

Paper size refers to
standardized
Standardization (American English) or standardisation (British English) is the process of implementing and developing technical standards based on the consensus of different parties that include firms, users, interest groups, standards organiza ...
dimensions for sheets of paper used globally in
stationery
Stationery refers to writing materials, including cut paper, envelopes, continuous form paper, and other office supplies. Stationery usually specifies materials to be written on by hand (e.g., letter paper) or by equipment such as computer p ...
,
printing
Printing is a process for mass reproducing text and images using a master form or template. The earliest non-paper products involving printing include cylinder seals and objects such as the Cyrus Cylinder and the Cylinders of Nabonidus. The ...
, and
technical drawing
Technical drawing, drafting or drawing, is the act and discipline of composing drawings that visually communicate how something functions or is constructed.
Technical drawing is essential for communicating ideas in industry and engineering. ...
. Most countries adhere to the
ISO 216
ISO 216 is an international standard for paper sizes, used around the world except in North America and parts of Latin America. The standard defines the "A", "B" and "C" series of paper sizes, which includes the A4, the most commonly availabl ...
standard, which includes the widely recognized A series (including
A4 paper
ISO 216 is an International Organization for Standardization, international standard for paper sizes, used around the world except in North America and parts of Latin America. The standard defines the "A", "B" and "C" series of paper sizes, wh ...
), defined by a consistent aspect ratio of √2. The system, first proposed in the 18th century and formalized in 1975, allows scaling between sizes without distortion. Regional variations exist, such as the
North American paper sizes (e.g.,
Letter,
Legal
Law is a set of rules that are created and are law enforcement, enforceable by social or governmental institutions to regulate behavior, with its precise definition a matter of longstanding debate. It has been variously described as a Socia ...
, and
Ledger
A ledger is a book or collection of accounts in which accounting transactions are recorded. Each account has:
* an opening or brought-forward balance;
*a list of transactions, each recorded as either a debit or credit in separate columns (usu ...
) which are governed by the
ANSI
The American National Standards Institute (ANSI ) is a private nonprofit organization that oversees the development of voluntary consensus standards for products, services, processes, systems, and personnel in the United States. The organiz ...
and are used in North America and parts of Central and South America.
The standardization of paper sizes emerged from practical needs for efficiency. The ISO 216 system originated in late-18th-century Germany as
DIN 476, later adopted internationally for its mathematical precision. The origins of North American sizes are lost in tradition and not well documented, although the Letter size () became dominant in the US and Canada due to historical trade practices and governmental adoption in the 20th century. Other historical systems, such as the British ''Foolscap'' and Imperial sizes, have largely been phased out in favour of ISO or ANSI standards.
Regional preferences reflect cultural and industrial legacies. In addition to ISO and ANSI standards, Japan uses its
JIS P 0138 system, which closely aligns with ISO 216 but includes unique B-series variants commonly used for books and posters. Specialized industries also employ non-standard sizes:
newspaper
A newspaper is a Periodical literature, periodical publication containing written News, information about current events and is often typed in black ink with a white or gray background. Newspapers can cover a wide variety of fields such as poli ...
s use custom formats like
Berliner and
broadsheet
A broadsheet is the largest newspaper format and is characterized by long Vertical and horizontal, vertical pages, typically of in height. Other common newspaper formats include the smaller Berliner (format), Berliner and Tabloid (newspaper ...
, while
envelope
An envelope is a common packaging item, usually made of thin, flat material. It is designed to contain a flat object, such as a letter (message), letter or Greeting card, card.
Traditional envelopes are made from sheets of paper cut to one o ...
s and
business card
Business cards are card stock, cards bearing business information about a company or individual. They are shared during formal introductions as a convenience and a memory aid. A business card typically includes the giver's name, types of co ...
s follow distinct sizing conventions. The international standard for envelopes is the
C series of
ISO 269
An envelope is a common packaging item, usually made of thin, flat material. It is designed to contain a flat object, such as a letter (message), letter or Greeting card, card.
Traditional envelopes are made from sheets of paper cut to one o ...
.
