

A tantalum electrolytic capacitor is an
electrolytic capacitor
An electrolyte is a substance that conducts electricity through the movement of ions, but not through the movement of electrons. This includes most soluble Salt (chemistry), salts, acids, and Base (chemistry), bases, dissolved in a polar solven ...
, a passive component of
electronic circuit
An electronic circuit is composed of individual electronic components, such as resistors, transistors, capacitors, inductors and diodes, connected by conductive wires or Conductive trace, traces through which electric current can flow. It is a t ...
s. It consists of a pellet of porous
tantalum
Tantalum is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ta and atomic number 73. It is named after Tantalus, a figure in Greek mythology. Tantalum is a very hard, ductility, ductile, lustre (mineralogy), lustrous, blue-gray transition ...
metal as an
anode
An anode usually is an electrode of a polarized electrical device through which conventional current enters the device. This contrasts with a cathode, which is usually an electrode of the device through which conventional current leaves the devic ...
, covered by an insulating oxide layer that forms the dielectric, surrounded by liquid or solid electrolyte as a
cathode
A cathode is the electrode from which a conventional current leaves a polarized electrical device such as a lead-acid battery. This definition can be recalled by using the mnemonic ''CCD'' for ''Cathode Current Departs''. Conventional curren ...
. The tantalum capacitor, because of its very thin and relatively high
permittivity
In electromagnetism, the absolute permittivity, often simply called permittivity and denoted by the Greek letter (epsilon), is a measure of the electric polarizability of a dielectric material. A material with high permittivity polarizes more ...
dielectric layer,
distinguishes itself from other conventional and electrolytic capacitors in having high
capacitance
Capacitance is the ability of an object to store electric charge. It is measured by the change in charge in response to a difference in electric potential, expressed as the ratio of those quantities. Commonly recognized are two closely related ...
per volume (high volumetric efficiency) and lower weight.
Tantalum is a
conflict resource
A resource war is a type of war caused by conflict over resources. In a resource war, there is typically a nation or group that controls the resource and an aggressor that wishes to seize control over said resource. This power dynamic between nati ...
. Tantalum electrolytic capacitors are considerably more expensive than comparable
aluminum electrolytic capacitor
Aluminium electrolytic capacitors are (usually) polarized electrolytic capacitors whose anode electrode (+) is made of a pure aluminium foil with an etching, etched surface. The aluminum forms a very thin insulating layer of aluminium oxide by ano ...
s.
Tantalum capacitors are inherently polarized components. Reverse voltage can destroy the capacitor. Non-polar or bipolar tantalum capacitors are made by effectively connecting two polarized capacitors in series, with the anodes oriented in opposite directions.
Tantalum electrolytic capacitors are extensively used in
electronic devices
Electronics is a scientific and engineering discipline that studies and applies the principles of physics to design, create, and operate devices that manipulate electrons and other electrically charged particles. It is a subfield of physics and ...
that require stable
capacitance
Capacitance is the ability of an object to store electric charge. It is measured by the change in charge in response to a difference in electric potential, expressed as the ratio of those quantities. Commonly recognized are two closely related ...
, low
leakage current
In electronics, leakage is the gradual transfer of electrical energy across a boundary normally viewed as insulating, such as the spontaneous discharge of a charged capacitor, magnetic coupling of a transformer with other components, or flow ...
, and where reliability is crucial. Due to its reliability, durability and performance under extreme conditions, it is used in medical equipment, aerospace and military applications. Other applications include
power supply units,
measuring instruments
Instrumentation is a collective term for measuring instruments, used for indicating, measuring, and recording physical quantities. It is also a field of study about the art and science about making measurement instruments, involving the related ...
, telecommunications equipment, and computer peripherals.
Basic information
Basic principle

Electrolytic capacitors use a chemical feature of some special metals, historically called ''valve metals'', which can form an insulating oxide layer. Applying a positive voltage to the tantalum anode material in an electrolytic bath forms an oxide barrier layer with a thickness proportional to the applied voltage. This oxide layer serves as the dielectric in an electrolytic capacitor. The properties of this oxide layer are compared with those of a niobium electrolytic capacitor oxide layer in the following table:
After forming a dielectric oxide on the rough anode structures, a cathode is needed. An electrolyte acts as the cathode of electrolytic capacitors. There are many different electrolytes in use. Generally, the electrolytes will be distinguished into two species, ''non-solid'' and ''solid'' electrolytes. Non-solid electrolytes are a liquid medium whose
conductivity is
ion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convent ...
ic.
The oxide layer may be destroyed if the polarity of the applied voltage is reversed.

Every electrolytic capacitor in principle forms a ''plate capacitor'' whose capacitance is greater the larger the electrode area, A, and the
permittivity
In electromagnetism, the absolute permittivity, often simply called permittivity and denoted by the Greek letter (epsilon), is a measure of the electric polarizability of a dielectric material. A material with high permittivity polarizes more ...
, ε, are and the thinner the thickness, d, of the dielectric is.
:
The dielectric thickness of electrolytic capacitors is very thin, in the range of
nanometers
330px, Different lengths as in respect to the molecular scale.
The nanometre (international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: nm), or nanometer (American and British English spelling differences#-r ...
per volt. Despite this, the dielectric strengths of these oxide layers are quite high. Thus, tantalum capacitors can achieve a high volumetric capacitance compared to other capacitor types.
All etched or sintered anodes have a much larger total surface area compared to a smooth surface of the same overall dimensions. This surface area increase boosts the capacitance value by a factor of up to 200 (depending on the rated voltage) for solid tantalum electrolytic capacitors.
[I. Horacek, T. Zednicek, S. Zednicek, T. Karnik, J. Petrzilek, P. Jacisko, P. Gregorova, AVX, "High CV Tantalum Capacitors: Challenges and Limitations]
PDF
/ref>
The volume of an electrolytic capacitor is defined by the product of capacitance and voltage, the so-called ''CV-volume''. However, in comparing the permittivities of different oxide materials, it is seen that tantalum pentoxide has an approximately 3 times higher permittivity than aluminum oxide. Tantalum electrolytic capacitors of a given CV value can therefore be smaller than aluminum electrolytic capacitors.
Basic construction of solid tantalum electrolytic capacitors
File:Tantalum sintered pellet.jpg, The capacitor cell of a tantalum electrolytic capacitor consists of sintered tantalum powder
File:Tantalum-Sintered-MnO2-slug.jpg, Schematic representation of the structure of a sintered tantalum electrolytic capacitor with solid electrolyte and the cathode contacting layers
File:Tantalum-SMD-Chip-Molded.jpg, Construction of a typical SMD tantalum electrolytic chip capacitor with solid electrolyte
A typical tantalum capacitor is a chip capacitor and consists of tantalum powder pressed and sintered
Sintering or frittage is the process of compacting and forming a solid mass of material by pressure or heat without melting it to the point of liquefaction. Sintering happens as part of a manufacturing process used with metals, ceramics, pla ...
into a pellet as the anode
An anode usually is an electrode of a polarized electrical device through which conventional current enters the device. This contrasts with a cathode, which is usually an electrode of the device through which conventional current leaves the devic ...
of the capacitor, with the oxide layer of tantalum pentoxide as a dielectric
In electromagnetism, a dielectric (or dielectric medium) is an Insulator (electricity), electrical insulator that can be Polarisability, polarised by an applied electric field. When a dielectric material is placed in an electric field, electric ...
, and a solid manganese dioxide electrolyte as the cathode
A cathode is the electrode from which a conventional current leaves a polarized electrical device such as a lead-acid battery. This definition can be recalled by using the mnemonic ''CCD'' for ''Cathode Current Departs''. Conventional curren ...
.
Materials, production and styles
Anode
 Tantalum capacitors are manufactured from a powder of relatively pure elemental
Tantalum capacitors are manufactured from a powder of relatively pure elemental tantalum
Tantalum is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ta and atomic number 73. It is named after Tantalus, a figure in Greek mythology. Tantalum is a very hard, ductility, ductile, lustre (mineralogy), lustrous, blue-gray transition ...
metal.[J. Gill, AVX, Basic Tantalum Capacitor Technology]
PDF
o
/ref> A common figure of merit
A figure of merit (FOM) is a performance metric that characterizes the performance of a device, system, or method, relative to its alternatives. Examples
*Absolute alcohol content per currency unit in an alcoholic beverage
*accurizing, Accuracy o ...
for comparing volumetric efficiency
Volumetric efficiency (VE) in internal combustion engine engineering is defined as the ratio of the equivalent volume of the fresh air drawn into the cylinder during the intake stroke (if the gases were at the reference condition for density) to th ...
of powders is expressed in capacitance (C, usually in μF) times volts (V) per gram (g). Since the mid-1980s, manufactured tantalum powders have exhibited around a ten-fold improvement in CV/g values (from approximately 20k to 200k). The powder is compressed around a tantalum wire (known as the riser wire) to form a "pellet".
The powder is compressed around a tantalum wire (known as the riser wire) to form a "pellet".[VISHAY, DC Leakage Failure Mode]
PDF
/ref> The riser wire ultimately becomes the anode connection to the capacitor. This pellet/wire combination is subsequently vacuum sintered
Sintering or frittage is the process of compacting and forming a solid mass of material by pressure or heat without melting it to the point of liquefaction. Sintering happens as part of a manufacturing process used with metals, ceramics, pla ...
at high temperature (typically 1200 to 1800 °C) which produces a mechanically strong pellet and drives off many impurities within the powder. During sintering, the powder takes on a sponge-like structure, with all the particles interconnected into a monolithic spatial lattice. This structure is of predictable mechanical strength and density, but is also highly porous, producing a large internal surface area (see Figure 2).
