Tempio Malatestiano on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
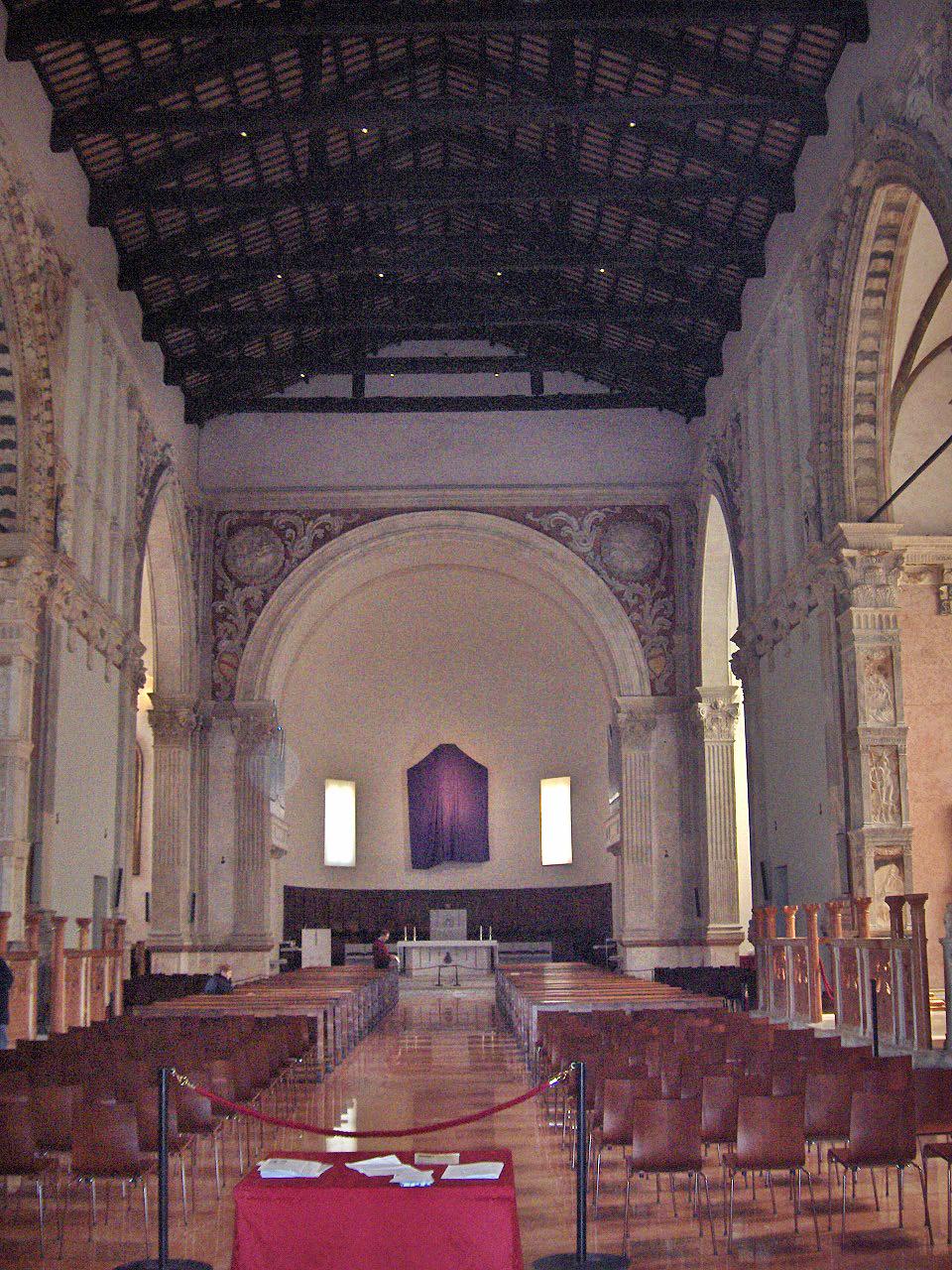
 The Tempio Malatestiano () is the unfinished
The Tempio Malatestiano () is the unfinished

 The church is immediately recognizable from its wide marble façade, decorated by sculptures probably made by Agostino di Duccio and Matteo de' Pasti. Alberti aspired to renew and rival the Roman structures of antiquity, though here his inspiration was drawn from the
The church is immediately recognizable from its wide marble façade, decorated by sculptures probably made by Agostino di Duccio and Matteo de' Pasti. Alberti aspired to renew and rival the Roman structures of antiquity, though here his inspiration was drawn from the
How the Monuments Men Saved Italy's Treasures ''Smithsonian magazine''
/ref>
Orsini Luigi, The Malatesta temple; sixtyfour illustrations, and text (1915).