International standard paper sizes

The international paper size standard is
ISO 216
ISO 216 is an international standard for paper sizes, used around the world except in North America and parts of Latin America. The standard defines the "A", "B" and "C" series of paper sizes, which includes the A4, the most commonly availabl ...
. It is based on the German
DIN 476 standard for paper sizes. Each ISO paper size is one half of the area of the next larger size in the same series. ISO paper sizes are all based on a single
aspect ratio
The aspect ratio of a geometry, geometric shape is the ratio of its sizes in different dimensions. For example, the aspect ratio of a rectangle is the ratio of its longer side to its shorter side—the ratio of width to height, when the rectangl ...
of the
square root of 2
The square root of 2 (approximately 1.4142) is the positive real number that, when multiplied by itself or squared, equals the number 2. It may be written as \sqrt or 2^. It is an algebraic number, and therefore not a transcendental number. Te ...
, or approximately 1:1.41421. There are different series, as well as several extensions.
The following international paper sizes are included in
Cascading Style Sheets (CSS): ''A3'', ''A4'', ''A5'', ''B4'', ''B5''.
A series

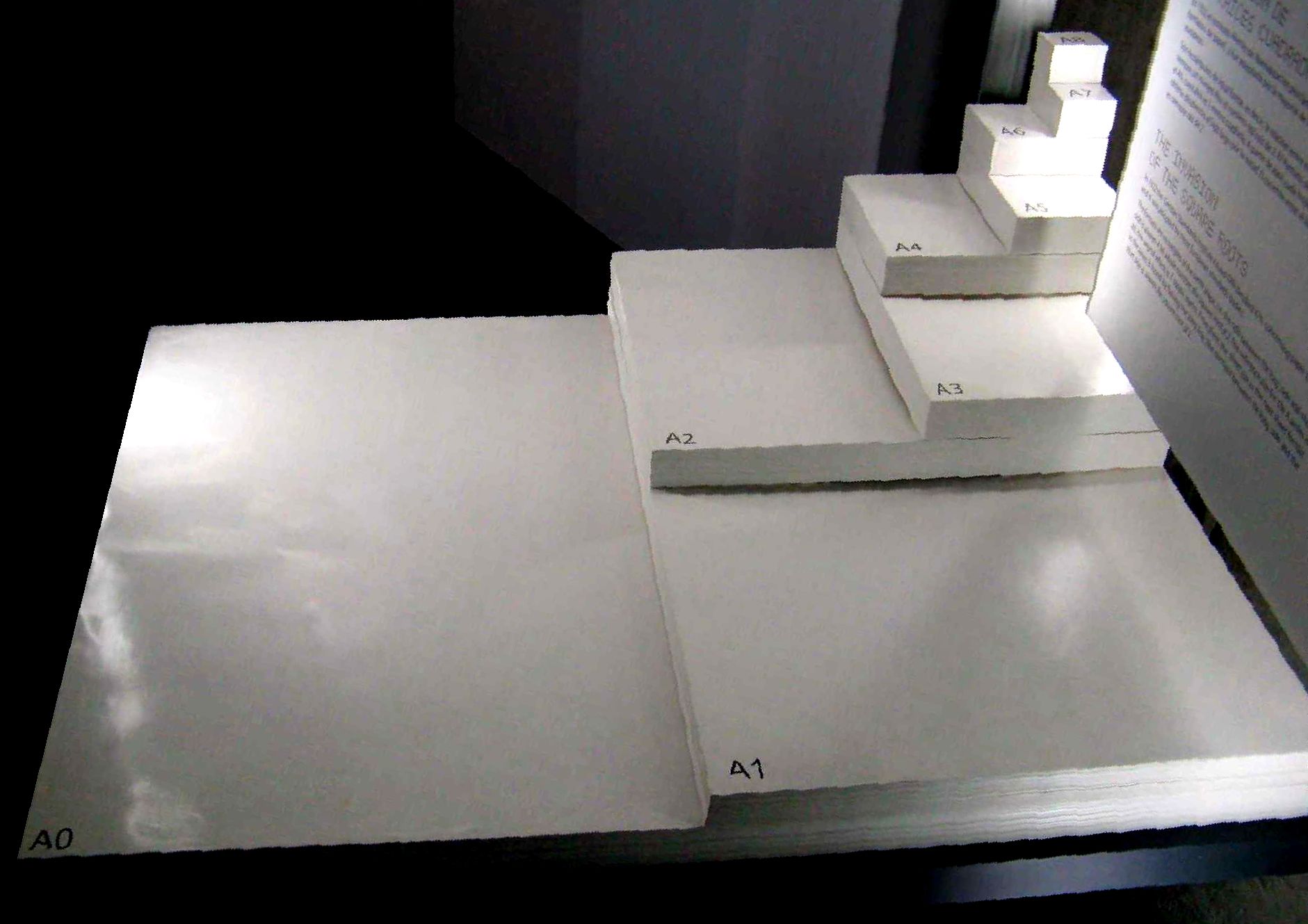
There are 11 sizes in the A series, designated A0–A10, all of which have an aspect ratio of
, where ''a'' is the long side and ''b'' is the short side.