Larger surface areas produce higher capacitance; thus high ''CV''/g powders, which have lower average particle sizes, are used for low voltage, high capacitance parts. By choosing the correct powder type and sintering temperature, a specific capacitance or voltage rating can be achieved. For example, a 220 μF 6 V capacitor will have a surface area close to 346 cm2, or 80% of the size of a sheet of paper (US Letter, 8.5×11 inch paper has area ~413 cm2), although the total volume of the pellet is only about 0.0016 cm3.
Dielectric
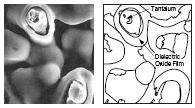 The
The dielectric
In electromagnetism, a dielectric (or dielectric medium) is an Insulator (electricity), electrical insulator that can be Polarisability, polarised by an applied electric field. When a dielectric material is placed in an electric field, electric ...
is then formed over all the tantalum particle surfaces by the electrochemical process of anodization. To achieve this, the "pellet" is submerged into a very weak solution of acid and DC voltage is applied. The total dielectric thickness is determined by the final voltage applied during the forming process. Initially the power supply is kept in a constant current mode until the correct voltage (i.e. dielectric thickness) has been reached; it then holds this voltage and the current decays to close to zero to provide a uniform thickness throughout the device and production lot.
The chemical equations describing the dielectric formation process at the anode
An anode usually is an electrode of a polarized electrical device through which conventional current enters the device. This contrasts with a cathode, which is usually an electrode of the device through which conventional current leaves the devic ...
are as follows:[
:2 Ta → 2 Ta5+ + 10 e−
:2 Ta5+ + 10 OH− → Ta2O5 + 5 H2O
The oxide forms on the surface of the tantalum, but it also grows into the material. For each unit thickness of oxide growth, one third grows out and two thirds grows in. Due to the limits of oxide growth, there is a limit on the maximum voltage rating of tantalum oxide for each of the presently available tantalum powders (see Figure 3).
The dielectric layer thickness generated by the forming voltage is directly proportional to the voltage proof of electrolytic capacitors.][K. H. Thiesbürger:'' Der Elektrolyt-Kondensator''. 4. Auflage. Roederstein, Landshut 1991, ] Electrolytic capacitors are manufactured with a safety margin in oxide layer thickness, which is the ratio between voltage used for electrolytical creation of dielectric and rated voltage of the capacitor, to ensure reliable functionality.
The safety margin for solid tantalum capacitors with manganese dioxide electrolyte is typically between 2 and 4. That means that for a 25 V tantalum capacitor with a safety margin of 4 the dielectric voltage proof can withstand 100 V to provide a more robust dielectric. This very high safety factor is substantiated by the failure mechanism of solid tantalum capacitors, "field crystallization".[B. Goudswaard, F. J. J. Driesens, "Failure Mechanism of Solid Tantalum Capacitors", Philips, ''Electrocomponent Science and Technology'', 1976, Vol. 3. pp. 171–17]
/ref>[H. W. Holland, Kemet, Solid Tantalum Capacitor Failure Mechanism and Determination of Failure Rates]
[P. Vasina, T. Zednicek, AVX, J. Sikula, J. Pavelka, AVX, Failure Modes of Tantalum Capacitors made by Different Technologies, CARTS US 200]
/ref>[Y. Pozdeev-Freeman, Vishay, How Far Can We Go with High CV Tantalum Capacitors, PCI, January/February 2005, p. 6]
PDF
For tantalum capacitors with solid polymer electrolyte the safety margin is much lower, typically around 2.[
]
Cathode
 The next stage for solid tantalum capacitors is the application of the cathode plate (wet tantalum capacitors use a liquid electrolyte as a cathode in conjunction with their casing). This is achieved by pyrolysis of manganese nitrate into
The next stage for solid tantalum capacitors is the application of the cathode plate (wet tantalum capacitors use a liquid electrolyte as a cathode in conjunction with their casing). This is achieved by pyrolysis of manganese nitrate into manganese dioxide
Manganese dioxide is the inorganic compound with the formula . This blackish or brown solid occurs naturally as the mineral pyrolusite, which is the main ore of manganese and a component of manganese nodules. The principal use for is for dry-cel ...
. The "pellet" is dipped into an aqueous solution of nitrate and then baked in an oven at approximately 250 °C to produce the dioxide coat. The chemical equation is:[
:Mn(NO3)2 → MnO2 + 2 NO2
This process is repeated several times through varying specific gravities of nitrate solution, to build up a thick coat over all internal and external surfaces of the "pellet", as shown in Figure 4.
In traditional construction, the "pellet" is successively dipped into ]graphite
Graphite () is a Crystallinity, crystalline allotrope (form) of the element carbon. It consists of many stacked Layered materials, layers of graphene, typically in excess of hundreds of layers. Graphite occurs naturally and is the most stable ...
and then silver
Silver is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag () and atomic number 47. A soft, whitish-gray, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. ...
to provide a good connection from the manganese dioxide cathode plate to the external cathode termination(see Figure 5).

Production flow
The picture below shows the production flow of tantalum electrolytic chip capacitors with sintered anode and solid manganese dioxide electrolyte.

Styles of tantalum capacitors
Tantalum electrolytic capacitors are made in three different styles:
Chip capacitors (case size)
More than 90% of all tantalum electrolytic capacitors are manufactured in SMD style as tantalum chip capacitors. It has contact surfaces on the end faces of the case and is manufactured in different sizes, typically following the EIA-535-BAAC standard. The different sizes can also be identified by case code letters. For some case sizes (A to E), which have been manufactured for many decades, the dimensions and case coding over all manufactures are still largely the same. However, new developments in tantalum electrolytic capacitors such as the multi-anode technique to reduce the ESR or the "face down" technique to reduce the inductance have led to a much wider range of chip sizes and their case codes. These departures from EIA standards mean devices from different manufacturers are no longer always uniform.
An overview of the dimensions of conventional tantalum rectangular chip capacitors and their coding is shown in the following table:
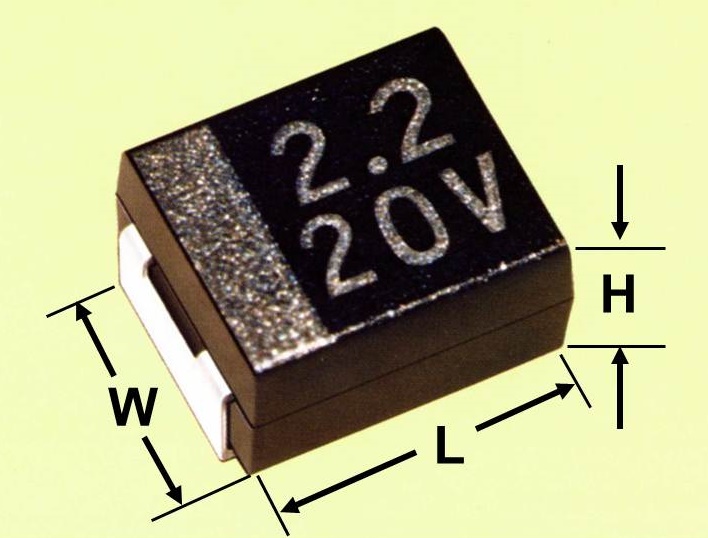 * Note: EIA 3528 metric is also known as EIA 1411 imperial (inches).
* Note: EIA 3528 metric is also known as EIA 1411 imperial (inches).
Wet tantalum capacitors
 The main feature of modern non-solid (wet) tantalum electrolytic capacitors is their energy density compared with that of solid tantalum and wet aluminum electrolytic capacitors within the same temperature range. Due to their self-healing properties (the non-solid electrolyte can deliver oxygen to form new oxide layer in weak areas of the dielectric), the dielectric thickness can be formed with much lower safety margins and consequently with much thinner dielectric than for solid types, resulting in a higher CV value per volume unit. Additionally, wet tantalum capacitors are able to operate at voltages in excess of 100 V up to 630 V, have a relatively low ESR, and have the lowest leakage current of all electrolytic capacitors.
The original wet tantalum capacitors developed in the 1930s were axial capacitors, having a wound cell consisting of a tantalum anode and foil cathode separated by a paper stripe soaked with an electrolyte, mounted in a silver case and non-hermetic elastomer sealed.
The main feature of modern non-solid (wet) tantalum electrolytic capacitors is their energy density compared with that of solid tantalum and wet aluminum electrolytic capacitors within the same temperature range. Due to their self-healing properties (the non-solid electrolyte can deliver oxygen to form new oxide layer in weak areas of the dielectric), the dielectric thickness can be formed with much lower safety margins and consequently with much thinner dielectric than for solid types, resulting in a higher CV value per volume unit. Additionally, wet tantalum capacitors are able to operate at voltages in excess of 100 V up to 630 V, have a relatively low ESR, and have the lowest leakage current of all electrolytic capacitors.
