Telephony In Greater Manchester on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Cities of
 The first UK public automatic exchange was brought into service at Epsom, Surrey, in May 1912 using the American Strowger 'step-by-step' system. It allowed subscribers to dial the local number themselves (instead of asking the operator to connect them manually). A permanent "junction telephone service" was inaugurated between Liverpool and Manchester during 1914. In 1922 the practice of using the first three letters of an exchange name was introduced in London, Manchester and Birmingham in preparation for automatic dialling. By 1924 there were over a quarter of million lines connected to more than 40 automatic exchanges. The main problem in large cities was directing a call over a complex series of interlinking circuits. The first fully automatic system in a large urban area was under an advanced form of the Strowger concept (which enabled one exchange to be connected automatically to another). Called the
The first UK public automatic exchange was brought into service at Epsom, Surrey, in May 1912 using the American Strowger 'step-by-step' system. It allowed subscribers to dial the local number themselves (instead of asking the operator to connect them manually). A permanent "junction telephone service" was inaugurated between Liverpool and Manchester during 1914. In 1922 the practice of using the first three letters of an exchange name was introduced in London, Manchester and Birmingham in preparation for automatic dialling. By 1924 there were over a quarter of million lines connected to more than 40 automatic exchanges. The main problem in large cities was directing a call over a complex series of interlinking circuits. The first fully automatic system in a large urban area was under an advanced form of the Strowger concept (which enabled one exchange to be connected automatically to another). Called the
 A system which is cited as being the forerunner of the modern mobile phone, was first launched from the
A system which is cited as being the forerunner of the modern mobile phone, was first launched from the
 When lists of subscribers were first produced in the 1880s there were so few that entire regions of the UK could easily be accommodated in little more than pamphlets. By the 1920s most telephone directories covered just counties or parts thereof. In 1922 MPs raised the possibility of adding Bolton and Bury to the Manchester Telephone directory (Oldham and Rochdale were already included).
The number of subscribers increased exponentially after the Second World War (reaching 5.7 million by March 1952 for example). London's telephone directories were split (initially into 2 books in 1931: A-K and L-Z) and eventually into four (A-D, E-K, L-R and S-Z) in the 1940s. From the 1970 issue onwards, Manchester was the only other UK urban area which, owing to the large number of subscribers, also required a split into two separate directories (A-K and L-Z, pictured, 1975 editions). Due to the huge print run and cost of production, the split was discontinued in 1977 with the first appearance of the 'Manchester Central' edition. Over the next 18 months Greater Manchester was divided up geographically – into 'Manchester North East', 'Manchester North West' and 'Manchester South'), so that split alphabetical directories were no longer required and each was more relevant to its local area. Design consultants
When lists of subscribers were first produced in the 1880s there were so few that entire regions of the UK could easily be accommodated in little more than pamphlets. By the 1920s most telephone directories covered just counties or parts thereof. In 1922 MPs raised the possibility of adding Bolton and Bury to the Manchester Telephone directory (Oldham and Rochdale were already included).
The number of subscribers increased exponentially after the Second World War (reaching 5.7 million by March 1952 for example). London's telephone directories were split (initially into 2 books in 1931: A-K and L-Z) and eventually into four (A-D, E-K, L-R and S-Z) in the 1940s. From the 1970 issue onwards, Manchester was the only other UK urban area which, owing to the large number of subscribers, also required a split into two separate directories (A-K and L-Z, pictured, 1975 editions). Due to the huge print run and cost of production, the split was discontinued in 1977 with the first appearance of the 'Manchester Central' edition. Over the next 18 months Greater Manchester was divided up geographically – into 'Manchester North East', 'Manchester North West' and 'Manchester South'), so that split alphabetical directories were no longer required and each was more relevant to its local area. Design consultants
Manchester
Manchester () is a city and the metropolitan borough of Greater Manchester, England. It had an estimated population of in . Greater Manchester is the third-most populous metropolitan area in the United Kingdom, with a population of 2.92&nbs ...
