Tensiometer (surface tension) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In
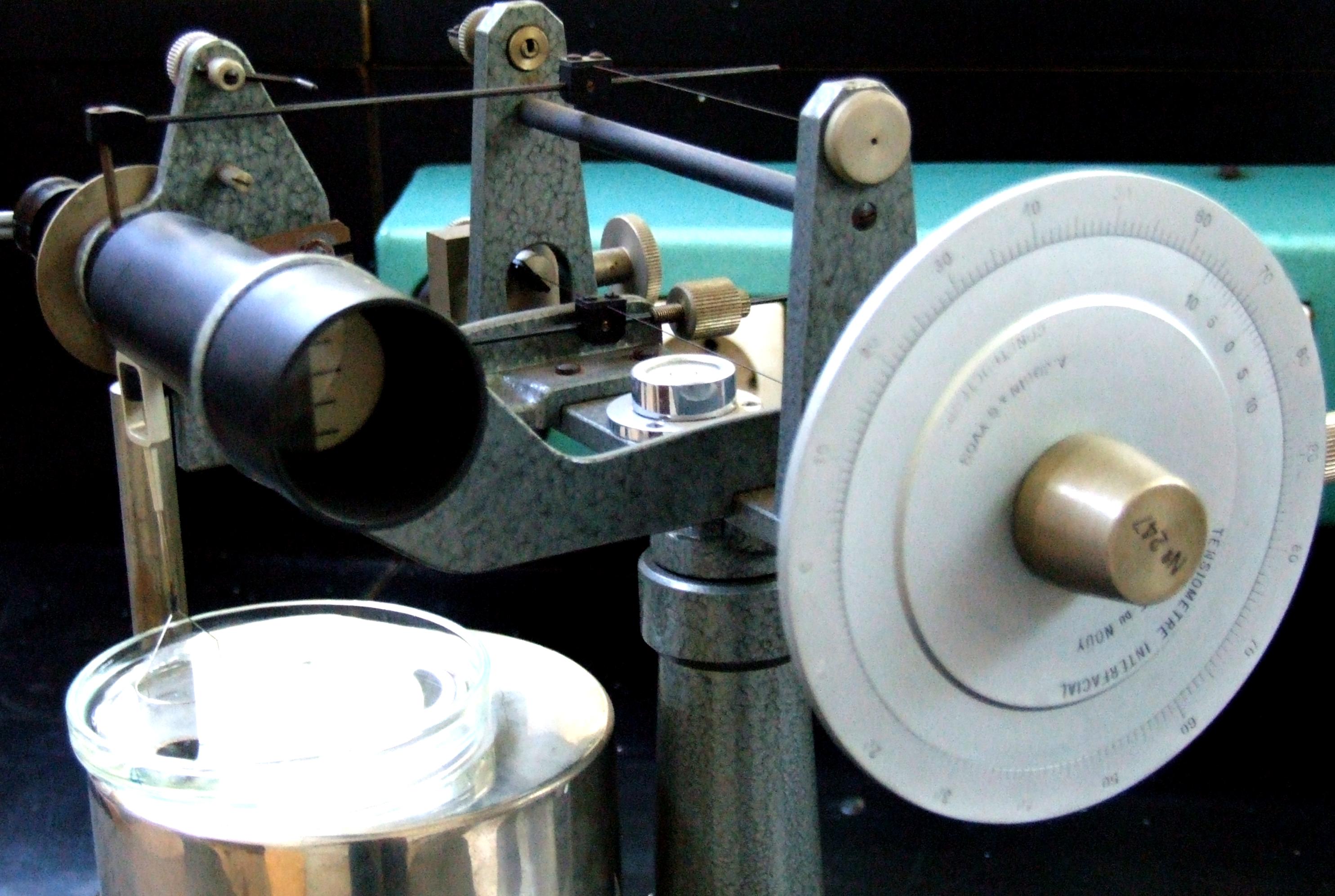

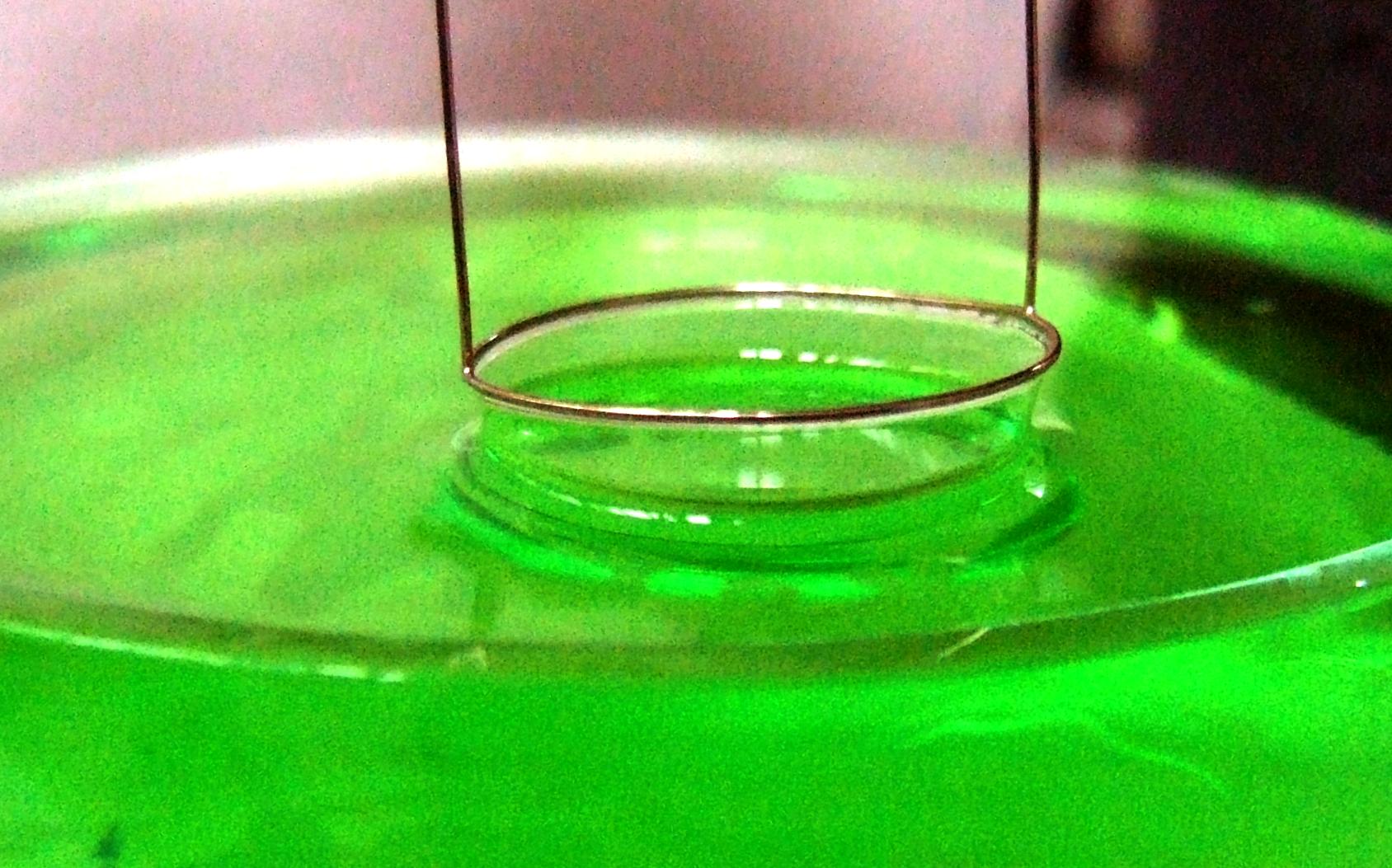 This type of tensiometer uses a platinum ring which is submersed in a liquid. As the ring is pulled out of the liquid, the force required is precisely measured in order to determine the surface tension of the liquid.