The original wet tantalum capacitors developed in the 1930s were axial capacitors, having a wound cell consisting of a tantalum anode and foil cathode separated by a paper stripe soaked with an electrolyte, mounted in a silver case and non-hermetic elastomer sealed.[D. F. Tailor, Tantalum and Tantalum Compounds, Fansteel Inc., ''Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology'', Vol. 19, 2nd ed. 1969 John Wiley & sons, Inc.] Because of the inertness and stability of the tantalum dielectric oxide layer against strong acids, the wet tantalum capacitors could use sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen, ...
as an electrolyte, thus providing them with a relatively low ESR.
Because in the past, silver casings had problems with silver migration and whiskers
Whiskers, also known as vibrissae (; vibrissa; ) are a type of stiff, functional hair used by most therian mammals to sense their environment. These hairs are finely specialised for this purpose, whereas other types of hair are coarser as ta ...
which led to increasing leakage currents and short circuits, new styles of wet tantalum capacitors use a sintered tantalum pellet cell and a gelled sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen, ...
electrolyte mounted in a pure tantalum case.
Due to their relatively high price, wet tantalum electrolytic capacitors have few consumer applications. They are used in ruggedized industrial applications, such as in probes for oil exploration. Types with military approvals can provide the extended capacitance and voltage ratings, along with the high quality levels required for avionics, military, and space applications.
History
The group of "valve metals" capable of forming an insulating oxide film was discovered in 1875. In 1896 Karol Pollak patented a capacitor using aluminum electrodes and a liquid electrolyte. Aluminum electrolytic capacitors were commercially manufactured in the 1930s.
The first tantalum electrolytic capacitors with wound tantalum foils and non-solid electrolyte were developed in 1930 by Tansitor Electronic Inc. (US), and were used for military purposes.[
Solid electrolyte tantalum capacitors were invented by ]Bell Laboratories
Nokia Bell Labs, commonly referred to as ''Bell Labs'', is an American industrial research and development company owned by Finnish technology company Nokia. With headquarters located in Murray Hill, New Jersey, the company operates several lab ...
in the early 1950s as a miniaturized and more reliable low-voltage support capacitor to complement their newly invented transistor
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch electrical signals and electric power, power. It is one of the basic building blocks of modern electronics. It is composed of semicondu ...
. The solution R. L. Taylor and H. E. Haring from the Bell Labs found for the new miniaturized capacitor found in early 1950 was based on experience with ceramics. They ground metallic tantalum to a powder, pressed this powder into a cylindrical form and then sintered the powder particles at high temperature between under vacuum conditions, into a pellet ("slug").
These first sintered tantalum capacitors used a liquid electrolyte. In 1952 Bell Labs researchers discovered the use of manganese dioxide as a solid electrolyte for a sintered tantalum capacitor.
Although the fundamental inventions came from the Bell Labs, the innovations for manufacturing commercially viable tantalum electrolytic capacitors were done by the researchers of the Sprague Electric Company. Preston Robinson, Sprague's Director of Research, is considered to be the actual inventor of tantalum capacitors in 1954. His invention was supported by R. J. Millard, who introduced the "reform" step in 1955, a significant improvement in which the dielectric of the capacitor was repaired after each dip-and-convert cycle of MnO2 deposition. This dramatically reduced the leakage current of the finished capacitors.
This first solid electrolyte manganese dioxide had 10 times better conductivity than all other types of non-solid electrolyte capacitors. In the style of tantalum pearls, they soon found wide use in radio and new television devices.
In 1971, Intel launched its first microcomputer (the MCS 4) and 1972 Hewlett Packard launched one of the first pocket calculators (the HP-35
The HP-35 was Hewlett-Packard's first pocket calculator and the world's first ''scientific'' pocket calculator: a calculator with trigonometric and exponential functions. It was introduced in 1972.
History
In about 1970 HP co-founder Bill He ...
). The requirements for capacitors increased, especially the demand for lower losses. The equivalent series resistance
Capacitors and inductors as used in electric circuits are not ideal components with only capacitance or inductance. However, they can be treated, to a very good degree of approximation, as being ideal capacitors and inductors in series with a re ...
(ESR) for bypass and decoupling capacitors of standard electrolytic capacitors needed to be decreased.
Although solid tantalum capacitors offered lower ESR and leakage current values than the aluminum electrolytics, in 1980 a price shock for tantalum in the industry dramatically reduced the usability of tantalum capacitors, especially in consumer entertainment electronics.
In search of cheaper alternatives, the industry switched back to using aluminum electrolytic capacitors.
The development of conducting polymers by Alan J. Heeger, Alan MacDiarmid and Hideki Shirakawa
is a Japanese chemist, engineer, and Professor Emeritus at the University of Tsukuba and Zhejiang University. He is best known for his discovery of conductive polymers. He was co-recipient of the 2000 Nobel Prize in Chemistry jointly with Alan ...
in 1975 was a break-through in point of lower ESR. The conductivities of conductive polymers such as polypyrrole
Polypyrrole (PPy) is an organic polymer obtained by oxidative polymerization of pyrrole. It is a solid with the formula H(C4H2NH)nH. It is an intrinsically conducting polymer, used in electronics, optical, biological and medical fields.
Histor ...
(PPy) or PEDOT
Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT or PEDT; ''IUPAC'' name poly(2,3-dihydrothieno ,4-''b''1,4]dioxane-5,7-diyl)) is a conducting polymer based on 3,4-Ethylenedioxythiophene, 3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene or EDOT. It was first reported by Bay ...
are better by a factor of 1000 than that of manganese dioxide, and are close to the conductivity of metals.
In 1993 NEC introduced their SMD polymer tantalum electrolytic capacitors, called "NeoCap". In 1997 Sanyo followed with their "POSCAP" polymer tantalum chips.
A new conductive polymer for tantalum polymer capacitors was presented by Kemet at the "1999 Carts" conference. This capacitor used the newly developed organic conductive polymer PEDT Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene), also known as PEDOT (trade name Baytron).
This development to low ESR capacitors with high CV-volumes in chip style for the rapid growing SMD technology in the 1990s increased the demand on tantalum chips dramatically. However, another price explosion for tantalum in 2000/2001 forced the development of niobium electrolytic capacitors with manganese dioxide electrolyte, which have been available since 2002. The materials and processes used to produce niobium-dielectric capacitors are essentially the same as for existing tantalum-dielectric capacitors. The characteristics of niobium electrolytic capacitors and tantalum electrolytic capacitors are roughly comparable.
Electrical characteristics
Series-equivalent circuit
 Tantalum electrolytic capacitors as discrete components are not ideal capacitors, as they have losses and parasitic inductive parts. All properties can be defined and specified by a series equivalent circuit composed of an idealized capacitance and additional electrical components which model all losses and inductive parameters of a capacitor. In this series-equivalent circuit the electrical characteristics are defined by:
* ''C'', the capacitance of the capacitor
* ''R''leak, the resistance representing the Leakage (electronics), leakage current of the capacitor
* ''R''ESR, the
Tantalum electrolytic capacitors as discrete components are not ideal capacitors, as they have losses and parasitic inductive parts. All properties can be defined and specified by a series equivalent circuit composed of an idealized capacitance and additional electrical components which model all losses and inductive parameters of a capacitor. In this series-equivalent circuit the electrical characteristics are defined by:
* ''C'', the capacitance of the capacitor
* ''R''leak, the resistance representing the Leakage (electronics), leakage current of the capacitor
* ''R''ESR, the equivalent series resistance
Capacitors and inductors as used in electric circuits are not ideal components with only capacitance or inductance. However, they can be treated, to a very good degree of approximation, as being ideal capacitors and inductors in series with a re ...
which summarizes all ohmic losses of the capacitor, usually abbreviated as "ESR"
* ''L''ESL, the equivalent series inductance
Equivalent series inductance (ESL) is an effective inductance that is used to describe the inductive part of the Electrical impedance, impedance of certain electrical components.
Overview
The theoretical treatment of devices such as capacitors a ...
which is the effective self-inductance of the capacitor, usually abbreviated as "ESL".
Using a series equivalent circuit rather than a parallel equivalent circuit is specified by IEC
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC; ) is an international standards organization that prepares and publishes international standards for all electrical, electronic and related technologies. IEC standards cover a vast range of ...
/EN 60384-1.
Capacitance standard values and tolerances
The electrical characteristics of tantalum electrolytic capacitors depend on the structure of the anode and the electrolyte used. This influences the capacitance value of tantalum capacitors, which depend on operating frequency and temperature. The basic unit of electrolytic capacitors capacitance is microfarad (μF).
The capacitance value specified in the data sheets of the manufacturers is called rated capacitance CR or nominal capacitance CN and is the value for which the capacitor has been designed. Standardized measuring condition for electrolytic capacitors is an AC measuring method with a frequency of 100 to 120 Hz. Electrolytic capacitors differ from other capacitor types, whose capacitances are typically measured at 1 kHz or higher. For tantalum capacitors a DC bias voltage of 1.1 to 1.5 V for types with a rated voltage of ≤2.5 V or 2.1 to 2.5 V for types with a rated voltage of >2.5 V may be applied during the measurement to avoid reverse voltage.
The percentage of allowed deviation of the measured capacitance from the rated value is called capacitance tolerance. Electrolytic capacitors are available in different tolerance series classifications, whose values are specified in the E series specified in IEC 60063. For abbreviated marking in tight spaces, a letter code for each tolerance is specified in IEC 60062.