{{DEFAULTSORT:Malatestiano Buildings and structures completed in 1468 Churches completed in the 1460s 15th-century Roman Catholic church buildings in Italy

 The Tempio Malatestiano () is the unfinished
The Tempio Malatestiano () is the unfinished cathedral
A cathedral is a church (building), church that contains the of a bishop, thus serving as the central church of a diocese, Annual conferences within Methodism, conference, or episcopate. Churches with the function of "cathedral" are usually s ...
church of Rimini
Rimini ( , ; or ; ) is a city in the Emilia-Romagna region of Northern Italy.
Sprawling along the Adriatic Sea, Rimini is situated at a strategically-important north-south passage along the coast at the southern tip of the Po Valley. It is ...
, Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
. Officially named for St. Francis, it takes the popular name from Sigismondo Pandolfo Malatesta
Sigismondo Pandolfo Malatesta (19 June 1417 – 7 October 1468) was an Italian condottiero and nobleman, a member of the House of Malatesta and lord of Rimini and Fano from 1432. He was widely considered by his contemporaries as one of the mos ...
, who commissioned its reconstruction by the famous Renaissance theorist and architect Leon Battista Alberti
Leon Battista Alberti (; 14 February 1404 – 25 April 1472) was an Italian Renaissance humanist author, artist, architect, poet, Catholic priest, priest, linguistics, linguist, philosopher, and cryptography, cryptographer; he epitomised the natu ...
around 1450.
History
San Francesco was originally a thirteenth-century Gothic church belonging to theFranciscan
The Franciscans are a group of related organizations in the Catholic Church, founded or inspired by the Italian saint Francis of Assisi. They include three independent Religious institute, religious orders for men (the Order of Friars Minor bei ...
s. The original church had a rectangular plan without side chapels, with a single nave ending with three apses. The central one was probably frescoed by Giotto
Giotto di Bondone (; – January 8, 1337), known mononymously as Giotto, was an List of Italian painters, Italian painter and architect from Florence during the Late Middle Ages. He worked during the International Gothic, Gothic and Italian Ren ...
, to whom is also attributed the crucifix now housed in the second right chapel.
Malatesta called on Alberti, as his first ecclesiastical architectural work, to transform the building and make it into a kind of personal mausoleum for him and his lover and later his wife, Isotta degli Atti. The execution of the project was handed over to the Veronese
Veronese is the Italian word denoting someone or something from Verona, Italy and may refer to:
* Veronese Riddle, a popular riddle in the Middle Ages
* Veronese (moth), ''Veronese'' (moth), a moth genus in the family Crambidae
* Monte Veronese, ...
Matteo di Andrea de' Pasti, hired at the Estense court. Of Alberti's project, the dome
A dome () is an architectural element similar to the hollow upper half of a sphere. There is significant overlap with the term cupola, which may also refer to a dome or a structure on top of a dome. The precise definition of a dome has been a m ...
that appears in Matteo's foundation medal of 1450—similar to that of the Pantheon of Rome and intended to be among the largest in Italy—was never built. Also the upper part of the façade, which was supposed to include a gable end, was never finished, though it had risen to a considerable height by the winter of 1454, as Malatesta's fortunes declined steeply after his excommunication
Excommunication is an institutional act of religious censure used to deprive, suspend, or limit membership in a religious community or to restrict certain rights within it, in particular those of being in Koinonia, communion with other members o ...
in 1460 and the structure remained as we see it, with its unexecuted east end, at his death in 1466. The two blind arcades at the side of the entrance arch were to house the sarcophagi of Sigismondo Pandolfo and Isotta, which instead are now in the interior.
Works for the renovation of the nave began some five years before those of the exterior shell that encases the church. Marble
Marble is a metamorphic rock consisting of carbonate minerals (most commonly calcite (CaCO3) or Dolomite (mineral), dolomite (CaMg(CO3)2) that have recrystallized under the influence of heat and pressure. It has a crystalline texture, and is ty ...
for the work was taken from the Roman ruins in Sant'Apollinare in Classe (near Ravenna
Ravenna ( ; , also ; ) is the capital city of the Province of Ravenna, in the Emilia-Romagna region of Northern Italy. It was the capital city of the Western Roman Empire during the 5th century until its Fall of Rome, collapse in 476, after which ...
) and in Fano
Fano () is a city and ''comune'' of the province of Pesaro and Urbino in the Marche region of Italy. It is a beach resort southeast of Pesaro, located where the ''Via Flaminia'' reaches the Adriatic Sea. It is the third city in the region by pop ...
