Syro-African Rift on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
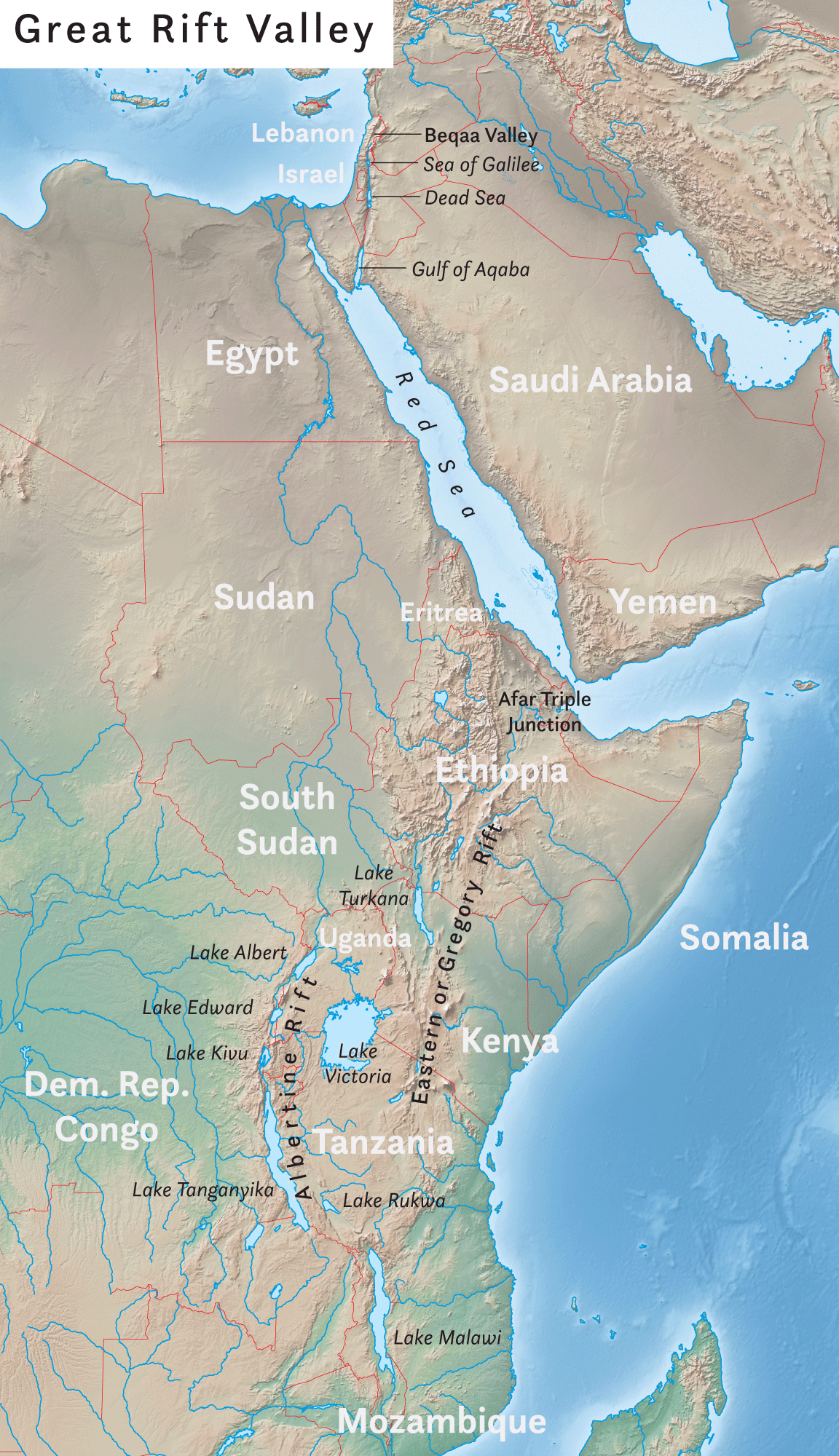 The Great Rift Valley () is a series of contiguous geographic depressions, approximately 6,000 or in total length, the definition varying between sources, that runs from the southern Turkish
The Great Rift Valley () is a series of contiguous geographic depressions, approximately 6,000 or in total length, the definition varying between sources, that runs from the southern Turkish 
 The term Great Rift Valley is most often used to refer to the valley of the
The term Great Rift Valley is most often used to refer to the valley of the
 Today these rifts and faults are seen as distinct, although connected. Originally, the Great Rift Valley was thought to be a single feature that extended from
Today these rifts and faults are seen as distinct, although connected. Originally, the Great Rift Valley was thought to be a single feature that extended from
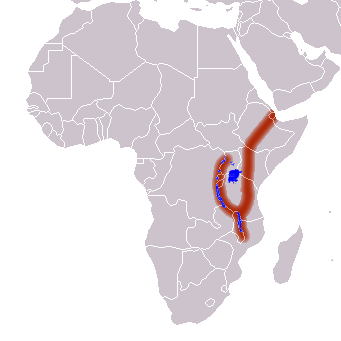 The East African Rift follows the Red Sea to the end before turning inland into the
The East African Rift follows the Red Sea to the end before turning inland into the
Big crack is evidence that East Africa could be splitting in two, by Lucia Perez Diaz, CNN. Updated April 5, 2018
Article on geology.com
* {{Authority control Great Rift Valley, * Rifts and grabens Landforms of Israel Landforms of Syria Landforms of Egypt Landforms of Lebanon Landforms of Ethiopia Landforms of Kenya Landforms of Saudi Arabia Landforms of Yemen Landforms of Tanzania Landforms of the Democratic Republic of the Congo Landforms of Uganda Landforms of Burundi Geology of Israel Geology of Syria Geology of Egypt Geology of Lebanon Geology of Ethiopia Geology of Kenya Geology of Saudi Arabia Geology of Yemen Geology of Tanzania Geology of the Democratic Republic of the Congo Geology of Uganda Geology of Burundi Physiographic provinces Prehistoric Afar Triangle
 The Great Rift Valley () is a series of contiguous geographic depressions, approximately 6,000 or in total length, the definition varying between sources, that runs from the southern Turkish