Since A series sizes share the same aspect ratio
they can be scaled to other A series sizes without being distorted, and two sheets can be reduced to fit on exactly one sheet without any cutoff or margins.
The A0 base size is defined as having an area of 1 m; given an aspect ratio of
, the dimensions of A0 are:
by
.
or, rounded to the nearest millimetre, .
A series sizes are related in that the smaller dimension of a given size is the larger dimension of the next smaller size, and folding an A series sheet in half in its larger dimension—that is, folding it in half parallel to its short edge—results in two halves that are each the size of the next smaller A series size. As such, a folded brochure of a given A-series size can be made by folding sheets of the next larger size in half, e.g. A4 sheets can be folded to make an A5 brochure. The fact that halving a sheet with an aspect ratio of
results in two sheets that themselves both have an aspect ratio of
is proven as follows:
where ''a'' is the long side and ''b'' is the short side. The aspect ratio for the new dimensions of the folded paper is:
The advantages of basing a paper size upon an aspect ratio of
were noted in 1786 by the German scientist and philosopher
Georg Christoph Lichtenberg
Georg Christoph Lichtenberg (; 1 July 1742 – 24 February 1799) was a German physicist, satirist, and Anglophile. He was the first person in Germany to hold a professorship explicitly dedicated to experimental physics. He is remembered for his p ...
. He also observed that some raw sizes already adhered to that ratio so that when a sheet is folded, the length to width ratio does not change.
Briefly after the introduction of the
metric system
The metric system is a system of measurement that standardization, standardizes a set of base units and a nomenclature for describing relatively large and small quantities via decimal-based multiplicative unit prefixes. Though the rules gover ...
, a handful of new paper formats equivalent to modern ones were developed in France, having been proposed by the mathematician
Lazare Carnot
Lazare Nicolas Marguerite, Comte Carnot (; 13 May 1753 – 2 August 1823) was a French mathematician, physicist, military officer, politician and a leading member of the Committee of Public Safety during the French Revolution. His military refor ...
, and published for judicial purposes in 1798 during the
French Revolution:
* (A2)
* (A3)
* (B3)
* (B4)
* (B5)
* (B6)
These were never widely adopted, however.
Early in the 20th century, the ratio was used to specify the
''world format'' starting with as the short edge of the smallest size. Walter Porstmann started with the largest sizes instead, assigning one an area of (A0) and the other a short edge of (B0). He thereby turned the forgotten French sizes (relatively few in number) into a logically-simple and comprehensive plan for a full range of paper sizes, while introducing systematic alphanumeric monikers for them. Generalized to nothing less than four series, this system was introduced as a
DIN standard (DIN 476) in Germany in 1922, replacing a vast variety of other paper formats. Even today, the paper sizes are called "DIN A4" () in everyday use in Germany and Austria.
The DIN 476 standard spread quickly to other countries. Before the outbreak of
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, it had been adopted by the following countries in Europe:
*
Belgium
Belgium, officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. Situated in a coastal lowland region known as the Low Countries, it is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeas ...
(1924)
*
Netherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Nether ...
(1925)
*
Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the archipelago of Svalbard also form part of the Kingdom of ...