* rated capacitance, E3 series, tolerance ±20%, letter code "M"
* rated capacitance, E6 series, tolerance ±20%, letter code "M"
* rated capacitance, E12 series, tolerance ±10%, letter code "K"
The required capacitance tolerance is determined by the particular application. Electrolytic capacitors, which are often used for filtering
Filtration is a physical process that separates solid matter and fluid from a mixture.
Filter, filtering, filters or filtration may also refer to:
Science and technology
Computing
* Filter (higher-order function), in functional programming
* Fil ...
and bypassing capacitors don't have the need for narrow tolerances because they are mostly not used for accurate frequency applications like oscillator
Oscillation is the repetitive or periodic variation, typically in time, of some measure about a central value (often a point of equilibrium) or between two or more different states. Familiar examples of oscillation include a swinging pendulum ...
s.
Rated and category voltage
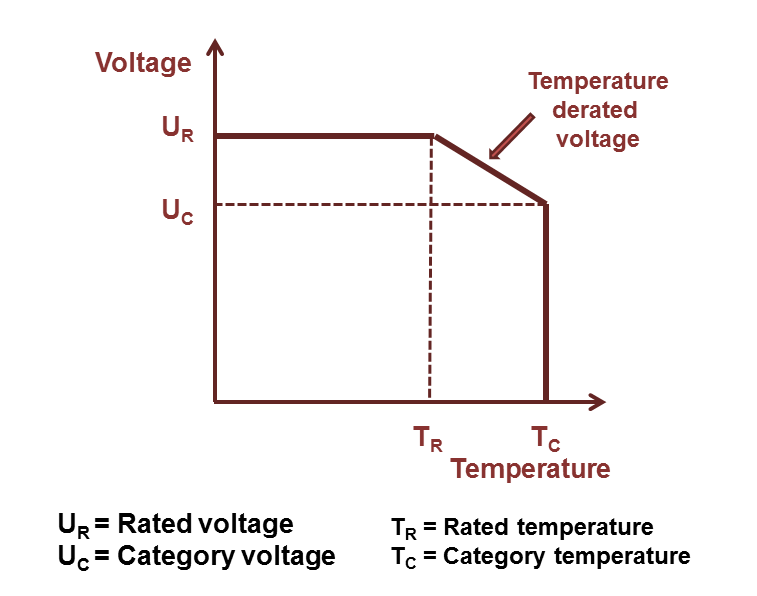 Referring to IEC/EN 60384-1 standard the allowed operating voltage for tantalum capacitors is called "rated voltage UR " or "nominal voltage UN". The rated voltage UR is the maximum DC voltage or peak pulse voltage that may be applied continuously at any temperature within the rated temperature range TR (IEC/EN 60384-1).
The voltage rating of electrolytic capacitors decreases with increasing temperature. For some applications it is important to use a higher temperature range. Lowering the voltage applied at a higher temperature maintains safety margins. For some capacitor types therefore the IEC standard specify a "temperature derated voltage" for a higher temperature, the "category voltage UC". The category voltage is the maximum DC voltage or peak pulse voltage that may be applied continuously to a capacitor at any temperature within the category temperature range TC. The relation between both voltages and temperatures is given in the picture right.
Lower voltage applied may have positive influences for tantalum electrolytic capacitors. Lowering the voltage applied increases the reliability and reduces the expected failure rate.
Referring to IEC/EN 60384-1 standard the allowed operating voltage for tantalum capacitors is called "rated voltage UR " or "nominal voltage UN". The rated voltage UR is the maximum DC voltage or peak pulse voltage that may be applied continuously at any temperature within the rated temperature range TR (IEC/EN 60384-1).
The voltage rating of electrolytic capacitors decreases with increasing temperature. For some applications it is important to use a higher temperature range. Lowering the voltage applied at a higher temperature maintains safety margins. For some capacitor types therefore the IEC standard specify a "temperature derated voltage" for a higher temperature, the "category voltage UC". The category voltage is the maximum DC voltage or peak pulse voltage that may be applied continuously to a capacitor at any temperature within the category temperature range TC. The relation between both voltages and temperatures is given in the picture right.
Lower voltage applied may have positive influences for tantalum electrolytic capacitors. Lowering the voltage applied increases the reliability and reduces the expected failure rate.[Ch. Reynolds, AVX, Technical Information, Reliability Management of Tantalum Capacitors]
PDF
/ref>
Applying a higher voltage than specified may destroy tantalum electrolytic capacitors.
Surge voltage
The surge voltage indicates the maximum peak voltage value that may be applied to electrolytic capacitors during their application for a limited number of cycles. The surge voltage is standardized in IEC/EN 60384-1. For tantalum electrolytic capacitors the surge voltage shall be 1.3 times of the rated voltage, rounded off to the nearest volt.
The surge voltage applied to tantalum capacitors may influence the capacitors failure rate.[J. Gill, AVX, Surge in Solid Tantalum Capacitor]
PDF
[A. Teverovsky, NASA, Effect of Surge Current Testing on Reliability of Solid Tantalum Capacitor]
PDF
Transient voltage
Transient voltage or a current spike applied to tantalum electrolytic capacitors with solid manganese dioxide electrolyte can cause some tantalum capacitors to fail and may directly lead to a short.
Reverse voltage
Tantalum electrolytic are polarized and generally require anode electrode voltage to be positive relative to the cathode voltage.
With a reverse voltage applied, a reverse leakage current flows in very small areas of microcracks or other defects across the dielectric layer to the anode of the electrolytic capacitor. Although the current may only be a few microamps, it represents a very high localized current density which can cause a tiny hot-spot. This can cause some conversion of amorphous tantalum pentoxide to the more conductive crystalline form. When a high current is available, this effect can avalanche and the capacitor may become a total short.
Nevertheless, tantalum electrolytic capacitors can withstand for short instants a reverse voltage for a limited number of cycles. The most common guidelines for tantalum reverse voltage are:
* 10% of rated voltage to a maximum of 1 V at 25 °C,
* 3% of rated voltage to a maximum of 0.5 V at 85 °C,
* 1% of rated voltage to a maximum of 0.1 V at 125 °C.
These guidelines apply for short excursion and should never be used to determine the maximum reverse voltage under which a capacitor can be used permanently.
Impedance
 Tantalum electrolytic capacitors, as well as other conventional capacitors, have two electrical functions. For
Tantalum electrolytic capacitors, as well as other conventional capacitors, have two electrical functions. For timer
A timer or countdown timer is a type of clock that starts from a specified time duration and stops upon reaching 00:00. It can also usually be stopped manually before the whole duration has elapsed. An example of a simple timer is an hourglass ...
s or similar applications, capacitors are seen as a storage component to store electrical energy. But for smoothing, bypassing, or decoupling applications like in power supplies
A power supply is an electrical device that supplies electric power to an electrical load. The main purpose of a power supply is to convert electric current from a source to the correct voltage, current, and frequency to power the load. As a r ...
, the capacitors work additionally as AC resistor
A resistor is a passive two-terminal electronic component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element. In electronic circuits, resistors are used to reduce current flow, adjust signal levels, to divide voltages, bias active e ...
s to filter undesired AC components from voltage rails. For this (biased) AC function the frequency dependent AC resistance ( impedance ''"Z"'') is as important as the capacitance value.
The impedance is the complex
Complex commonly refers to:
* Complexity, the behaviour of a system whose components interact in multiple ways so possible interactions are difficult to describe
** Complex system, a system composed of many components which may interact with each ...
ratio of the voltage to the current with both magnitude and phase
Phase or phases may refer to:
Science
*State of matter, or phase, one of the distinct forms in which matter can exist
*Phase (matter), a region of space throughout which all physical properties are essentially uniform
*Phase space, a mathematica ...
at a particular frequency in an AC circuit. In this sense impedance is a measure of the ability of the capacitor to attenuate alternating currents and can be used like Ohms law
:
The impedance is a frequency dependent AC resistance and possesses both magnitude and phase at a particular frequency. In data sheets of electrolytic capacitors, only the impedance magnitude '', Z, '' is specified, and simply written as ''"Z"''. Regarding to the IEC/EN 60384-1 standard, the impedance values of tantalum electrolytic capacitors are measured and specified at 10 kHz or 100 kHz depending on the capacitance and voltage of the capacitor.
Besides measuring, the impedance can also be calculated using the idealized components out of a capacitor's series-equivalent circuit, including an ideal capacitor ''C'', a resistor ''ESR'', and an inductance ''ESL''. In this case the impedance at the angular frequency ''ω'' therefore is given by the geometric (complex) addition of ''ESR'', by a capacitive reactance ''XC''
:
and by an inductive reactance ''XL'' (Inductance
Inductance is the tendency of an electrical conductor to oppose a change in the electric current flowing through it. The electric current produces a magnetic field around the conductor. The magnetic field strength depends on the magnitude of the ...
)
.
Then ''Z'' is given by
: .
In the special case of resonance
Resonance is a phenomenon that occurs when an object or system is subjected to an external force or vibration whose frequency matches a resonant frequency (or resonance frequency) of the system, defined as a frequency that generates a maximu ...
, in which the both reactive resistances ''XC'' and ''XL'' have the same value (''XC=XL''), then the impedance will only be determined by ''ESR''. With frequencies above the resonance the impedance increases again due to the ''ESL'' of the capacitor. At this point, the capacitor begins to behave primarily as an inductance.