The method is well-established as shown by a number of international standards on it such as ASTM D971. This method is widely used for interfacial tension measurement between two liquids but care should be taken to make sure to keep the platinum ring undeformed.
This type of tensiometer uses a platinum ring which is submersed in a liquid. As the ring is pulled out of the liquid, the force required is precisely measured in order to determine the surface tension of the liquid.
The method is well-established as shown by a number of international standards on it such as ASTM D971. This method is widely used for interfacial tension measurement between two liquids but care should be taken to make sure to keep the platinum ring undeformed.
 Due to internal attractive forces of a liquid, air bubbles within the liquids are compressed. The resulting pressure (bubble pressure) rises at a decreasing bubble radius. The bubble pressure method makes use of this bubble pressure which is higher than in the surrounding environment (water). A gas stream is pumped into a capillary that is immersed in a fluid. The resulting bubble at the end of the capillary tip continually becomes bigger in surface; thereby, the bubble radius is decreasing.
The pressure rises to a maximum level. At this point the bubble has achieved its smallest radius (the capillary radius) and begins to form a hemisphere. Beyond this point the bubble quickly increases in size and soon bursts, tearing away from the capillary, thereby allowing a new bubble to develop at the capillary tip. It is during this process that a characteristic pressure pattern develops (see picture), which is evaluated for determining the surface tension.
Because of the easy handling and the low cleaning effort of the capillary, bubble pressure tensiometers are a common alternative for monitoring the detergent concentration in cleaning or electroplating processes.
Due to internal attractive forces of a liquid, air bubbles within the liquids are compressed. The resulting pressure (bubble pressure) rises at a decreasing bubble radius. The bubble pressure method makes use of this bubble pressure which is higher than in the surrounding environment (water). A gas stream is pumped into a capillary that is immersed in a fluid. The resulting bubble at the end of the capillary tip continually becomes bigger in surface; thereby, the bubble radius is decreasing.
The pressure rises to a maximum level. At this point the bubble has achieved its smallest radius (the capillary radius) and begins to form a hemisphere. Beyond this point the bubble quickly increases in size and soon bursts, tearing away from the capillary, thereby allowing a new bubble to develop at the capillary tip. It is during this process that a characteristic pressure pattern develops (see picture), which is evaluated for determining the surface tension.
Because of the easy handling and the low cleaning effort of the capillary, bubble pressure tensiometers are a common alternative for monitoring the detergent concentration in cleaning or electroplating processes.
surface science
Surface science is the study of physical and chemical phenomena that occur at the interface of two phases, including solid–liquid interfaces, solid–gas interfaces, solid–vacuum interfaces, and liquid–gas interfaces. It includes the fiel ...
, a tensiometer is a measuring instrument used to measure the surface tension
Surface tension is the tendency of liquid surfaces at rest to shrink into the minimum surface area possible. Surface tension is what allows objects with a higher density than water such as razor blades and insects (e.g. water striders) to f ...
() of liquid
A liquid is a nearly incompressible fluid that conforms to the shape of its container but retains a (nearly) constant volume independent of pressure. As such, it is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being solid, gas, a ...
s or surfaces. Tensiometers are used in research and development laboratories to determine the surface tension of liquids like coatings, lacquer
Lacquer is a type of hard and usually shiny coating or finish applied to materials such as wood or metal. It is most often made from resin extracted from trees and waxes and has been in use since antiquity.
Asian lacquerware, which may be ca ...
s or adhesive
Adhesive, also known as glue, cement, mucilage, or paste, is any non-metallic substance applied to one or both surfaces of two separate items that binds them together and resists their separation.
The use of adhesives offers certain advant ...
s. A further application field of tensiometers is the monitoring of industrial production
Industrial production is a measure of output of the industrial sector of the economy. The industrial sector includes manufacturing, mining, and utilities. Although these sectors contribute only a small portion of gross domestic product (GDP), the ...
processes like parts cleaning or electroplating
Electroplating, also known as electrochemical deposition or electrodeposition, is a process for producing a metal coating on a solid substrate through the reduction of cations of that metal by means of a direct electric current. The part to be ...
