Terço on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A ''tercio'' (), Spanish for " third") was a military unit of the
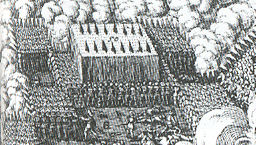 Although other powers adopted the battle formations and tactics perfected by the ''tercios'', their armies fell short of the fearsome reputation of the Spanish army, which possessed a core of experienced professional soldiers. This army was further supplemented by "an army of different nations", a reference to the varied origins of the troops from the
Although other powers adopted the battle formations and tactics perfected by the ''tercios'', their armies fell short of the fearsome reputation of the Spanish army, which possessed a core of experienced professional soldiers. This army was further supplemented by "an army of different nations", a reference to the varied origins of the troops from the
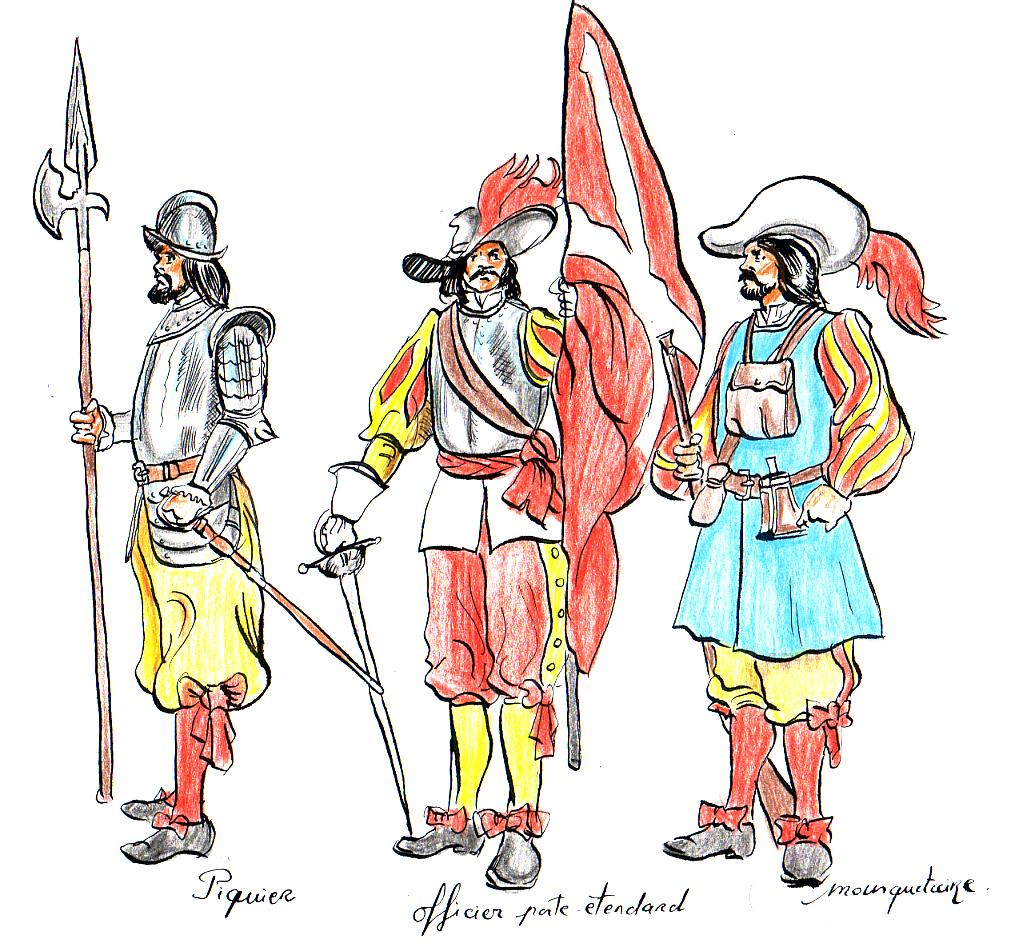 Similar to military organization today, a ''tercio'' was led by a ''maestre de campo'' (commanding officer) appointed by the king, with a guard of eight halberdiers. Assisting the maestre was the
Similar to military organization today, a ''tercio'' was led by a ''maestre de campo'' (commanding officer) appointed by the king, with a guard of eight halberdiers. Assisting the maestre was the
 Within a ''tercio''
Within a ''tercio'' Groups of squares were typically arrayed in dragon-toothed formation, staggered, with the leading edge of one unit level with the trailing edge of the preceding, similar to hedgehog defence. This enabled
Groups of squares were typically arrayed in dragon-toothed formation, staggered, with the leading edge of one unit level with the trailing edge of the preceding, similar to hedgehog defence. This enabled
File:Cross of Burgundy (Template).svg, The
Spanish Tercio Tactics
(myArmoury.com article)
Spanish web site
вҖ“ Honors Alonso '' Pita da Veiga'' the most heroic Spaniard at the
Non-Official Web siteof the Modern "Spanish Marines" (in existence since 1537 few years after ''
The Spanish Army of the Thirty YearsвҖҷ WarList of Tercios
* Lorraine White вҖ
The Experience of SpainвҖҷs Early Modern Soldiers: Combat, Welfare and Violence
* Pierre de Bourdeille, ''Gentilezas y bravuconadas de los espaГұoles'' (r/p Mosand, Madrid, 1996) * Marcos de Isaba, ''Cuerpo enfermo de la milicia espaГұola'' Ministry of Defence, Madrid (Brussels, 1589) * Sancho de LondoГұo, ''El discurso sobre la forma de reducir la disciplina militar a mejor y antiguo estado'' Ministry of Defence, Madrid (Brussels, 1589) * Bernardino de Escalante, ''DiГЎlogos del arte militar'' Ministry of Defence, Madrid (1583) * MartГӯn de Eguiluz, Milicia, ''Discurso y Regla militar'' Ministry of Defence, Madrid (pre-1591) * Diego de Salazar, ''Tratado de Re Militari'' Ministry of Defence, Madrid(1590) * SerafГӯn MarГӯa de Soto, ''Conde de Clonard, Album de la infanterГӯa espaГұola'' (1861) * Rene Quatrefages, ''Los Tercios'' (Madrid, ediciones EjГ©rcito, 1983) * InspecciГіn de InfanterГӯa, ''La infanterГӯa en torno al siglo del oro'' (Madrid, ediciones EjГ©rcito, 1993) * Julio Albi de la Cuesta, ''De Pavia a Rocroi: los Tercios de InfanterГӯa espaГұola en los siglos XVI y XVII'' (Madrid, Balkan, 1999) * Enrique MartГӯnez Ruiz, ''Los soldados del Rey'' (Madrid, Actas, 2008) * Pierre Picouet, ''Les Tercios Espagnols 1600вҖ“1660'' (in French вҖ“ Auzielle, LRT, 2010) {{Spanish Empire Infantry units and formations Military units and formations of the early modern period Military units and formations of Spain Military strategy Military tactics Spanish Empire House of Habsburg Military units and formations of the Italian Wars Spanish inventions
Spanish Army
The Spanish Army () is the terrestrial army of the Spanish Armed Forces responsible for land-based military operations. It is one of the oldest Standing army, active armies вҖ“ dating back to the late 15th century.
The Spanish Army has existed ...
during the reign of the Catholic Monarchs of Spain
The Catholic Monarchs were Queen Isabella I of Castile () and King Ferdinand II of Aragon (), whose marriage and joint rule marked the '' de facto'' unification of Spain. They were both from the House of TrastГЎmara and were second cousins, ...
and Habsburg Spain
Habsburg Spain refers to Spain and the Hispanic Monarchy (political entity), Hispanic Monarchy, also known as the Rex Catholicissimus, Catholic Monarchy, in the period from 1516 to 1700 when it was ruled by kings from the House of Habsburg. In t ...
in the early modern period
The early modern period is a Periodization, historical period that is defined either as part of or as immediately preceding the modern period, with divisions based primarily on the history of Europe and the broader concept of modernity. There i ...
. They were the elite military units of the Spanish monarchy
The monarchy of Spain or Spanish monarchy () is the constitutional form of government of Spain. It consists of a hereditary monarch who reigns as the head of state, being the highest office of the country.
The Spanish monarchy is constitu ...
and essential pieces of the powerful land forces of the Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire, sometimes referred to as the Hispanic Monarchy (political entity), Hispanic Monarchy or the Catholic Monarchy, was a colonial empire that existed between 1492 and 1976. In conjunction with the Portuguese Empire, it ushered ...
, sometimes also fighting along with the navy
A navy, naval force, military maritime fleet, war navy, or maritime force is the military branch, branch of a nation's armed forces principally designated for naval warfare, naval and amphibious warfare; namely, lake-borne, riverine, littoral z ...
.
The Spanish ''tercios'' were one of the finest professional infantries in the world due to the effectiveness of their battlefield formations and were a crucial step in the formation of modern European armies, made up of professional volunteers, instead of levies raised for a campaign or hired mercenaries
A mercenary is a private individual who joins an War, armed conflict for personal profit, is otherwise an outsider to the conflict, and is not a member of any other official military. Mercenaries fight for money or other forms of payment rath ...
typically used by other European countries of the time.