and Salford
Salford ( ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, city in Greater Manchester, England, on the western bank of the River Irwell which forms its boundary with Manchester city centre. Landmarks include the former Salford Town Hall, town hall, ...
and some surrounding urban areas such as Stockport
Stockport is a town in Greater Manchester, England, south-east of Manchester, south-west of Ashton-under-Lyne and north of Macclesfield. The River Goyt, Rivers Goyt and River Tame, Greater Manchester, Tame merge to create the River Mersey he ...
, Oldham
Oldham is a town in Greater Manchester, England. It lies amongst the Pennines on elevated ground between the rivers River Irk, Irk and River Medlock, Medlock, southeast of Rochdale, and northeast of Manchester. It is the administrative cent ...
and Bolton
Bolton ( , locally ) is a town in Greater Manchester in England. In the foothills of the West Pennine Moors, Bolton is between Manchester, Blackburn, Wigan, Bury, Greater Manchester, Bury and Salford. It is surrounded by several towns and vill ...
, (now forming parts of Greater Manchester
Greater Manchester is a ceremonial county in North West England. It borders Lancashire to the north, Derbyshire and West Yorkshire to the east, Cheshire to the south, and Merseyside to the west. Its largest settlement is the city of Manchester. ...
), were the location of several advances in the development of telephony in the United Kingdom. A Manchester company installed the country's first regular telephone system in the city, wiring solutions which were adopted across Britain were initiated in Manchester and Stockport, the city was (arguably) the site of the UK's first telephone exchange
A telephone exchange, telephone switch, or central office is a central component of a telecommunications system in the public switched telephone network (PSTN) or in large enterprises. It facilitates the establishment of communication circuits ...
and a service which was the forerunner of modern mobile phones was controlled from the city.
UK’s first regular telephone service
In November 1877, while telephony was in its infancy, just 18 months afterAlexander Graham Bell
Alexander Graham Bell (; born Alexander Bell; March 3, 1847 – August 2, 1922) was a Scottish-born Canadian Americans, Canadian-American inventor, scientist, and engineer who is credited with patenting the first practical telephone. He als ...
had made the world's first phone call, Charles Moseley, the son of a Manchester rubber manufacturer (then making telegraph
Telegraphy is the long-distance transmission of messages where the sender uses symbolic codes, known to the recipient, rather than a physical exchange of an object bearing the message. Thus flag semaphore is a method of telegraphy, whereas ...
equipment), took an interest in Bell's work. Moseley employed an engineer called William Fereday Bottomley to obtain telephone instruments from the Bell Company
The Bell Telephone Company was the initial corporate entity from which the Bell System originated to build a continental conglomerate and monopoly in telecommunication services in the United States and Canada.
The company was organized in Bost ...
in Boston
Boston is the capital and most populous city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts in the United States. The city serves as the cultural and Financial centre, financial center of New England, a region of the Northeas ...
, United States, and provided the Post Office with its first telephones.
Bell himself had first demonstrated the telephone to Queen Victoria
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until Death and state funeral of Queen Victoria, her death in January 1901. Her reign of 63 year ...
who placed the UK's first long-distance call from Osborne House
Osborne House is a former royal residence in East Cowes, Isle of Wight, United Kingdom. The house was built between 1845 and 1851 for Queen Victoria and Prince Albert as a summer home and rural retreat. Albert designed the house in the style ...
on the Isle of Wight
The Isle of Wight (Help:IPA/English, /waɪt/ Help:Pronunciation respelling key, ''WYTE'') is an island off the south coast of England which, together with its surrounding uninhabited islets and Skerry, skerries, is also a ceremonial county. T ...