The Great Rift Valley () is a series of contiguous geographic depressions, approximately 6,000 or in total length, the definition varying between sources, that runs from the southern Turkish Hatay Province
Hatay Province (, ) is the southernmost province and metropolitan municipality of Turkey. Its area is , and its population is 1,686,043 (2022). It is situated mostly outside Anatolia, along the eastern coast of the Levantine Sea. The province ...
in Asia, through the Red Sea
The Red Sea is a sea inlet of the Indian Ocean, lying between Africa and Asia. Its connection to the ocean is in the south, through the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait and the Gulf of Aden. To its north lie the Sinai Peninsula, the Gulf of Aqaba, and th ...
, to Mozambique
Mozambique, officially the Republic of Mozambique, is a country located in Southeast Africa bordered by the Indian Ocean to the east, Tanzania to the north, Malawi and Zambia to the northwest, Zimbabwe to the west, and Eswatini and South Afr ...
in Southeast Africa
Southeast Africa, or Southeastern Africa, is an African region that is intermediate between East Africa and Southern Africa. It comprises the countries Botswana, Eswatini, Kenya, Lesotho, Malawi, Mozambique, Namibia, Rwanda, South Africa, Tanza ...
. While the name remains in some usages, it is rarely used in geology
Geology (). is a branch of natural science concerned with the Earth and other astronomical objects, the rocks of which they are composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Earth ...
where the term "Afro-Arabian Rift System" is preferred.
This valley extends southward from Western Asia
West Asia (also called Western Asia or Southwest Asia) is the westernmost region of Asia. As defined by most academics, UN bodies and other institutions, the subregion consists of Anatolia, the Arabian Peninsula, Iran, Mesopotamia, the Armenian ...
into the eastern part of Africa, where several deep, elongated lakes, called ribbon lake
A ribbon lake is a long and very deep, finger-shaped lake, usually found in a glacial trough. As such, a ribbon lake is one of a number of glacial landscapes, including arêtes, corries, rock lips, rock basins and terminal moraines.