(1926)
*
Finland
Finland, officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It borders Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bothnia to the west and the Gulf of Finland to the south, ...
(1927)
*
Switzerland
Switzerland, officially the Swiss Confederation, is a landlocked country located in west-central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the south, France to the west, Germany to the north, and Austria and Liechtenstein to the east. Switzerland ...
(1929)
* Sweden (1930) with
later extensions
*
Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
(1934) with
custom extensions
*
Hungary
Hungary is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning much of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and ...
(1938)
* Italy (1939)
During World War II, the standard spread to South America and was adopted by
Uruguay
Uruguay, officially the Oriental Republic of Uruguay, is a country in South America. It shares borders with Argentina to its west and southwest and Brazil to its north and northeast, while bordering the Río de la Plata to the south and the A ...
(1942),
Argentina
Argentina, officially the Argentine Republic, is a country in the southern half of South America. It covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourt ...
(1943) and Brazil (1943), and afterwards spread to other countries:
*
Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
(1974)
*
Austria
Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine Federal states of Austria, states, of which the capital Vienna is the List of largest cities in Aust ...
(1948)
*
Bangladesh
Bangladesh, officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, eighth-most populous country in the world and among the List of countries and dependencies by ...
(1972)
*
Barbados
Barbados, officially the Republic of Barbados, is an island country in the Atlantic Ocean. It is part of the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies and the easternmost island of the Caribbean region. It lies on the boundary of the South American ...
(1973)
*
Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in western South America. It is the southernmost country in the world and the closest to Antarctica, stretching along a narrow strip of land between the Andes, Andes Mountains and the Paci ...
(1968)
*
Colombia
Colombia, officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country primarily located in South America with Insular region of Colombia, insular regions in North America. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Caribbean Sea to the north, Venezuel ...
(1975)
*
Czechoslovakia
Czechoslovakia ( ; Czech language, Czech and , ''Česko-Slovensko'') was a landlocked country in Central Europe, created in 1918, when it declared its independence from Austria-Hungary. In 1938, after the Munich Agreement, the Sudetenland beca ...
(1953)
*
Denmark
Denmark is a Nordic countries, Nordic country in Northern Europe. It is the metropole and most populous constituent of the Kingdom of Denmark,, . also known as the Danish Realm, a constitutionally unitary state that includes the Autonomous a ...
(1953)
*
Ecuador
Ecuador, officially the Republic of Ecuador, is a country in northwestern South America, bordered by Colombia on the north, Peru on the east and south, and the Pacific Ocean on the west. It also includes the Galápagos Province which contain ...
(1974)
*
France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
(1967)
*
Greece
Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. Located on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, it shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to th ...
(1970)
*
Iceland
Iceland is a Nordic countries, Nordic island country between the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic and Arctic Oceans, on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge between North America and Europe. It is culturally and politically linked with Europe and is the regi ...
(1964)
*
India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
(1957) with
custom extensions
*
Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
(1948)
*
Ireland
Ireland (, ; ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe. Geopolitically, the island is divided between the Republic of Ireland (officially Names of the Irish state, named Irelan ...
(1959)
*
Israel
Israel, officially the State of Israel, is a country in West Asia. It Borders of Israel, shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the north-east, Jordan to the east, Egypt to the south-west, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. Isr ...
(1954)
*
Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
(1951) with
different B series
*
Kuwait
Kuwait, officially the State of Kuwait, is a country in West Asia and the geopolitical region known as the Middle East. It is situated in the northern edge of the Arabian Peninsula at the head of the Persian Gulf, bordering Iraq to Iraq–Kuwait ...
(1975)
*
Mexico
Mexico, officially the United Mexican States, is a country in North America. It is the northernmost country in Latin America, and borders the United States to the north, and Guatemala and Belize to the southeast; while having maritime boundar ...
(1965)
*
New Zealand
New Zealand () is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and List of islands of New Zealand, over 600 smaller islands. It is the List of isla ...
(1963)
*
Peru
Peru, officially the Republic of Peru, is a country in western South America. It is bordered in the north by Ecuador and Colombia, in the east by Brazil, in the southeast by Bolivia, in the south by Chile, and in the south and west by the Pac ...