, on 14 January 1878. Just twelve days later, after obtaining a licence from the Post Office, Moseley installed a telephone between a hardware merchant's establishment (Thomas Hudson Ltd) on Shudehill, Manchester to the offices of the company on Dantzic Street: the first such telephone in regular use in the country
Telephone manufacturers
Moseley and Sons as a licensed telephone agent supplied private telephones to local customers. Their head of construction, Alexander Marr, patented in 1879, a type of granularcarbon microphone
The carbon microphone, also known as carbon button microphone, button microphone, or carbon transmitter, is a type of microphone, a transducer that converts sound to an electrical audio signal. It consists of two metal plates separated by granu ...
(originally for the transmission of the sound of opera), which enabled them to get a foothold in the business of manufacturing telephones in the UK. Together with another local company (Peel–Conner) they both supplied the first telephone apparatus to the Post Office and also to railway companies and other private enterprises.
Engineering pioneers
An experimental system for separating wires on telephone poles was erected from Manchester to Stockport and another to Oldham. This “twist” system (though never patented) was universally adopted in the UK for pole-mounted wiring.First telephone exchange
There are claims that Manchester was also home to the UK's first telephone exchange after a reported July 1879 commencement of operations by 'Lancashire Telephonic Exchange Limited' (LTE) on Faulkner Street using equipment licensed under Bell's patent. LTE joint manager James Lorrain claimed that their exchange opened in July 1879 – effectively making Britain's first.(this claim is disputed). It is certainly known that theTelephone Company
A telecommunications company is a kind of electronic communications service provider, more precisely a telecommunications service provider (TSP), that provides telecommunications services such as telephony and data communications access. Many t ...
opened two exchanges in London in August 1879 (the first was an Edison exchange in Queen Victoria Street, the second, a Bell company one, was situated in Coleman Street
Coleman Street is one of the Wards of the City of London, 25 ancient wards of the City of London, England, and lies on the City's northern boundary with the London Borough of Islington.
The ward, which includes land lying on either side of the ...
, both in the City of London
The City of London, also known as ''the City'', is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county and Districts of England, local government district with City status in the United Kingdom, city status in England. It is the Old town, his ...
), and there was also a very early exchange in Glasgow
Glasgow is the Cities of Scotland, most populous city in Scotland, located on the banks of the River Clyde in Strathclyde, west central Scotland. It is the List of cities in the United Kingdom, third-most-populous city in the United Kingdom ...
. David Moseley & Sons planned to open their own telephone exchange in their warehouse on Manchester's New Brown Street but before this happened in October of that year, the 'Lancashire and Cheshire Telephonic Exchange' company bought Moseley's licence to stall his opening. Other reports (for example from the Manchester Guardian
''The Guardian'' is a British daily newspaper. It was founded in Manchester in 1821 as ''The Manchester Guardian'' and changed its name in 1959, followed by a move to London. Along with its sister paper, ''The Guardian Weekly'', ''The Guardi ...
) suggest the first Manchester exchange opened in mid-September 1879.
A second telephone exchange opened in Manchester during 1880 run by the 'Edison Telephone Company of London Ltd'. The Museum of Science and Industry holds the earliest surviving list of telephone subscribers in Manchester (for the Edison Manchester and District Telephonic Exchange), which consists of ''a printed list of 125 subscribers, with one handwritten deletion and 13 handwritten additions''.
Consolidation of local telephone companies and trunk lines
By 1881 the Lancashire exchanges had 420 subscribers. By March of that year the Edison and Bell companies were merged forming the United Telephone Company (13 May 1880). To consolidate the two companies operations in Manchester, The Lancashire & Cheshire Telephonic Exchange Company (LCTEC) was set up in the original Faulkner Street offices and exchange building. By 1888 the LCTE had opened a new switchboard in the city's main trading area, the Royal Exchange (location of 5 ''soundproof telephone boxes'' – which in March 1881 were used to place 430 calls in one day). The equipment which had the potential capacity for over 4000 subscribers, was manufactured byWestern Electric
Western Electric Co., Inc. was an American electrical engineering and manufacturing company that operated from 1869 to 1996. A subsidiary of the AT&T Corporation for most of its lifespan, Western Electric was the primary manufacturer, supplier, ...