ESR and dissipation factor tan δ
File:Elko-Impedanzverlauf-mit-ESR.svg, Typical impedance and ESR as a function of frequency
File: E-cap-100uF-impedance-ESR-curves.jpg, Typical impedance and ESR curves over frequency for different electrolytic capacitor styles compared with MLCC
The equivalent series resistance
Capacitors and inductors as used in electric circuits are not ideal components with only capacitance or inductance. However, they can be treated, to a very good degree of approximation, as being ideal capacitors and inductors in series with a re ...
(''ESR'') summarizes all resistive losses of the capacitor. These are the terminal resistances, the contact resistance of the electrode contact, the line resistance of the electrodes, the electrolyte resistance, and the dielectric losses in the dielectric oxide layer.
ESR influences the remaining superimposed AC ripple behind smoothing and may influence the circuit functionality. Related to the capacitor ESR is accountable for internal heat generation if a #ripple current flows over the capacitor. This internal heat may influence the reliability of tantalum electrolytic capacitors.
Generally, the ESR decreases with increasing frequency and temperature.[Joelle Arnold, Uprating of Electrolytic Capacitors, DfR Solutions]
/ref>
Discussions of electrolytic capacitors historically sometimes refer to the dissipation factor, ''tan δ'', in the relevant data sheets instead of ''ESR''. The dissipation factor is determined by the tangent of the phase angle between the subtraction of capacitive reactance ''XC'' from inductive reactance ''XL'', and the ''ESR''. If the capacitor's inductance ''ESL'' is small, the dissipation factor can be approximated as:
:
The dissipation factor ''tan δ'' is used for capacitors with very low losses in frequency determining circuits or resonant circuit
An LC circuit, also called a resonant circuit, tank circuit, or tuned circuit, is an electric circuit consisting of an inductor, represented by the letter L, and a capacitor, represented by the letter C, connected together. The circuit can act ...
s where the reciprocal value of the dissipation factor is called the quality factor
In physics and engineering, the quality factor or factor is a dimensionless parameter that describes how underdamped an oscillator or resonator is. It is defined as the ratio of the initial energy stored in the resonator to the energy lost in ...
(''Q'') which represents a resonator's bandwidth
Bandwidth commonly refers to:
* Bandwidth (signal processing) or ''analog bandwidth'', ''frequency bandwidth'', or ''radio bandwidth'', a measure of the width of a frequency range
* Bandwidth (computing), the rate of data transfer, bit rate or thr ...
.
Ripple current
A "ripple current" is the RMS value of a superimposed AC current of any frequency upon a DC current. It arises mainly in power supplies (including switched-mode power supplies) after rectifying an AC voltage and flows as charge and discharge current through the decoupling or smoothing capacitor.
Ripple currents generate heat inside the capacitor body. This dissipation power loss ''PL'' is caused by ''ESR'' and is the squared value of the effective (RMS) ripple current ''IR''.
:
This internal generated heat, in addition to the ambient temperature and possibly other external heat sources, leads to a capacitor body temperature having a temperature difference of ''Δ T'' against the ambient. This heat has to be distributed as thermal losses ''Pth'' over the capacitors surface ''A'' and the thermal resistance ''β'' to the ambient.
:
The internal generated heat has to be distributed to the ambient by thermal radiation
Thermal radiation is electromagnetic radiation emitted by the thermal motion of particles in matter. All matter with a temperature greater than absolute zero emits thermal radiation. The emission of energy arises from a combination of electro ...
, convection
Convection is single or Multiphase flow, multiphase fluid flow that occurs Spontaneous process, spontaneously through the combined effects of material property heterogeneity and body forces on a fluid, most commonly density and gravity (see buoy ...
, and thermal conduction
Thermal conduction is the diffusion of thermal energy (heat) within one material or between materials in contact. The higher temperature object has molecules with more kinetic energy; collisions between molecules distributes this kinetic energy ...
. The temperature of the capacitor, which is established on the balance between heat produced and distributed, should not exceed the capacitors maximum specified temperature.
The ripple current is specified as an effective (RMS) value at 100 or 120 Hz or at 10 kHz at upper category temperature. Non-sinusoidal ripple currents have to be analyzed and separated into their component sinusoidal frequencies by means of Fourier analysis
In mathematics, Fourier analysis () is the study of the way general functions may be represented or approximated by sums of simpler trigonometric functions. Fourier analysis grew from the study of Fourier series, and is named after Joseph Fo ...
and the equivalent ripple current calculated as the square root of the sum of the squares of the individual currents.[Vishay BCcomponents, Introduction Aluminum Capacitors, Revision: 10-Sep-13 1 Document Number: 28356]
PDF
:
In solid tantalum electrolytic capacitors the heat generated by the ripple current influences the reliability of the capacitors. Exceeding the limit tends to result in catastrophic failures with shorts and burning components.
Current surge, peak or pulse current
Solid tantalum electrolytic capacitors can be damaged by surge, peak or pulse currents.
Leakage current
 The DC leakage current is a special characteristic for electrolytic capacitors other conventional capacitors don't have. This current is represented by the resistor ''Rleak'' in parallel with the capacitor in the series-equivalent circuit of electrolytic capacitors. The main causes of leakage current for solid tantalum capacitors are electrical breakdown of the dielectric, conductive paths due to impurities or due to poor anodization, bypassing of dielectric due to excess manganese dioxide, due to moisture paths or due to cathode conductors (carbon, silver). This leakage current in solid electrolyte capacitors cannot be reduced by "healing" in the sense of generating new oxide because under normal conditions solid electrolytes are unable to deliver oxygen for forming processes. This statement should not be confused with the self-healing process during field crystallization, as described in Reliability (failure rate).
The specification of the leakage current in datasheets often will be given by multiplication of the rated capacitance value ''CR'' with the value of the rated voltage ''UR'' together with an addendum figure, measured after a measuring time of 2 or 5 minutes, for example:
:
The value of the leakage current depends on the voltage applied, on temperature of the capacitor, on measuring time, and on influence of moisture caused by case sealing conditions. They normally have a very low leakage current, most much lower than the specified worst-case.
The DC leakage current is a special characteristic for electrolytic capacitors other conventional capacitors don't have. This current is represented by the resistor ''Rleak'' in parallel with the capacitor in the series-equivalent circuit of electrolytic capacitors. The main causes of leakage current for solid tantalum capacitors are electrical breakdown of the dielectric, conductive paths due to impurities or due to poor anodization, bypassing of dielectric due to excess manganese dioxide, due to moisture paths or due to cathode conductors (carbon, silver). This leakage current in solid electrolyte capacitors cannot be reduced by "healing" in the sense of generating new oxide because under normal conditions solid electrolytes are unable to deliver oxygen for forming processes. This statement should not be confused with the self-healing process during field crystallization, as described in Reliability (failure rate).
The specification of the leakage current in datasheets often will be given by multiplication of the rated capacitance value ''CR'' with the value of the rated voltage ''UR'' together with an addendum figure, measured after a measuring time of 2 or 5 minutes, for example:
:
The value of the leakage current depends on the voltage applied, on temperature of the capacitor, on measuring time, and on influence of moisture caused by case sealing conditions. They normally have a very low leakage current, most much lower than the specified worst-case.
Dielectric absorption (soakage)
Dielectric absorption occurs when a capacitor that has remained charged for a long time retains some charge when briefly discharged. Although an ideal capacitor would reach zero volts after discharge, real capacitors develop a small voltage from time-delayed dipole discharging, a phenomenon that is also called dielectric relaxation
In electromagnetism, a dielectric (or dielectric medium) is an electrical insulator that can be polarised by an applied electric field. When a dielectric material is placed in an electric field, electric charges do not flow through the materia ...
, "soakage" or "battery action".
Dielectric absorption can cause a problem in circuits where very small currents are used, such as long- time-constant integrator
An integrator in measurement and control applications is an element whose output signal is the time integral of its input signal. It accumulates the input quantity over a defined time to produce a representative output.
Integration is an importan ...
s or sample-and-hold circuits. However, in most applications where tantalum electrolytic capacitors are supporting power supply lines, dielectric absorption is not a problem.
Reliability and life time
Reliability (failure rate)
 The
The reliability
Reliability, reliable, or unreliable may refer to:
Science, technology, and mathematics Computing
* Data reliability (disambiguation), a property of some disk arrays in computer storage
* Reliability (computer networking), a category used to des ...
of a component is a property that indicates how well a component performs its function in a time interval. It is subject to a stochastic process
In probability theory and related fields, a stochastic () or random process is a mathematical object usually defined as a family of random variables in a probability space, where the index of the family often has the interpretation of time. Sto ...
and can be described qualitatively and quantitatively; it is not directly measurable. The reliability of electrolytic capacitors are empirically determined by identifying the failure rate
Failure is the social concept of not meeting a desirable or intended objective, and is usually viewed as the opposite of success. The criteria for failure depends on context, and may be relative to a particular observer or belief system. On ...
in production-accompanying endurance tests, see Reliability engineering#Reliability testing.
The reliability normally is shown in a bathtub curve
The bathtub curve is a particular shape of a failure rate graph. This graph is used in reliability engineering and deterioration modeling. The 'bathtub' refers to the shape of a line that curves up at both ends, similar in shape to a bathtub. Th ...
and is divided into three areas: Early failures or infant mortality failures, constant random failures and wear out failures. Failure types included in the total failure rate are short circuit, open circuit, and degradation failures (exceeding electrical parameters).
