Tempered Steel on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Tempering is a process of heat treating, which is used to increase the
Tempering is a process of heat treating, which is used to increase the
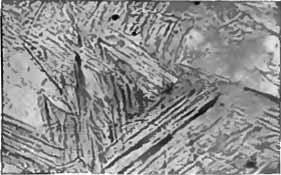 Tempering is a
Tempering is a
 Tempering is a process of heat treating, which is used to increase the
Tempering is a process of heat treating, which is used to increase the toughness
In materials science and metallurgy, toughness is the ability of a material to absorb energy and plastically deform without fracturing.iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
-based alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which in most cases at least one is a metal, metallic element, although it is also sometimes used for mixtures of elements; herein only metallic alloys are described. Metallic alloys often have prop ...
s. Tempering is usually performed after hardening, to reduce some of the excess hardness
In materials science, hardness (antonym: softness) is a measure of the resistance to plastic deformation, such as an indentation (over an area) or a scratch (linear), induced mechanically either by Pressing (metalworking), pressing or abrasion ...
, and is done by heating the metal to some temperature below the critical point for a certain period of time, then allowing it to cool in still air. The exact temperature determines the amount of hardness removed, and depends on both the specific composition of the alloy and on the desired properties in the finished product. For instance, very hard tools
A tool is an object that can extend an individual's ability to modify features of the surrounding environment or help them accomplish a particular task. Although many animals use simple tools, only human beings, whose use of stone tools dates ...
are often tempered at low temperatures, while springs are tempered at much higher temperatures.
Introduction
 Tempering is a
Tempering is a heat treatment
Heat treating (or heat treatment) is a group of industrial, thermal and metalworking processes used to alter the physical, and sometimes chemical, properties of a material. The most common application is metallurgical. Heat treatments are a ...
technique applied to ferrous alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which in most cases at least one is a metal, metallic element, although it is also sometimes used for mixtures of elements; herein only metallic alloys are described. Metallic alloys often have prop ...
s, such as steel
Steel is an alloy of iron and carbon that demonstrates improved mechanical properties compared to the pure form of iron. Due to steel's high Young's modulus, elastic modulus, Yield (engineering), yield strength, Fracture, fracture strength a ...
or cast iron
Cast iron is a class of iron–carbon alloys with a carbon content of more than 2% and silicon content around 1–3%. Its usefulness derives from its relatively low melting temperature. The alloying elements determine the form in which its car ...
, to achieve greater toughness
In materials science and metallurgy, toughness is the ability of a material to absorb energy and plastically deform without fracturing.hardness
In materials science, hardness (antonym: softness) is a measure of the resistance to plastic deformation, such as an indentation (over an area) or a scratch (linear), induced mechanically either by Pressing (metalworking), pressing or abrasion ...
of the alloy. The reduction in hardness is usually accompanied by an increase in ductility
Ductility refers to the ability of a material to sustain significant plastic Deformation (engineering), deformation before fracture. Plastic deformation is the permanent distortion of a material under applied stress, as opposed to elastic def ...
, thereby decreasing the brittleness
A material is brittle if, when subjected to stress (physics), stress, it fractures with little elastic deformation and without significant plastic deformation. Brittle materials absorb relatively little energy prior to fracture, even those of h ...
of the metal. Tempering is usually performed after quenching
In materials science, quenching is the rapid cooling of a workpiece in water, gas, oil, polymer, air, or other fluids to obtain certain material properties. A type of heat treating, quenching prevents undesired low-temperature processes, suc ...
, which is rapid cooling
Cooling is removal of heat, usually resulting in a lower temperature and/or Phase transition, phase change. Temperature lowering achieved by any other means may also be called cooling.
The Heat transfer, transfer of Internal energy, thermal energ ...
of the metal to put it in its hardest state. Tempering is accomplished by controlled heating of the quenched workpiece to a temperature below its "lower critical temperature
Critical or Critically may refer to:
*Critical, or critical but stable, medical states
**Critical, or intensive care medicine
*Critical juncture, a discontinuous change studied in the social sciences.
*Critical Software, a company specializing in ...
". This is also called the lower transformation temperature or lower arrest (A1) temperature: the temperature at which the crystalline phases of the alloy, called ferrite and cementite
Cementite (or iron carbide) is a compound of iron and carbon, more precisely an intermediate transition metal carbide with the formula Fe3C. By weight, it is 6.67% carbon and 93.3% iron. It has an orthorhombic crystal structure. It is a hard, b ...
, begin combining to form a single-phase solid solution
A solid solution, a term popularly used for metals, is a homogeneous mixture of two compounds in solid state and having a single crystal structure. Many examples can be found in metallurgy, geology, and solid-state chemistry. The word "solutio ...
referred to as austenite. Heating above this temperature is avoided, so as not to destroy the very-hard, quenched microstructure, called martensite
Martensite is a very hard form of steel crystalline structure. It is named after German metallurgist Adolf Martens. By analogy the term can also refer to any crystal structure that is formed by diffusionless transformation.
Properties
Mar ...
.''Steel metallurgy for the non-metallurgist'' By John D. Verhoeven - ASM International 2007 Page 99-105
Precise control of time and temperature during the tempering process is crucial to achieve the desired balance of physical properties. Low tempering temperatures may only relieve the internal stresses, decreasing brittleness while maintaining a majority of the hardness. Higher tempering temperatures tend to produce a greater reduction in the hardness, sacrificing some yield strength
In materials science and engineering, the yield point is the point on a stress–strain curve that indicates the limit of elastic behavior and the beginning of plastic behavior. Below the yield point, a material will deform elastically and w ...
and tensile strength
Ultimate tensile strength (also called UTS, tensile strength, TS, ultimate strength or F_\text in notation) is the maximum stress that a material can withstand while being stretched or pulled before breaking. In brittle materials, the ultimate ...
for an increase in elasticity and plasticity. However, in some low alloy steel
Alloy steel is steel that is Alloy, alloyed with a variety of elements in amounts between 1.0% and 50% by weight, typically to improve its List of materials properties#Mechanical properties, mechanical properties.