(1967)
*
Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukrai ...
(1957)
*
Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic, is a country on the Iberian Peninsula in Southwestern Europe. Featuring Cabo da Roca, the westernmost point in continental Europe, Portugal borders Spain to its north and east, with which it share ...
(1954)
*
Rhodesia
Rhodesia ( , ; ), officially the Republic of Rhodesia from 1970, was an unrecognised state, unrecognised state in Southern Africa that existed from 1965 to 1979. Rhodesia served as the ''de facto'' Succession of states, successor state to the ...
(1970)
*
Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe. It borders Ukraine to the north and east, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Bulgaria to the south, Moldova to ...
(1949)
*
Singapore
Singapore, officially the Republic of Singapore, is an island country and city-state in Southeast Asia. The country's territory comprises one main island, 63 satellite islands and islets, and one outlying islet. It is about one degree ...
(1970)
*
South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. Its Provinces of South Africa, nine provinces are bounded to the south by of coastline that stretches along the Atlantic O ...
(1966)
*
Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
(1947)
*
Thailand
Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and historically known as Siam (the official name until 1939), is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. With a population of almost 66 million, it spa ...
(1973)
*
Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
(1967)
*
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
(1971)
*
Venezuela
Venezuela, officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela, is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many Federal Dependencies of Venezuela, islands and islets in the Caribbean Sea. It com ...
(1962)
*
Yugoslavia
, common_name = Yugoslavia
, life_span = 1918–19921941–1945: World War II in Yugoslavia#Axis invasion and dismemberment of Yugoslavia, Axis occupation
, p1 = Kingdom of SerbiaSerbia
, flag_p ...
(1956)
By 1975, so many countries were using the German system that it was established as an
ISO
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO ; ; ) is an independent, non-governmental, international standard development organization composed of representatives from the national standards organizations of member countries.
Me ...
standard, as well as the official United Nations document format. By 1977, A4 was the standard letter format in 88 of 148 countries. Today the standard has been adopted by all countries in the world except the United States and Canada. In Mexico,
Costa Rica
Costa Rica, officially the Republic of Costa Rica, is a country in Central America. It borders Nicaragua to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the northeast, Panama to the southeast, and the Pacific Ocean to the southwest, as well as Maritime bo ...
,
Colombia
Colombia, officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country primarily located in South America with Insular region of Colombia, insular regions in North America. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Caribbean Sea to the north, Venezuel ...
,
Venezuela
Venezuela, officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela, is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many Federal Dependencies of Venezuela, islands and islets in the Caribbean Sea. It com ...
, Chile, and the
Philippines
The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. Located in the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of List of islands of the Philippines, 7,641 islands, with a tot ...
, the
US letter format is still in common use, despite their official adoption of the ISO standard.
The weight of an A-series sheet of a given
paper weight can be calculated by knowing the ratio of its size to the A0 sheet. For example, an A4 sheet is the size of an A0 sheet, so if it is made from paper, it weighs of , which is .
B series

The B series paper sizes are less common than the A series. They have the same aspect ratio as the A series:
However, they have a different area. The area of B series sheets is in fact the
geometric mean
In mathematics, the geometric mean is a mean or average which indicates a central tendency of a finite collection of positive real numbers by using the product of their values (as opposed to the arithmetic mean which uses their sum). The geometri ...
of successive A series sheets. B1 is between A0 and A1 in size, with an area of
m, or about . As a result, B0 is 1 metre wide, and other sizes of the series are a half, a quarter, or further fractions of a metre wide: in general, every B size has exactly one side of length
for
. That side is the short side for B0, B2, B4, etc., and the long side for B1, B3, B5, etc.
While less common in office use, the B series is used for a variety of applications in which one A-series size would be too small but the next A-series size is too large, or because they are convenient for a particular purpose.
* B4, B5, and B6 are used for
envelope
An envelope is a common packaging item, usually made of thin, flat material. It is designed to contain a flat object, such as a letter (message), letter or Greeting card, card.
Traditional envelopes are made from sheets of paper cut to one o ...
s that will hold C-series envelopes.
* B4 is quite common in printed music sheets.
