TIC Complex on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The TIC and TOC complexes are
The TIC and TOC complexes are
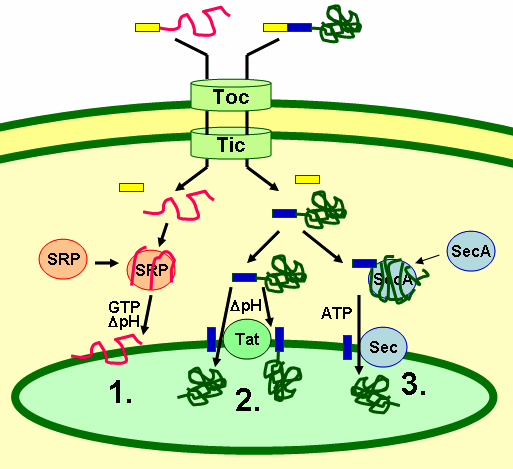 This protein complex is functionally similar to the TOM/TIM Complex located on the outer and inner membranes of the mitochondria, in the sense that it too transports proteins across multiple membranes and into the lumen of an organelle. Both complexes (TOC/TIC) are GTPases, that is, they must both hydrolyze GTP in order to power the translocation. The chloroplast also harnesses the power of an electrochemical gradient using protons. The gradient is only used to power transport across the thylakoid membrane, however, while the gradient in the mitochondria is used to power transport across its inner membrane.
Furthermore, due to the thylakoid membrane located inside of the chloroplast, a second transit peptide sequence must be located on the imported protein. In the cytosol, a transit peptide that signals for transit of the protein to the chloroplast is exposed. This initiates transport and translocation through the TIC/TOC complexes into the stroma of the chloroplast. It is there that a signal peptidase cleaves the stromal transit peptide, only to reveal a second transit peptide sequence underneath; this time directing to the thylakoid membrane. There are at least three ways for the protein to go through the thylakoid membrane: through a ATP-hydrolyzing
This protein complex is functionally similar to the TOM/TIM Complex located on the outer and inner membranes of the mitochondria, in the sense that it too transports proteins across multiple membranes and into the lumen of an organelle. Both complexes (TOC/TIC) are GTPases, that is, they must both hydrolyze GTP in order to power the translocation. The chloroplast also harnesses the power of an electrochemical gradient using protons. The gradient is only used to power transport across the thylakoid membrane, however, while the gradient in the mitochondria is used to power transport across its inner membrane.
Furthermore, due to the thylakoid membrane located inside of the chloroplast, a second transit peptide sequence must be located on the imported protein. In the cytosol, a transit peptide that signals for transit of the protein to the chloroplast is exposed. This initiates transport and translocation through the TIC/TOC complexes into the stroma of the chloroplast. It is there that a signal peptidase cleaves the stromal transit peptide, only to reveal a second transit peptide sequence underneath; this time directing to the thylakoid membrane. There are at least three ways for the protein to go through the thylakoid membrane: through a ATP-hydrolyzing
- description of the entire complex Integral membrane proteins Protein complexes
translocon The translocon (also known as a translocator or translocation channel) is a complex of proteins associated with the translocation of polypeptides across membranes. In eukaryotes the term translocon most commonly refers to the complex that transport ...
s located in the chloroplast
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant and algal cells. The photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll captures the energy from sunlight, converts it, and stores it ...
of a eukaryotic cell, that is, protein complex
A protein complex or multiprotein complex is a group of two or more associated polypeptide chains. Protein complexes are distinct from multienzyme complexes, in which multiple catalytic domains are found in a single polypeptide chain.
Protein ...
es that facilitate the transfer of proteins in and out through the chloroplast's membrane. It mainly transports proteins made in the cytoplasm into the chloroplast. The TIC complex ''(translocon on the inner chloroplast membrane)'' is located in the inner envelope of the chloroplast. The TOC complex ''(translocon on the outer chloroplast membrane)'' is located in the outer envelope of the chloroplast.
TOM/TIM complex vs. TOC/TIC complex
 This protein complex is functionally similar to the TOM/TIM Complex located on the outer and inner membranes of the mitochondria, in the sense that it too transports proteins across multiple membranes and into the lumen of an organelle. Both complexes (TOC/TIC) are GTPases, that is, they must both hydrolyze GTP in order to power the translocation. The chloroplast also harnesses the power of an electrochemical gradient using protons. The gradient is only used to power transport across the thylakoid membrane, however, while the gradient in the mitochondria is used to power transport across its inner membrane.
Furthermore, due to the thylakoid membrane located inside of the chloroplast, a second transit peptide sequence must be located on the imported protein. In the cytosol, a transit peptide that signals for transit of the protein to the chloroplast is exposed. This initiates transport and translocation through the TIC/TOC complexes into the stroma of the chloroplast. It is there that a signal peptidase cleaves the stromal transit peptide, only to reveal a second transit peptide sequence underneath; this time directing to the thylakoid membrane. There are at least three ways for the protein to go through the thylakoid membrane: through a ATP-hydrolyzing
This protein complex is functionally similar to the TOM/TIM Complex located on the outer and inner membranes of the mitochondria, in the sense that it too transports proteins across multiple membranes and into the lumen of an organelle. Both complexes (TOC/TIC) are GTPases, that is, they must both hydrolyze GTP in order to power the translocation. The chloroplast also harnesses the power of an electrochemical gradient using protons. The gradient is only used to power transport across the thylakoid membrane, however, while the gradient in the mitochondria is used to power transport across its inner membrane.
Furthermore, due to the thylakoid membrane located inside of the chloroplast, a second transit peptide sequence must be located on the imported protein. In the cytosol, a transit peptide that signals for transit of the protein to the chloroplast is exposed. This initiates transport and translocation through the TIC/TOC complexes into the stroma of the chloroplast. It is there that a signal peptidase cleaves the stromal transit peptide, only to reveal a second transit peptide sequence underneath; this time directing to the thylakoid membrane. There are at least three ways for the protein to go through the thylakoid membrane: through a ATP-hydrolyzing Type II secretion system
The type 2 secretion system (often referred to as the type II secretion system or by the initials T2SS) is a type of protein secretion machinery found in various species of Gram-negative bacteria, including many human pathogens such as ''Pseudomo ...
, through a SecY translocon, or through the Tat/VSP pathway.
See also
*Chloroplast DNA
Chloroplast DNA (cpDNA) is the DNA located in chloroplasts, which are photosynthetic organelles located within the cells of some eukaryotic organisms. Chloroplasts, like other types of plastid, contain a genome separate from that in the cell n ...
*Chloroplast
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant and algal cells. The photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll captures the energy from sunlight, converts it, and stores it ...
References
{{reflistExternal links
* TCDBbr>3.A.9- description of the entire complex Integral membrane proteins Protein complexes