Such a la ...
s, exist on the rift valley floor, Lake Malawi
Lake Malawi, also known as Lake Nyasa in Tanzania and Lago Niassa in Mozambique, () is an African Great Lakes, African Great Lake and the southernmost lake in the East African Rift system, located between Malawi, Mozambique and Tanzania.
It is ...
and Lake Tanganyika
Lake Tanganyika ( ; ) is an African Great Lakes, African Great Lake. It is the world's List of lakes by volume, second-largest freshwater lake by volume and the List of lakes by depth, second deepest, in both cases after Lake Baikal in Siberia. ...
being two such examples. The region has a unique ecosystem and contains a number of Africa's wildlife parks.

East African Rift
The East African Rift (EAR) or East African Rift System (EARS) is an active continental rift zone in East Africa. The EAR began developing around the onset of the Miocene, 22–25 million years ago. It was formerly considered to be part of a l ...
, the divergent plate boundary which extends from the Afar triple junction
The Afar triple junction is a triple junction located along a divergent plate boundary dividing the Nubian, Somali, and Arabian plates. This area is considered a present-day example of continental rifting leading to seafloor spreading and prod ...
southward through eastern Africa
East Africa, also known as Eastern Africa or the East of Africa, is a region at the eastern edge of the Africa, African continent, distinguished by its unique geographical, historical, and cultural landscape. Defined in varying scopes, the regi ...
, and is in the process of splitting the African plate into two new and separate plates. Geologists generally refer to these evolving plates as the Nubian plate and the Somali plate.
Theoretical extent
 Today these rifts and faults are seen as distinct, although connected. Originally, the Great Rift Valley was thought to be a single feature that extended from
Today these rifts and faults are seen as distinct, although connected. Originally, the Great Rift Valley was thought to be a single feature that extended from Lebanon
Lebanon, officially the Republic of Lebanon, is a country in the Levant region of West Asia. Situated at the crossroads of the Mediterranean Basin and the Arabian Peninsula, it is bordered by Syria to the north and east, Israel to the south ...
in the north to Mozambique
Mozambique, officially the Republic of Mozambique, is a country located in Southeast Africa bordered by the Indian Ocean to the east, Tanzania to the north, Malawi and Zambia to the northwest, Zimbabwe to the west, and Eswatini and South Afr ...
in the south, where it constitutes one of two distinct physiographic provinces of the East African mountains
The East African mountains are a mountain region in the African Great Lakes, within Kenya, Uganda, Tanzania, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Rwanda and Burundi.
Location and description
The mountains are related to the East African Rift, and ar ...
. It included what today is called the Lebanese section of the Dead Sea Transform
The Dead Sea Transform (DST) fault system, also sometimes referred to as the Dead Sea Rift, is a series of Fault (geology), faults that run for about 1,000 km from the Marash triple junction (a junction with the East Anatolian Fault in south ...
(Turkey to Straits of Tiran
The Straits of Tiran ( ') are the narrow sea passages between the Sinai Peninsula, Sinai and Arabian Peninsula, Arabian peninsulas that connect the Gulf of Aqaba and the Red Sea. The distance between the two peninsulas is about . The Multinatio ...
), the Jordan Rift Valley
The Jordan Rift Valley, also Jordan Valley ( ''Bīqʿāt haYardēn'', Al-Ghor or Al-Ghawr), is an elongated endorheic basin located in modern-day Israel, Jordan and the West Bank, Palestine. This geographic region includes the entire length o ...
(geographic term for section including entire course of the Jordan River
The Jordan River or River Jordan (, ''Nahr al-ʾUrdunn''; , ''Nəhar hayYardēn''), also known as ''Nahr Al-Sharieat'' (), is a endorheic river in the Levant that flows roughly north to south through the Sea of Galilee and drains to the Dead ...