The internal administrative organization of the ''tercios'' and their battlefield formations and tactics grew out of the innovations of Gonzalo FernГЎndez de CГіrdoba
Gonzalo FernГЎndez de CГіrdoba (1 September 1453 вҖ“ 2 December 1515) was a Spanish general and statesman. He led military campaigns during the Conquest of Granada and the Italian Wars, after which he served as Viceroy of Naples. For his e ...
during the conquest of Granada
The Granada War was a series of military campaigns between 1482 and 1492 during the reign of the Catholic Monarchs, Isabella I of Castile and Ferdinand II of Aragon, against the Nasrid dynasty's Emirate of Granada. It ended with the defeat of G ...
and the Italian Wars
The Italian Wars were a series of conflicts fought between 1494 and 1559, mostly in the Italian Peninsula, but later expanding into Flanders, the Rhineland and Mediterranean Sea. The primary belligerents were the House of Valois, Valois kings o ...
in the 1490s and 1500s, being among the first to effectively mix pikes and firearms (arquebus
An arquebus ( ) is a form of long gun that appeared in Europe and the Ottoman Empire during the 15th century. An infantryman armed with an arquebus is called an arquebusier.
The term ''arquebus'' was applied to many different forms of firearms ...
es). The ''tercios'' marked a rebirth of the use of infantry
Infantry, or infantryman are a type of soldier who specialize in ground combat, typically fighting dismounted. Historically the term was used to describe foot soldiers, i.e. those who march and fight on foot. In modern usage, the term broadl ...
forces comparable to the Macedonian phalanx
The Macedonian phalanx () was an infantry formation developed by Philip II from the classical Greek phalanx, of which the main innovation was the use of the sarissa, a 6-metre pike. It was famously commanded by Philip's son Alexander the Grea ...
es and the Roman legions
The Roman legion (, ) was the largest military unit of the Roman army, composed of Roman citizens serving as legionaries. During the Roman Republic the manipular legion comprised 4,200 infantry and 300 cavalry. After the Marian reforms in 1 ...
. Such formations distinguished themselves in famous battles such as the Battle of Bicocca
The Battle of Bicocca or La Bicocca () was fought on 27 April 1522, during the Italian War of 1521вҖ“26. A combined French and Venetian force under Odet de Foix, Vicomte de Lautrec, was decisively defeated by an ImperialвҖ“ Spanish and ...
(1522) and the Battle of Pavia
The Battle of Pavia, fought on the morning of 24 February 1525, was the decisive engagement of the Italian War of 1521вҖ“1526 between the Kingdom of France and the Habsburg Empire of Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor, Charles V, Holy Roman Empero ...
(1525). Following their formal establishment in 1534, the reputation of the ''tercio'' was built upon their effective training and high proportion of "old soldiers" (''veteranos''), in conjunction with the particular elan imparted by the lower nobility
The minor or petty nobility is the lower nobility classes.
Finland
Petty nobility in Finland is dated at least back to the 13th century and was formed by nobles around their strategic interests. The idea was more capable peasants with leader role ...
who commanded them. The ''tercios'' were finally replaced by other regiments in the early eighteenth century.
From 1920, the name of ''tercio'' was given to the formations of the newly created Spanish Legion
For centuries, Spain recruited foreign soldiers to its army, forming the foreign regiments () such as the Regiment of Hibernia (formed in 1709 from Irishmen who fled their own country in the wake of the Flight of the Earls and the Penal la ...
, professional units then created to fight colonial wars in North Africa
North Africa (sometimes Northern Africa) is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region. However, it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of t ...
, similar to the French Foreign Legion
The French Foreign Legion (, also known simply as , "the Legion") is a corps of the French Army created to allow List of militaries that recruit foreigners, foreign nationals into French service. The Legion was founded in 1831 and today consis ...
. These formations were actually regiment
A regiment is a military unit. Its role and size varies markedly, depending on the country, military service, service, or administrative corps, specialisation.
In Middle Ages, Medieval Europe, the term "regiment" denoted any large body of l ...
s bearing the name of ''tercio'' as an honorary title.
History
During theGranada War
The Granada War was a series of military campaigns between 1482 and 1492 during the reign of the Catholic Monarchs, Isabella I of Castile and Ferdinand II of Aragon, against the Nasrid dynasty's Emirate of Granada. It ended with the defeat o ...
(1482вҖ“1491), the soldiers of the Catholic Monarchs of Spain
The Catholic Monarchs were Queen Isabella I of Castile () and King Ferdinand II of Aragon (), whose marriage and joint rule marked the '' de facto'' unification of Spain. They were both from the House of TrastГЎmara and were second cousins, ...
were divided into three classes: pikemen
A pike is a long thrusting spear formerly used in European warfare from the Late Middle Ages and most of the early modern period, and wielded by foot soldiers deployed in pike square formation, until it was largely replaced by bayonet-equipped ...
(modelled after the Swiss
Swiss most commonly refers to:
* the adjectival form of Switzerland
* Swiss people
Swiss may also refer to: Places
* Swiss, Missouri
* Swiss, North Carolina
* Swiss, West Virginia
* Swiss, Wisconsin
Other uses
* Swiss CafГ©, an old cafГ© located ...
), sword
A sword is an edged and bladed weapons, edged, bladed weapon intended for manual cutting or thrusting. Its blade, longer than a knife or dagger, is attached to a hilt and can be straight or curved. A thrusting sword tends to have a straighter ...
smen with shield
A shield is a piece of personal armour held in the hand, which may or may not be strapped to the wrist or forearm. Shields are used to intercept specific attacks, whether from close-ranged weaponry like spears or long ranged projectiles suc ...
s, and crossbow
A crossbow is a ranged weapon using an Elasticity (physics), elastic launching device consisting of a Bow and arrow, bow-like assembly called a ''prod'', mounted horizontally on a main frame called a ''tiller'', which is hand-held in a similar f ...
men supplemented with an early firearm
A firearm is any type of gun that uses an explosive charge and is designed to be readily carried and operated by an individual. The term is legally defined further in different countries (see legal definitions).
The first firearms originate ...
, the arquebus
An arquebus ( ) is a form of long gun that appeared in Europe and the Ottoman Empire during the 15th century. An infantryman armed with an arquebus is called an arquebusier.
The term ''arquebus'' was applied to many different forms of firearms ...
. As shields disappeared and firearms replaced crossbows, Spain won victory after victory in Italy against powerful French armies, starting under the leadership of Gonzalo FernГЎndez de CГіrdoba
Gonzalo FernГЎndez de CГіrdoba (1 September 1453 вҖ“ 2 December 1515) was a Spanish general and statesman. He led military campaigns during the Conquest of Granada and the Italian Wars, after which he served as Viceroy of Naples. For his e ...
(1453вҖ“1515), nicknamed ''El Gran CapitГЎn'' (''The Great Captain''). The military organizational and tactical changes made by CГіrdoba to the armies of Spanish monarchs are seen as the precursors of the tercios and their methods of warfare. The combat effectiveness of the Spanish pike and shot
Pike and shot was a historical infantry tactical formation that first appeared during the late 15th and early 16th centuries, and was used until the development of the bayonet in the late 17th century. This type of formation combined soldiers ...
armies pioneered by CГіrdoba was based on an armament system that effectively united the pike with the compact firepower of the arquebus. An advantage of the Spanish pike and shot formation over its inspiration, the Swiss compact frame, was its ability to divide into mobile units and even individual melee units without the loss of cohesion.
Initially, the term ''tercio'' denoted not a combat unit, but an administrative unit under a general staff, commanding garrisons throughout Italy for battles on various distant fronts. This peculiar character was maintained when it mobilized to fight the Protestant rebels in Flanders. Command of a tercio and its companies of soldiers was granted directly by the king, and companies could easily be added or removed and moved between tercios. By the middle of the 17th century, the tercios began to be raised by nobles at their own expense, patrons who appointed the captains and were effective owners of the units, as in other contemporaneous European armies.
From the conquest of Granada in 1492 to the campaigns of ''El Gran CapitГЎn'' in the kingdom of Naples
Naples ( ; ; ) is the Regions of Italy, regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 908,082 within the city's administrative limits as of 2025, while its Metropolitan City of N ...
in 1495, three ordinances laid the foundations of Spanish military administration. In 1503, the ''Great Ordinance'' reflected the adoption of the long pike and the distribution of infantry in specialized companies. In 1534, the first official ''tercio'' was created, that of Lombardy
The Lombardy Region (; ) is an administrative regions of Italy, region of Italy that covers ; it is located in northern Italy and has a population of about 10 million people, constituting more than one-sixth of Italy's population. Lombardy is ...