Types
Alloy steels divide into ...
s, containing other elements like chromium
Chromium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in Group 6 element, group 6. It is a steely-grey, Luster (mineralogy), lustrous, hard, and brittle transition metal.
Chromium ...
and molybdenum
Molybdenum is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mo (from Neo-Latin ''molybdaenum'') and atomic number 42. The name derived from Ancient Greek ', meaning lead, since its ores were confused with lead ores. Molybdenum minerals hav ...
, tempering at low temperatures may produce an increase in hardness, while at higher temperatures the hardness will decrease. Many steels with high concentrations of these alloying elements behave like precipitation hardening alloys, which produces the opposite effects under the conditions found in quenching and tempering, and are referred to as maraging steels.
In carbon steel
Carbon steel is a steel with carbon content from about 0.05 up to 2.1 percent by weight. The definition of carbon steel from the American Iron and Steel Institute (AISI) states:
* no minimum content is specified or required for chromium, cobalt ...
s, tempering alters the size and distribution of carbide
In chemistry, a carbide usually describes a compound composed of carbon and a metal. In metallurgy, carbiding or carburizing is the process for producing carbide coatings on a metal piece.
Interstitial / Metallic carbides
The carbides of th ...
s in the martensite, forming a microstructure called "tempered martensite". Tempering is also performed on normalized steels and cast irons, to increase ductility, machinability, and impact strength. Steel is usually tempered evenly, called "through tempering," producing a nearly uniform hardness, but it is sometimes heated unevenly, referred to as "differential tempering," producing a variation in hardness.
History
Tempering is an ancient heat-treating technique. The oldest known example of tempered martensite is a pick axe which was found inGalilee
Galilee (; ; ; ) is a region located in northern Israel and southern Lebanon consisting of two parts: the Upper Galilee (, ; , ) and the Lower Galilee (, ; , ).
''Galilee'' encompasses the area north of the Mount Carmel-Mount Gilboa ridge and ...
, dating from around 1200 to 1100 BC. The process was used throughout the ancient world, from Asia to Europe and Africa. Many different methods and cooling baths for quenching have been attempted during ancient times, from quenching in urine, blood, or metals like mercury or lead, but the process of tempering has remained relatively unchanged over the ages. Tempering was often confused with quenching and, often, the term was used to describe both techniques. In 1889, Sir William Chandler Roberts-Austen wrote, "There is still so much confusion between the words "temper," "tempering," and "hardening," in the writings of even eminent authorities, that it is well to keep these old definitions carefully in mind. I shall employ the word tempering in the same sense as softening."
Terminology
Inmetallurgy
Metallurgy is a domain of materials science and engineering that studies the physical and chemical behavior of metallic elements, their inter-metallic compounds, and their mixtures, which are known as alloys.
Metallurgy encompasses both the ...
, one may encounter many terms that have very specific meanings within the field, but may seem rather vague when viewed from the outside. Terms such as "hardness," "impact resistance," "toughness," and "strength" can carry many different connotations, making it sometimes difficult to discern the specific meaning. Some of the terms encountered, and their specific definitions are:
* Strength – Resistance to permanent deformation and tearing. Strength, in metallurgy, is still a rather vague term, so is usually divided into yield strength
In materials science and engineering, the yield point is the point on a stress–strain curve that indicates the limit of elastic behavior and the beginning of plastic behavior. Below the yield point, a material will deform elastically and w ...
(strength beyond which deformation becomes permanent), tensile strength
Ultimate tensile strength (also called UTS, tensile strength, TS, ultimate strength or F_\text in notation) is the maximum stress that a material can withstand while being stretched or pulled before breaking. In brittle materials, the ultimate ...
(the ultimate tearing strength), shear strength (resistance to transverse, or cutting forces), and compressive strength
In mechanics, compressive strength (or compression strength) is the capacity of a material or Structural system, structure to withstand Structural load, loads tending to reduce size (Compression (physics), compression). It is opposed to ''tensil ...
(resistance to elastic shortening under a load).
* Toughness
In materials science and metallurgy, toughness is the ability of a material to absorb energy and plastically deform without fracturing.fracture
Fracture is the appearance of a crack or complete separation of an object or material into two or more pieces under the action of stress (mechanics), stress. The fracture of a solid usually occurs due to the development of certain displacemen ...
, as measured by the Charpy test. Toughness often increases as strength decreases, because a material that bends is less likely to break.
* Hardness
In materials science, hardness (antonym: softness) is a measure of the resistance to plastic deformation, such as an indentation (over an area) or a scratch (linear), induced mechanically either by Pressing (metalworking), pressing or abrasion ...
– A surface's resistance to scratching, abrasion, or indentation. In conventional metal alloys, there is a linear relation between indentation hardness and tensile strength, which eases the measurement of the latter.
* Brittleness
A material is brittle if, when subjected to stress (physics), stress, it fractures with little elastic deformation and without significant plastic deformation. Brittle materials absorb relatively little energy prior to fracture, even those of h ...
– Brittleness describes a material's tendency to break before bending or deforming either elastically or plastically. Brittleness increases with decreased toughness, but is greatly affected by internal stresses as well.
* Plasticity – The ability to mold, bend or deform in a manner that does not spontaneously return to its original shape. This is proportional to the ductility
Ductility refers to the ability of a material to sustain significant plastic Deformation (engineering), deformation before fracture. Plastic deformation is the permanent distortion of a material under applied stress, as opposed to elastic def ...
or malleability
Ductility refers to the ability of a material to sustain significant plastic Deformation (engineering), deformation before fracture. Plastic deformation is the permanent distortion of a material under applied stress, as opposed to elastic def ...
of the substance.
* Elasticity – Also called flexibility, this is the ability to deform, bend, compress, or stretch and return to the original shape once the external stress is removed. Elasticity is inversely related to the Young's modulus
Young's modulus (or the Young modulus) is a mechanical property of solid materials that measures the tensile or compressive stiffness when the force is applied lengthwise. It is the modulus of elasticity for tension or axial compression. Youn ...
of the material.