, the Dead Sea
The Dead Sea (; or ; ), also known by #Names, other names, is a landlocked salt lake bordered by Jordan to the east, the Israeli-occupied West Bank to the west and Israel to the southwest. It lies in the endorheic basin of the Jordan Rift Valle ...
, and the Arabah
The Arabah/Araba () or Aravah/Arava () is a loosely defined geographic area in the Negev Desert, south of the Dead Sea basin, which forms part of the border between Israel to the west and Jordan to the east.
The old meaning, which was in use ...
Valley), Red Sea Rift
The Red Sea Rift is a mid-ocean ridge between two tectonic plates, the African plate and the Arabian plate. It extends from the Dead Sea Transform fault system, and ends at an intersection with the Aden Ridge and the East African Rift, forming ...
, and the East African Rift
The East African Rift (EAR) or East African Rift System (EARS) is an active continental rift zone in East Africa. The EAR began developing around the onset of the Miocene, 22–25 million years ago. It was formerly considered to be part of a l ...
. These rifts and faults are considered to having been formed 35 million years ago.
Asia
The northernmost part of the Rift corresponds to the central section of what is today called theDead Sea Transform
The Dead Sea Transform (DST) fault system, also sometimes referred to as the Dead Sea Rift, is a series of Fault (geology), faults that run for about 1,000 km from the Marash triple junction (a junction with the East Anatolian Fault in south ...
(DST) or Rift. This midsection of the DST forms the Beqaa Valley
The Beqaa Valley (, ; Bekaa, Biqâ, Becaa) is a fertile valley in eastern Lebanon and its most important farming region. Industry, especially the country's agricultural industry, also flourishes in Beqaa. The region broadly corresponds to th ...
in Lebanon, separating the Mount Lebanon range from the Anti-Lebanon Mountains
The Anti-Lebanon mountains (), also called Mount Amana, are a southwest–northeast-trending, c. long mountain range that forms most of the border between Syria and Lebanon. The border is largely defined along the crest of the range. Most of ...
. Further south it is known as the Hula Valley
The Hula Valley () is a valley and fertile agricultural region in northern Israel with abundant fresh water that used to be Lake Hula before it was drained. It is a major stopover for birds migrating along the Great Rift Valley between Africa ...
separating the Galilee
Galilee (; ; ; ) is a region located in northern Israel and southern Lebanon consisting of two parts: the Upper Galilee (, ; , ) and the Lower Galilee (, ; , ).
''Galilee'' encompasses the area north of the Mount Carmel-Mount Gilboa ridge and ...
mountains and the Golan Heights
The Golan Heights, or simply the Golan, is a basaltic plateau at the southwest corner of Syria. It is bordered by the Yarmouk River in the south, the Sea of Galilee and Hula Valley in the west, the Anti-Lebanon mountains with Mount Hermon in t ...
.
The Jordan River
The Jordan River or River Jordan (, ''Nahr al-ʾUrdunn''; , ''Nəhar hayYardēn''), also known as ''Nahr Al-Sharieat'' (), is a endorheic river in the Levant that flows roughly north to south through the Sea of Galilee and drains to the Dead ...
begins here and flows southward through Lake Hula
The Hula Valley () is a valley and fertile agriculture, agricultural region in northern Israel with abundant fresh water that used to be Lake Hula before it was drained. It is a major stopover for birds migrating along the Great Rift Valley be ...
into the Sea of Galilee
The Sea of Galilee (, Judeo-Aramaic languages, Judeo-Aramaic: יַמּא דטבריא, גִּנֵּיסַר, ), also called Lake Tiberias, Genezareth Lake or Kinneret, is a freshwater lake in Israel. It is the lowest freshwater lake on Earth ...
in Israel
Israel, officially the State of Israel, is a country in West Asia. It Borders of Israel, shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the north-east, Jordan to the east, Egypt to the south-west, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. Isr ...