, and a year later it helped in the conquest of the Duchy of Milan
The Duchy of Milan (; ) was a state in Northern Italy, created in 1395 by Gian Galeazzo Visconti, then the lord of Milan, and a member of the important Visconti of Milan, Visconti family, which had been ruling the city since 1277. At that time, ...
. The ''tercios'' of Naples and Sicily were created in 1536, thanks to the Genoa ordinance of Charles V Charles V may refer to:
Kings and Emperors
* Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor (1500вҖ“1558)
* Charles V of Naples (1661вҖ“1700), better known as Charles II of Spain
* Charles V of France (1338вҖ“1380), called the Wise
Others
* Charles V, Duke ...
.
At the Battle of MГјhlberg
The Battle of MГјhlberg took place near MГјhlberg in the Electorate of Saxony in 1547, during the Schmalkaldic War. The Catholic princes of the Holy Roman Empire led by the Holy Roman Emperor Charles V decisively defeated the Lutheran Schmal ...
in 1547, the imperial troops of Charles V defeated a league of Protestant princes in Germany, thanks mainly to the action of the Spanish ''tercios''. In 1557, the Spanish army completely defeated the French at the Battle of San Quentin, and again in 1558 at Gravelines
Gravelines ( , ; ) is a Communes of France, commune in the Nord (French department), Nord departments of France, department in Northern France. It lies at the mouth of the river Aa (France), Aa southwest of Dunkirk, France, Dunkirk. It was form ...
, which led to a peace greatly favoring Spain. In all these battles, the effectiveness of the ''tercio'' units stood out.
The origin of the term ''tercio'' is doubtful. Some historians believe the name was inspired by the ''tercГӯa'', a Roman Legion
The Roman legion (, ) was the largest military List of military legions, unit of the Roman army, composed of Roman citizenship, Roman citizens serving as legionary, legionaries. During the Roman Republic the manipular legion comprised 4,200 i ...
of Hispania. Some think that it designated the threefold division of the Spanish forces in Italy. Others trace it to the three types of combatants (pikemen, harquebusiers, musketeers). According to an ordinance for "people of war" of 1497, where the formation of the infantry is changed into three parts.
The pawns he infantrywere divided into three parts. The one tercio with spears, as the Germans brought them, which they called pikes; and the other had the name of shields eople of swords and the other, of crossbowmen and spit bearers. ater replaced by arquebusiersYet others derive the name from the three thousand men mustered in the first units. This last explanation is supported by the field master Sancho de LondoГұo in a report to the Duke of Alba in the 16th century:
The tercios, although they were instituted in imitation of theoman Oman, officially the Sultanate of Oman, is a country located on the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula in West Asia and the Middle East. It shares land borders with Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, and Yemen. OmanвҖҷs coastline ...legions, in few things can be compared to them, that the number is half, and although formerly there were three thousand soldiers, for which they were called tercios and not legions, already it is said like this even if they do not have more than a thousand men.
Composition and characteristics
 Although other powers adopted the battle formations and tactics perfected by the ''tercios'', their armies fell short of the fearsome reputation of the Spanish army, which possessed a core of experienced professional soldiers. This army was further supplemented by "an army of different nations", a reference to the varied origins of the troops from the
Although other powers adopted the battle formations and tactics perfected by the ''tercios'', their armies fell short of the fearsome reputation of the Spanish army, which possessed a core of experienced professional soldiers. This army was further supplemented by "an army of different nations", a reference to the varied origins of the troops from the German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany, the country of the Germans and German things
**Germania (Roman era)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizenship in Germany, see also Ge ...
and Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, a Romance ethnic group related to or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance languag ...
states, the Spanish Netherlands
The Spanish Netherlands (; ; ; ) (historically in Spanish: , the name "Flanders" was used as a '' pars pro toto'') was the Habsburg Netherlands ruled by the Spanish branch of the Habsburgs from 1556 to 1714. They were a collection of States of t ...
, and smaller units from other countries such as Ireland
Ireland (, ; ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe. Geopolitically, the island is divided between the Republic of Ireland (officially Names of the Irish state, named Irelan ...
. In 1621, for example, of the 47 military units of the Spanish army, counting together the larger Spanish, Spanish Netherlands, and Italian ''tercios'', and the much smaller German, Burgundian, and Irish regiments, only seven were manned by troops of Spanish origin. Such international musters were characteristic of European warfare before the levies of the Napoleonic Wars
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Napoleonic Wars
, partof = the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars
, image = Napoleonic Wars (revision).jpg
, caption = Left to right, top to bottom:Battl ...
. However, the core Spanish troops were Spanish subjects, admired for their cohesiveness, superior discipline, and overall professionalism.
Organization
Initially, each ''tercio'' that served in Italy and the Spanish Netherlands was organized into: * 10 companies of 300 soldiers each led by captains, in which ** 8 were pikemen's companies ** 2 were of arquebusier companies The companies were later reduced to 250 men and the ratio of arquebusiers (later musketmen) to pikemen steadily increased. During the early actions in the Netherlands, the ''tercios'' were reorganized into three ''coronelias'' ("colonelcies"), led by ''coronels'' ("colonels") each composed of a headquarters unit and four companies each (the predecessor of today'sbattalion
A battalion is a military unit, typically consisting of up to one thousand soldiers. A battalion is commanded by a lieutenant colonel and subdivided into several Company (military unit), companies, each typically commanded by a Major (rank), ...
s), but as a whole continued to be subdivided into the same 10 companies of 250 personnel each: two of arquebusiers and 8 of pikemen. Colonels were also of royal appointment.
Staff
* ''Maestre de Campo'' вҖ“colonel
Colonel ( ; abbreviated as Col., Col, or COL) is a senior military Officer (armed forces), officer rank used in many countries. It is also used in some police forces and paramilitary organizations.
In the 17th, 18th, and 19th centuries, a colon ...
* ''Coronel'' вҖ“ colonel/ lieutenant colonel
* '' Sargento mayor'' вҖ“ major
Major most commonly refers to:
* Major (rank), a military rank
* Academic major, an academic discipline to which an undergraduate student formally commits
* People named Major, including given names, surnames, nicknames
* Major and minor in musi ...
* ''Furriel mayor'' вҖ“ quartermaster
Quartermaster is a military term, the meaning of which depends on the country and service. In land army, armies, a quartermaster is an officer who supervises military logistics, logistics and requisitions, manages stores or barracks, and distri ...
* ''CapellГЎn mayor'' вҖ“ chaplain
A chaplain is, traditionally, a cleric (such as a minister, priest, pastor, rabbi, purohit, or imam), or a lay representative of a religious tradition, attached to a secular institution (such as a hospital, prison, military unit, intellige ...
* ''Pifano mayor'' вҖ“ fife major
* ''Tambor mayor'' вҖ“ drum major
Company
* 1 ''CapitГЎn'' вҖ“captain
Captain is a title, an appellative for the commanding officer of a military unit; the supreme leader or highest rank officer of a navy ship, merchant ship, aeroplane, spacecraft, or other vessel; or the commander of a port, fire or police depa ...
* 1 ''AlfГ©rez'' вҖ“ lieutenant
A lieutenant ( , ; abbreviated Lt., Lt, LT, Lieut and similar) is a Junior officer, junior commissioned officer rank in the armed forces of many nations, as well as fire services, emergency medical services, Security agency, security services ...
* ''Abanderado'' вҖ“ standard-bearer
A standard-bearer, also known as a colour-bearer or flag-bearer, is a person who bears an emblem known as a standard or military colours, i.e. either a type of flag or an inflexible but mobile image, which is used (and often honoured) as ...
* ''Sargento'' вҖ“ sergeant
Sergeant (Sgt) is a Military rank, rank in use by the armed forces of many countries. It is also a police rank in some police services. The alternative spelling, ''serjeant'', is used in The Rifles and in other units that draw their heritage f ...
* ''CapellГЎn'' вҖ“ chaplain
* ''Furriel'' вҖ“ quartermaster
* ''Tambor'' вҖ“ drummer
* ''Pifano'' вҖ“ fifer
* ''Barbero'' вҖ“ barber surgeon
The barber surgeon was one of the most common European medical practitioners of the Middle Ages, generally charged with caring for soldiers during and after battle. In this era, surgery was seldom conducted by physicians. Instead, barbers, who ...
* ''Cabos de escuadra'' вҖ“ corporal
Corporal is a military rank in use by the armed forces of many countries. It is also a police rank in some police services. The rank is usually the lowest ranking non-commissioned officer. In some militaries, the rank of corporal nominally corr ...
s
* 150 ''piqueros'' вҖ“ pikemen
A pike is a long thrusting spear formerly used in European warfare from the Late Middle Ages and most of the early modern period, and wielded by foot soldiers deployed in pike square formation, until it was largely replaced by bayonet-equipped ...
* 100 ''arcabuceros'' вҖ“ arquebus
An arquebus ( ) is a form of long gun that appeared in Europe and the Ottoman Empire during the 15th century. An infantryman armed with an arquebus is called an arquebusier.