* Impact resistance
In materials science and metallurgy, toughness is the ability of a material to absorb energy and plastically deform without fracturing.Wear resistance – Usually synonymous with hardness, this is resistance to
 If steel has been freshly ground, sanded, or polished, it will form an
If steel has been freshly ground, sanded, or polished, it will form an
 Differential tempering is a method of providing different amounts of temper to different parts of the steel. The method is often used in bladesmithing, for making knives and
Differential tempering is a method of providing different amounts of temper to different parts of the steel. The method is often used in bladesmithing, for making knives and
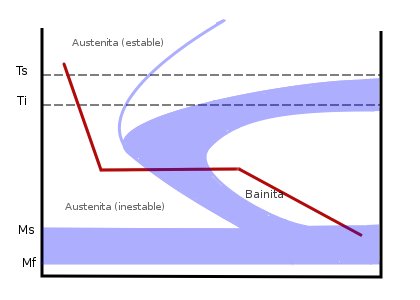 Austempering is a technique used to form pure bainite, a transitional microstructure found between pearlite and martensite. In normalizing, both upper and lower bainite are usually found mixed with pearlite. To avoid the formation of pearlite or martensite, the steel is quenched in a bath of molten metals or salts. This quickly cools the steel past the point where pearlite can form and into the bainite-forming range. The steel is then held at the bainite-forming temperature, beyond the point where the temperature reaches an equilibrium, until the bainite fully forms. The steel is then removed from the bath and allowed to air-cool, without the formation of either pearlite or martensite.
Depending on the holding temperature, austempering can produce either upper or lower bainite. Upper bainite is a laminate structure formed at temperatures typically above and is a much tougher microstructure. Lower bainite is a needle-like structure, produced at temperatures below 350 °C, and is stronger but much more brittle. In either case, austempering produces greater strength and toughness for a given hardness, which is determined mostly by composition rather than cooling speed, and reduced internal stresses which could lead to breakage. This produces steel with superior impact resistance. Modern punches and chisels are often austempered. Because austempering does not produce martensite, the steel does not require further tempering.
Austempering is a technique used to form pure bainite, a transitional microstructure found between pearlite and martensite. In normalizing, both upper and lower bainite are usually found mixed with pearlite. To avoid the formation of pearlite or martensite, the steel is quenched in a bath of molten metals or salts. This quickly cools the steel past the point where pearlite can form and into the bainite-forming range. The steel is then held at the bainite-forming temperature, beyond the point where the temperature reaches an equilibrium, until the bainite fully forms. The steel is then removed from the bath and allowed to air-cool, without the formation of either pearlite or martensite.
Depending on the holding temperature, austempering can produce either upper or lower bainite. Upper bainite is a laminate structure formed at temperatures typically above and is a much tougher microstructure. Lower bainite is a needle-like structure, produced at temperatures below 350 °C, and is stronger but much more brittle. In either case, austempering produces greater strength and toughness for a given hardness, which is determined mostly by composition rather than cooling speed, and reduced internal stresses which could lead to breakage. This produces steel with superior impact resistance. Modern punches and chisels are often austempered. Because austempering does not produce martensite, the steel does not require further tempering.
A thorough discussion of tempering processes
{{Authority control Metal heat treatments
erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as Surface runoff, water flow or wind) that removes soil, Rock (geology), rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust#Crust, Earth's crust and then sediment transport, tran ...
, ablation
Ablation ( – removal) is the removal or destruction of something from an object by vaporization, chipping, erosion, erosive processes, or by other means. Examples of ablative materials are described below, including spacecraft material for as ...
, spalling
Spall are fragments of a material that are broken off a larger solid body. It can be produced by a variety of mechanisms, including as a result of projectile impact, corrosion, weathering, cavitation, or excessive rolling pressure (as in a ball ...
, or galling.
* Structural integrity – The ability to withstand a maximum-rated load while resisting fracture, resisting fatigue
Fatigue is a state of tiredness (which is not sleepiness), exhaustion or loss of energy. It is a signs and symptoms, symptom of any of various diseases; it is not a disease in itself.
Fatigue (in the medical sense) is sometimes associated wit ...
, and producing a minimal amount of flexing or deflection, to provide a maximum service life.
Carbon steel
Very few metals react to heat treatment in the same manner, or to the same extent, thatcarbon steel
Carbon steel is a steel with carbon content from about 0.05 up to 2.1 percent by weight. The definition of carbon steel from the American Iron and Steel Institute (AISI) states:
* no minimum content is specified or required for chromium, cobalt ...
does, and carbon-steel heat-treating behavior can vary radically depending on alloying elements. Steel can be softened to a very malleable
Ductility refers to the ability of a material to sustain significant plastic deformation before fracture. Plastic deformation is the permanent distortion of a material under applied stress, as opposed to elastic deformation, which is reversi ...
state through annealing, or it can be hardened to a state as hard and brittle as glass by quenching
In materials science, quenching is the rapid cooling of a workpiece in water, gas, oil, polymer, air, or other fluids to obtain certain material properties. A type of heat treating, quenching prevents undesired low-temperature processes, suc ...
. However, in its hardened state, steel is usually far too brittle, lacking the fracture toughness
In materials science, fracture toughness is the critical stress intensity factor of a sharp Fracture, crack where propagation of the crack suddenly becomes rapid and unlimited. It is a material property that quantifies its ability to resist crac ...
to be useful for most applications. Tempering is a method used to decrease the hardness, thereby increasing the ductility of the quenched steel, to impart some springiness and malleability to the metal. This allows the metal to bend before breaking. Depending on how much temper is imparted to the steel, it may bend elastically (the steel returns to its original shape once the load is removed), or it may bend plastically (the steel does not return to its original shape, resulting in permanent deformation), before fracturing. Tempering is used to precisely balance the mechanical properties of the metal, such as shear strength, yield strength
In materials science and engineering, the yield point is the point on a stress–strain curve that indicates the limit of elastic behavior and the beginning of plastic behavior. Below the yield point, a material will deform elastically and w ...