. To complete the temple's covering, marble was also taken from headstones in the surrounding cemetery.
Overview

 The church is immediately recognizable from its wide marble façade, decorated by sculptures probably made by Agostino di Duccio and Matteo de' Pasti. Alberti aspired to renew and rival the Roman structures of antiquity, though here his inspiration was drawn from the
The church is immediately recognizable from its wide marble façade, decorated by sculptures probably made by Agostino di Duccio and Matteo de' Pasti. Alberti aspired to renew and rival the Roman structures of antiquity, though here his inspiration was drawn from the triumphal arch
A triumphal arch is a free-standing monumental structure in the shape of an archway with one or more arched passageways, often designed to span a road, and usually standing alone, unconnected to other buildings. In its simplest form, a triumphal ...
, in which his main inspiration was the tripartite Arch of Constantine in Rome. But as Rudolf Wittkower remarked, he drew details (the base, the half-columns, the discs, moldings) from the Arch of Augustus. The large arcades on the sides are reminiscent of the Roman aqueduct
The Romans constructed aqueducts throughout their Republic and later Empire, to bring water from outside sources into cities and towns. Aqueduct water supplied public baths, latrines, fountains, and private households; it also supported min ...
s. In each blind arch is a sarcophagus, a gothic tradition of interment under the exterior side arches of a church.
The entrance portal has a triangular pediment over the door set within the center arch; geometrical decorations fill the tympanum. In the interior, where Matteo de' Pasti took credit as architect in an inscription, under the large arcades on the right side, are seven chapels with the tombs of illustrious Riminese citizens, including that of the philosopher Gemistus Pletho, whose remains were brought back by Sigismondo Pandolfo from his wars in the Balkans. The left side has no chapels (outside is a 16th-century bell tower).
Immediately right of the main door is Sigismondo Pandolfo's sepulchre. The next chapel is dedicated to St. Sigismund, patron of soldiers (Sigismondo Pandolfo was a renowned condottiero
Condottieri (; singular: ''condottiero'' or ''condottiere'') were Italian military leaders active during the Middle Ages and the early modern period. The term originally referred specifically to commanders of mercenary companies, derived from the ...
), and has fine sculptures by Agostino di Duccio. There is also a fresco by Piero della Francesca
Piero della Francesca ( , ; ; ; – 12 October 1492) was an Italian Renaissance painter, Italian painter, mathematician and List of geometers, geometer of the Early Renaissance, nowadays chiefly appreciated for his art. His painting is charact ...
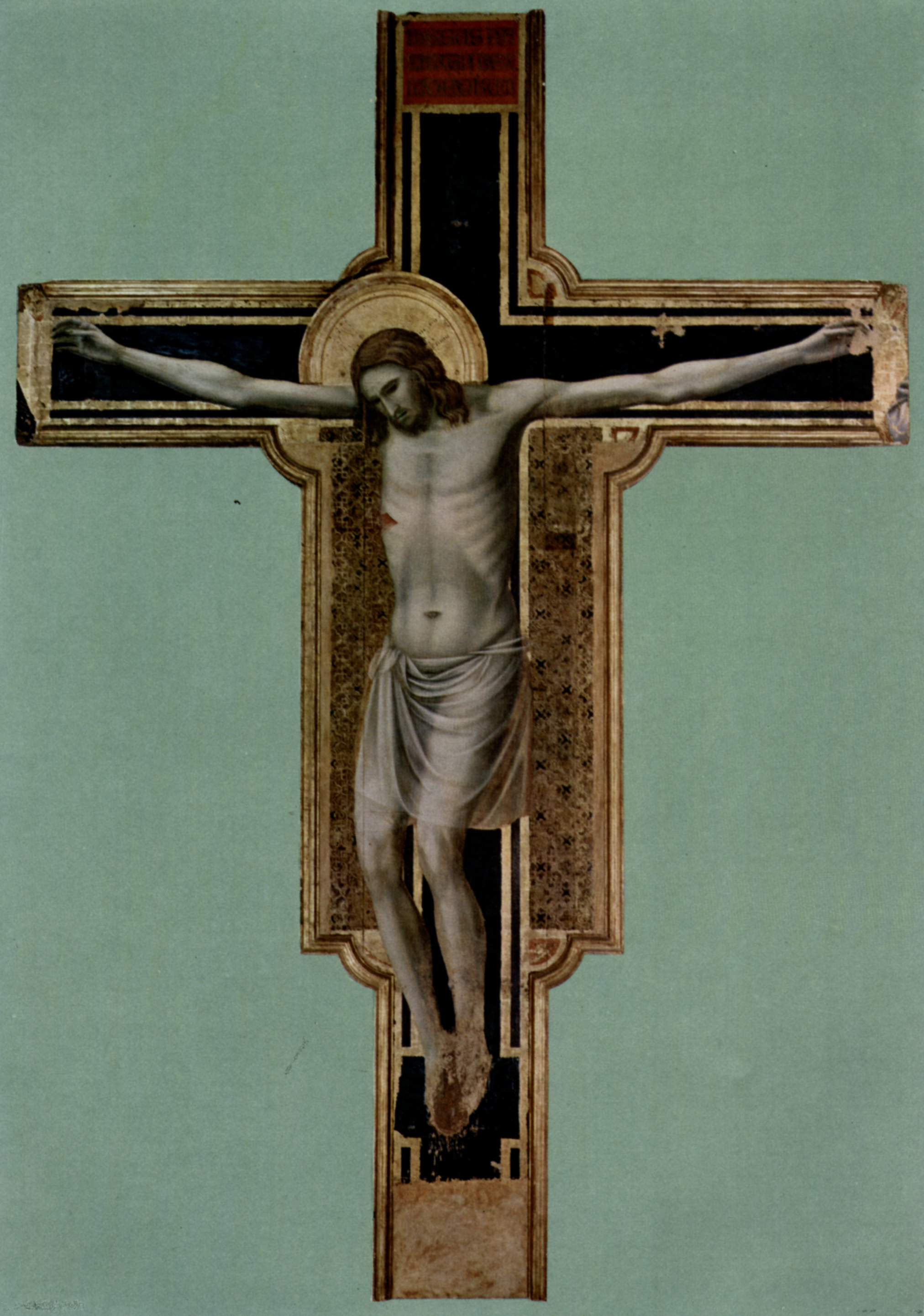