. The Rift then continues south through the Jordan Rift Valley
The Jordan Rift Valley, also Jordan Valley ( ''Bīqʿāt haYardēn'', Al-Ghor or Al-Ghawr), is an elongated endorheic basin located in modern-day Israel, Jordan and the West Bank, Palestine. This geographic region includes the entire length o ...
into the Dead Sea
The Dead Sea (; or ; ), also known by #Names, other names, is a landlocked salt lake bordered by Jordan to the east, the Israeli-occupied West Bank to the west and Israel to the southwest. It lies in the endorheic basin of the Jordan Rift Valle ...
, on the Israel
Israel, officially the State of Israel, is a country in West Asia. It Borders of Israel, shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the north-east, Jordan to the east, Egypt to the south-west, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. Isr ...
i-Jordan
Jordan, officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan, is a country in the Southern Levant region of West Asia. Jordan is bordered by Syria to the north, Iraq to the east, Saudi Arabia to the south, and Israel and the occupied Palestinian ter ...
ian border. From the Dead Sea southwards, the Rift is occupied by the Wadi Arabah
The Arabah/Araba () or Aravah/Arava () is a loosely defined geographic area in the Negev Desert, south of the Dead Sea basin, which forms part of the border between Israel to the west and Jordan to the east.
The old meaning, which was in use ...
, then the Gulf of Aqaba
The Gulf of Aqaba () or Gulf of Eilat () is a large gulf at the northern tip of the Red Sea, east of the Sinai Peninsula and west of the Arabian Peninsula. Its coastline is divided among four countries: Egypt, Israel, Jordan, and Saudi Arabia.
...
, and then the Red Sea
The Red Sea is a sea inlet of the Indian Ocean, lying between Africa and Asia. Its connection to the ocean is in the south, through the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait and the Gulf of Aden. To its north lie the Sinai Peninsula, the Gulf of Aqaba, and th ...
.
Off the southern tip of Sinai in the Red Sea, the Dead Sea Transform
The Dead Sea Transform (DST) fault system, also sometimes referred to as the Dead Sea Rift, is a series of Fault (geology), faults that run for about 1,000 km from the Marash triple junction (a junction with the East Anatolian Fault in south ...
meets the Red Sea Rift
The Red Sea Rift is a mid-ocean ridge between two tectonic plates, the African plate and the Arabian plate. It extends from the Dead Sea Transform fault system, and ends at an intersection with the Aden Ridge and the East African Rift, forming ...
which runs the length of the Red Sea. The Red Sea Rift comes ashore to meet the East African Rift
The East African Rift (EAR) or East African Rift System (EARS) is an active continental rift zone in East Africa. The EAR began developing around the onset of the Miocene, 22–25 million years ago. It was formerly considered to be part of a l ...
and the Aden Ridge
The Aden Ridge is a part of an active oblique rift system located in the Gulf of Aden, between Somalia and the Arabian Peninsula to the north. The rift system marks the divergent boundary between the Somali plate, Somali and Arabian plate, Arabi ...
, in the Afar Depression
The Afar Triangle (also called the Afar Depression) is a geological depression caused by the Afar triple junction, which is part of the Great Rift Valley in East Africa. The region has disclosed fossil specimens of the very earliest hominins; ...
of East Africa. The junction of these three rifts is called the Afar triple junction
The Afar triple junction is a triple junction located along a divergent plate boundary dividing the Nubian, Somali, and Arabian plates. This area is considered a present-day example of continental rifting leading to seafloor spreading and prod ...
.
Africa
 The East African Rift follows the Red Sea to the end before turning inland into the
The East African Rift follows the Red Sea to the end before turning inland into the Ethiopian highlands
The Ethiopian Highlands (also called the Abyssinian Highlands) is a rugged mass of mountains in Ethiopia in Northeast Africa. It forms the largest continuous area of its elevation in the continent, with little of its surface falling below , whil ...
, dividing the country into two large and adjacent but separate mountainous regions. In Kenya, Uganda, and the fringes of South Sudan, the Great Rift runs along two separate branches that are joined to each other only at their southern end, in Southern Tanzania
Tanzania, officially the United Republic of Tanzania, is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It is bordered by Uganda to the northwest; Kenya to the northeast; the Indian Ocean to the east; Mozambique and Malawi to t ...
along its border with Zambia
Zambia, officially the Republic of Zambia, is a landlocked country at the crossroads of Central Africa, Central, Southern Africa, Southern and East Africa. It is typically referred to being in South-Central Africa or Southern Africa. It is bor ...