, hardness
In materials science, hardness (antonym: softness) is a measure of the resistance to plastic deformation, such as an indentation (over an area) or a scratch (linear), induced mechanically either by Pressing (metalworking), pressing or abrasion ...
, ductility
Ductility refers to the ability of a material to sustain significant plastic Deformation (engineering), deformation before fracture. Plastic deformation is the permanent distortion of a material under applied stress, as opposed to elastic def ...
, and tensile strength
Ultimate tensile strength (also called UTS, tensile strength, TS, ultimate strength or F_\text in notation) is the maximum stress that a material can withstand while being stretched or pulled before breaking. In brittle materials, the ultimate ...
, to achieve any number of a combination of properties, making the steel useful for a wide variety of applications. Tools such as hammers and wrenches require good resistance to abrasion, impact resistance, and resistance to deformation. Springs do not require as much wear resistance, but must deform elastically without breaking. Automotive parts tend to be a little less strong, but need to deform plastically before breaking.
Except in rare cases where maximum hardness or wear resistance is needed, such as the untempered steel used for files, quenched steel is almost always tempered to some degree. However, steel is sometimes annealed through a process called normalizing, leaving the steel only partially softened. Tempering is sometimes used on normalized steels to further soften it, increasing the malleability and machinability for easier metalworking
Metalworking is the process of shaping and reshaping metals in order to create useful objects, parts, assemblies, and large scale structures. As a term, it covers a wide and diverse range of processes, skills, and tools for producing objects on e ...
. Tempering may also be used on welded steel, to relieve some of the stresses and excess hardness created in the heat affected zone around the weld.
Quenched steel
Tempering is most often performed on steel that has been heated above its upper critical (A3) temperature and then quickly cooled, in a process calledquenching
In materials science, quenching is the rapid cooling of a workpiece in water, gas, oil, polymer, air, or other fluids to obtain certain material properties. A type of heat treating, quenching prevents undesired low-temperature processes, suc ...
, using methods such as immersing the hot steel in water, oil, or forced-air. The quenched steel, being placed in or very near its hardest possible state, is then tempered to incrementally decrease the hardness to a point more suitable for the desired application. The hardness of the quenched steel depends on both cooling speed and on the composition of the alloy. Steel with a high carbon content will reach a much harder state than steel with a low carbon content. Likewise, tempering high-carbon steel to a certain temperature will produce steel that is considerably harder than low-carbon steel that is tempered at the same temperature. The amount of time held at the tempering temperature also has an effect. Tempering at a slightly elevated temperature for a shorter time may produce the same effect as tempering at a lower temperature for a longer time. Tempering times vary, depending on the carbon content, size, and desired application of the steel, but typically range from a few minutes to a few hours.
Tempering quenched steel at very low temperatures, between , will usually not have much effect other than a slight relief of some of the internal stresses and a decrease in brittleness. Tempering at higher temperatures, from , will produce a slight reduction in hardness, but will primarily relieve much of the internal stresses. In some steels with low alloy content, tempering in the range of causes a decrease in ductility and an increase in brittleness, and is referred to as the "tempered martensite embrittlement" (TME) range. Except in the case of blacksmithing, this range is usually avoided. Steel requiring more strength than toughness, such as tools, are usually not tempered above . Instead, a variation in hardness is usually produced by varying only the tempering time. When increased toughness is desired at the expense of strength, higher tempering temperatures, from , are used. Tempering at even higher temperatures, between , will produce excellent toughness, but at a serious reduction in strength and hardness. At , the steel may experience another stage of embrittlement, called "temper embrittlement" (TE), which occurs if the steel is held within the temperature range of temper embrittlement for too long. When heating above this temperature, the steel will usually not be held for any amount of time, and quickly cooled to avoid temper embrittlement.
Normalized steel
Steel that has been heated above its upper critical temperature and then cooled in standing air is called normalized steel. Normalized steel consists of pearlite,martensite
Martensite is a very hard form of steel crystalline structure. It is named after German metallurgist Adolf Martens. By analogy the term can also refer to any crystal structure that is formed by diffusionless transformation.
Properties
Mar ...
, and sometimes bainite grains, mixed together within the microstructure. This produces steel that is much stronger than full-annealed steel, and much tougher than tempered quenched steel. However, added toughness is sometimes needed at a reduction in strength. Tempering provides a way to carefully decrease the hardness of the steel, thereby increasing the toughness to a more desirable point. Cast steel is often normalized rather than annealed, to decrease the amount of distortion that can occur. Tempering can further decrease the hardness, increasing the ductility to a point more like annealed steel. Tempering is often used on carbon steels, producing much the same results. The process, called "normalize and temper", is used frequently on steels such as 1045 carbon steel, or most other steels containing 0.35 to 0.55% carbon. These steels are usually tempered after normalizing, to increase the toughness and relieve internal stresses. This can make the metal more suitable for its intended use and easier to machine
A machine is a physical system that uses power to apply forces and control movement to perform an action. The term is commonly applied to artificial devices, such as those employing engines or motors, but also to natural biological macromol ...
.