and installed under the direction of Joseph Poole. The first permanent trunk line between two distant cities was not installed between Manchester and Liverpool
Liverpool is a port City status in the United Kingdom, city and metropolitan borough in Merseyside, England. It is situated on the eastern side of the River Mersey, Mersey Estuary, near the Irish Sea, north-west of London. With a population ...
until 1910., but lesser connections were possible from south east Lancashire
Lancashire ( , ; abbreviated ''Lancs'') is a ceremonial county in North West England. It is bordered by Cumbria to the north, North Yorkshire and West Yorkshire to the east, Greater Manchester and Merseyside to the south, and the Irish Sea to ...
via connecting lines to Birmingham
Birmingham ( ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, city and metropolitan borough in the metropolitan county of West Midlands (county), West Midlands, within the wider West Midlands (region), West Midlands region, in England. It is the Lis ...
, Bradford
Bradford is a city status in the United Kingdom, city in West Yorkshire, England. It became a municipal borough in 1847, received a city charter in 1897 and, since the Local Government Act 1972, 1974 reform, the city status in the United Kingdo ...
, Huddersfield
Huddersfield is a town in the Metropolitan Borough of Kirklees in West Yorkshire, England. It is the administrative centre and largest settlement in the Kirklees district. The town is in the foothills of the Pennines. The River Holme's confl ...
, Liverpool, Leeds
Leeds is a city in West Yorkshire, England. It is the largest settlement in Yorkshire and the administrative centre of the City of Leeds Metropolitan Borough, which is the second most populous district in the United Kingdom. It is built aro ...
, Nottingham
Nottingham ( , East Midlands English, locally ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, city and Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority area in Nottinghamshire, East Midlands, England. It is located south-east of Sheffield and nor ...
and Sheffield
Sheffield is a city in South Yorkshire, England, situated south of Leeds and east of Manchester. The city is the administrative centre of the City of Sheffield. It is historically part of the West Riding of Yorkshire and some of its so ...
– at a time when it is understood that (despite the experimental connections between the Isle of Wight and another to Norwich, both in 1878) the sole permanent long-distance telephone trunk line connection from the capital was to Brighton
Brighton ( ) is a seaside resort in the city status in the United Kingdom, city of Brighton and Hove, East Sussex, England, south of London.
Archaeological evidence of settlement in the area dates back to the Bronze Age Britain, Bronze Age, R ...
.
During the late 1880s the National Telephone Company was engaged in a series of amalgamations and however it was not until 1889 that national consolidation was achieved when the LCTE, which by then had 1551 lines, and United Telephone and the National Telephone Co were brought together. The resulting merger was called the National Telephone Company of Britain (NTC) and this company continued in existence until 1911 when it was compulsorily purchased by the Postmaster General
A Postmaster General, in Anglosphere countries, is the chief executive officer of the postal service of that country, a ministerial office responsible for overseeing all other postmasters.
History
The practice of having a government official ...
. One Manchester telephony company held out against take over for several years: the Mutual Telephone Company (MTC) had opened a rival exchange to the LCTE in Manchester in February 1891. They offered cheaper call rates but their equipment was said to be inferior to their competitors. After only a year of operation it was bought out by the New telephone Company which itself was absorbed by the NTC in 1896.