. The two branches are called the Western Rift Valley and the Eastern Rift Valley.
The Western Rift, also called the Albertine Rift
The Albertine Rift is the western branch of the East African Rift, covering parts of Uganda, the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), Rwanda, Burundi and Tanzania.
It extends from the northern end of Lake Albert to the southern end of Lake Tan ...
, is bordered by some of the highest mountains in Africa, including the Virunga Mountains
The Virunga Mountains (also known as Mufumbiro) are a chain of volcanoes in East Africa, in the area where Rwanda, the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), and Uganda meet. The mountain range is a branch of the Albertine Rift Mountains, ...
, Mitumba Mountains
The Mitumba Mountains stretch along the Western Rift Valley in Eastern Congo (DRC), west of Lake Tanganyika and Lake Kivu. The two main peaks, Mount Kahuzi (3,308 m) and Mount Biéga (2,790 m) are dormant volcanoes. The northern po ...
, and Ruwenzori Range. It contains the Rift Valley lakes
The Rift Valley lakes are a series of lakes in the East African Rift valley that runs through eastern Africa from Ethiopia in the north to Malawi in the south, and includes the African Great Lakes in the south. These include some of the world's ...
, which include some of the deepest lakes in the world (up to deep at Lake Tanganyika
Lake Tanganyika ( ; ) is an African Great Lakes, African Great Lake. It is the world's List of lakes by volume, second-largest freshwater lake by volume and the List of lakes by depth, second deepest, in both cases after Lake Baikal in Siberia. ...
).
Much of this area lies within the boundaries of national parks, such as Virunga National Park
Virunga National Park is a national park in the Albertine Rift Valley in the eastern part of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It was created in 1925. In elevation, it ranges from in the Semliki River valley to in the Rwenzori Mountains. ...
in the Democratic Republic of Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), also known as the DR Congo, Congo-Kinshasa, or simply the Congo (the last ambiguously also referring to the neighbouring Republic of the Congo), is a country in Central Africa. By land area, it is t ...
, Rwenzori National Park and Queen Elizabeth National Park
Queen Elizabeth National Park is a national park in the Western Region, Uganda, Western Region of Uganda.
Location
Queen Elizabeth National Park (QENP) spans the districts of Kasese District, Kasese, Kamwenge District, Kamwenge, Rubirizi Distri ...
in Uganda, and Volcanoes National Park
Volcanoes National Park is a national park in northwestern Rwanda. It covers of rainforest and encompasses five of the eight volcanoes in the Virunga Mountains, namely Karisimbi, Bisoke, Muhabura, Gahinga and Sabyinyo. It borders Virunga ...
in Rwanda
Rwanda, officially the Republic of Rwanda, is a landlocked country in the Great Rift Valley of East Africa, where the African Great Lakes region and Southeast Africa converge. Located a few degrees south of the Equator, Rwanda is bordered by ...
. Lake Victoria
Lake Victoria is one of the African Great Lakes. With a surface area of approximately , Lake Victoria is Africa's largest lake by area, the world's largest tropics, tropical lake, and the world's second-largest fresh water lake by surface are ...
is considered to be part of the rift valley system although it actually lies between the two branches. All of the African Great Lakes
The African Great Lakes (; ) are a series of lakes constituting the part of the Rift Valley lakes in and around the East African Rift. The series includes Lake Victoria, the second-largest freshwater lake in the world by area; Lake Tangan ...
were formed as the result of the rift, and most lie in territories within the rift.
In Kenya
Kenya, officially the Republic of Kenya, is a country located in East Africa. With an estimated population of more than 52.4 million as of mid-2024, Kenya is the 27th-most-populous country in the world and the 7th most populous in Africa. ...