Welded steel
Steel that has been arc welded, gas welded, or welded in any other manner besides forge welded, is affected in a localized area by the heat from the welding process. This localized area, called the heat-affected zone (HAZ), consists of steel that varies considerably in hardness, from normalized steel to steel nearly as hard as quenched steel near the edge of this heat-affected zone. Thermal contraction from the uneven heating, solidification, and cooling creates internal stresses in the metal, both within and surrounding the weld. Tempering is sometimes used in place of stress relieving (even heating and cooling of the entire object to just below the A1 temperature) to both reduce the internal stresses and to decrease the brittleness around the weld. Localized tempering is often used on welds when the construction is too large, intricate, or otherwise too inconvenient to heat the entire object evenly. Tempering temperatures for this purpose are generally around and .Quench and self-temper
Modernreinforcing bar
Rebar (short for reinforcement bar or reinforcing bar), known when massed as reinforcing steel or steel reinforcement, is a Tension (physics), tension device added to concrete to form ''reinforced concrete'' and reinforced masonry structures to ...
of 500 MPa strength can be made from expensive microalloyed steel
Microalloyed steel is a type of alloy steel that contains small amounts of alloying elements (0.05 to 0.15%), including niobium, vanadium, titanium, molybdenum, zirconium, boron, and rare-earth metals. They are used to refine the grain microstructu ...
or by a quench and self-temper (QST) process. After the bar exits the final rolling pass, where the final shape of the bar is applied, the bar is then sprayed with water which quenches the outer surface of the bar. The bar speed and the amount of water are carefully controlled in order to leave the core of the bar unquenched. The hot core then tempers the already quenched outer part, leaving a bar with high strength but with a certain degree of ductility too.
Blacksmithing
Tempering was originally a process used and developed by blacksmiths (forgers of iron). The process was most likely developed by theHittites
The Hittites () were an Anatolian peoples, Anatolian Proto-Indo-Europeans, Indo-European people who formed one of the first major civilizations of the Bronze Age in West Asia. Possibly originating from beyond the Black Sea, they settled in mo ...
of Anatolia
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
(modern-day Turkey), in the twelfth or eleventh century BC. Without knowledge of metallurgy, tempering was originally devised through a trial-and-error method.
Because few methods of precisely measuring temperature existed until modern times, the temperature was usually judged by watching the tempering colors of the metal. Tempering often consisted of heating above a charcoal or coal forge
A forge is a type of hearth used for heating metals, or the workplace (smithy) where such a hearth is located. The forge is used by the smith to heat a piece of metal to a temperature at which it becomes easier to shape by forging, or to the ...
, or by fire, so holding the work at exactly the right temperature for the correct amount of time was usually not possible. Tempering was usually performed by slowly, evenly overheating the metal, as judged by the color, and then immediately cooling, either in open air or by immersing it in water. This produced much the same effect as heating at the proper temperature for the right amount of time, and avoided embrittlement by tempering within a short time period. However, although tempering-color guides exist, this method of tempering usually requires a good amount of practice to perfect, because the final outcome depends on many factors, including the composition of the steel, the speed at which it was heated, the type of heat source (oxidizing
Redox ( , , reduction–oxidation or oxidation–reduction) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of the reactants change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is ...
or carburizing), the cooling rate, oil films or impurities on the surface, and many other circumstances which vary from smith to smith or even from job to job. The thickness of the steel also plays a role. With thicker items, it becomes easier to heat only the surface to the right temperature, before the heat can penetrate through. However, very thick items may not be able to harden all the way through during quenching.
Tempering colors
oxide
An oxide () is a chemical compound containing at least one oxygen atom and one other element in its chemical formula. "Oxide" itself is the dianion (anion bearing a net charge of −2) of oxygen, an O2− ion with oxygen in the oxidation st ...
layer on its surface when heated. As the temperature of the steel is increased, the thickness of the iron oxide
An iron oxide is a chemical compound composed of iron and oxygen. Several iron oxides are recognized. Often they are non-stoichiometric. Ferric oxyhydroxides are a related class of compounds, perhaps the best known of which is rust.
Iron ...
will also increase. Although iron oxide is not normally transparent, such thin layers do allow light to pass through, reflecting off both the upper and lower surfaces of the layer. This causes a phenomenon called thin-film interference
Thin-film interference is a natural phenomenon in which light waves reflected by the upper and lower boundaries of a thin film Interference (wave propagation), interfere with one another, increasing reflection at some wavelengths and decreasing it ...
, which produces colors on the surface. As the thickness of this layer increases with temperature, it causes the colors to change from a very light yellow, to brown, to purple, and then to blue. These colors appear at very precise temperatures and provide the blacksmith with a very accurate gauge for measuring the temperature. The various colors, their corresponding temperatures, and some of their uses are:
* Faint-yellow – – gravers, razors, scrapers
* Light-straw – – rock drills, reamers, metal-cutting saws
* Dark-straw – – scribers, planer blades
* Brown – – taps, dies, drill bits, hammers, cold chisels
* Purple – – surgical tools, punches, stone carving tools
* Dark blue – – screwdrivers, wrenches
* Light blue – – springs, wood-cutting saws
* Grey-blue – and higher – structural steel
For carbon steel, beyond the grey-blue color the iron oxide loses its transparency, and the temperature can no longer be judged in this way, although other alloys like stainless steel may produce a much broader range including golds, teals, and magentas. The layer will also increase in thickness as time passes, which is another reason overheating and immediate cooling is used. Steel in a tempering oven, held at for a long time, will begin to turn brown, purple, or blue, even though the temperature did not exceed that needed to produce a light-straw color. Oxidizing
Redox ( , , reduction–oxidation or oxidation–reduction) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of the reactants change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is ...
or carburizing heat sources may also affect the final result. The iron oxide layer, unlike rust
Rust is an iron oxide, a usually reddish-brown oxide formed by the reaction of iron and oxygen in the catalytic presence of water or air moisture. Rust consists of hydrous iron(III) oxides (Fe2O3·nH2O) and iron(III) oxide-hydroxide (FeO(OH) ...
, also protects the steel from corrosion through passivation.
Differential tempering
 Differential tempering is a method of providing different amounts of temper to different parts of the steel. The method is often used in bladesmithing, for making knives and
Differential tempering is a method of providing different amounts of temper to different parts of the steel. The method is often used in bladesmithing, for making knives and sword
A sword is an edged and bladed weapons, edged, bladed weapon intended for manual cutting or thrusting. Its blade, longer than a knife or dagger, is attached to a hilt and can be straight or curved. A thrusting sword tends to have a straighter ...
s, to provide a very hard edge while softening the spine or center of the blade. This increased the toughness while maintaining a very hard, sharp, impact-resistant edge, helping to prevent breakage. This technique was more often found in Europe, as opposed to the differential hardening
Differential heat treatment (also called selective heat treatment or local heat treatment) is a technique used during heat treating of steel to harden or soften certain areas of an object, creating a difference in hardness between these areas. Ther ...
techniques more common in Asia, such as in Japanese swordsmithing.