Telephone exchange staff
During their early years of operation, it was young boys who the exchanges first employed, but as they caused problems, women were increasingly taken on as the main body of staff. Becoming a Telephone Operator was seen as a respectable employment for middle-class women. The Museum of Science & Industry cites the case of Annie Wright who started work as an operator in 1892 for the MTC. When it was taken over by the NTC she was promoted to supervisor. By 1907 she became Clerk in Charge of the Manchester Central Exchange which was the largest outside London.Exchange names
As the number of subscribers and exchanges proliferated in Manchester and surrounding areas new names were needed for exchanges. In the central area those used included ARDwick, BLAckfriars, CENtral, CHEetham Hill, COLlyhurst, DEAnsgate, MOSs Side and RUSholme. As in London there were also permutations that were required that were not based on genuine geographic names but corresponded to letters on the rotary dial for example PYRamid (covering Northenden – NOR could not be used as the numbers 6, 0 and 7 were already used by MOSs Side), MAIn (covering Oldham – as areas starting with “O” could not be used), and MERcury (covering Heald Green as HEA was already in use (HEAton Moor)). MERcury was chosen as a name because HG is the chemical symbol for mercury. Cheadle was covered by GATley as CHE was already in use for CHEetham Hill).Automatic exchanges & the Director system
Director telephone system
The director telephone system was a development of the Strowger or step-by-step (SXS) switching system used in London and five other large cities in the UK from the 1920s to the 1980s.
A large proportion (c. 70% to 80%) of telephone traffic in ...
, this was first tried on a large scale in London's Holborn
Holborn ( or ), an area in central London, covers the south-eastern part of the London Borough of Camden and a part (St Andrew Holborn (parish), St Andrew Holborn Below the Bars) of the Wards of the City of London, Ward of Farringdon Without i ...
Tandem exchange in 1927. The concept was envisaged to be effective for many major built-up areas and the first three exchanges outside London to be 'cut-over' to the automatic Director system were: Ardwick
Ardwick is an area of Manchester, England, southeast of the city centre. The population at the 2011 census was 19,250.
Historically in Lancashire, by the mid-nineteenth century Ardwick had grown from being a village into a pleasant and wealt ...
, Collyhurst
Collyhurst is an inner city area of Manchester, England, northeast of the Manchester city centre, city centre on Rochdale Road (A664) and A62 road, Oldham Road (A62), bounded by Smedley, Manchester, Smedley, Harpurhey and Monsall tram stop, Mo ...
and Moss Side
Moss Side is an Inner city, inner-city area of Manchester, England, south of the Manchester city centre, city centre. It had a population of 20,745 at the United Kingdom Census 2021, 2021 census. Moss Side is bounded by Hulme to the north, Cho ...
in Manchester during 1930. The exchanges covering the city centre and some suburbs with 7 and a half miles were progressively converted to the same system during the next few years. The automation process meant that a large number of mainly female telephone operators in the Manchester exchanges became redundant – a crisis that was mentioned in Parliament in 1933. But it had revolutionised call-making across the city. For example, subscribers in Collyhurst and Moss Side were then able to dial the letters A (=2), R (=7) and D (=3) followed by the four digit Ardwick subscribers number to connect them directly without talking with an operator. (3 exchanges in Birmingham were next, in 1931, one in Glasgow in 1937, one in Liverpool in 1941, Edinburgh's automatic system did not start until 1950). By the time the system was superseded in 1966, there were around 50 three-letter exchange name codes in the Manchester Automatic System (list inside a telephone drawer, pictured), more than in any other director area outside the capital.
Subscriber Trunk Dialling
Automatically dialled calls from Manchester to other cities were possible from 1954 onwards (for example it was possible to dial automatically without involvement of a manual operator to most exchanges in London, Birmingham, Edinburgh and Bristol). But the switching on of the STD equipment in December 1958 meant that it was possible for almost 430 exchanges across Britain to be dialled automatically.Car radio-phone
 A system which is cited as being the forerunner of the modern mobile phone, was first launched from the
A system which is cited as being the forerunner of the modern mobile phone, was first launched from the Peterloo
The Peterloo Massacre took place at St Peter's Square, Manchester, St Peter's Field, Manchester, Lancashire, England, on Monday 16 August 1819. Eighteen people died and 400–700 were injured when the cavalry of the Yeomen charged into a crow ...