The term ''arquebus'' was applied to many different forms of firearms ...
iers (later musketeers)
* 40 ''coseletes'' вҖ“ sword-and-buckler men
Leadership of the ''tercio''
 Similar to military organization today, a ''tercio'' was led by a ''maestre de campo'' (commanding officer) appointed by the king, with a guard of eight halberdiers. Assisting the maestre was the
Similar to military organization today, a ''tercio'' was led by a ''maestre de campo'' (commanding officer) appointed by the king, with a guard of eight halberdiers. Assisting the maestre was the sergeant major
Sergeant major is a senior Non-commissioned officer, non-commissioned Military rank, rank or appointment in many militaries around the world.
History
In 16th century Spain, the ("sergeant major") was a general officer. He commanded an army's ...
and a furir
Furir (from French '' fourrier'', a person responsible for the feed) is a Swedish military rank (OR5) reintroduced in 2019, after having been abolished in 2009.
Duties
The ''Furir'' is a Squad Leader at Skill Level B (Intermediate). Promotion fr ...
major in charge of logistics and armaments. Companies were led by a captain
Captain is a title, an appellative for the commanding officer of a military unit; the supreme leader or highest rank officer of a navy ship, merchant ship, aeroplane, spacecraft, or other vessel; or the commander of a port, fire or police depa ...
(also royally appointed), with an ensign
Ensign most often refers to:
* Ensign (flag), a flag flown on a vessel to indicate nationality
* Ensign (rank), a navy (and former army) officer rank
Ensign or The Ensign may also refer to:
Places
* Ensign, Alberta, Alberta, Canada
* Ensign, Ka ...
in charge of the company color.
The company non-commissioned officers were sergeant
Sergeant (Sgt) is a Military rank, rank in use by the armed forces of many countries. It is also a police rank in some police services. The alternative spelling, ''serjeant'', is used in The Rifles and in other units that draw their heritage f ...
s, ''furrieles'' (furirs) and corporal
Corporal is a military rank in use by the armed forces of many countries. It is also a police rank in some police services. The rank is usually the lowest ranking non-commissioned officer. In some militaries, the rank of corporal nominally corr ...
s. A sergeant served as second-in-command of a company and transmitted the captain's orders; furrieles provided weapons and munitions, as well as additional manpower; corporals led groups of 25 (similar to today's platoon
A platoon is a Military organization, military unit typically composed of two to four squads, Section (military unit), sections, or patrols. Platoon organization varies depending on the country and the Military branch, branch, but a platoon can ...
s), watching for disorder in the unit.
Each company had corps of drums
A corps of drums, sometimes known as a fife and drum corps or simply field music, is a traditional European military music formation. Historically, a Corps of Drums' primary role was communication. Today, the primary role of a Corps of Dru ...
made up of drummers and fifers, sounding duty calls in battle, with the drum major and fife major being provided by the ''tercio'' headquarters.
The ''tercio'' staff included a medical component (made up of a professional medic, a barber, and surgeons), chaplains and preachers, and a judicial unit, plus military constable
A constable is a person holding a particular office, most commonly in law enforcement. The office of constable can vary significantly in different jurisdictions. ''Constable'' is commonly the rank of an officer within a police service. Other peo ...
s enforcing order. They all reported directly to the ''maestre de campo''.
Battle formations
 Within a ''tercio''
Within a ''tercio''cavalry
Historically, cavalry (from the French word ''cavalerie'', itself derived from ''cheval'' meaning "horse") are groups of soldiers or warriors who Horses in warfare, fight mounted on horseback. Until the 20th century, cavalry were the most mob ...
and other forces along its front, the long-range fire of its arquebusiers could be easily shifted to the flanks, making it versatile in both attack and defense.
 Groups of squares were typically arrayed in dragon-toothed formation, staggered, with the leading edge of one unit level with the trailing edge of the preceding, similar to hedgehog defence. This enabled
Groups of squares were typically arrayed in dragon-toothed formation, staggered, with the leading edge of one unit level with the trailing edge of the preceding, similar to hedgehog defence. This enabled enfilade
Enfilade and defilade are concepts in military tactics used to describe a military formation's exposure to enemy fire. A formation or position is "in enfilade" if weapon fire can be directed along its longest axis. A unit or position is "in de ...
lines of fire and somewhat defiladed the army units themselves. Odd units stood forward, alternating with even units stepped back, providing gaps for an unwary enemy to enter and expose its flanks to raking crossfire
A crossfire (also known as interlocking fire) is a military term for the siting of weapons (often automatic weapons such as assault rifles or sub-machine guns) so that their arcs of fire overlap. This tactic came to prominence in World War I.
...
from the guns of three separate squares. ''Tercio'' companies also conducted some operations independently of the main formations.
''Tercios'' and the Spanish Empire
''Tercios'' were deployed all over Europe under theHabsburg
The House of Habsburg (; ), also known as the House of Austria, was one of the most powerful dynasties in the history of Europe and Western civilization. They were best known for their inbreeding and for ruling vast realms throughout Europe d ...
rulers. They were made up of volunteers and built up around a core of professional soldiers and were highly trained. Sometime later ''tercios'' did not conform to the all-volunteer model of the regular Imperial Spanish army вҖ“ when the Habsburg king Philip II found himself in need of more troops, he raised a ''tercio'' of Catalan criminals to fight in Flanders
Flanders ( or ; ) is the Dutch language, Dutch-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to culture, la ...
, a trend he continued with mostly Catalan criminals for the rest of his reign. A large proportion of the Spanish army, the ''Tercio'' of Savoy and the ''Tercio'' of Sicily were deployed in the Netherlands to quell the increasingly difficult rebellion
Rebellion is an uprising that resists and is organized against one's government. A rebel is a person who engages in a rebellion. A rebel group is a consciously coordinated group that seeks to gain political control over an entire state or a ...
against the Habsburgs in the later half or the 16th century. By this time, the Spanish army was entirely composed of ''tercio'' units. Ironically, many units of the Spanish ''tercios'' became part of the problem, rather than the solution when the time came to pay them: with the Spanish coffers depleted by constant warfare, unpaid units often mutinied. For example, in April 1576, just after winning a major victory, unpaid ''tercios'' mutinied and occupied the friendly town of Antwerp
Antwerp (; ; ) is a City status in Belgium, city and a Municipalities of Belgium, municipality in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is the capital and largest city of Antwerp Province, and the third-largest city in Belgium by area at , after ...
, in the so-called Spanish Fury at Antwerp, and sacked it for three days. Completely reliant on his troops, the Spanish commander could only comply.
Specialized ''tercios''
On 24 February 1537, the ''Tercio de Galeras'' (''Tercio'' of Galleys) was created. Today, the ''Real InfanterГӯa de Marina'' (Spanish Marine Infantry
The Marine Infantry () are the marines of the Spanish Navy. Responsible for conducting amphibious warfare. Fully integrated into the Spanish Navy's structure, the branch's history dates back to 1537 when Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor formed the ...
) consider themselves successors of the legacy and heritage of the Galleys ''Tercio'', making it the oldest currently operating marines unit in the world. There were other units of naval ''tercios'' such as ''Tercio Viejo de Armada'' (Old Navy ''Tercio'') or ''Tercio Fijo de la Mar de NГЎpoles'' (Permanent Sea ''Tercio'' of Naples). Such specialized units were needed for the protracted war with the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
over the entire Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern ...
.
Naming conventions
Most ''tercios'' were named according to the place where they were raised or first deployed: ''Tercio de Sicilia'', ''de LombardГӯa'', ''de NГЎpoles'' (''Tercio'' of Sicily, of Lombardy, of Naples) and so on. Other ''tercios'' were named for their commanding officer, such as ''Tercio de Moncada'' for its commander Miguel de Moncada (whose most famous soldier wasMiguel de Cervantes
Miguel de Cervantes Saavedra ( ; ; 29 September 1547 (assumed) вҖ“ 22 April 1616 Old Style and New Style dates, NS) was a Spanish writer widely regarded as the greatest writer in the Spanish language and one of the world's pre-eminent novelist ...
). Some tercios were named by their main function, such as ''Galeras'' or ''Viejo de Armada''.
Colours
Cross of Burgundy
The Cross of Burgundy (; ; ; ; ; Portuguese language, Portuguese: ''Cruz de Borgonha'') is a saw-toothed (wiktionary:raguly, raguly) form of the Saltire, Cross of Saint Andrew, the patron saint of Burgundy, and a historical banner and battle fla ...
was adopted as the symbol of the ''Tercios'' and the Spanish Empire.