Differential tempering consists of applying heat to only a portion of the blade, usually the spine, or the center of double-edged blades. For single-edged blades, the heat, often in the form of a flame or a red-hot bar, is applied to the spine of the blade only. The blade is then carefully watched as the tempering colors form and slowly creep toward the edge. The heat is then removed before the light-straw color reaches the edge. The colors will continue to move toward the edge for a short time after the heat is removed, so the smith typically removes the heat a little early, so that the pale yellow just reaches the edge, and travels no farther. A similar method is used for double-edged blades, but the heat source is applied to the center of the blade, allowing the colors to creep out toward each edge.
Interrupted quenching
Interrupted quenching methods are often referred to as tempering, although the processes are very different from traditional tempering. These methods consist of quenching to a specific temperature that is above the martensite start (Ms) temperature, and then holding at that temperature for extended amounts of time. Depending on the temperature and the amount of time, this allows either pure bainite to form, or holds off forming the martensite until much of the internal stresses relax. These methods are known as austempering and martempering.''Elements of metallurgy and engineering alloys'' By Flake C. Campbell - ASM International 2008 Page 195-196Austempering
 Austempering is a technique used to form pure bainite, a transitional microstructure found between pearlite and martensite. In normalizing, both upper and lower bainite are usually found mixed with pearlite. To avoid the formation of pearlite or martensite, the steel is quenched in a bath of molten metals or salts. This quickly cools the steel past the point where pearlite can form and into the bainite-forming range. The steel is then held at the bainite-forming temperature, beyond the point where the temperature reaches an equilibrium, until the bainite fully forms. The steel is then removed from the bath and allowed to air-cool, without the formation of either pearlite or martensite.
Depending on the holding temperature, austempering can produce either upper or lower bainite. Upper bainite is a laminate structure formed at temperatures typically above and is a much tougher microstructure. Lower bainite is a needle-like structure, produced at temperatures below 350 °C, and is stronger but much more brittle. In either case, austempering produces greater strength and toughness for a given hardness, which is determined mostly by composition rather than cooling speed, and reduced internal stresses which could lead to breakage. This produces steel with superior impact resistance. Modern punches and chisels are often austempered. Because austempering does not produce martensite, the steel does not require further tempering.
Austempering is a technique used to form pure bainite, a transitional microstructure found between pearlite and martensite. In normalizing, both upper and lower bainite are usually found mixed with pearlite. To avoid the formation of pearlite or martensite, the steel is quenched in a bath of molten metals or salts. This quickly cools the steel past the point where pearlite can form and into the bainite-forming range. The steel is then held at the bainite-forming temperature, beyond the point where the temperature reaches an equilibrium, until the bainite fully forms. The steel is then removed from the bath and allowed to air-cool, without the formation of either pearlite or martensite.
Depending on the holding temperature, austempering can produce either upper or lower bainite. Upper bainite is a laminate structure formed at temperatures typically above and is a much tougher microstructure. Lower bainite is a needle-like structure, produced at temperatures below 350 °C, and is stronger but much more brittle. In either case, austempering produces greater strength and toughness for a given hardness, which is determined mostly by composition rather than cooling speed, and reduced internal stresses which could lead to breakage. This produces steel with superior impact resistance. Modern punches and chisels are often austempered. Because austempering does not produce martensite, the steel does not require further tempering.
Martempering
Martempering is similar to austempering, in that the steel is quenched in a bath of molten metal or salts to quickly cool it past the pearlite-forming range. However, in martempering, the goal is to create martensite rather than bainite. The steel is quenched to a much lower temperature than is used for austempering; to just above the martensite start temperature. The metal is then held at this temperature until the temperature of the steel reaches an equilibrium. The steel is then removed from the bath before any bainite can form, and then is allowed to air-cool, turning it into martensite. The interruption in cooling allows much of the internal stresses to relax before the martensite forms, decreasing the brittleness of the steel. However, the martempered steel will usually need to undergo further tempering to adjust the hardness and toughness, except in rare cases where maximum hardness is needed but the accompanying brittleness is not. Modern files are often martempered.Physical processes
Tempering involves a three-step process in which unstable martensite decomposes into ferrite and unstable carbides, and finally into stable cementite, forming various stages of a microstructure called tempered martensite. The martensite typically consists of laths (strips) or plates, sometimes appearing acicular (needle-like) or lenticular (lens-shaped). Depending on the carbon content, it also contains a certain amount of "retained austenite." Retained austenite are crystals that are unable to transform into martensite, even after quenching below the martensite finish (Mf) temperature. An increase in alloying agents or carbon content causes an increase in retained austenite. Austenite has much higher stacking-fault energy than martensite or pearlite, lowering the wear resistance and increasing the chances of galling, although some or most of the retained austenite can be transformed into martensite by cold and cryogenic treatments prior to tempering. The martensite forms during a diffusionless transformation, in which the transformation occurs due to shear stresses created in the crystal lattices rather than by chemical changes that occur during precipitation. The shear stresses create many defects, or "dislocation
In materials science, a dislocation or Taylor's dislocation is a linear crystallographic defect or irregularity within a crystal structure that contains an abrupt change in the arrangement of atoms. The movement of dislocations allow atoms to sli ...
s," between the crystals, providing less-stressful areas for the carbon atoms to relocate. Upon heating, the carbon atoms first migrate to these defects and then begin forming unstable carbides. This reduces the amount of total martensite by changing some of it to ferrite. Further heating reduces the martensite even more, transforming the unstable carbides into stable cementite.