The reliability
Reliability, reliable, or unreliable may refer to:
Science, technology, and mathematics Computing
* Data reliability (disambiguation), a property of some disk arrays in computer storage
* Reliability (computer networking), a category used to des ...
prediction is generally expressed in a failure rate
Failure is the social concept of not meeting a desirable or intended objective, and is usually viewed as the opposite of success. The criteria for failure depends on context, and may be relative to a particular observer or belief system. On ...
λ, abbreviation FIT (failures in time). This is the number of failures that can be expected in one billion (109) component-hours of operation (e.g. 1000 components for 1 million hours, or 1 million components for 1000 hours which is 1 ppm/1000 hours) at fixed working conditions during the period of constant random failures. These failure rate model implicitly assume the idea of "random failure". Individual components fail at random times but at a predictable rate. The standard operation conditions for the failure rate FIT are 40 °C and 0.5 UR.
The reciprocal value of FIT is mean time between failures (MTBF).
For tantalum capacitors, often the failure rate is specified at 85 °C and rated voltage UR as reference conditions and expressed as per cent failed components per thousand hours (n %/1000 h). That is "n" number of failed components per 105 hours or in FIT the ten-thousand-fold value per 109 hours.
For conditions other than the standard operation conditions 40 °C and 0.5 UR, for other temperature and voltage applied, for current load, capacitance value, circuit resistance, mechanical influences and humidity, the FIT figure can recalculated with acceleration factors standardized for industrial or military contexts. For example, higher temperature and applied voltage cause the failure rate to increase.
The most often cited source for recalculation the failure rate is the MIL-HDBK-217F, the "bible" of failure rate calculations for electronic components. SQC Online, the online statistical calculators for acceptance sampling and quality control gives an online tool for short examination to calculate given failure rate values to application conditions.
Some manufacturers of tantalum capacitors may have their own FIT calculation tables.
Tantalum capacitors are reliable components. Continuous improvement in tantalum powder and capacitor technologies have resulted in a significant reduction in the amount of impurities present, which formerly have caused most of the field crystallization failures. Commercially available tantalum capacitors now have reached as standard products the high MIL standard "C" level which is 0.01%/1000h at 85 °C and UR or 1 failure per 107 hours at 85 °C and UR.[T.Zednicek, AVX, A Study of Field Crystallization in Tantalum Capacitors and its effect on DCL and Reliability]
/ref> Recalculated in FIT with the acceleration factors coming from MIL HDKB 217F at 40 °C and 0.5 UR is this failure rate for a 100 μF/25 V tantalum chip capacitor used with a series resistance of 0.1 Ω the failure rate is 0.02 FIT.
Life time
The Service life, life time, service life
A product's service life is its period of use in service. Several related terms describe more precisely a product's life, from the point of manufacture, storage, and distribution, and eventual use.
Service life has been defined as "a product' ...
, load life or useful life of tantalum electrolytic capacitors depends entirely on the electrolyte used:
* Those using liquid electrolytes ''do not'' have a life time specification. (When hermetically sealed)
* Those using manganese dioxide electrolytes ''do not'' have a life time specification.
* Those using polymer electrolytes ''do'' have a life time specification.
The polymer electrolyte have a small deterioration of conductivity by a thermal degradation mechanism of the conductive polymer. The electrical conductivity decreased, as a function of time, in agreement with a granular metal type structure, in which aging is due to the shrinking of the conductive polymer grains. The life time of polymer electrolytic capacitors is specified in similar terms to the non-solid electrolytic caps, but its life time calculation follows other rules which lead to much longer operational life times.
Failure modes and self-healing mechanism
Tantalum capacitors show different electrical long-term behaviors depending on the electrolyte used. Application rules for types with an inherent failure mode are specified to ensure high reliability and long life.
Tantalum capacitors are reliable on the same very high level as other electronic components with very low failure rates. However, they have a single unique failure mode called "field crystallization".dielectric breakdown
In electronics, electrical breakdown or dielectric breakdown is a process that occurs when an electrically insulating material (a dielectric), subjected to a high enough voltage, suddenly becomes a conductor and current flows through it. All ...
is characterized by a sudden rise in leakage current within a few milliseconds, from nanoamp magnitude to amp magnitude in low-impedance circuits. Increasing current flow can accelerate in an "avalanche effect" and rapidly spread through the metal/oxide. This can result in various degrees of destruction from rather small, burned areas on the oxide to zigzag burned streaks covering large areas of the pellet or complete oxidation of the metal.short circuit
A short circuit (sometimes abbreviated to short or s/c) is an electrical circuit that allows a current to travel along an unintended path with no or very low electrical impedance. This results in an excessive current flowing through the circuit ...
. In this circumstance, the failure can be catastrophic if there is nothing to limit the available current, as the series resistance of the capacitor can become very low.
 Impurities, tiny mechanical damages, or imperfections in the dielectric can affect the structure, changing it from amorphous to crystalline structure and thus lowering the dielectric strength. The purity of the tantalum powder is one of the most important parameters for defining its risk of crystallization. Since the mid-1980s, manufactured tantalum powders have exhibited an increase in purity.
Surge currents after soldering-induced stresses may start crystallization, leading to insulation breakdown. The only way to avoid catastrophic failures is to limit the current which can flow from the source in order to reduce the breakdown to a limited area. Current flowing through the crystallized area causes heating in the manganese dioxide cathode near the fault. At increased temperatures a chemical reaction then reduces the surrounding conductive manganese dioxide to the insulating
Impurities, tiny mechanical damages, or imperfections in the dielectric can affect the structure, changing it from amorphous to crystalline structure and thus lowering the dielectric strength. The purity of the tantalum powder is one of the most important parameters for defining its risk of crystallization. Since the mid-1980s, manufactured tantalum powders have exhibited an increase in purity.
Surge currents after soldering-induced stresses may start crystallization, leading to insulation breakdown. The only way to avoid catastrophic failures is to limit the current which can flow from the source in order to reduce the breakdown to a limited area. Current flowing through the crystallized area causes heating in the manganese dioxide cathode near the fault. At increased temperatures a chemical reaction then reduces the surrounding conductive manganese dioxide to the insulating manganese(III) oxide
Manganese(III) oxide is a chemical compound with the formula Mn2O3. It occurs in nature as the mineral bixbyite (recently changed to bixbyite-(Mn)IMA 21-H: Redefinition of bixbyite and definition of bixbyite-(Fe) and bixbyite-(Mn). CNMNC Newslett ...
(Mn2O3) and insulates the crystallized oxide in the tantalum oxide layer, stopping local current flow.
Failure avoidance
Solid tantalum capacitors with crystallization are most likely to fail at power-on. It is believed that the voltage across the dielectric layer is the trigger mechanism for the breakdown and that the switch-on current pushes the collapse to a catastrophic failure. To prevent such sudden failures, manufacturers recommend:
Additional information
Capacitor symbols
Electrolytic capacitor symbols
Parallel connection
Small or low voltage electrolytic capacitors may be safely connected in parallel. Large sizes capacitors, especially large sizes and high voltage types should be individually protected against sudden discharge of the whole bank due to a failed capacitor.
Series connection
Some applications like AC/AC converters with DC-link for frequency controls in three-phase grids need higher voltages than aluminum electrolytic capacitors usually offer. For such applications electrolytic capacitors can be connected in series for increased voltage withstanding capability. During charging, the voltage across each of the capacitors connected in series is proportional to the inverse of the individual capacitor's leakage current. Since every capacitor differs a little bit in individual leakage current the capacitors with a higher leakage current will get less voltage. The voltage balance over the series connected capacitors is not symmetrically. Passive or active voltage balance has to be provided in order to stabilize the voltage over each individual capacitor.[Epcos, Aluminum electrolytic capacitors, General technical information]
PDF
/ref>
Polarity marking
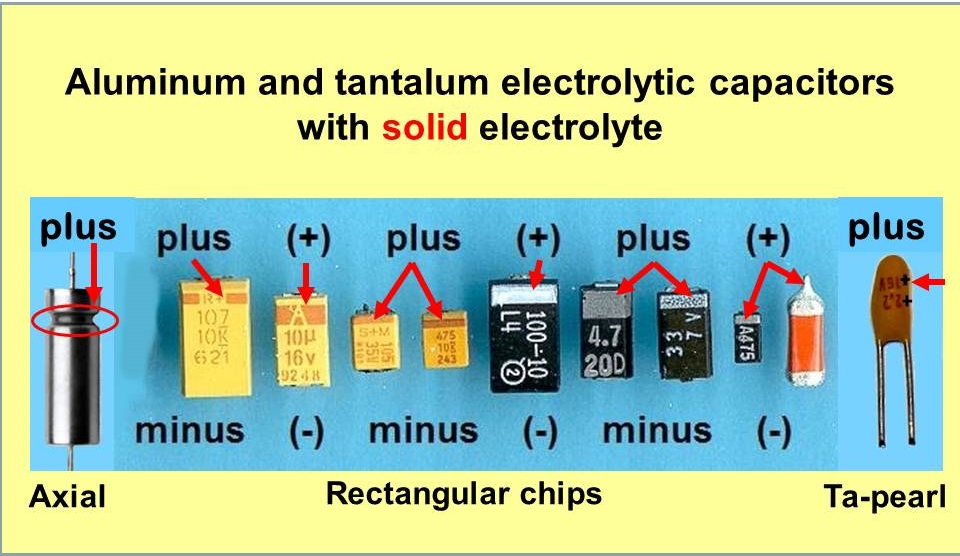 All tantalum capacitors are polarized components, with distinctly marked positive or negative terminals. When subjected to reversed polarity (even briefly), the capacitor depolarizes and the dielectric oxide layer breaks down, which can cause it to fail even when later operated with correct polarity. If the failure is a short circuit (the most common occurrence), and current is not limited to a safe value, catastrophic thermal runaway may occur. This failure can even result in the capacitor forcefully ejecting its burning core.