, the valley is deepest to the north of Nairobi
Nairobi is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Kenya. The city lies in the south-central part of Kenya, at an elevation of . The name is derived from the Maasai language, Maasai phrase , which translates to 'place of cool waters', a ...
. As the lakes in the Eastern Rift have no output to the sea and tend to be shallow, they have a high mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid substance with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2011): Mi ...
content as the evaporation of water leaves the salts behind. For example, Lake Magadi
Lake Magadi is the southernmost lake in the Kenyan Rift Valley, lying in a catchment of faulted volcanic rocks, north of Tanzania's Lake Natron. During the dry season, it is 80% covered by soda and is known for its wading birds, including f ...
has high concentrations of soda (sodium carbonate
Sodium carbonate (also known as washing soda, soda ash, sal soda, and soda crystals) is the inorganic compound with the formula and its various hydrates. All forms are white, odourless, water-soluble salts that yield alkaline solutions in water ...
) and Lake Elmenteita
Lake Elmenteita is a soda lake, in the Great Rift Valley, about 120 km northwest of Nairobi, Kenya.
Geography
Elmenteita is derived from the Maasai word , meaning "dust place", a reference to the dryness and dustiness of the area, esp ...
, Lake Bogoria
Lake Bogoria (formerly Lake Hannington) is a saline, alkaline lake that lies in a volcanic region in a half-graben basin south of Lake Baringo, Kenya, a little north of the equator. Lake Bogoria, like Lake Nakuru, Lake Elementeita, and Lake Ma ...
, and Lake Nakuru
Lake Nakuru is one of the Rift Valley lakes, located at an elevation of above sea level. It lies to the south of Nakuru, in the rift valley of Kenya and is protected by Lake Nakuru National Park.
About 10,000 years ago, Lake Nakuru, together wi ...
are all strongly alkaline
In chemistry, an alkali (; from the Arabic word , ) is a basic salt of an alkali metal or an alkaline earth metal. An alkali can also be defined as a base that dissolves in water. A solution of a soluble base has a pH greater than 7.0. The ...
, while the freshwater springs supplying Lake Naivasha
Lake Naivasha is a freshwater lake in Kenya, outside the town of Naivasha in Nakuru County, which lies north west of Nairobi. It is situated in the Great Rift Valley. The name derives from the local Maasai name ''ɛnaɨpɔ́sha '', meaning ...
are essential to support its current biological variety.
The southern section of the Rift Valley includes Lake Malawi
Lake Malawi, also known as Lake Nyasa in Tanzania and Lago Niassa in Mozambique, () is an African Great Lakes, African Great Lake and the southernmost lake in the East African Rift system, located between Malawi, Mozambique and Tanzania.
It is ...
, the third-deepest freshwater body in the world, which reaches in depth and separates the Nyassa plateau of Northern Mozambique from Malawi. The rift extends southwards from Lake Malawi as the valley of the Shire River
The Shire is the largest river in Malawi. It is the only outlet of Lake Malawi and flows into the Zambezi River in Mozambique. Its length is . The upper Shire River issues from Lake Malawi and runs approximately before it enters shallow Lake Malo ...
, which flows from the lake into the Zambezi
The Zambezi (also spelled Zambeze and Zambesi) is the fourth-longest river in Africa, the longest east-flowing river in Africa and the largest flowing into the Indian Ocean from Africa. Its drainage basin covers , slightly less than half of t ...
River. The rift continues south of the Zambezi as the Urema Valley of central Mozambique.Steinbruch, Franziska (2010). Geology and geomorphology of the Urema Graben with emphasis on the evolution of Lake Urema, ''Journal of African Earth Sciences'', Volume 58, Issue 2, 2010, Pages 272-284. ISSN 1464-343X, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2010.03.007.
See also
;Africa *Great Rift Valley, Ethiopia
The Great Rift Valley of Ethiopia, (or Main Ethiopian Rift or Ethiopian Rift Valley) is a branch of the East African Rift that runs through Ethiopia in a southwest direction from the Afar triple junction. In the past, it was seen as part of a "G ...