The first stage of tempering occurs between room temperature and . In the first stage, carbon precipitates into ε-carbon (Fe2,4C). In the second stage, occurring between and , the retained austenite transforms into a form of lower-bainite containing ε-carbon rather than cementite (archaically referred to as "troostite"). The third stage occurs at and higher. In the third stage, ε-carbon precipitates into cementite, and the carbon content in the martensite decreases. If tempered at higher temperatures, between and , or for longer amounts of time, the martensite may become fully ferritic and the cementite may become coarser or more spherical. In spheroidized steel, the cementite network breaks apart and recedes into rods or spherical-shaped globules, and the steel becomes softer than annealed steel; nearly as soft as pure iron, making it very easy to form or machine
A machine is a physical system that uses power to apply forces and control movement to perform an action. The term is commonly applied to artificial devices, such as those employing engines or motors, but also to natural biological macromol ...
.
Embrittlement
Embrittlement occurs during tempering when, through a specific temperature range, the steel experiences an increase in hardness and a reduction in ductility, as opposed to the normal decrease in hardness that occurs on either side of this range. The first type is called tempered martensite embrittlement (TME) or one-step embrittlement. The second is referred to as temper embrittlement (TE) or two-step embrittlement. One-step embrittlement usually occurs in carbon steel at temperatures between and , and was historically referred to as "500 degree ahrenheitembrittlement." This embrittlement occurs due to the precipitation of Widmanstatten needles or plates, made of cementite, in the interlath boundaries of the martensite. Impurities such asphosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol P and atomic number 15. All elemental forms of phosphorus are highly Reactivity (chemistry), reactive and are therefore never found in nature. They can nevertheless be prepared ar ...
, or alloying agents like manganese
Manganese is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese was first isolated in the 1770s. It is a transition m ...
, may increase the embrittlement, or alter the temperature at which it occurs. This type of embrittlement is permanent, and can only be relieved by heating above the upper critical temperature and then quenching again. However, these microstructures usually require an hour or more to form, so are usually not a problem in the blacksmith method of tempering.
Two-step embrittlement typically occurs by aging the metal within a critical temperature range, or by slowly cooling it through that range, For carbon steel, this is typically between and , although impurities like phosphorus and sulfur
Sulfur ( American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphur ( Commonwealth spelling) is a chemical element; it has symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms ...
increase the effect dramatically. This generally occurs because the impurities are able to migrate to the grain boundaries, creating weak spots in the structure. The embrittlement can often be avoided by quickly cooling the metal after tempering. Two-step embrittlement, however, is reversible. The embrittlement can be eliminated by heating the steel above and then quickly cooling.
Alloy steels
Many elements are often alloyed with steel. The main purpose for alloying most elements with steel is to increase itshardenability
Jominy test dimensioning
Jominy test apparatus
Used Jominy test-piece
Hardenability is the depth to which a steel is hardened after putting it through a heat treatment process. It should not be confused with hardness, which is a measure of a s ...
and to decrease softening under temperature. Tool steels, for example, may have elements like chromium
Chromium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in Group 6 element, group 6. It is a steely-grey, Luster (mineralogy), lustrous, hard, and brittle transition metal.
Chromium ...
or vanadium
Vanadium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol V and atomic number 23. It is a hard, silvery-grey, malleable transition metal. The elemental metal is rarely found in nature, but once isolated artificially, the formation of an ...
added to increase both toughness and strength, which is necessary for things like wrenches and screwdriver
A screwdriver is a tool, manual or powered, used for turning screws.
Description
A typical simple screwdriver has a handle and a shaft, ending in a tip the user puts into the screw head before turning the handle. This form of the screwdriver ...
s. On the other hand, drill bit
A drill bit is a cutting tool used in a drill to remove material to create holes, almost always of circular cross-section. Drill bits come in many sizes and shapes and can create different kinds of holes in many different materials. In orde ...
s and rotary files need to retain their hardness at high temperatures. Adding cobalt
Cobalt is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Co and atomic number 27. As with nickel, cobalt is found in the Earth's crust only in a chemically combined form, save for small deposits found in alloys of natural meteoric iron. ...
or molybdenum
Molybdenum is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mo (from Neo-Latin ''molybdaenum'') and atomic number 42. The name derived from Ancient Greek ', meaning lead, since its ores were confused with lead ores. Molybdenum minerals hav ...
can cause the steel to retain its hardness, even at red-hot temperatures, forming high-speed steels. Often, small amounts of many different elements are added to the steel to give the desired properties, rather than just adding one or two.
Most alloying elements (solutes) have the benefit of not only increasing hardness, but also lowering both the martensite start temperature and the temperature at which austenite transforms into ferrite and cementite. During quenching, this allows a slower cooling rate, which allows items with thicker cross-sections to be hardened to greater depths than is possible in plain carbon steel, producing more uniformity in strength.
Tempering methods for alloy steels may vary considerably, depending on the type and amount of elements added. In general, elements like manganese
Manganese is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese was first isolated in the 1770s. It is a transition m ...
, nickel
Nickel is a chemical element; it has symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive, but large pieces are slo ...
, silicon
Silicon is a chemical element; it has symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic lustre, and is a tetravalent metalloid (sometimes considered a non-metal) and semiconductor. It is a membe ...
, and aluminum
Aluminium (or aluminum in North American English) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Al and atomic number 13. It has a density lower than that of other common metals, about one-third that of steel. Aluminium has ...
will remain dissolved in the ferrite during tempering while the carbon precipitates. When quenched, these solutes will usually produce an increase in hardness over plain carbon steel of the same carbon content. When hardened alloy-steels, containing moderate amounts of these elements, are tempered, the alloy will usually soften somewhat proportionately to carbon steel.