Tantalum electrolytic capacitors with solid electrolyte are marked at their positive terminal with a bar or a "+". Tantalum electrolytic capacitors with non-solid electrolyte (axial leaded style) are marked on the negative terminal with a bar or a "-" (minus). The polarity better can be identified on the shaped side of the case, which has the positive terminal. The different marking styles can cause dangerous confusion.
A particular cause of confusion is that on surface mount tantalum capacitors the positive terminal is marked with a bar. Whereas on aluminium surface mount capacitors it is the ''negative'' terminal that is so marked.
For Tantalum capacitors from the early 1970s the polarity is indicated by a dot. Positive lead is the lead on the right when the side with the dot is facing you. The positive lead may also be very slightly longer. Furthermore the polarity is marked on PCBs by differently-shaped solder points if there are no "+" or "-" signs printed on the PCB. For example a square-shaped solder point is used for positive polarity (needs to be verified on particular case measuring connection against ground, negative or positive voltage pins)
All tantalum capacitors are polarized components, with distinctly marked positive or negative terminals. When subjected to reversed polarity (even briefly), the capacitor depolarizes and the dielectric oxide layer breaks down, which can cause it to fail even when later operated with correct polarity. If the failure is a short circuit (the most common occurrence), and current is not limited to a safe value, catastrophic thermal runaway may occur. This failure can even result in the capacitor forcefully ejecting its burning core.
Tantalum electrolytic capacitors with solid electrolyte are marked at their positive terminal with a bar or a "+". Tantalum electrolytic capacitors with non-solid electrolyte (axial leaded style) are marked on the negative terminal with a bar or a "-" (minus). The polarity better can be identified on the shaped side of the case, which has the positive terminal. The different marking styles can cause dangerous confusion.
A particular cause of confusion is that on surface mount tantalum capacitors the positive terminal is marked with a bar. Whereas on aluminium surface mount capacitors it is the ''negative'' terminal that is so marked.
For Tantalum capacitors from the early 1970s the polarity is indicated by a dot. Positive lead is the lead on the right when the side with the dot is facing you. The positive lead may also be very slightly longer. Furthermore the polarity is marked on PCBs by differently-shaped solder points if there are no "+" or "-" signs printed on the PCB. For example a square-shaped solder point is used for positive polarity (needs to be verified on particular case measuring connection against ground, negative or positive voltage pins)
Imprinted markings
Tantalum capacitors, like most other electronic components and if enough space is available, have imprinted markings to indicate manufacturer, type, electrical and thermal characteristics, and date of manufacture. But most tantalum capacitors are chip types so the reduced space limits the imprinted signs to capacitance, tolerance, voltage and polarity.
Smaller capacitors use a shorthand notation. The most commonly used format is: XYZ J/K/M "V", where XYZ represents the capacitance (calculated as XY × 10Z pF), the letters K or M indicate the tolerance (±10% and ±20% respectively) and "V" represents the working voltage.
Examples:
* 105K 330V implies a capacitance of 10 × 105 pF = 1 μF (K = ±10%) with a working voltage of 330 V.
* 476M 100V implies a capacitance of 47 × 106 pF = 47 μF (M = ±20%) with a working voltage of 100 V.
Capacitance, tolerance and date of manufacture can be indicated with a short code specified in IEC/EN 60062. Examples of short-marking of the rated capacitance (microfarads): μ47 = 0,47 μF, 4μ7 = 4.7 μF, 47μ = 47 μF
The date of manufacture is often printed in accordance with international standards.
* Version 1: coding with year/week numeral code, "1208" is "2012, week number 8".
* Version 2: coding with year code/month code. The year codes are: "R" = 2003, "S"= 2004, "T" = 2005, "U" = 2006, "V" = 2007, "W" = 2008, "X" = 2009, "A" = 2010, "B" = 2011, "C" = 2012, "D" = 2013, "E" = 2014 etc. Month codes are: "1" to "9" = Jan. to Sept., "O" = October, "N" = November, "D" = December. "X5" is then "2009, May"
For very small capacitors no marking is possible, only the component's packaging or the assembly manufacturer's records of the components used can be used to identify a component fully.
Standardization
Standard definitions of characteristics and test methods for electrical
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter possessing an electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by Maxwel ...
and electronic components and related technologies are published by the International Electrotechnical Commission
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC; ) is an international standards organization that prepares and publishes international standards for all electrical, electronics, electronic and related technologies. IEC standards cover a va ...
(IEC), a non-profit
A nonprofit organization (NPO), also known as a nonbusiness entity, nonprofit institution, not-for-profit organization, or simply a nonprofit, is a non-governmental (private) legal entity organized and operated for a collective, public, or so ...
, non-governmental international standards organization
A standards organization, standards body, standards developing organization (SDO), or standards setting organization (SSO) is an organization whose primary function is developing, coordinating, promulgating, revising, amending, reissuing, interpr ...
, which defer to the standards of other industry organizations for particular application characteristics, e.g. the EIA size standards, IPC solderability standards, etc. The quality and reliability standards and methods of the US MIL-STD specifications are used for components requiring a higher reliability or a less benign operating environment are required.
The definition of the characteristics and the procedure of the test methods for capacitor
In electrical engineering, a capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy by accumulating electric charges on two closely spaced surfaces that are insulated from each other. The capacitor was originally known as the condenser, a term st ...
s for use in electronic equipment are set out in the Generic specification:
* IEC/EN 60384-1: Fixed capacitors for use in electronic equipment
The tests and requirements to be met by aluminum and tantalum electrolytic capacitors for use in electronic equipment for approval as standardized types are set out in the following sectional specifications:
* IEC/EN 60384-3—''Surface mount fixed tantalum electrolytic capacitors with manganese dioxide solid electrolyte''
* IEC/EN 60384-15—''fixed tantalum capacitors with non-solid and solid electrolyte''
* IEC/EN 60384-24—''Surface mount fixed tantalum electrolytic capacitors with conductive polymer solid electrolyte''
Tantalum ore
Tantalum capacitors are the main use of the element tantalum. Tantalum ore is one of the conflict minerals
The eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) has a Kivu conflict, history of conflict, where various armies, rebel groups, and outside actors have profited from mining while contributing to violence and exploitation during wars in the regio ...
. Some non-governmental organization
A non-governmental organization (NGO) is an independent, typically nonprofit organization that operates outside government control, though it may get a significant percentage of its funding from government or corporate sources. NGOs often focus ...
s are working together to raise awareness of the relationship between consumer electronic devices and conflict minerals.
Market
The market of tantalum electrolytic capacitors in 2008 was approximately US$2.2 billion, which was roughly 12% of the total capacitor market.[Electronic Capacitors, SIC 3675, NAICS 334414: Electronic Capacitor Manufacturing, Industry report]
/ref>
Uses
The low leakage and high capacity of tantalum capacitors favor their use in sample and hold
In electronics, a sample and hold (also known as sample and follow) circuit is an analog device that samples (captures, takes) the voltage of a continuously varying analog signal and holds (locks, freezes) its value at a constant level for a ...
circuits to achieve long hold duration, and some long duration timing circuits where precise timing is not critical. They are also often used for power supply rail decoupling in parallel with film or ceramic capacitors which provide low ESR and low reactance at high frequency. Tantalum capacitors can replace aluminum electrolytic capacitors in situations where the external environment or dense component packing results in a sustained hot internal environment and where high reliability is important. Equipment such as medical electronics and space equipment that require high quality and reliability makes use of tantalum capacitors.
An especially common application for low-voltage tantalum capacitors is power supply filtering
Filtration is a physical process that separates solid matter and fluid from a mixture.
Filter, filtering, filters or filtration may also refer to:
Science and technology
Computing
* Filter (higher-order function), in functional programming
* Fil ...
on computer motherboards and in peripherals, due to their small size and long-term reliability.[Tamara Schmitz and Mike Won]
Choosing and Using Bypass Capacitors
/ref>
See also
* Aluminum electrolytic capacitor
Aluminium electrolytic capacitors are (usually) polarized electrolytic capacitors whose anode electrode (+) is made of a pure aluminium foil with an etching, etched surface. The aluminum forms a very thin insulating layer of aluminium oxide by ano ...
* Coltan mining and ethics
* Electrolytic capacitor
An electrolyte is a substance that conducts electricity through the movement of ions, but not through the movement of electrons. This includes most soluble Salt (chemistry), salts, acids, and Base (chemistry), bases, dissolved in a polar solven ...
* List of capacitor manufacturers
* Niobium capacitor
A niobium electrolytic capacitor (historically also ''Columbium capacitor'') is an electrolytic capacitor whose anode (+) is made of passivated niobium metal or niobium monoxide, on which an insulating niobium pentoxide layer acts as a dielectr ...
