Sürgün on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Sürgün or verb form sürmek (to displace) was a practice within the
Sürgün or verb form sürmek (to displace) was a practice within the
 The
The
 Sürgün or verb form sürmek (to displace) was a practice within the
Sürgün or verb form sürmek (to displace) was a practice within the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
that entailed the movement of a large group of people from one region to another, often a form of forced migration
Forced displacement (also forced migration or forced relocation) is an involuntary or coerced movement of a person or people away from their home or home region. The United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees, UNHCR defines 'forced displaceme ...
imposed by state policy or international authority. The practice was also a form of banishment or exile
Exile or banishment is primarily penal expulsion from one's native country, and secondarily expatriation or prolonged absence from one's homeland under either the compulsion of circumstance or the rigors of some high purpose. Usually persons ...
often applied to the elites of Ottoman society, the Pashas
Pasha (; ; ) was a high rank in the Ottoman political and military system, typically granted to governors, generals, dignitaries, and others. ''Pasha'' was also one of the highest titles in the 20th-century Kingdom of Egypt and it was also us ...
. It was most famously used as a method to forcefully displace the native ethnic Armenians by the Young Turk
The Young Turks (, also ''Genç Türkler'') formed as a constitutionalist broad opposition-movement in the late Ottoman Empire against the absolutist régime of Sultan Abdul Hamid II (). The most powerful organization of the movement, a ...
government in 1915, in order to deal with a perceived threat from Armenian
Armenian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Armenia, a country in the South Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Armenians, the national people of Armenia, or people of Armenian descent
** Armenian diaspora, Armenian communities around the ...
partisan groups receiving military support from the Ottoman hostile Russian Empire. These events are listed as one of the methods used to complete the Armenian Genocide
The Armenian genocide was the systematic destruction of the Armenians, Armenian people and identity in the Ottoman Empire during World War I. Spearheaded by the ruling Committee of Union and Progress (CUP), it was implemented primarily t ...
.
The practice was also used to enforce population exchanges such as the Balkan population exchanges in 1913 and the exchanges between the new Republic of Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
and Greece
Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. Located on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, it shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to th ...
in 1923.
Exile as a Tool
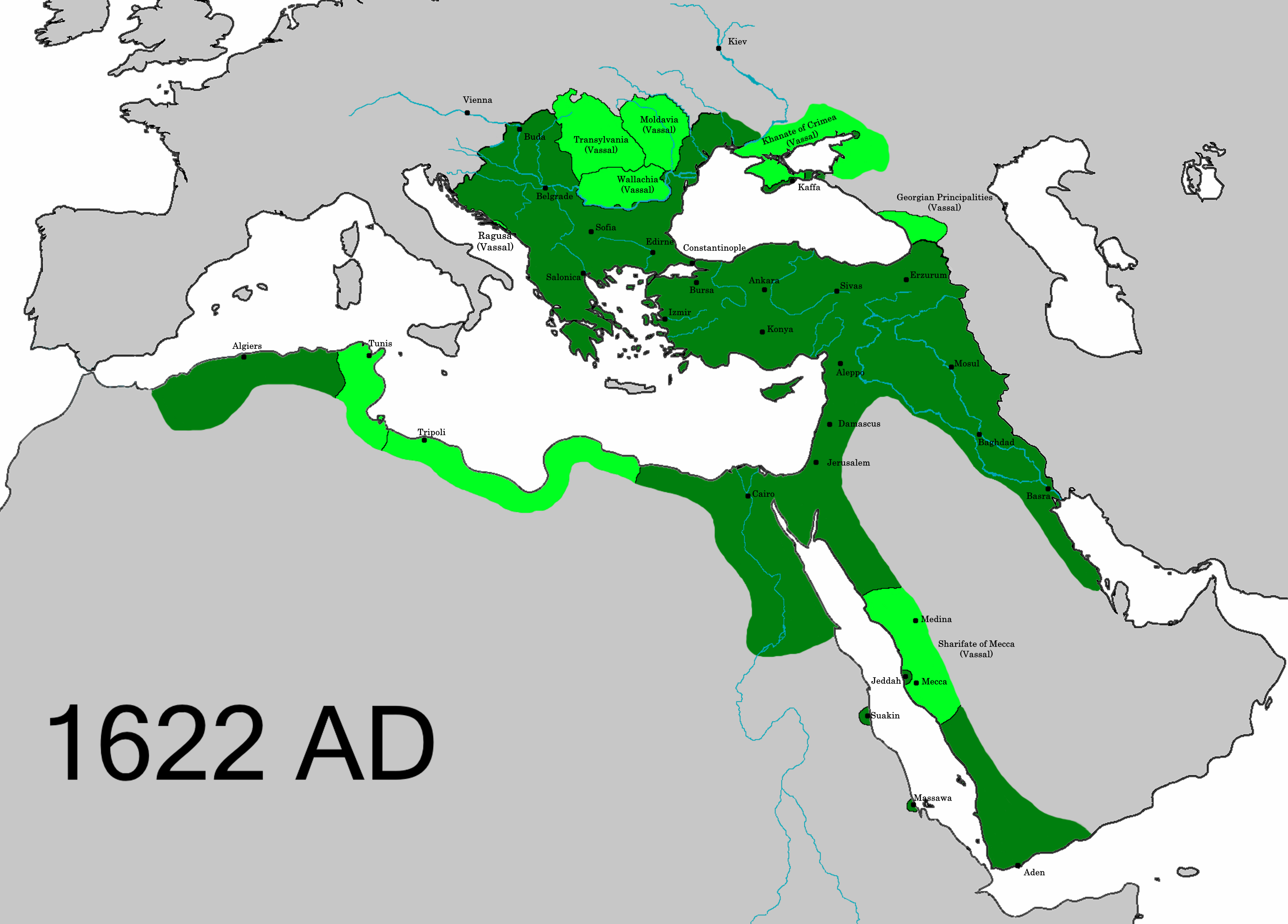
At its height, the Ottoman Empire spanned over the entirety ofAnatolia
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
and ruled over many different cultures and peoples. Mass migrations would often be used as a tool to settle political unrest and to bolster Ottoman presence in areas. During the expansionist reign of Mehmet I
Mehmed I (; – 26 May 1421), also known as Mehmed Çelebi (, "the noble-born") or ''Kirişçi'' (, "lord's son"), was the sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1413 to 1421. Son of Sultan Bayezid I and his concubine Devlet Hatun, he fought with ...