However, during tempering, elements like chromium, vanadium, and molybdenum precipitate with the carbon. If the steel contains fairly low concentrations of these elements, the softening of the steel can be retarded until much higher temperatures are reached, when compared to those needed for tempering carbon steel. This allows the steel to maintain its hardness in high-temperature or high-friction applications. However, this also requires very high temperatures during tempering, to achieve a reduction in hardness. If the steel contains large amounts of these elements, tempering may produce an increase in hardness until a specific temperature is reached, at which point the hardness will begin to decrease. For instance, molybdenum steels will typically reach their highest hardness around whereas vanadium steels will harden fully when tempered to around . When very large amounts of solutes are added, alloy steels may behave like precipitation-hardening alloys, which do not soften at all during tempering.''Steels: Microstructure and Properties: Microstructure and Properties By Harry Bhadeshia, Robert Honeycombe -- Elsevier 2006Page 191--207
Cast iron
Cast iron comes in many types, depending on the carbon content. However, they are usually divided into grey and white cast iron, depending on the form that the carbides take. In grey cast iron, the carbon is mainly in the form ofgraphite
Graphite () is a Crystallinity, crystalline allotrope (form) of the element carbon. It consists of many stacked Layered materials, layers of graphene, typically in excess of hundreds of layers. Graphite occurs naturally and is the most stable ...
, but in white cast iron, the carbon is usually in the form of cementite
Cementite (or iron carbide) is a compound of iron and carbon, more precisely an intermediate transition metal carbide with the formula Fe3C. By weight, it is 6.67% carbon and 93.3% iron. It has an orthorhombic crystal structure. It is a hard, b ...
. Grey cast iron consists mainly of the microstructure called pearlite, mixed with graphite and sometimes ferrite. Grey cast iron is usually used as cast, with its properties being determined by its composition.
White cast iron is composed mostly of a microstructure called ledeburite mixed with pearlite. Ledeburite is very hard, making cast iron very brittle. If the white cast iron has a hypoeutectic composition, it is usually tempered to produce malleable or ductile cast iron. Two methods of tempering are used, called "white tempering" and "black tempering." The purpose of both tempering methods is to cause the cementite within the ledeburite to decompose, increasing the ductility.''Physical metallurgy for engineers'' By Miklós Tisza - ASM International 2002 Page 348-350
White tempering
Malleable (porous) cast iron is manufactured by white tempering. White tempering is used to burn off excess carbon, by heating it for extended amounts of time in an oxidizing environment. The cast iron will usually be held at temperatures as high as for as long as 60 hours. The heating is followed by a slow cooling rate of around 10 °C (18 °F) per hour. The entire process may last 160 hours or more. This causes the cementite to decompose from the ledeburite, and then the carbon burns out through the surface of the metal, increasing the malleability of the cast iron.Black tempering
Ductile (non-porous) cast iron (often called "black iron") is produced by black tempering. Unlike white tempering, black tempering is done in aninert gas
An inert gas is a gas that does not readily undergo chemical reactions with other chemical substances and therefore does not readily form chemical compounds. Though inert gases have a variety of applications, they are generally used to prevent u ...
environment, so that the decomposing carbon does not burn off. Instead, the decomposing carbon turns into a type of graphite called "temper graphite" or "flaky graphite," increasing the malleability of the metal. Tempering is usually performed at temperatures as high as for up to 20 hours. The tempering is followed by slow cooling through the lower critical temperature, over a period that may last from 50 to over 100 hours.
Precipitation hardening alloys
Precipitation-hardening alloys first came into use during the early 1900s. Most heat-treatable alloys fall into the category of precipitation-hardening alloys, including alloys ofaluminum
Aluminium (or aluminum in North American English) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Al and atomic number 13. It has a density lower than that of other common metals, about one-third that of steel. Aluminium has ...
, magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 ...
, titanium
Titanium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ti and atomic number 22. Found in nature only as an oxide, it can be reduced to produce a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density, and high strength, resistant to corrosion in ...
, and nickel
Nickel is a chemical element; it has symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive, but large pieces are slo ...
. Several high-alloy steel
Alloy steel is steel that is Alloy, alloyed with a variety of elements in amounts between 1.0% and 50% by weight, typically to improve its List of materials properties#Mechanical properties, mechanical properties.
Types
Alloy steels divide into ...
s are also precipitation-hardening alloys. These alloys become softer than normal when quenched and then harden over time. For this reason, precipitation hardening is often referred to as "aging."
Although most precipitation-hardening alloys will harden at room temperature, some will only harden at elevated temperatures and, in others, the process can be sped up by aging at elevated temperatures. Aging at temperatures higher than room-temperature is called "artificial aging". Although the method is similar to tempering, the term "tempering" is usually not used to describe artificial aging, because the physical processes, (i.e.: precipitation of intermetallic
An intermetallic (also called intermetallic compound, intermetallic alloy, ordered intermetallic alloy, long-range-ordered alloy) is a type of metallic alloy that forms an ordered solid-state compound between two or more metallic elements. Inte ...
phases from a supersaturated
In physical chemistry, supersaturation occurs with a solution when the concentration of a solute exceeds the concentration specified by the value of solubility at equilibrium. Most commonly the term is applied to a solution of a solid in a ...
alloy) the desired results, (i.e.: strengthening rather than softening), and the amount of time held at a certain temperature is very different from tempering as used in carbon-steel.
See also
*Annealing (metallurgy)
In metallurgy and materials science, annealing is a heat treatment that alters the physical and sometimes chemical properties of a material to increase its ductility and reduce its hardness, making it more workable. It involves heating a mater ...
* Austempering
* Precipitation strengthening
Precipitation hardening, also called age hardening or particle hardening, is a heat treatment technique used to increase the Yield (engineering), yield strength of malleable materials, including most structural alloys of aluminium, magnesium, nic ...
* Tempered glass
Tempered or toughened glass is a type of safety glass processed by controlled heat treatment, thermal or chemical treatments to increase its strength compared with normal glass. Tempering puts the outer surfaces into Compression (physics), comp ...
References
Further reading
*Manufacturing Processes Reference Guide by Robert H. Todd, Dell K. Allen, and Leo Alting pg. 410External links
A thorough discussion of tempering processes
{{Authority control Metal heat treatments