File:Tercio - Liga.svg, ''Tercio de la Liga'' (1571)
File:Tercio - SpГӯnola.svg, ''Unknown Tercio flag (appears near commander Ambrogio Spinola in the painting "The Surrender of Breda" of Diego VelГЎzquez)'' (1621)
File:Tercio - Alburquerque.svg, ''Tercio de Alburquerque'' (1643)
File:Tercio - Morados Viejos.svg, ''Tercio Morados Viejos'' (1670)
File:Tercio - Amarillos Viejos.svg, ''Tercio Amarillos Viejos'' (1680)
The Portuguese ''terços''
Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic, is a country on the Iberian Peninsula in Southwestern Europe. Featuring Cabo da Roca, the westernmost point in continental Europe, Portugal borders Spain to its north and east, with which it share ...
adopted the Spanish model of ''tercio'' in the 16th century, calling it ''terço''. In 1578, during the reorganization of the Portuguese Army
The Portuguese Army () is the land component of the Portuguese Armed Forces, Armed Forces of Portugal and is also its largest branch. It is charged with the defence of Portugal, in co-operation with other branches of the Armed Forces. With its ...
conducted by King Sebastian
Sebastian may refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Sebastian (name), including a list of persons and fictional characters with the name
* Saint Sebastian, a Christian saint martyred in the 3rd century
* Sebastian of Portugal (1554вҖ“1578 ...
, four ''terços'' were established: the ''Terço'' of Lisbon
Lisbon ( ; ) is the capital and largest city of Portugal, with an estimated population of 567,131, as of 2023, within its administrative limits and 3,028,000 within the Lisbon Metropolitan Area, metropolis, as of 2025. Lisbon is mainlan ...
, the ''Terço'' of Estremadura, the ''Terço'' of Alentejo
Alentejo ( , , ) is a geographical, historical, and cultural region of southвҖ“central and southern Portugal. In Portuguese, its name means "beyond the Tagus" ().
Alentejo includes the regions of Alto Alentejo Province, Alto Alentejo and Bai ...
, and the ''Terço'' of Algarve
The Algarve (, , ) is the southernmost NUTS statistical regions of Portugal, NUTS II region of continental Portugal. It has an area of with 467,495 permanent inhabitants and incorporates 16 municipalities (concelho, ''concelhos'' or ''municГӯpio ...
. Each had about 2,000 men, formed into eight companies.
The infantry of the army organized for the expedition to Morocco
Morocco, officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It has coastlines on the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to AlgeriaвҖ“Morocc ...
in 1578 was made up of these four ''terços'', together with the ''Terço'' of the Adventurers (totally made up of young nobles), three mercenary ''terços'' (the German, the Italian, and the Castilian), and a unit of elite sharpshooter
A sharpshooter is one who is highly proficient at firing firearms or other projectile weapons accurately. Military units composed of sharpshooters were important factors in 19th-century combat. Along with " marksman" and "expert", "sharpshooter" ...
s of the Portuguese garrison of Tangier
Tangier ( ; , , ) is a city in northwestern Morocco, on the coasts of the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean. The city is the capital city, capital of the Tanger-Tetouan-Al Hoceima region, as well as the Tangier-Assilah Prefecture of Moroc ...
. This was the Portuguese force which fought the Battle of AlcГЎcer Quibir
The Battle of AlcГЎcer Quibir (also known as "Battle of Three Kings" () or "Battle of Wadi al-Makhazin" () in Morocco) was fought in northern Morocco, near the town of Ksar-el-Kebir (variant spellings: ''Ksar El Kebir'', ''AlcГЎcer-Quivir'', ...
.
While united with the Spanish Crown, from 1580 to 1640, Portugal kept the organization of ''terços'', although the Army had declined. Several Spanish ''tercios'' were sent to Portugal; the principal of them, the Spanish infantry ''Tercio'' of the City of Lisbon, occupied the main fortresses of the Portuguese capital. The ''Terço'' of the Navy of the Crown of Portugal, the ancestor of the modern Portuguese Marines
The Portuguese Marine Corps () is the special operations capable amphibious warfare, amphibious force of the Portuguese Navy.
It has roles similar to the ones of the United States Marine Corps Reconnaissance Battalions, USMC Reconnaissance Batta ...
, was created in this period.
After the restoration of Portuguese sovereignty in 1640, the Army was reorganized by King John IV of Portugal
''Dom (honorific), Dom'' John IV (; 19 March 1604 вҖ“ 6 November 1656), also known by the Portuguese as John the Restorer (), was the List of Portuguese monarchs, King of Portugal from 1640 until his death in 1656. He Portuguese Restoration War, ...
. The terços remained the basic units of the Portuguese infantry. Two types of ''terços'' were organized: the paid ''terços'' (first line permanent units) and the auxiliary ''terços'' (second line militia units). Portugal won the Restoration War with these ''terços''.
At the end of the 17th century, the ''terços'' were already organized as modern regiments. However, the first line ''terços'' were only transformed into regiments in 1707, during the War of the Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was a European great power conflict fought between 1701 and 1714. The immediate cause was the death of the childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700, which led to a struggle for control of the Spanish E ...
вҖ“ after the Spanish ''tercios'' were transformed into regiments in 1704. The second line ''terГ§os'' were only transformed into militia regiments in 1796. Some of the old ''terГ§os'' are direct ancestors of modern regiments of the Portuguese Army.
Evolution and replacement
The first real challenge to the dominance of the Spanish ''tercios'' on the open battlefield came at theBattle of Nieuwpoort
The Battle of Nieuwpoort (also known as the Battle of the Dunes) was fought on 2 July 1600 during the Eighty Years War and the Anglo-Spanish war in the dunes near Nieuwpoort. A Dutch army met a Spanish force head-on which, although their left f ...
(1600). The victor of Nieuwpoort, the Dutch ''stadtholder'' Maurice, Prince of Orange
Maurice of Orange (; 14 November 1567 вҖ“ 23 April 1625) was ''stadtholder'' of all the provinces of the Dutch Republic except for Lordship of Frisia, Friesland from 1585 at the earliest until his death on 23 April 1625. Before he became P ...
, believed he could improve on the ''tercio'' by combining its methods with the organisation of the Roman legion
The Roman legion (, ) was the largest military List of military legions, unit of the Roman army, composed of Roman citizenship, Roman citizens serving as legionary, legionaries. During the Roman Republic the manipular legion comprised 4,200 i ...
. These shallower linear formations brought a greater proportion of available guns to bear on the enemy simultaneously. The result was that the tercio squares at Nieuwpoort were badly damaged by the weight of Dutch firepower. Yet the Spanish army very nearly succeeded, in spite of internal dissensions that had compromised its regular command. The Eighty Years' War
The Eighty Years' War or Dutch Revolt (; 1566/1568вҖ“1648) was an armed conflict in the Habsburg Netherlands between disparate groups of rebels and the Spanish Empire, Spanish government. The Origins of the Eighty Years' War, causes of the w ...
(1568вҖ“1648) in the Low Countries
The Low Countries (; ), historically also known as the Netherlands (), is a coastal lowland region in Northwestern Europe forming the lower Drainage basin, basin of the RhineвҖ“MeuseвҖ“Scheldt delta and consisting today of the three modern "Bene ...
continued to be characterized by sieges of cities and forts, while field battles were of secondary importance. Maurice's reforms did not lead to a revolution in warfare, but he had created an army that could meet the ''tercios''Thirty Years War
The Thirty Years' War, fought primarily in Central Europe between 1618 and 1648, was one of the most destructive conflicts in European history. An estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died from battle, famine, or disease, whil ...
(1618вҖ“1648) ''tercio'' style battle formations of the Holy Roman Empire suffered major defeats at the hands of more linear formations created and led by the Swedish soldier-king Gustavus Adolphus
Gustavus Adolphus (9 December N.S 19 December">Old_Style_and_New_Style_dates.html" ;"title="/nowiki>Old Style and New Style dates">N.S 19 December15946 November Old Style and New Style dates">N.S 16 November] 1632), also known in English as ...
. However, the tried-and-true tactics and professionalism of the Spanish ''tercios'' played a decisive role in defeating the Swedish army at the Battle of Nördlingen (1634), Battle of Nördlingen.
Throughout its history, the ''tercios''Wimpfen
Bad Wimpfen () is a historic spa town in the Heilbronn (district), district of Heilbronn in the Baden-WГјrttemberg region of southern Germany. It lies north of the city of Heilbronn, on the river Neckar.
Geography
Bad Wimpfen is located on the w ...
(1622), Fleurus
Fleurus (; ) is a city and municipality of Wallonia located in the province of Hainaut, Belgium. It has been the site of four major battles.
The municipality consists of the following districts: Brye, Heppignies, Fleurus, Lambusart, Saint-Am ...
(1622), Breda
Breda ( , , , ) is a List of cities in the Netherlands by province, city and List of municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality in the southern part of the Netherlands, located in the Provinces of the Netherlands, province of North Brabant. ...
(1624), Nördlingen
Nördlingen (; Swabian: ''Nearle'' or ''Nearleng'') is a town in the Donau-Ries district, in Swabia, Bavaria, Germany, with a population of approximately 20,674. It is located approximately east of Stuttgart, and northwest of Munich. It was ...
(1634), Thionville
Thionville (; ; ) is a city in the northeastern French Departments of France, department of Moselle (department), Moselle. The city is located on the left bank of the river Moselle (river), Moselle, opposite its suburb Yutz.
