T Tauri Star on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
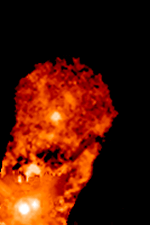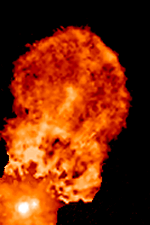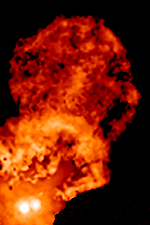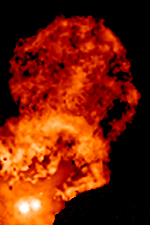
T Tauri stars (TTS) are a class of
 Their spectra show a higher
Their spectra show a higher
Discussion of V471 Tauri observations and general T-Tauri properties
Frederick M. Walter, Stony Brook University, April 2004
An empirical criterion to classify T Tauri stars and substellar analogs using low-resolution optical spectroscopy
David Barrado y Navascues, 2003 {{Authority control Star types * Star formation
variable star
A variable star is a star whose brightness as seen from Earth (its apparent magnitude) changes systematically with time. This variation may be caused by a change in emitted light or by something partly blocking the light, so variable stars are ...
s that are less than about ten million years old. This class is named after the prototype, T Tauri, a young star in the Taurus star-forming region. They are found near molecular cloud
A molecular cloud—sometimes called a stellar nursery if star formation is occurring within—is a type of interstellar cloud of which the density and size permit absorption nebulae, the formation of molecules (most commonly molecular hydrogen, ...
s and identified by their optical variability and strong chromospheric lines. T Tauri stars are pre-main-sequence stars in the process of contracting to the main sequence along the Hayashi track, a luminosity–temperature relationship obeyed by infant stars of less than 3 solar masses () in the pre-main-sequence phase of stellar evolution
Stellar evolution is the process by which a star changes over the course of time. Depending on the mass of the star, its lifetime can range from a few million years for the most massive to trillions of years for the least massive, which is consi ...
. It ends when a star of or larger develops a radiative zone, or when a smaller star commences nuclear fusion
Nuclear fusion is a nuclear reaction, reaction in which two or more atomic nuclei combine to form a larger nuclei, nuclei/neutrons, neutron by-products. The difference in mass between the reactants and products is manifested as either the rele ...
on the main sequence
In astronomy, the main sequence is a classification of stars which appear on plots of stellar color index, color versus absolute magnitude, brightness as a continuous and distinctive band. Stars on this band are known as main-sequence stars or d ...
.
History
While T Tauri itself was discovered in 1852, the T Tauri class of stars were initially defined by Alfred Harrison Joy in 1945.Characteristics
T Tauri stars comprise the youngest visible F, G, K and M spectral type stars (). Their surface temperatures are similar to those of main-sequence stars of the same mass, but they are significantly more luminous because their radii are larger. Their central temperatures are too low for hydrogen fusion. Instead, they are powered bygravitational energy
Gravitational energy or gravitational potential energy is the potential energy an object with mass has due to the gravitational potential of its position in a gravitational field. Mathematically, it is the minimum mechanical work that has to be do ...
released as the stars contract, while moving towards the main sequence
In astronomy, the main sequence is a classification of stars which appear on plots of stellar color index, color versus absolute magnitude, brightness as a continuous and distinctive band. Stars on this band are known as main-sequence stars or d ...
, which they reach after about 100 million years. They typically rotate with a period between one and twelve days, compared to a month for the Sun, and are very active and variable.
There is evidence of large areas of starspot coverage, and they have intense and variable X-ray
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ran ...
and radio
Radio is the technology of communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 3 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a transmitter connec ...
emissions (approximately 1000 times that of the Sun). Many have extremely powerful stellar wind
A stellar wind is a flow of gas ejected from the stellar atmosphere, upper atmosphere of a star. It is distinguished from the bipolar outflows characteristic of young stars by being less collimated, although stellar winds are not generally spheri ...
s; some eject gas in high-velocity bipolar jets. Another source of brightness variability are clumps (protoplanet
A protoplanet is a large planetary embryo that originated within a protoplanetary disk and has undergone internal melting to produce a differentiated interior. Protoplanets are thought to form out of kilometer-sized planetesimals that gravitatio ...
s and planetesimals) in the disk surrounding T Tauri stars.