forced migration was used as a method of strengthening border regions and exerting influence in newly conquered areas.
With Mehmet's takeover of Constantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empire ...
in 1453. Mehmet also brought in a large population from previous outlying Ottoman cities.
In 1356 Sultan Orhan
Orhan Ghazi (; , also spelled Orkhan; died 1362) was the second sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1323/4 to 1362. He was born in Söğüt, as the son of Osman I.
In the early stages of his reign, Orhan focused his energies on conquering mos ...
displaced a large group of "dark skinned Arab nomadic households" or "kara göçer arap evleri" to the newly subjugated region of Rumeli
Rumelia (; ; ) was a historical region in Southeastern Europe that was administered by the Ottoman Empire, roughly corresponding to the Balkans. In its wider sense, it was used to refer to all Ottoman possessions and vassals in Europe. These ...
at the request of his son Suleiman Pasha, in order to better secure a fortress captured in Thrace so he could move forward.
Movements like this where commonplace through the expansion of the empire.
Within the Sultanate
In the early period (from the 14th through the late 16th centuries), the Ottomans practiced open succession, or what historianDonald Quataert
Donald George Quataert (September 10, 1941 – February 10, 2011) was a historian at Binghamton University. He taught courses on Middle East/Ottoman history, with an interest in labor, social and economics, during the early and modern periods. ...
has described as "survival of the fittest
"Survival of the fittest" is a phrase that originated from Darwinian evolutionary theory as a way of describing the mechanism of natural selection. The biological concept of fitness is defined as reproductive success. In Darwinian terms, th ...
, not eldest, son." During their father's lifetime, all of the adult sons of the reigning sultan
Sultan (; ', ) is a position with several historical meanings. Originally, it was an Arabic abstract noun meaning "strength", "authority", "rulership", derived from the verbal noun ', meaning "authority" or "power". Later, it came to be use ...
would hold provincial governorships. Accompanied and mentored by their mothers, they would gather supporters while ostensibly following a Ghazw
A ''ghazi'', or ''gazi'' (, , plural ''ġuzāt'') is an individual who participated in ''ghazw'' (, '' ''), meaning military expeditions or raids against non-Muslims. The latter term was applied in early Islamic literature to expeditions led by ...
ethos. Upon the death of their father, the sons would fight among themselves until one emerged triumphant. How remote a province the son governed was of great significance. The closer the region that a particular son was in charge of the better the chances were of that son succeeding, simply because he would be told of the news of his father's death and be able to get to Constantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empire ...
first and declare himself Sultan. Thus a father could hint at whom he preferred by giving his favorite son a closer governorship.
Exile and Transfer 1300-1600
Ottoman population transfers through the reign ofMehmet I
Mehmed I (; – 26 May 1421), also known as Mehmed Çelebi (, "the noble-born") or ''Kirişçi'' (, "lord's son"), was the sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1413 to 1421. Son of Sultan Bayezid I and his concubine Devlet Hatun, he fought with ...
