Tevenvirinae on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Tevenvirinae'' is a subfamily of
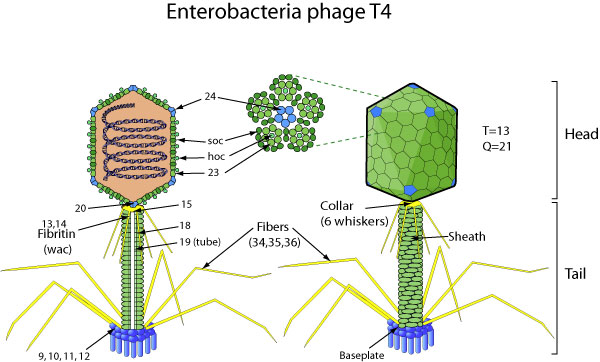 Viruses in ''Tevenvirinae'' are non-enveloped, with head-tail geometries. These viruses are about 70 nm wide and 140 nm long. Genomes are linear, around 170-245kb in length. The genome codes for 300 to 415 proteins.
Viruses in ''Tevenvirinae'' are non-enveloped, with head-tail geometries. These viruses are about 70 nm wide and 140 nm long. Genomes are linear, around 170-245kb in length. The genome codes for 300 to 415 proteins.
Viralzone: Tevenvirinae
ICTV
{{Use dmy dates, date=April 2017 Myoviridae Virus subfamilies
viruses
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Viruses are found in almo ...
in the family ''Straboviridae
''Straboviridae'' is a family of viruses in the order '' Pantevenvirales'', class ''Caudoviricetes''. The viruses in this family were formerly place in the morphology-based family '' Myoviridae'', which was found to be paraphyletic in genome stud ...
'' of class ''Caudoviricetes
''Caudoviricetes'' is a class of viruses known as tailed viruses and head-tail viruses (''cauda'' is Latin for "tail"). It is the sole representative of its own phylum, ''Uroviricota'' (from ''ouros'' (ουρος), a Greek word for "tailed" + ...
''. The subfamily was previously placed in the morphology-based family ''Myoviridae
''Myoviridae'' was a family of bacteriophages in the order '' Caudovirales''. The family ''Myoviridae'' and order '' Caudovirales'' have now been abolished, with the term myovirus now used to refer to the morphology of viruses in this former famil ...
'', which was found to be paraphyletic
Paraphyly is a taxonomic term describing a grouping that consists of the grouping's last common ancestor and some but not all of its descendant lineages. The grouping is said to be paraphyletic ''with respect to'' the excluded subgroups. In co ...
in genome
A genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as ...
studies and abolished in the 2021 International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses
The International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) authorizes and organizes the taxonomic classification of and the nomenclature for viruses. The ICTV develops a universal taxonomic scheme for viruses, and thus has the means to appropri ...
(ICTV) classification. Bacteria and archaea
Archaea ( ) is a Domain (biology), domain of organisms. Traditionally, Archaea only included its Prokaryote, prokaryotic members, but this has since been found to be paraphyletic, as eukaryotes are known to have evolved from archaea. Even thou ...
serve as natural hosts. The subfamily contains 15 genera.
Taxonomy
The following genera are recognized: * '' Centumtrigintavirus'' * '' Dhakavirus'' * '' Gaprivervirus'' * '' Gelderlandvirus'' * '' Jiaodavirus'' * '' Kagamiyamavirus'' * '' Kanagawavirus'' * '' Karamvirus'' * '' Moonvirus'' * '' Mosigvirus'' * '' Mosugukvirus'' * '' Risoevirus'' * '' Tegunavirus'' * ''Tequatrovirus
''Tequatrovirus'' is a genus of viruses in subfamily ''Tevenvirinae'' of family ''Straboviridae''. Gram-negative bacteria serve as the natural host, with transmission achieved through passive diffusion. There are 82 species in this genus.
Taxon ...
''
* '' Winklervirus''
Structure
 Viruses in ''Tevenvirinae'' are non-enveloped, with head-tail geometries. These viruses are about 70 nm wide and 140 nm long. Genomes are linear, around 170-245kb in length. The genome codes for 300 to 415 proteins.
Viruses in ''Tevenvirinae'' are non-enveloped, with head-tail geometries. These viruses are about 70 nm wide and 140 nm long. Genomes are linear, around 170-245kb in length. The genome codes for 300 to 415 proteins.
Life cycle
Viral replication is cytoplasmic. Entry into the host cell is achieved by adsorption into the host cell. DNA-templated transcription is the method of transcription. The virus exits the host cell by lysis, and holin/endolysin/spanin proteins. Bacteria and archaea serve as the natural host. Transmission routes are passive diffusion.References
External links
Viralzone: Tevenvirinae
ICTV
{{Use dmy dates, date=April 2017 Myoviridae Virus subfamilies