* B5 is a relatively common choice for books.
* B7 is equal to the passport size ID-3 from
ISO/IEC 7810
International Organization for Standardization, ISO/International Electrotechnical Commission, IEC 7810 ''Identification cards — Physical characteristics'' is an international standard that defines the physical characteristics for identifica ...
.
* Many posters use B-series paper or a close approximation, such as 50 cm × 70 cm ~ B2.
The B-series is widely used in the printing industry to describe both paper sizes and
printing press
A printing press is a mechanical device for applying pressure to an inked surface resting upon a printing, print medium (such as paper or cloth), thereby transferring the ink. It marked a dramatic improvement on earlier printing methods in whi ...
sizes, including
digital presses. B3 paper is used to print two US letter or A4 pages side by side using
imposition
Imposition is one of the fundamental steps in the prepress printing process. It consists of the arrangement of the printed product's pages on the printer's sheet, in order to obtain faster printing, simplify binding and reduce paper waste.
Corr ...
; four pages would be printed on B2, eight on B1, etc.
C series

The C series is defined in
ISO 269
An envelope is a common packaging item, usually made of thin, flat material. It is designed to contain a flat object, such as a letter (message), letter or Greeting card, card.
Traditional envelopes are made from sheets of paper cut to one o ...
, which was withdrawn in 2009 without a replacement, but is still specified in several national standards. It is primarily used for envelopes. The area of C series sheets is the geometric mean of the areas of the
A and
B series sheets of the same number; for instance, the area of a C4 sheet is the geometric mean of the areas of an A4 sheet and a B4 sheet. This means that C4 is slightly larger than A4, and slightly smaller than B4. The practical usage of this is that a letter written on A4 paper fits inside a C4 envelope, and both A4 paper and C4 envelopes fit inside a B4 envelope.
Some envelope formats with mixed sides from adjacent sizes (and thus an approximate aspect ratio of 2:1) are also defined in national adaptations of the ISO standard, e.g. DIN C6/C5 (also known as C65) is 114 mm × 229 mm where the common side to C5 and C6 is 162 mm. This format allows an envelope holding an A-sized paper folded in three, e.g. for the C65, an A4.
Overview of ISO paper sizes
The
variables are the distinct first terms in the three
geometric progressions of the same ''common ratio'' equal to the square root of two. Each of the three geometric progressions (corresponding to the three
series A,
B, and
C) is formed by all possible paper dimensions (length and width) of the series arranged in decreasing order. This interesting arrangement of dimensions is also very useful—not only does it form a geometric progression with easy-to-remember formulae, but also each consecutive pair of values (like a sliding window of size 2) will automatically correspond to the dimensions of a standard paper format in the series.
The
tolerances specified in the standard are
* ± for dimensions up to ,
* ± for lengths in the range and
* ± for any dimension above .
Related regional sizes
German original
The German standard DIN 476 was published on 18 August 1922 and is the original specification of the
A,
B and
C sizes. In 1991, it was split into DIN 476-1 for the A and B formats and 476-2 for the C series. The former has been withdrawn in 2002 in favour of adopting the international standard as DIN EN ISO 216, but part 2 has been retained and was last updated in 2008.
The first and the second editions of DIN 476 from 1922 and 1925 also included a D series.
The smallest formats in the original specifications for each series were A13, B13, C8, and D8. Sizes A11 through A13 were no longer listed in the 1930 edition, nor were B11 through B13. C9 and C10 were added in the 1976 revision for compatibility with photography sizes: C8 closely matches
6×9 photos, and C9 and C10 closely match 7×7 and 5×5
slides, respectively.
DIN 476 provides for formats larger than A0, denoted by a prefix factor. In particular, it lists the formats 2A0 and 4A0, which are twice and four times the size of A0 respectively. However, ISO 216:2007 notes 2A0 and 4A0 in the table of ''Main series of trimmed sizes'' (ISO A series) as well: "The rarely used sizes
A0 and 4A0which follow also belong to this series."
DIN 476 also used to specify slightly tighter tolerances than ISO 216:
* ± for dimensions up to ,
* ± for lengths in the range and
* ± for any dimension above .