History
Thionvi ...
(1639), and Honnecourt (1641). It was not until Rocroi
Rocroi () is a Communes of France, commune in the Ardennes (dГ©partement), Ardennes Departments of France, department in northern France.
The central area is a notable surviving example of a bastion fort.
Population
History
Rocroi was forti ...
(1643) that the Spanish ''tercio's'' reputation of invincibility in open battle was shattered. Still, the Rocroi defeat was precipitated by the collapse of the supporting cavalry rather than the failure of the ''tercios''Tuttlingen
Tuttlingen (; Alemannic: ''Duttlinga'') is a town in Baden-WГјrttemberg, capital of the district Tuttlingen. Nendingen, ''MГ¶hringen'' and ''EГҹlingen'' are three former municipalities that belong to Tuttlingen. Tuttlingen is located in Swabia ...
(1643) and Valenciennes
Valenciennes (, also , , ; ; or ; ) is a communes of France, commune in the Nord (French department), Nord Departments of France, department, Hauts-de-France, France.
It lies on the Scheldt () river. Although the city and region experienced ...
(1656), although their composition and battlefield style had continued to evolve. In this period steady improvements in firearms and field artillery were increasingly favoring the linear style. By the late 17th century the ''tercios'' had adopted so much of the linear style that their battlefield formations and tactics often had little resemblance to the battle formations and tactics a century earlier.
Royal Military and Mathematics Academy of Brussels
In 1675 the first modernRoyal Military and Mathematics Academy of Brussels
The Royal Military and Mathematics Academy of Brussels (Spanish language, Spanish: ''la Academia Militar de Bruselas''), also known as the ''Academia Militar del EjГ©rcito de los PaГӯses Bajos'', was established in 1675 in Brussels, capital of ...
was founded in Brussels
Brussels, officially the Brussels-Capital Region, (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) is a Communities, regions and language areas of Belgium#Regions, region of Belgium comprising #Municipalit ...
by its sole-director Don SebastiГЎn FernГЎndez de Medrano, at the request of the Governor of the Habsburg Netherlands
The governor () or governor-general () of the Habsburg Netherlands was a representative appointed by the Holy Roman emperor (1504-1556), the king of Spain (1556-1598, 1621-1706), and the archduke of Austria (1716-1794), to administer the Burgund ...
, Carlos de AragГіn de Gurrea, 9th Duke of Villahermosa
Carlos may refer to:
Places
;Canada
* Carlos, Alberta, a locality
;United States
* Carlos, Indiana, an unincorporated community
* Carlos, Maryland, a place in Allegany County
* Carlos, Minnesota, a small city
* Carlos, West Virginia
;Elsewher ...
, in order to correct the shortage of artillerymen
Artillery consists of ranged weapons that launch munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during sieges, and led to heavy ...
and engineers from the Spanish ''tercios''.
This Royal Military and Mathematics Academy in Flanders was renowned for the diverse origin of its officer cadets, for the innovative features of its plan of studies produced by SebastiГЎn FernГЎndez de Medrano, the theoretical and practical basis of its learning process apart from the relevant assignments given to its officer cadets who were also known as the вҖңGreat Masters of WarвҖқ coined by the treatise writer, Count of Clonard. It was created in Brussels to train the most distinguished officers in the peninsula in the Art of War.
The Royal Military Academy of Flanders was an educational institution to train military engineers with various fields of education such as arithmetic, geometry, artillery, fortification, algebra, cosmography, astronomy, navigation, etc.
Transformation of the Spanish ''Tercio''
In 1704, the regular Spanish ''tercios'' were transformed into regiments and the pikeman as an infantry type was dropped. Those of the reserves and the militia would later be transformed into similar organisations.Famous battles
Victories
Pre-official nomenclature
*Cerignola
Cerignola (; ) is a town and ''comune'' of Apulia, Italy, in the province of Foggia, southeast from the town of Foggia. It has the third-largest land area of any ''comune'' in Italy, at , after Rome and Ravenna and it has the largest land ar ...
(1503)
* Garigliano
The Garigliano () is a river in central Italy.
It forms at the confluence of the rivers Gari (also known as the Rapido) and Liri. Garigliano is actually a deformation of "Gari-Lirano" (which in Italian means something like "Gari from the Liri" ...
(1503)
* Mers-el-KГ©bir (1505)
* Oran
Oran () is a major coastal city located in the northwest of Algeria. It is considered the second most important city of Algeria, after the capital, Algiers, because of its population and commercial, industrial and cultural importance. It is w ...
(1509)
* La Motta (1513)
* NoГЎin (1521)
* Bicocca (1522)
* Sesia (1524)
* Pavia
Pavia ( , ; ; ; ; ) is a town and comune of south-western Lombardy, in Northern Italy, south of Milan on the lower Ticino (river), Ticino near its confluence with the Po (river), Po. It has a population of c. 73,086.
The city was a major polit ...
(1525)
* Rome
Rome (Italian language, Italian and , ) is the capital city and most populated (municipality) of Italy. It is also the administrative centre of the Lazio Regions of Italy, region and of the Metropolitan City of Rome. A special named with 2, ...
(1527)
* Landriano
Landriano is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Province of Pavia in the Italian region Lombardy, located about southeast of Milan and about northeast of Pavia.
Landriano borders the following municipalities: BascapГЁ, Carpiano, Siziano, Torreve ...
(1529)
* Vienna
Vienna ( ; ; ) is the capital city, capital, List of largest cities in Austria, most populous city, and one of Federal states of Austria, nine federal states of Austria. It is Austria's primate city, with just over two million inhabitants. ...
(1529)
* Gavinana (1530)
Official nomenclature
*Tunis
Tunis (, ') is the capital city, capital and largest city of Tunisia. The greater metropolitan area of Tunis, often referred to as "Grand Tunis", has about 2,700,000 inhabitants. , it is the third-largest city in the Maghreb region (after Casabl ...
(1535)
* Serravalle (1544)
* MГјhlberg (1547)
* St. Quentin (1557)
* Gravelines
Gravelines ( , ; ) is a Communes of France, commune in the Nord (French department), Nord departments of France, department in Northern France. It lies at the mouth of the river Aa (France), Aa southwest of Dunkirk, France, Dunkirk. It was form ...
(1558)
* Malta
Malta, officially the Republic of Malta, is an island country in Southern Europe located in the Mediterranean Sea, between Sicily and North Africa. It consists of an archipelago south of Italy, east of Tunisia, and north of Libya. The two ...
(1565)
* Lannoy (1566)
* Dahlen (1566)
* Oosterweel (1567)
* Jemmingen (1568)
* Jodoigne
Jodoigne (; ; ) is a city and municipality of Wallonia located in the province of Walloon Brabant, Belgium.
On January 1, 2006, Jodoigne had a total population of 12,440. The total area is which gives a population density of .
The municipalit ...
(1568)
* Lepanto (1571)
* Mons
Mons commonly refers to:
* Mons, Belgium, a city in Belgium
* Mons pubis (mons Venus or mons veneris), in mammalian anatomy, the adipose tissue lying above the pubic bone
* Mons (planetary nomenclature), a sizable extraterrestrial mountain
* Batt ...
(1572)
* Goes
The Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES), operated by the United States' National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA)'s National Environmental Satellite, Data, and Information Service division, supports weather fo ...
(1572)
* Haarlem
Haarlem (; predecessor of ''Harlem'' in English language, English) is a List of cities in the Netherlands by province, city and Municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality in the Netherlands. It is the capital of the Provinces of the Nether ...
(1573)
* Mook
Mook or Mooks may refer to:
Places
* Mook, Iran (disambiguation)
* Mook, Kentucky, an unincorporated community, United States
* Mook en Middelaar, a municipality in the Netherlands
Entertainment
* Mook (publishing), a portmanteau of magazine ...
(1574)
* Valkenburg (1574)
* Schoonhoven
Schoonhoven () is a city and was a former municipality in the western Netherlands, in the province of South Holland. Since 2015 it has been a part of the municipality of Krimpenerwaard, before it had been an independent municipality.
The former mu ...
(1575)
* Oudewater (1575)
* Zierikzee
Zierikzee () is a small city in the southwest Netherlands, 50 km southwest of Rotterdam. It is situated in the municipality of Schouwen-Duiveland, Zeeland. The city hall of Schouwen-Duiveland is located in Zierikzee, its largest city. Zierikze ...
(1576)
* Gembloux
Gembloux (; ; ) is a municipality and city of Wallonia located in the province of Namur, Belgium.
On 1 January 2006, the municipality had 21,964 inhabitants. The total area is 95.86 km2, yielding a population density of 229 inhabitants per ...
(1578)
* Borgerhout
Borgerhout () is the smallest districts of Antwerp, district of Antwerp, Belgium. , the district housed 45,769 inhabitants on 3.93 kmВІ.
It was an independent municipality until January 1983. The postal area code for Borgerhout is 2140.
Geography ...