 Their spectra show a higher
Their spectra show a higher lithium
Lithium (from , , ) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Li and atomic number 3. It is a soft, silvery-white alkali metal. Under standard temperature and pressure, standard conditions, it is the least dense metal and the ...
abundance than the Sun and other main-sequence stars because lithium is destroyed at temperatures above 2,500,000 K. From a study of lithium abundances in 53 T Tauri stars, it has been found that lithium depletion varies strongly with size, suggesting that " lithium burning" by the p-p chain during the last highly convective and unstable stages during the later pre–main sequence phase of the Hayashi contraction may be one of the main sources of energy for T Tauri stars. Rapid rotation tends to improve mixing and increase the transport of lithium into deeper layers where it is destroyed. T Tauri stars generally increase their rotation rates as they age, through contraction and spin-up, as they conserve angular momentum. This causes an increased rate of lithium loss with age. Lithium burning will also increase with higher temperatures and mass, and will last for at most a little over 100 million years.
The p-p chain for lithium burning is as follows
:
It will not occur in stars with less than sixty times the mass of Jupiter (). The rate of lithium depletion can be used to calculate the age of the star.
Types
Several types of TTSs exist: *Classical T Tauri star (CTTS) *Weak-line T Tauri star (WTTS) **Naked T Tauri star (NTTS), which is a subset of WTTS. Roughly half of T Tauri stars have circumstellar disks, which in this case are called protoplanetary discs because they are probably the progenitors of planetary systems like the Solar System. Circumstellar discs are estimated to dissipate on timescales of up to 10 million years. Most T Tauri stars are in binary star systems. In various stages of their life, they are called young stellar object (YSOs). It is thought that the activemagnetic field
A magnetic field (sometimes called B-field) is a physical field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular ...
s and strong solar wind
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles released from the Sun's outermost atmospheric layer, the Stellar corona, corona. This Plasma (physics), plasma mostly consists of electrons, protons and alpha particles with kinetic energy betwee ...
of Alfvén waves of T Tauri stars are one means by which angular momentum
Angular momentum (sometimes called moment of momentum or rotational momentum) is the rotational analog of Momentum, linear momentum. It is an important physical quantity because it is a Conservation law, conserved quantity – the total ang ...
gets transferred from the star to the protoplanetary disc. A T Tauri stage for the Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Sola ...
would be one means by which the angular momentum of the contracting Sun was transferred to the protoplanetary disc and hence, eventually to the planets
A planet is a large, rounded astronomical body that is generally required to be in orbit around a star, stellar remnant, or brown dwarf, and is not one itself. The Solar System has eight planets by the most restrictive definition of the te ...
.
Analogs of T Tauri stars in the higher mass range (2–8 solar mass
The solar mass () is a frequently used unit of mass in astronomy, equal to approximately . It is approximately equal to the mass of the Sun. It is often used to indicate the masses of other stars, as well as stellar clusters, nebulae, galaxie ...
es)—A and B spectral type pre–main-sequence stars, are called Herbig Ae/Be-type stars. More massive (>8 solar masses) star
A star is a luminous spheroid of plasma (physics), plasma held together by Self-gravitation, self-gravity. The List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs, nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night sk ...
s in pre–main sequence stage are not observed, because they evolve very quickly: when they become visible (i.e. disperses surrounding circumstellar gas and dust cloud), the hydrogen in the center is already burning and they are main sequence
In astronomy, the main sequence is a classification of stars which appear on plots of stellar color index, color versus absolute magnitude, brightness as a continuous and distinctive band. Stars on this band are known as main-sequence stars or d ...
objects.
Planets
Planets around T Tauri stars include: * 1RXS J160929.1−210524b around a K-type star * PDS 70b around a K-type starSee also
* Orion variable * EX Lupi * P Cygni profileReferences
Discussion of V471 Tauri observations and general T-Tauri properties
Frederick M. Walter, Stony Brook University, April 2004
An empirical criterion to classify T Tauri stars and substellar analogs using low-resolution optical spectroscopy
David Barrado y Navascues, 2003 {{Authority control Star types * Star formation