Thunderstorm Training on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
MCS Movement and Behavior
by Stephen Corfidi
by Mike Evan Precipitation Weather hazards Mesoscale meteorology Severe weather and convection fr:Orage#Orages en V ou en série
 In
In meteorology
Meteorology is the scientific study of the Earth's atmosphere and short-term atmospheric phenomena (i.e. weather), with a focus on weather forecasting. It has applications in the military, aviation, energy production, transport, agricultur ...
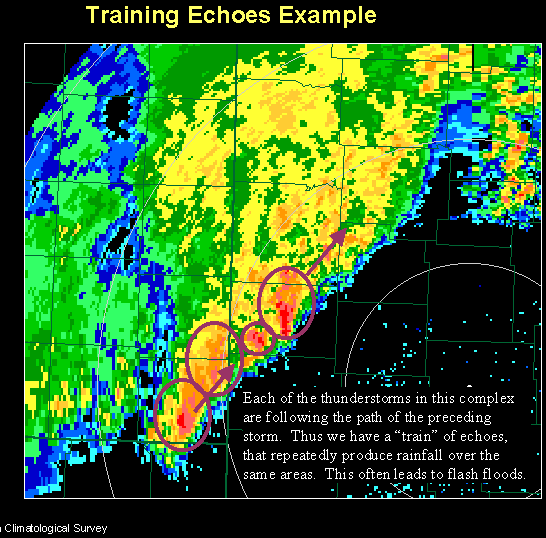
, training denotes repeated areas of rain
Rain is a form of precipitation where water drop (liquid), droplets that have condensation, condensed from Water vapor#In Earth's atmosphere, atmospheric water vapor fall under gravity. Rain is a major component of the water cycle and is res ...
, typically associated with thunderstorm
A thunderstorm, also known as an electrical storm or a lightning storm, is a storm characterized by the presence of lightning and its acoustics, acoustic effect on the Earth's atmosphere, known as thunder. Relatively weak thunderstorm ...
s, that move over the same region in a relatively short period. Training thunderstorms are capable of producing excessive rain
Rain is a form of precipitation where water drop (liquid), droplets that have condensation, condensed from Water vapor#In Earth's atmosphere, atmospheric water vapor fall under gravity. Rain is a major component of the water cycle and is res ...
fall totals, often causing flash flooding. The name ''training'' is derived from how a train
A train (from Old French , from Latin">-4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to talk of the beginnings of French, that is, when it wa ... , from Latin , "to pull, to draw") is a series of connected vehicles th ...
and its cars
A car, or an automobile, is a motor vehicle with wheels. Most definitions of cars state that they run primarily on roads, seat one to eight people, have four wheels, and mainly transport people rather than cargo. There are around one billio ...
travel along a track (moving along a single path), without the track moving.
Formation
Showers and thunderstorms along thunderstorm trains usually develop in one area of stationary instability, and are advanced along a single path by prevailing winds. Additional showers and storms can also develop when the gust front from a storm collides with warmer air outside of the storm. The exact process repeats in the new storms until overall conditions in the surrounding atmosphere become too stable to support thunderstorm activity. Showers and storms can also develop along stationary fronts, and winds move them down the front. The showers that often accompany thunderstorms are usually thunderstorms that are not entirely developed.Hazards
A series of storms continually moving over the same area, dumping heavy rains, can cause flash flooding. Each storm usually produces heavy rain, and after a significant amount of rain falls from the storms which have moved over the same area, flooding occurs.Thunderstorm training
''Thunderstorm training'' is used to refer specifically to training occurring with thunderstorms. It forms when storms tend to back build. This type of training can quickly causeflash flood
A flash flood is a rapid flooding of low-lying areas: washes, rivers, dry lakes and depressions. It may be caused by heavy rain associated with a severe thunderstorm, hurricane, or tropical storm, or by meltwater from ice and snow. Flash f ...
ing, especially if the thunderstorms are strong.
References
{{ReflistExternal links
MCS Movement and Behavior
by Stephen Corfidi
by Mike Evan Precipitation Weather hazards Mesoscale meteorology Severe weather and convection fr:Orage#Orages en V ou en série