(1579)
* Maastricht
Maastricht ( , , ; ; ; ) is a city and a Municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality in the southeastern Netherlands. It is the capital city, capital and largest city of the province of Limburg (Netherlands), Limburg. Maastricht is loca ...
(1579)
* Alcantara
Alcantara, AlcГўntara ( Portuguese), AlcГЎntara (Spanish), AlcГ ntara, AlcГ ntera, El-Qantarah and (El) Kantara are all transliterations of the Arabic word ''al-qantara'' (Ш§Щ„ЩӮЩҶШ·ШұШ©), meaning "the bridge".
Alcantara may refer to:
People
* ...
(1580)
* Noordhorn (1581)
* Terceira
Terceira () is a volcanic island in the Azores archipelago, about a third of the way across the North Atlantic Ocean at a similar latitude to Portugal's capital Lisbon, with the island group forming an insular part of Portugal. It is one of the ...
(1582)
* Eindhoven
Eindhoven ( ; ) is a city and List of municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality of the Netherlands, located in the southern Provinces of the Netherlands, province of North Brabant, of which it is the largest municipality, and is also locat ...
(1583)
* Steenbergen
Steenbergen () is a Municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality and a town in the province of North Brabant in the south of the Netherlands. The municipality had a population of in and covers an area of of which is water. The municipality ...
(1583)
* Empel
Empel is a village and former municipality, which is now a quarter of 's-Hertogenbosch in the Dutch province of North Brabant.
History
Archaeological evidence shows Celtic and Roman traces in the area. The site of a Roman temple was of speci ...
(1585)
* Antwerp
Antwerp (; ; ) is a City status in Belgium, city and a Municipalities of Belgium, municipality in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is the capital and largest city of Antwerp Province, and the third-largest city in Belgium by area at , after ...
(1585)
* Neuss
Neuss (; written ''NeuГҹ'' until 1968; ; ) is a city in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is on the west bank of the Rhine opposite DГјsseldorf. Neuss is the largest city within the Rhein-Kreis Neuss district. It is primarily known for its ...
(1586)
* Zutphen
Zutphen () is a city and municipality located in the province of Gelderland, Netherlands. It lies some northeast of Arnhem, on the eastern bank of the river IJssel at the point where it is joined by the Berkel. First mentioned in the 11th centur ...
(1586)
* Sluis
Sluis (; ; ) is a city and municipality located in the west of Zeelandic Flanders, in the south-western Dutch province of Zeeland.
The current incarnation of the municipality has existed since 1 January 2003. The former municipalities of Oostb ...
(1587)
* Rheinberg
Rheinberg () is a town in the district of Wesel, in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is situated on the left bank of the Rhine, approx. north of Moers and south of Wesel.
It comprises the municipal districts of Rheinberg, Borth, Budberg, an ...
(1590)
* Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, largest city of France. With an estimated population of 2,048,472 residents in January 2025 in an area of more than , Paris is the List of ci ...
(1590)
* Craon (1592)
* Doullens
Doullens (; ; former ) is a commune in the Somme department, Hauts-de-France, France.
Its inhabitants are called ''Doullennais'' and ''Doullennaises''.
Geography
Doullens is situated on the N25 road, in the northern part of the department, st ...
and Groenlo
Groenlo () is a city in the municipality of Oost Gelre, situated in the eastern part of the Netherlands, on the German border, within a region in the province of Gelderland called the Achterhoek (literally: "back corner"). Groenlo was a municipal ...
(1595)
* Lippe
Lippe () is a ''Kreis'' (district) in the east of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. Neighboring districts are Herford, Minden-Lübbecke, Höxter, Paderborn, Gütersloh, and district-free Bielefeld, which forms the region Ostwestfalen-Lippe. ...
(1595)
* Calais
Calais ( , , traditionally , ) is a French port city in the Pas-de-Calais department, of which it is a subprefecture. Calais is the largest city in Pas-de-Calais. The population of the city proper is 67,544; that of the urban area is 144,6 ...
(1596)
* Groenlo
Groenlo () is a city in the municipality of Oost Gelre, situated in the eastern part of the Netherlands, on the German border, within a region in the province of Gelderland called the Achterhoek (literally: "back corner"). Groenlo was a municipal ...
(1606)
* Oppenheim
Oppenheim ( or ) is a town in the Mainz-Bingen district of Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany.
Geography
Location
The town lies on the Upper Rhine in Rhenish Hesse between Mainz and Worms. It is the seat of the Verbandsgemeinde (special ad ...
(1620)
* Bacharach
Bacharach (, also known as ''Bacharach am Rhein'') is a town in the Mainz-Bingen district in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It belongs to the ''Verbandsgemeinde'' of Rhein-Nahe, whose seat is in Bingen am Rhein, although that town is not with ...
(1620)
* JГјlich
Jülich (; in old spellings also known as ''Guelich'' or ''Gülich'', , , Ripuarian: ''Jöllesch'') is a town in the district of Düren, in the federal state of North Rhine-Westphalia, in western Germany. As a border region between the competin ...
(1621)
* Wimpfen
Bad Wimpfen () is a historic spa town in the Heilbronn (district), district of Heilbronn in the Baden-WГјrttemberg region of southern Germany. It lies north of the city of Heilbronn, on the river Neckar.
Geography
Bad Wimpfen is located on the w ...
(1622)
* Fleurus
Fleurus (; ) is a city and municipality of Wallonia located in the province of Hainaut, Belgium. It has been the site of four major battles.
The municipality consists of the following districts: Brye, Heppignies, Fleurus, Lambusart, Saint-Am ...
(1622)
* Heidelberg
Heidelberg (; ; ) is the List of cities in Baden-WГјrttemberg by population, fifth-largest city in the States of Germany, German state of Baden-WГјrttemberg, and with a population of about 163,000, of which roughly a quarter consists of studen ...
(1622)
* Höchst (1622)
* Mannheim
Mannheim (; Palatine German language, Palatine German: or ), officially the University City of Mannheim (), is the List of cities in Baden-WГјrttemberg by population, second-largest city in Baden-WГјrttemberg after Stuttgart, the States of Ger ...
(1622)
* Breda
Breda ( , , , ) is a List of cities in the Netherlands by province, city and List of municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality in the southern part of the Netherlands, located in the Provinces of the Netherlands, province of North Brabant. ...
(1625)
* CГЎdiz
CГЎdiz ( , , ) is a city in Spain and the capital of the Province of CГЎdiz in the Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Andalusia. It is located in the southwest of the Iberian Peninsula off the Atlantic Ocean separated fr ...
(1625)
* Genoa
Genoa ( ; ; ) is a city in and the capital of the Italian region of Liguria, and the sixth-largest city in Italy. As of 2025, 563,947 people live within the city's administrative limits. While its metropolitan city has 818,651 inhabitan ...
(1625)
* Salvador de Bahia
Salvador () is a Municipalities of Brazil, Brazilian municipality and capital city of the Federative units of Brazil, state of Bahia. Situated in the Zona da Mata in the Northeast Region, Brazil, Northeast Region of Brazil, Salvador is recognize ...
(1625)
* Nördlingen
Nördlingen (; Swabian: ''Nearle'' or ''Nearleng'') is a town in the Donau-Ries district, in Swabia, Bavaria, Germany, with a population of approximately 20,674. It is located approximately east of Stuttgart, and northwest of Munich. It was ...
(1634)
* Leuven
Leuven (, , ), also called Louvain (, , ), is the capital and largest City status in Belgium, city of the Provinces of Belgium, province of Flemish Brabant in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is located about east of Brussels. The municipalit ...
(1635)
* Somme __NOTOC__
Somme or The Somme may refer to: Places
*Somme (department), a department of France
* Somme, Queensland, Australia
* Canal de la Somme, a canal in France
*Somme (river), a river in France
Arts, entertainment, and media
* ''Somme'' (book), ...
(1636)
* Venlo
Venlo () is a List of cities in the Netherlands by province, city and List of municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality in southeastern Netherlands, close to the border with Germany. It is situated in the province of Limburg (Netherlands), ...
(1637)
* Kallo (1638)
* Thionville
Thionville (; ; ) is a city in the northeastern French Departments of France, department of Moselle (department), Moselle. The city is located on the left bank of the river Moselle (river), Moselle, opposite its suburb Yutz.
History
Thionvi ...
(1639)
* Honnecourt (1642)
* Tuttlingen
Tuttlingen (; Alemannic: ''Duttlinga'') is a town in Baden-WГјrttemberg, capital of the district Tuttlingen. Nendingen, ''MГ¶hringen'' and ''EГҹlingen'' are three former municipalities that belong to Tuttlingen. Tuttlingen is located in Swabia ...
(1643)
* Valenciennes
Valenciennes (, also , , ; ; or ; ) is a communes of France, commune in the Nord (French department), Nord Departments of France, department, Hauts-de-France, France.
It lies on the Scheldt () river. Although the city and region experienced ...