(d. 1421) shuttled tribal Turkmen and Tatar
Tatar may refer to:
Peoples
* Tatars, an umbrella term for different Turkic ethnic groups bearing the name "Tatar"
* Volga Tatars, a people from the Volga-Ural region of western Russia
* Crimean Tatars, a people from the Crimea peninsula by the B ...
groups from the state's Asiatic territories to the Balkans
The Balkans ( , ), corresponding partially with the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throug ...
(Rumeli). Many of these groups were supported as paramilitary forces along the frontier with Christian
A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a Monotheism, monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the wo ...
Europe. Simultaneously, Christian communities were transported from newly conquered lands in the Balkans into Thrace
Thrace (, ; ; ; ) is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe roughly corresponding to the province of Thrace in the Roman Empire. Bounded by the Balkan Mountains to the north, the Aegean Sea to the south, and the Black Se ...
and Anatolia
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
. While these general flows back and forth across the Dardanelles continued, the reigns of Murad II
Murad II (, ; June 1404 – 3 February 1451) was twice the sultan of the Ottoman Empire, from 1421 to 1444 and from 1446 to 1451.
Early life
Murad was born in June 1404 to Mehmed I, while the identity of his mother is disputed according to v ...
(d. 1451) and Mehmet II
Mehmed II (; , ; 30 March 14323 May 1481), commonly known as Mehmed the Conqueror (; ), was twice the sultan of the Ottoman Empire from August 1444 to September 1446 and then later from February 1451 to May 1481.
In Mehmed II's first reign, ...
(d. 1481) concentrated on the demographic reorganization of the empire's urban centers. Murad II's conquest of Salonika
Thessaloniki (; ), also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, Salonika, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece (with slightly over one million inhabitants in its Thessaloniki metropolitan area, metropolitan area) and the capital cit ...
was followed by its state-enforced settlement by Muslims from Yenice Vardar and Anatolia. Mehmet II's transfers focused on the re-population of the city of Istanbul
Istanbul is the List of largest cities and towns in Turkey, largest city in Turkey, constituting the country's economic, cultural, and historical heart. With Demographics of Istanbul, a population over , it is home to 18% of the Demographics ...
following its conquest in 1453, transporting Christians, Muslims, and Jews into the new capital from across the empire. To this day, the huge Belgrade Forest, to the north of Istanbul and named after re-settled people from Belgrade
Belgrade is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Serbia, largest city of Serbia. It is located at the confluence of the Sava and Danube rivers and at the crossroads of the Pannonian Basin, Pannonian Plain and the Balkan Peninsula. T ...
, is a reminder of those times.
Beginning in the reign of Bayezid II
Bayezid II (; ; 3 December 1447 – 26 May 1512) was the sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1481 to 1512. During his reign, Bayezid consolidated the Ottoman Empire, thwarted a pro-Safavid dynasty, Safavid rebellion and finally abdicated his throne ...
(d. 1512), the Ottoman state used to manage the difficulty with the heterodox ''Qizilbash
Qizilbash or Kizilbash (Latin script: ) ; ; (modern Iranian reading: ); were a diverse array of mainly Turkoman "The Qizilbash, composed mainly of Turkman tribesmen, were the military force introduced by the conquering Safavis to the Irani ...
'' (''kizilbas'') movement in eastern Anatolia. Forced relocation of the Qizilbash continued until at least the end of the 16th century. Selim I
Selim I (; ; 10 October 1470 – 22 September 1520), known as Selim the Grim or Selim the Resolute (), was the List of sultans of the Ottoman Empire, sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1512 to 1520. Despite lasting only eight years, his reign is ...
(d. 1520) ordered merchants, artisans, and scholars transported to Istanbul from Tabriz
Tabriz (; ) is a city in the Central District (Tabriz County), Central District of Tabriz County, in the East Azerbaijan province, East Azerbaijan province of northwestern Iran. It serves as capital of the province, the county, and the distric ...
and Cairo
Cairo ( ; , ) is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Egypt and the Cairo Governorate, being home to more than 10 million people. It is also part of the List of urban agglomerations in Africa, largest urban agglomeration in Africa, L ...
. The state mandated Muslim immigration to Rhodes
Rhodes (; ) is the largest of the Dodecanese islands of Greece and is their historical capital; it is the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, ninth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea. Administratively, the island forms a separ ...
and Cyprus
Cyprus (), officially the Republic of Cyprus, is an island country in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Situated in West Asia, its cultural identity and geopolitical orientation are overwhelmingly Southeast European. Cyprus is the List of isl ...
following their conquests in 1522 and 1571, respectively, and resettled Greek Cypriots
Greek Cypriots (, ) are the ethnic Greeks, Greek population of Cyprus, forming the island's largest Ethnolinguistic group, ethnolinguistic community. According to the 2023 census, 719,252 respondents recorded their ethnicity as Greek, forming al ...
on the Anatolia coast.
Knowledge on the practice throughout the 17th through the 19th century are vague though it seems that the state did not utilize population transfer as much during this time period as it had earlier.