There used to be a standard, DIN 198, that was just a table of recommended A series formats for a number of business applications. The 1976 edition of this standard introduced a size A4 and suggested it for some forms and slips.
Swedish extensions

The Swedish standard
SIS 01 47 11
generalized the ISO system of
A,
B, and
C formats by adding D, E, F, and G formats to it. Its D format sits between a B format and the next larger A format (just like C sits between A and the next larger B). The remaining formats fit in between all these formats, such that the
sequence of formats A4, E4, C4, G4, B4, F4, D4, *H4, A3 is a
geometric progression, in which the dimensions grow by a factor


 Paper size refers to
Paper size refers to  The international paper size standard is
The international paper size standard is  There are 11 sizes in the A series, designated A0–A10, all of which have an aspect ratio of , where ''a'' is the long side and ''b'' is the short side.
Since A series sizes share the same aspect ratio they can be scaled to other A series sizes without being distorted, and two sheets can be reduced to fit on exactly one sheet without any cutoff or margins.
The A0 base size is defined as having an area of 1 m; given an aspect ratio of , the dimensions of A0 are:
by .
or, rounded to the nearest millimetre, .
A series sizes are related in that the smaller dimension of a given size is the larger dimension of the next smaller size, and folding an A series sheet in half in its larger dimension—that is, folding it in half parallel to its short edge—results in two halves that are each the size of the next smaller A series size. As such, a folded brochure of a given A-series size can be made by folding sheets of the next larger size in half, e.g. A4 sheets can be folded to make an A5 brochure. The fact that halving a sheet with an aspect ratio of results in two sheets that themselves both have an aspect ratio of is proven as follows:
where ''a'' is the long side and ''b'' is the short side. The aspect ratio for the new dimensions of the folded paper is:
The advantages of basing a paper size upon an aspect ratio of were noted in 1786 by the German scientist and philosopher
There are 11 sizes in the A series, designated A0–A10, all of which have an aspect ratio of , where ''a'' is the long side and ''b'' is the short side.
Since A series sizes share the same aspect ratio they can be scaled to other A series sizes without being distorted, and two sheets can be reduced to fit on exactly one sheet without any cutoff or margins.
The A0 base size is defined as having an area of 1 m; given an aspect ratio of , the dimensions of A0 are:
by .
or, rounded to the nearest millimetre, .
A series sizes are related in that the smaller dimension of a given size is the larger dimension of the next smaller size, and folding an A series sheet in half in its larger dimension—that is, folding it in half parallel to its short edge—results in two halves that are each the size of the next smaller A series size. As such, a folded brochure of a given A-series size can be made by folding sheets of the next larger size in half, e.g. A4 sheets can be folded to make an A5 brochure. The fact that halving a sheet with an aspect ratio of results in two sheets that themselves both have an aspect ratio of is proven as follows:
where ''a'' is the long side and ''b'' is the short side. The aspect ratio for the new dimensions of the folded paper is:
The advantages of basing a paper size upon an aspect ratio of were noted in 1786 by the German scientist and philosopher  The B series paper sizes are less common than the A series. They have the same aspect ratio as the A series:
However, they have a different area. The area of B series sheets is in fact the
The B series paper sizes are less common than the A series. They have the same aspect ratio as the A series:
However, they have a different area. The area of B series sheets is in fact the  The C series is defined in
The C series is defined in  The Swedish standard SIS 01 47 11 generalized the ISO system of A, B, and C formats by adding D, E, F, and G formats to it. Its D format sits between a B format and the next larger A format (just like C sits between A and the next larger B). The remaining formats fit in between all these formats, such that the sequence of formats A4, E4, C4, G4, B4, F4, D4, *H4, A3 is a geometric progression, in which the dimensions grow by a factor
The Swedish standard SIS 01 47 11 generalized the ISO system of A, B, and C formats by adding D, E, F, and G formats to it. Its D format sits between a B format and the next larger A format (just like C sits between A and the next larger B). The remaining formats fit in between all these formats, such that the sequence of formats A4, E4, C4, G4, B4, F4, D4, *H4, A3 is a geometric progression, in which the dimensions grow by a factor