telephone exchange in Manchester in 1959. Initially called the 'Post Office South Lancashire Radiophone Service', it was inaugurated on 28 October and along with South Lancs also covered North Cheshire
Cheshire ( ) is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in North West England. It is bordered by Merseyside to the north-west, Greater Manchester to the north-east, Derbyshire to the east, Staffordshire to the south-east, and Shrop ...
and parts of The Wirral
The Wirral Peninsula (), known locally as the Wirral, is a peninsula in North West England. The roughly rectangular peninsula is about long and wide, and is bounded by the Dee Estuary to the west, the Mersey Estuary to the east, and Liverpool ...
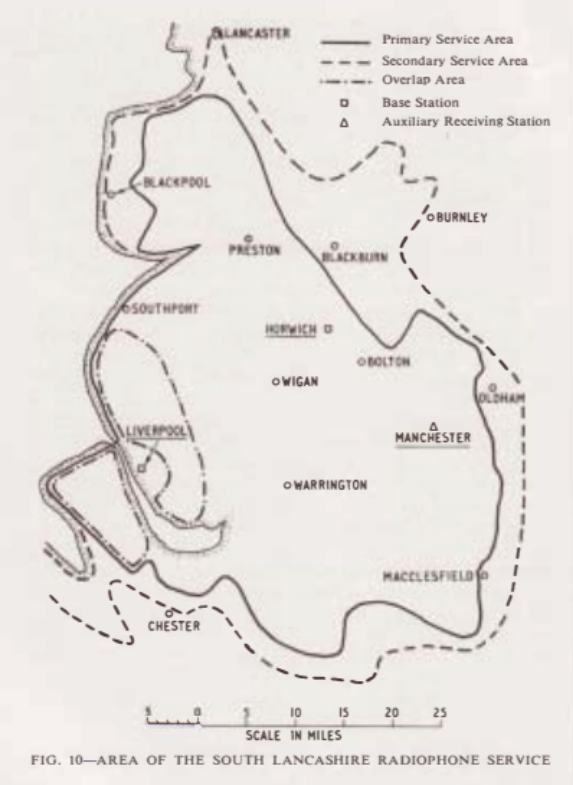
. The signals were operated through two antennas (one on Liverpool's Lancaster House, and the other at Horwich on Winter Hill, with an in-fill for the City Centre on Manchester's Dial House.). A map coverage map was published in the 1960 Post Office Engineers Journal (pictured) along with detailed technical specifications of the system.
It was possible for customers to make or receive phone calls to and from any UK telephone subscriber (via an operator) from an apparatus installed inside their car. If the motorist drove outside of the South Lancashire coverage area the signal would drop out as there were no other transmitters equipped to take the calls until the service was switched on for Londoners in 1965 and to other major urban centres by summer 1972.
All-Figure Dialling
By the early 1960s, following the introduction ofSubscriber Trunk Dialling
Subscriber trunk dialling (STD), also known as subscriber toll dialing, is a telephone numbering plan feature and telecommunications technology in the United Kingdom and various Commonwealth countries for the dialling of trunk calls by telephon ...
, the number of possible exchange name permutations were running out in London and the potential expansion of international direct dialling (where different letters were assigned to alternate numbers than those on UK phones) called for the creation of an alternative, modern system of numbering. Called All Figure Numbering, the first three letters of the exchange name (e.g. CENtral) were to be permanently replaced by digits (in this example: 236). The first six places to introduce the system were the Director cities including Manchester – the process began in 1966. London was allocated the simplest primary code of ‘01’. Manchester was then given a new dialling code of ‘061’, the number 6 corresponded with the letter ‘M’ on the dial (The 2 of Birmingham's 021 corresponded with B, Edinburgh's 031 with E, Glasgow's 041 the G and Liverpool's L with the 5 giving 051).