portraying Malatesta kneeling before the saint (1451). The following chapel (Cappella degli Angeli) houses the tomb of Isotta and the Giotto crucifix, allegedly painted during his sojourn in Rimini of 1308–1312.
The next chapel is the Cappella dei Pianeti ("Chapel of the Planets"), dedicated to St. Jerome. The zodiacal figures are by Agostino di Duccio. It houses also an interesting panorama of Rimini as it was in the 15th century. Then comes the Chapel of Liberal Arts, with di Duccio's portrayal of Philosophy, Rhetoric and Grammar. The subsequent Chapel of the Childhood Games houses the tombs of Sigismondo Pandolfo's first wives, Ginevra d'Este and Polissena Sforza, encircled by 61 figures of young angels playing and dancing, again by Agostino di Duccio.
The bodies of some of Malatesta's ancestors are housed in the Cappella della Pietà, with two statues of prophets and ten of sibyl
The sibyls were prophetesses or oracles in Ancient Greece.
The sibyls prophet, prophesied at holy sites.
A sibyl at Delphi has been dated to as early as the eleventh century BC by Pausanias (geographer), PausaniasPausanias 10.12.1 when he desc ...
s. The chapel, like numerous other places in the church, is characterized by the presence of the SI monogram (from the initial of Sigismondo and Isotta's names, or, according to others, the first two letters of the former) sporting a rose, an elephant and three heads.
Evaluation
Due to the strong presence of elements referring to the Malatesta's history, and to Sigismondo Pandolfo himself (in particular, his lover Isotta), the church was considered by some contemporaries to be an exaltation of Paganism.Pope Pius II
Pope Pius II (, ), born Enea Silvio Bartolomeo Piccolomini (; 18 October 1405 – 14 August 1464), was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 19 August 1458 to his death in 1464.
Aeneas Silvius was an author, diplomat, ...
, Sigismondo's deadliest enemy, declared it as "full of pagan gods and profane things".
Destruction and restoration
The church was heavily damaged duringWorld War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, and afterward reconstructed using pieces salvaged from the rubble by men from the Allies-affiliated Monuments, Fine Arts, and Archives unit./ref>
Sources
*References
External links
Orsini Luigi, The Malatesta temple; sixtyfour illustrations, and text (1915).
{{DEFAULTSORT:Malatestiano Buildings and structures completed in 1468 Churches completed in the 1460s 15th-century Roman Catholic church buildings in Italy
Rimini
Rimini ( , ; or ; ) is a city in the Emilia-Romagna region of Northern Italy.
Sprawling along the Adriatic Sea, Rimini is situated at a strategically-important north-south passage along the coast at the southern tip of the Po Valley. It is ...
Roman Catholic churches in Rimini
Renaissance architecture in Emilia-Romagna
Sigismondo Pandolfo Malatesta
Cathedrals in Emilia-Romagna
Leon Battista Alberti church buildings