Armenian genocide
Armenian genocide
The Armenian genocide was the systematic destruction of the Armenians, Armenian people and identity in the Ottoman Empire during World War I. Spearheaded by the ruling Committee of Union and Progress (CUP), it was implemented primarily t ...
entailed the forcible relocation of almost all Armenians from Anatolia to the Syrian desert. This relocation was inherently genocidal as those who ordered it did not intend for Armenians to survive; and one of their goals was to ensure in all parts of the empire Armenian population did not exceed 5 to 10 percent (a goal that could not be accomplished without mass extermination). Talat Pasha
Mehmed Talât (1 September 187415 March 1921), commonly known as Talaat Pasha or Talat Pasha, was an Ottoman Young Turk activist, revolutionary, politician, and convicted war criminal who served as the leader of the Ottoman Empire from 191 ...
explained, "They can live in the desert but nowhere else."
*
In May 1915, Mehmed Talaat Pasha requested that the cabinet and Grand Vizier
Grand vizier (; ; ) was the title of the effective head of government of many sovereign states in the Islamic world. It was first held by officials in the later Abbasid Caliphate. It was then held in the Ottoman Empire, the Mughal Empire, the Soko ...
Said Halim Pasha
Mehmed Said Halim Pasha (; ; 18 or 28 January 1865 or 19 February 1864 – 6 December 1921) was a writer and statesman who served as the Grand Vizier of the Ottoman Empire from 1913 to 1917. He was one of the perpetrators of the Armenian genocide ...
legalize a measure for the deportation of Armenians to other places due to what Talaat Pasha
Mehmed Talât (1 September 187415 March 1921), commonly known as Talaat Pasha or Talat Pasha, was an Ottoman Young Turk activist, revolutionary, politician, and convicted war criminal who served as the leader of the Ottoman Empire from 191 ...
called "the Armenian riots and massacres, which had arisen in a number of places in the country". However, Talaat Pasha was referring specifically to events in Van
A van is a type of road vehicle used for transporting goods or people. There is some variation in the scope of the word across the different English-speaking countries. The smallest vans, microvans, are used for transporting either goods or ...
and extending the implementation to the regions in which alleged "riots and massacres" would affect the security of the war zone of the Caucasus Campaign
The Caucasus campaign comprised armed conflicts between the Russian Empire and the Ottoman Empire, later including Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, the Mountainous Republic of the Northern Caucasus, the German Empire, the Central Caspian Dict ...
. Later, the scope of the deportation was widened in order to include the Armenians in the other provinces.
On 29 May 1915, the Central Committee passed the laws known as the Temporary Law of Deportation (" Tehjir Law"). These laws gave the Ottoman government and military authorization to deport anyone it "sensed" as a threat to national security.
The "Tehjir Law" brought with it some measures regarding the property of the deportees, but during September a new law was put forth. According to the new "Abandoned Properties" Law (Law Concerning Property, Dept's and Assets Left Behind Deported Persons, also referred as the "Temporary Law on Expropriation and Confiscation"), the Ottoman government took possession of all "abandoned" Armenian goods and properties. Some Ottoman parliamentary representatives like, Ahmed Riza protested this legislation:
On 13 September 1915, the Ottoman parliament also passed the "Temporary Law of Expropriation and Confiscation", stating that all property, including land, livestock, and homes belonging to Armenians, was to be confiscated by the authorities.
See also
*Ottoman dynasty
The Ottoman dynasty () consisted of the members of the imperial House of Osman (), also known as the Ottomans (). According to Ottoman tradition, the family originated from the Kayı tribe branch of the Oghuz Turks, under the leadership of Os ...
* Line of succession to the former Ottoman throne
The Ottoman dynasty () consisted of the members of the imperial House of Osman (), also known as the Ottomans (). According to Ottoman tradition, the family originated from the Kayı tribe branch of the Oghuz Turks, under the leadership of ...
* Demographic engineering
* Population transfer
Population transfer or resettlement is a type of mass migration that is often imposed by a state policy or international authority. Such mass migrations are most frequently spurred on the basis of ethnicity or religion, but they also occur d ...
* Population exchange between Greece and Turkey
The 1923 population exchange between Greece and Turkey stemmed from the "Convention Concerning the Exchange of Greek and Turkish Populations" signed at Lausanne, Switzerland, on 30 January 1923, by the governments of Greece and Turkey. It involv ...
References
{{Ottoman Empire topics Demographic history Demographics of the Ottoman Empire Ethnic cleansing Ethnicity in politics Exile Forced migration in Asia Forced migrations in Europe Internal migration Persecution of Christians Political and cultural purges Politically motivated migrations Politics of the Ottoman Empire Settlement schemes in Europe Settlement schemes in the Middle East Society of the Ottoman Empire Turkish settlement schemes Armenian genocide