*Great Rift Valley, Kenya
The Great Rift Valley is part of an intra-continental ridge system that runs through Kenya from north to south. It is part of the Gregory Rift, the eastern branch of the East African Rift, which starts in Tanzania to the south and continues no ...
*Rift Valley fever
Rift Valley fever (RVF) is a viral disease of humans and livestock that can cause mild to severe symptoms. The mild symptoms may include: fever, muscle pains, and headaches which often last for up to a week. The severe symptoms may include: loss ...
*Rift Valley lakes
The Rift Valley lakes are a series of lakes in the East African Rift valley that runs through eastern Africa from Ethiopia in the north to Malawi in the south, and includes the African Great Lakes in the south. These include some of the world's ...
*Rift Valley Province
Rift Valley Province () of Kenya, bordering Uganda, was one of Kenya's eight provinces, before the 2013 Kenyan general election.
Rift Valley Province was the largest and one of the most economically important provinces in Kenya. It was dominated ...
*Rift Valley Railways
Rift Valley Railways (RVR) was a consortium established to manage the parastatal railways of Kenya Railways, Kenya and Uganda Railways Corporation, Uganda. The consortium won the bid for private management of the century-old Uganda Railway in 2 ...
* Rift Valley Technical Training Institute
*'' The Great Rift: Africa's Wild Heart'', a BBC
The British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) is a British public service broadcaster headquartered at Broadcasting House in London, England. Originally established in 1922 as the British Broadcasting Company, it evolved into its current sta ...
/Animal Planet
Animal Planet (stylized in all lowercase since 2018) is an American multinational pay television channel focusing on the animal kingdom owned by the Warner Bros. Discovery Networks unit of Warner Bros. Discovery. First established on June 1 ...
production
;Major earthquakes
*1837 Galilee earthquake
The Galilee earthquake of 1837, often called the Safed earthquake, shook the Galilee on January 1 and is one of a number of moderate to large events that have occurred along the Dead Sea Transform fault system that marks the boundary of two tecto ...
*1995 Gulf of Aqaba earthquake
The 1995 Gulf of Aqaba earthquake (also known as Nuweiba earthquake) occurred on November 22 at 06:15 local time (04:15 UTC) and registered 7.3 on the scale. The epicenter was located in the central segment of the Gulf of Aqaba, the narrow body ...
* 2005 Lake Tanganyika earthquake
*2006 Mozambique earthquake
The 2006 Mozambique earthquake occurred at 22:19 Coordinated Universal Time, UTC on 22 February. It had a magnitude of 7.0 on the moment magnitude scale and caused 4 deaths and 36 injuries. The epicenter was near Machaze in Manica Province of sou ...
* 2008 Lake Kivu earthquake
References
Further reading
*''Africa's Great Rift Valley'', 2001, *''Tribes of the Great Rift Valley'', 2007, *''East African Rift Valley lakes'', 2006, *''Photographic atlas of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge Rift Valley'', 1977, *''Rift Valley fever : an emerging human and animal problem'', 1982, *''Rift valley: definition and geologic significance'', Giacomo Corti (National Research Council of Italy, Institute of Geosciences and Earth Resources) – The Ethiopian Rift Valley, 2013Big crack is evidence that East Africa could be splitting in two, by Lucia Perez Diaz, CNN. Updated April 5, 2018
External links
Article on geology.com
* {{Authority control Great Rift Valley, * Rifts and grabens Landforms of Israel Landforms of Syria Landforms of Egypt Landforms of Lebanon Landforms of Ethiopia Landforms of Kenya Landforms of Saudi Arabia Landforms of Yemen Landforms of Tanzania Landforms of the Democratic Republic of the Congo Landforms of Uganda Landforms of Burundi Geology of Israel Geology of Syria Geology of Egypt Geology of Lebanon Geology of Ethiopia Geology of Kenya Geology of Saudi Arabia Geology of Yemen Geology of Tanzania Geology of the Democratic Republic of the Congo Geology of Uganda Geology of Burundi Physiographic provinces Prehistoric Afar Triangle