The start of the changeover was also used to group batches of numbers into "sectors" so that subscribers could more easily identify in which part of the conurbation the number was based. In Greater Manchester for example, all of the numbers starting with the digit 3 were located in the eastern side of the urban area. On the more westerly side of the central area, were numbers commencing with 8, etc. (see map pictured). However some previous exchange names didn't fit the pattern so it was not possible for all of the old exchange name mapping to be kept. Therefore, during the period 1966–1970, some subscribers were allocated new 3 digit exchange numbers (for example ALTrincham was previously reached by the numbers 258, but it was re-allocated the new numbers: 061 928 xxxx so that all the numbers starting with 9 were in the south western sector. BLAckfriars – previously 252 – became 834 so that it fitted the inner western sector. Longford (which covered parts of Chorlton), previously 506, was transferred to 865. Since it was the only former exchange name which started with the 5 digit, numbers beginning 061 5xx xxxx were never allocated (until 2015, when a small number of new levels - 0161 5xx xxxx - were released into circulation, primarily for business customers). Most of the switch to All Figure Numbering was achieved in the mid to late 1960s, however the switchover took until 1970 for all 061 exchanges to be converted.
Since the 1990s and the introduction of private operators (e.g. Mercury Communications
Mercury Communications was a national telephone company in the United Kingdom, formed in 1981 as a subsidiary of Cable & Wireless, to challenge the then-monopoly of British Telecom (BT). Although it proved only moderately successful at challen ...
, Nynex
NYNEX Corporation was an American telephone company that served five states of New England (Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island and Vermont) as well as most of the state of New York from January 1, 1984 to August 14, 1997.
Histo ...
, Virgin Media
Virgin Media Limited is a British telecommunications company which provides telephone, television and internet services in the United Kingdom. Its headquarters are at Green Park in Reading, England. It is owned by Virgin Media O2, a 50:50 ...
etc.), plus the natural exhaustion of certain number ranges, the "sector" concept has broken down, and it is now possible to find numbers commencing with digits that do not fit their original 1960's geographical districts.
Transatlantic dialling
Having completed the switchover to numbers rather than letters, the six British cities on the Director system were first given access to transatlantic dialling in 1971 which enabled callers from Manchester to ring directly to any US mainline number by prefixing the call with '0101'. International Direct Dialling (IDD) was not made available nationwide until 1982.Confravision
Despite the fact that the concept did not really take off at the time, 'Confravision', the world's first public bothway television system, allowed conference facilities to groups of people in different cities. It was made available by the Post Office at its studios in Manchester and four other locations from 1972.Telephone directory redesign
Wolff Olins
Wolff Olins is a global brand consultancy agency that specialises in corporate identity. It was founded in 1965 in London, where its main office is still based, as well as having offices in New York City, San Francisco and Los Angeles. It emplo ...
were appointed in 1983 to re-design the UK's phone directories using type which took up less space and therefore less paper, ink, weight in transportation etc. The first revised look directory (called "The Phone Book") was produced for 'Central Manchester' in March 1984.
Current situation
There are now over 660 levels assigned under the 0161 code (second only in the UK to the number assigned under the 020 code for London), although this includes numbers set aside as ''"Free for National Dialling Only"'' (for example: 0161 002 xxxx). With more than 200 telecoms operators (the most prolific still being BT,) the 0161 code area also has the UK's second largest number of operators outside the capital.See also
*Timeline of the telephone
This timeline of the telephone covers landline, radio, and cellular telephony technologies and provides many important dates in the history of the telephone.
1667 to 1875
* 1667: Robert Hooke creates an acoustic string telephone ...
References
External links
* * * *{{cite web, url=https://www.bbc.co.uk/manchester/content/articles/2008/03/06/060308_telephone_feature.shtml, title=Ahoy hoy Manchester, website=Bbc.co.uk, accessdate=7 December 2018 Telecommunications in the United Kingdom History of Manchester Greater Manchester