.
Types
Goniometer/Tensiometer
Surface scientists commonly use an opticalgoniometer
A goniometer is an instrument that either measures an angle or allows an object to be rotated to a precise angular position. The term goniometry derives from two Greek words, γωνία (''gōnía'') 'angle' and μέτρον (''métron'') 'me ...
/tensiometer to measure the surface tension
Surface tension is the tendency of liquid surfaces at rest to shrink into the minimum surface area possible. Surface tension is what allows objects with a higher density than water such as razor blades and insects (e.g. water striders) to f ...
and interfacial tension
Surface tension is the tendency of liquid surfaces at rest to shrink into the minimum surface area possible. Surface tension is what allows objects with a higher density than water such as razor blades and insects (e.g. water striders) to ...
of a liquid using the pendant or sessile drop methods. A drop is produced and captured using a CCD camera
A charge-coupled device (CCD) is an integrated circuit containing an array of linked, or coupled, capacitors. Under the control of an external circuit, each capacitor can transfer its electric charge to a neighboring capacitor. CCD sensors are a ...
. The drop profile is subsequently extracted, and sophisticated software routines then fit the theoretical Young-Laplace equation to the experimental drop profile. The surface tension can then be calculated from the fitted parameters. Unlike other methods, this technique requires only a small amount of liquid making it suitable for measuring interfacial tensions of expensive liquids.de Gennes, PG, Brochard-Wyart, F and Quere D, "Capillarity and Wetting Phenomena: Drops, Bubbles, Pearls, Waves", 2004, p58
Du Noüy ring tensiometer

 This type of tensiometer uses a platinum ring which is submersed in a liquid. As the ring is pulled out of the liquid, the force required is precisely measured in order to determine the surface tension of the liquid.
The method is well-established as shown by a number of international standards on it such as ASTM D971. This method is widely used for interfacial tension measurement between two liquids but care should be taken to make sure to keep the platinum ring undeformed.
This type of tensiometer uses a platinum ring which is submersed in a liquid. As the ring is pulled out of the liquid, the force required is precisely measured in order to determine the surface tension of the liquid.
The method is well-established as shown by a number of international standards on it such as ASTM D971. This method is widely used for interfacial tension measurement between two liquids but care should be taken to make sure to keep the platinum ring undeformed.
Wilhelmy plate tensiometer
The Wilhelmy plate tensiometer requires a plate to make contact with the liquid surface. It is widely considered the simplest and most accurate method for surface tension measurement. Due to a large wetted length of the platinum plate, the surface tension reading is typically very stable compared to alternative methods. As an additional benefit, the Wilhelmy plate can also be made from paper for disposable use. For interfacial tension measurements, buoyancy of the probe needs to be taken into account which complicates the measurement.Du Noüy-Padday method
This method uses a rod which is lowered into a test liquid. The rod is then pulled out of the liquid and the force required to pull the rod is precisely measured. The method isn't standardized but is sometimes used. The Du Noüy-Padday rod pull tensiometer will take measurements quickly and will work with liquids with a wide range of viscosities. Interfacial tensions cannot be measured.Bubble pressure tensiometer
See also
*Surface tension
Surface tension is the tendency of liquid surfaces at rest to shrink into the minimum surface area possible. Surface tension is what allows objects with a higher density than water such as razor blades and insects (e.g. water striders) to f ...
* Young-Laplace equation
* Capillary action
*Piezometer
A piezometer is either a device used to measure liquid pressure in a system by measuring the height to which a column of the liquid rises against gravity, or a device which measures the pressure (more precisely, the piezometric head) of groundwat ...
* Pierre Lecomte du Nouy
* Interfacial rheology
References
External links
{{Commonscat-inline, Tensiometer (surface tension) Surface science Laboratory equipment