(1656)
Defeats
*Ravenna
Ravenna ( ; , also ; ) is the capital city of the Province of Ravenna, in the Emilia-Romagna region of Northern Italy. It was the capital city of the Western Roman Empire during the 5th century until its Fall of Rome, collapse in 476, after which ...
(1512)
* Castelnuovo (1539)
* Algiers
Algiers is the capital city of Algeria as well as the capital of the Algiers Province; it extends over many Communes of Algeria, communes without having its own separate governing body. With 2,988,145 residents in 2008Census 14 April 2008: Offi ...
(1541)
* Ceresole (1544)
* Leiden
Leiden ( ; ; in English language, English and Archaism, archaic Dutch language, Dutch also Leyden) is a List of cities in the Netherlands by province, city and List of municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality in the Provinces of the Nethe ...
(1574)
* Rijmenam (1578)
* AlcГЎcer Quibir (1578)
* Ivry (1590)
* Caudebec (1592)
* Siege of Coevorden
* Morlaix
Morlaix (; , ) is a commune in the FinistГЁre department of Brittany in northwestern France. It is a sub-prefecture of the department.
History
The Battle of Morlaix, part of the Hundred Years' War, was fought near the town on 30 Septembe ...
(1594)
* Fort Crozon (1594)
* Fontaine-française
Fontaine-FranГ§aise () is a commune in the CГҙte-d'Or department in eastern France.
Population
See also
*Communes of the CГҙte-d'Or department
The following is a list of the 698 communes of the CГҙte-d'Or department of France.
The ...
(1595)
* Amiens
Amiens (English: or ; ; , or ) is a city and Communes of France, commune in northern France, located north of Paris and south-west of Lille. It is the capital of the Somme (department), Somme Departments of France, department in the region ...
(1597)
* Turnhout
Turnhout () is a Belgium, Belgian Municipalities in Belgium, municipality and city located in the Flemish Region, Flemish Provinces of Belgium, province of Antwerp (province), Antwerp. The municipality comprises only the city of Turnhout proper. ...
(1597)
* Zaltbommel
Zaltbommel (), also known, historically and colloquially, as Bommel, is a municipality and a city in the Netherlands.
History
The city of Zaltbommel
The town of Zaltbommel was first mentioned as "Bomela" in the year 850. Zaltbommel received ...
(1599)
* Nieuwpoort (1600)
* Kinsale
Kinsale ( ; ) is a historic port and fishing town in County Cork, Ireland. Located approximately south of Cork (city), Cork City on the southeast coast near the Old Head of Kinsale, it sits at the mouth of the River Bandon, and has a populatio ...
(1601)
* Sluis
Sluis (; ; ) is a city and municipality located in the west of Zeelandic Flanders, in the south-western Dutch province of Zeeland.
The current incarnation of the municipality has existed since 1 January 2003. The former municipalities of Oostb ...
(1604)
* Les Avins (1635)
* Tornavento (1636)
* Schenkenschans (1636)
* Turin
Turin ( , ; ; , then ) is a city and an important business and cultural centre in northern Italy. It is the capital city of Piedmont and of the Metropolitan City of Turin, and was the first Italian capital from 1861 to 1865. The city is main ...
(1640)
* MontjuГҜc
MontjuГҜc () is a hill in Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain.
MontjuГҜc or Montjuich, meaning "Jewish Mountain" in medieval Latin and Catalan, is a broad, shallow hill in Barcelona with a rich history. It was the birthplace of the city, and its st ...
(1641)
* Lleida
Lleida (, ; ; '' see below'') is a city in the west of Catalonia, Spain. It is the capital and largest town in SegriГ county, the Ponent region and the province of Lleida. Geographically, it is located in the Catalan Central Depression. It ...
(1642)
* Rocroi
Rocroi () is a Communes of France, commune in the Ardennes (dГ©partement), Ardennes Departments of France, department in northern France.
The central area is a notable surviving example of a bastion fort.
Population
History
Rocroi was forti ...
(1643)
* Lens
A lens is a transmissive optical device that focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (''elements'') ...
(1648)
* Arras
Arras ( , ; ; historical ) is the prefecture of the Pas-de-Calais department, which forms part of the region of Hauts-de-France; before the reorganization of 2014 it was in Nord-Pas-de-Calais. The historic centre of the Artois region, with a ...
(1654)
* The Dunes (1658)
* The Lines of Elvas (1659)
* Ameixial (1663)
* Castelo Rodrigo (1664)
* Montes Claros
Montes Claros is a Municipalities of Brazil, Brazilian municipality located in the northern region of the Federative units of Brazil, state of Minas Gerais. Situated north of the state capital, Belo Horizonte, it lies approximately away. The mun ...
(1665)
See also
*Pike and shot
Pike and shot was a historical infantry tactical formation that first appeared during the late 15th and early 16th centuries, and was used until the development of the bayonet in the late 17th century. This type of formation combined soldiers ...
* Musketeer
A musketeer ( ) was a type of soldier equipped with a musket. Musketeers were an important part of early modern warfare, particularly in Europe, as they normally comprised the majority of their infantry. The musketeer was a precursor to the rifl ...
* '' Captain Alatriste''
* Military history
Military history is the study of War, armed conflict in the Human history, history of humanity, and its impact on the societies, cultures and economies thereof, as well as the resulting changes to Politics, local and international relationship ...
* Spanish Navy Marines
The Marine Infantry () are the marines of the Spanish Navy. Responsible for conducting amphibious warfare. Fully integrated into the Spanish Navy's structure, the branch's history dates back to 1537 when Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor formed the ...
units are called ''tercios''
* The units of the modern Spanish Legion
For centuries, Spain recruited foreign soldiers to its army, forming the foreign regiments () such as the Regiment of Hibernia (formed in 1709 from Irishmen who fled their own country in the wake of the Flight of the Earls and the Penal la ...
are also called ''tercios''.
* , roughly contemporaneous and organizationally similar Japanese unit
References
Further reading
* Christon I. Archer, John R. Ferris, Holger H. Herwig, Timothy H. E. Travers вҖ“ For a history of Spanish arms in the 16th and 17th centuries. * * * *Spanish Tercio Tactics
(myArmoury.com article)
Spanish web site
вҖ“ Honors Alonso '' Pita da Veiga'' the most heroic Spaniard at the
Battle of Pavia
The Battle of Pavia, fought on the morning of 24 February 1525, was the decisive engagement of the Italian War of 1521вҖ“1526 between the Kingdom of France and the Habsburg Empire of Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor, Charles V, Holy Roman Empero ...
(Italy) 1525.Non-Official Web siteof the Modern "Spanish Marines" (in existence since 1537 few years after ''
Battle of Pavia
The Battle of Pavia, fought on the morning of 24 February 1525, was the decisive engagement of the Italian War of 1521вҖ“1526 between the Kingdom of France and the Habsburg Empire of Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor, Charles V, Holy Roman Empero ...
'' (Italy) 1525 and well before the '' Battle of Lepanto (1571), Battle of Lepanto'' (Greece) 1571).The Spanish Army of the Thirty YearsвҖҷ War
* Lorraine White вҖ
The Experience of SpainвҖҷs Early Modern Soldiers: Combat, Welfare and Violence
* Pierre de Bourdeille, ''Gentilezas y bravuconadas de los espaГұoles'' (r/p Mosand, Madrid, 1996) * Marcos de Isaba, ''Cuerpo enfermo de la milicia espaГұola'' Ministry of Defence, Madrid (Brussels, 1589) * Sancho de LondoГұo, ''El discurso sobre la forma de reducir la disciplina militar a mejor y antiguo estado'' Ministry of Defence, Madrid (Brussels, 1589) * Bernardino de Escalante, ''DiГЎlogos del arte militar'' Ministry of Defence, Madrid (1583) * MartГӯn de Eguiluz, Milicia, ''Discurso y Regla militar'' Ministry of Defence, Madrid (pre-1591) * Diego de Salazar, ''Tratado de Re Militari'' Ministry of Defence, Madrid(1590) * SerafГӯn MarГӯa de Soto, ''Conde de Clonard, Album de la infanterГӯa espaГұola'' (1861) * Rene Quatrefages, ''Los Tercios'' (Madrid, ediciones EjГ©rcito, 1983) * InspecciГіn de InfanterГӯa, ''La infanterГӯa en torno al siglo del oro'' (Madrid, ediciones EjГ©rcito, 1993) * Julio Albi de la Cuesta, ''De Pavia a Rocroi: los Tercios de InfanterГӯa espaГұola en los siglos XVI y XVII'' (Madrid, Balkan, 1999) * Enrique MartГӯnez Ruiz, ''Los soldados del Rey'' (Madrid, Actas, 2008) * Pierre Picouet, ''Les Tercios Espagnols 1600вҖ“1660'' (in French вҖ“ Auzielle, LRT, 2010) {{Spanish Empire Infantry units and formations Military units and formations of the early modern period Military units and formations of Spain Military strategy Military tactics Spanish Empire House of Habsburg Military units and formations of the Italian Wars Spanish inventions