, Late Roman Republic (147 BC – 27 BC)
*** Principate, Principate of the Roman Empire (27 BC – 284 AD)
*** Late Antiquity (284 AD – 500 AD)
** Migration Period (Europe, 300 AD – 700 AD)
* Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
(Europe, 476–1453)
** Byzantine Empire, Byzantine era (330–1453)
** Early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages (historiography), Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th to the 10th century. They marked the start o ...
(Europe, 476–1066)
*** Viking Age (Scandinavia, Europe, 793–1066)
** High Middle Ages
The High Middle Ages, or High Medieval Period, was the periodization, period of European history between and ; it was preceded by the Early Middle Ages and followed by the Late Middle Ages, which ended according to historiographical convention ...
(Europe, 1066 – c. 1300)
** Late Middle Ages
The late Middle Ages or late medieval period was the Periodization, period of History of Europe, European history lasting from 1300 to 1500 AD. The late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period ( ...
(Europe, c. 1300 – 1453)
** The Renaissance (Europe, c. 1300 – c. 1601)
* Early modern Europe, Early modern period (Europe, 1453–1789)
** Age of Discovery
The Age of Discovery (), also known as the Age of Exploration, was part of the early modern period and overlapped with the Age of Sail. It was a period from approximately the 15th to the 17th century, during which Seamanship, seafarers fro ...
(or Exploration) (Europe, c. 1400 – 1770)
** Polish Golden Age (Poland, 1507–1572)
** Golden Age of Piracy (1650–1730)
** Tudor period (England, 1485–1603)
*** Elizabethan era (England, 1558–1603)
** Stuart period (British Isles, 1603–1714)
*** Jacobean era (British Isles, 1603–1625)
*** Caroline era (British Isles, 1625–1649)
*** British Interregnum (British Isles, 1649–1660)
*** Stuart Restoration (British Isles, 1660–1714)
**** Carolean era (British Isles, 1660–1685)
** Protestant Reformation (Europe, 16th century)
** Classicism (Europe, 16th – 18th centuries)
** Industrious Revolution, (Europe, 16th – 18th centuries)
** Peter the Great, Petrine Era (Russia, 1689–1725)
** Age of Enlightenment (or Reason) (Europe, 18th century)
** Scientific Revolution (Europe, 18th century)
* Long nineteenth century (1789–1914)
** Georgian era (the United Kingdom, 1714–1830)
** Industrial Revolution (Europe, United States, and elsewhere 18th and 19th centuries, though with its beginnings in Britain)
** Age of European colonialism and imperialism
** Romanticism, Romantic era (1770–1850)
** Napoleonic era (1799–1815)
** Victorian era (the United Kingdom, 1837–1901); British Empire, British hegemony (1815–1914) much of world, around the same time period.
** Belle Époque (Europe, primarily France, 1871–1914)
** Edwardian era (the United Kingdom, 1901–1914)
* World War I, First, interwar period and World War II, Second World Wars (1914–1945)
** Interwar Britain (United Kingdom, 1918–1939)
* Cold War (1945–1991)
* Post–Cold War era, Post-Cold War (1991–present)
Oceanian periods
Australian periods
* Prehistory of Australia, Ancient Australia, History of Indigenous Australians (between 65,000 and 50,000 BC – 1788 AD) *Age of Discovery
The Age of Discovery (), also known as the Age of Exploration, was part of the early modern period and overlapped with the Age of Sail. It was a period from approximately the 15th to the 17th century, during which Seamanship, seafarers fro ...
, European maritime exploration of Australia (1606–1802)
* Convicts in Australia, Convict era (1788–1868)
* Victorian era (1837–1901)
* Federation of Australia, Federation era (1890–1918)
* Military history of Australia during World War II, World War II (1939–1945)
* Second Elizabethan era (1952–2022)
See also
* Geologic time scale * List of fossil sites with link directory. * List of timelines around the world. * Orders of magnitude (time) * Periodization for a discussion of the tendency to try to fit history into non-overlapping periods. * Time ** Planck TimeReferences
Citations
Sources cited
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Time periods, List of Wikipedia timelines History-related lists