* Polymer capacitor
* Solid aluminum capacitor (SAL)
* Surface-mount technology
Surface-mount technology (SMT), originally called planar mounting, is a method in which the electrical components are mounted directly onto the surface of a printed circuit board (PCB). An electrical component mounted in this manner is referred ...
* Types of capacitor
Type may refer to:
Science and technology Computing
* Typing, producing text via a keyboard, typewriter, etc.
* Data type, collection of values used for computations.
* File type
* TYPE (DOS command), a command to display contents of a file.
* Ty ...
References
External links
*
{{DEFAULTSORT:Tantalum Capacitor
Capacitors

 A tantalum electrolytic capacitor is an
A tantalum electrolytic capacitor is an 
 * Note: EIA 3528 metric is also known as EIA 1411 imperial (inches).
* Note: EIA 3528 metric is also known as EIA 1411 imperial (inches).
 The main feature of modern non-solid (wet) tantalum electrolytic capacitors is their energy density compared with that of solid tantalum and wet aluminum electrolytic capacitors within the same temperature range. Due to their self-healing properties (the non-solid electrolyte can deliver oxygen to form new oxide layer in weak areas of the dielectric), the dielectric thickness can be formed with much lower safety margins and consequently with much thinner dielectric than for solid types, resulting in a higher CV value per volume unit. Additionally, wet tantalum capacitors are able to operate at voltages in excess of 100 V up to 630 V, have a relatively low ESR, and have the lowest leakage current of all electrolytic capacitors.
The original wet tantalum capacitors developed in the 1930s were axial capacitors, having a wound cell consisting of a tantalum anode and foil cathode separated by a paper stripe soaked with an electrolyte, mounted in a silver case and non-hermetic elastomer sealed.D. F. Tailor, Tantalum and Tantalum Compounds, Fansteel Inc., ''Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology'', Vol. 19, 2nd ed. 1969 John Wiley & sons, Inc. Because of the inertness and stability of the tantalum dielectric oxide layer against strong acids, the wet tantalum capacitors could use
The main feature of modern non-solid (wet) tantalum electrolytic capacitors is their energy density compared with that of solid tantalum and wet aluminum electrolytic capacitors within the same temperature range. Due to their self-healing properties (the non-solid electrolyte can deliver oxygen to form new oxide layer in weak areas of the dielectric), the dielectric thickness can be formed with much lower safety margins and consequently with much thinner dielectric than for solid types, resulting in a higher CV value per volume unit. Additionally, wet tantalum capacitors are able to operate at voltages in excess of 100 V up to 630 V, have a relatively low ESR, and have the lowest leakage current of all electrolytic capacitors.
The original wet tantalum capacitors developed in the 1930s were axial capacitors, having a wound cell consisting of a tantalum anode and foil cathode separated by a paper stripe soaked with an electrolyte, mounted in a silver case and non-hermetic elastomer sealed.D. F. Tailor, Tantalum and Tantalum Compounds, Fansteel Inc., ''Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology'', Vol. 19, 2nd ed. 1969 John Wiley & sons, Inc. Because of the inertness and stability of the tantalum dielectric oxide layer against strong acids, the wet tantalum capacitors could use  Referring to IEC/EN 60384-1 standard the allowed operating voltage for tantalum capacitors is called "rated voltage UR " or "nominal voltage UN". The rated voltage UR is the maximum DC voltage or peak pulse voltage that may be applied continuously at any temperature within the rated temperature range TR (IEC/EN 60384-1).
The voltage rating of electrolytic capacitors decreases with increasing temperature. For some applications it is important to use a higher temperature range. Lowering the voltage applied at a higher temperature maintains safety margins. For some capacitor types therefore the IEC standard specify a "temperature derated voltage" for a higher temperature, the "category voltage UC". The category voltage is the maximum DC voltage or peak pulse voltage that may be applied continuously to a capacitor at any temperature within the category temperature range TC. The relation between both voltages and temperatures is given in the picture right.
Lower voltage applied may have positive influences for tantalum electrolytic capacitors. Lowering the voltage applied increases the reliability and reduces the expected failure rate.Ch. Reynolds, AVX, Technical Information, Reliability Management of Tantalum Capacitors
Referring to IEC/EN 60384-1 standard the allowed operating voltage for tantalum capacitors is called "rated voltage UR " or "nominal voltage UN". The rated voltage UR is the maximum DC voltage or peak pulse voltage that may be applied continuously at any temperature within the rated temperature range TR (IEC/EN 60384-1).
The voltage rating of electrolytic capacitors decreases with increasing temperature. For some applications it is important to use a higher temperature range. Lowering the voltage applied at a higher temperature maintains safety margins. For some capacitor types therefore the IEC standard specify a "temperature derated voltage" for a higher temperature, the "category voltage UC". The category voltage is the maximum DC voltage or peak pulse voltage that may be applied continuously to a capacitor at any temperature within the category temperature range TC. The relation between both voltages and temperatures is given in the picture right.
Lower voltage applied may have positive influences for tantalum electrolytic capacitors. Lowering the voltage applied increases the reliability and reduces the expected failure rate.Ch. Reynolds, AVX, Technical Information, Reliability Management of Tantalum Capacitors The
The  Impurities, tiny mechanical damages, or imperfections in the dielectric can affect the structure, changing it from amorphous to crystalline structure and thus lowering the dielectric strength. The purity of the tantalum powder is one of the most important parameters for defining its risk of crystallization. Since the mid-1980s, manufactured tantalum powders have exhibited an increase in purity.
Surge currents after soldering-induced stresses may start crystallization, leading to insulation breakdown. The only way to avoid catastrophic failures is to limit the current which can flow from the source in order to reduce the breakdown to a limited area. Current flowing through the crystallized area causes heating in the manganese dioxide cathode near the fault. At increased temperatures a chemical reaction then reduces the surrounding conductive manganese dioxide to the insulating
Impurities, tiny mechanical damages, or imperfections in the dielectric can affect the structure, changing it from amorphous to crystalline structure and thus lowering the dielectric strength. The purity of the tantalum powder is one of the most important parameters for defining its risk of crystallization. Since the mid-1980s, manufactured tantalum powders have exhibited an increase in purity.
Surge currents after soldering-induced stresses may start crystallization, leading to insulation breakdown. The only way to avoid catastrophic failures is to limit the current which can flow from the source in order to reduce the breakdown to a limited area. Current flowing through the crystallized area causes heating in the manganese dioxide cathode near the fault. At increased temperatures a chemical reaction then reduces the surrounding conductive manganese dioxide to the insulating  All tantalum capacitors are polarized components, with distinctly marked positive or negative terminals. When subjected to reversed polarity (even briefly), the capacitor depolarizes and the dielectric oxide layer breaks down, which can cause it to fail even when later operated with correct polarity. If the failure is a short circuit (the most common occurrence), and current is not limited to a safe value, catastrophic thermal runaway may occur. This failure can even result in the capacitor forcefully ejecting its burning core.
Tantalum electrolytic capacitors with solid electrolyte are marked at their positive terminal with a bar or a "+". Tantalum electrolytic capacitors with non-solid electrolyte (axial leaded style) are marked on the negative terminal with a bar or a "-" (minus). The polarity better can be identified on the shaped side of the case, which has the positive terminal. The different marking styles can cause dangerous confusion.
A particular cause of confusion is that on surface mount tantalum capacitors the positive terminal is marked with a bar. Whereas on aluminium surface mount capacitors it is the ''negative'' terminal that is so marked.
For Tantalum capacitors from the early 1970s the polarity is indicated by a dot. Positive lead is the lead on the right when the side with the dot is facing you. The positive lead may also be very slightly longer. Furthermore the polarity is marked on PCBs by differently-shaped solder points if there are no "+" or "-" signs printed on the PCB. For example a square-shaped solder point is used for positive polarity (needs to be verified on particular case measuring connection against ground, negative or positive voltage pins)
All tantalum capacitors are polarized components, with distinctly marked positive or negative terminals. When subjected to reversed polarity (even briefly), the capacitor depolarizes and the dielectric oxide layer breaks down, which can cause it to fail even when later operated with correct polarity. If the failure is a short circuit (the most common occurrence), and current is not limited to a safe value, catastrophic thermal runaway may occur. This failure can even result in the capacitor forcefully ejecting its burning core.
Tantalum electrolytic capacitors with solid electrolyte are marked at their positive terminal with a bar or a "+". Tantalum electrolytic capacitors with non-solid electrolyte (axial leaded style) are marked on the negative terminal with a bar or a "-" (minus). The polarity better can be identified on the shaped side of the case, which has the positive terminal. The different marking styles can cause dangerous confusion.
A particular cause of confusion is that on surface mount tantalum capacitors the positive terminal is marked with a bar. Whereas on aluminium surface mount capacitors it is the ''negative'' terminal that is so marked.
For Tantalum capacitors from the early 1970s the polarity is indicated by a dot. Positive lead is the lead on the right when the side with the dot is facing you. The positive lead may also be very slightly longer. Furthermore the polarity is marked on PCBs by differently-shaped solder points if there are no "+" or "-" signs printed on the PCB. For example a square-shaped solder point is used for positive polarity (needs to be verified on particular case measuring connection against ground, negative or positive voltage pins)