Synthetic Chord on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
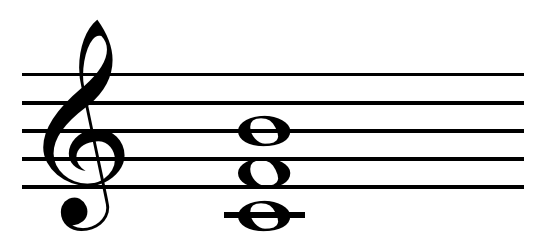 In
In  For example, if a composer uses a
For example, if a composer uses a
 In
In music theory
Music theory is the study of theoretical frameworks for understanding the practices and possibilities of music. ''The Oxford Companion to Music'' describes three interrelated uses of the term "music theory": The first is the "Elements of music, ...
and harmonic
In physics, acoustics, and telecommunications, a harmonic is a sinusoidal wave with a frequency that is a positive integer multiple of the ''fundamental frequency'' of a periodic signal. The fundamental frequency is also called the ''1st har ...
analysis
Analysis (: analyses) is the process of breaking a complex topic or substance into smaller parts in order to gain a better understanding of it. The technique has been applied in the study of mathematics and logic since before Aristotle (38 ...
, a synthetic chord is a made-up or non-traditional (synthetic) chord (collection of pitches) which cannot be analyzed in terms of traditional harmonic structures, such as the triad or seventh chord
A seventh chord is a chord (music), chord consisting of a triad (music), triad plus a note forming an interval (music), interval of a Interval (music), seventh above the chord's root (chord), root. When not otherwise specified, a "seventh chord" ...
.
However, synthetic chords originated not with Roslavets but with musicologist Sabaneev and his study of composer Scriabin
Alexander Nikolayevich Scriabin, scientific transliteration: ''Aleksandr Nikolaevič Skrjabin''; also transliterated variously as Skriabin, Skryabin, and (in French) Scriabine. The composer himselused the French spelling "Scriabine" which was a ...
's ''Prometheus
In Greek mythology, Prometheus (; , , possibly meaning "forethought")Smith"Prometheus". is a Titans, Titan. He is best known for defying the Olympian gods by taking theft of fire, fire from them and giving it to humanity in the form of technol ...
'' published in 1910.Hakobian, Levon (1998). ''Music of the Soviet Age, 1917-1987'', p.26-7. . See: Mystic chord
In music, the mystic chord or Prometheus chord is a six-note synthetic chord and its associated scale (music), scale, or pitch collection; which loosely serves as the harmony, harmonic and melody, melodic basis for some of the later pieces by Russ ...
.
 For example, if a composer uses a
For example, if a composer uses a synthetic scale
In music, a synthetic scale is a scale that derives from a traditional diatonic major scale by altering of one degree by a semitone in either direction."Synthetic Musical Scales". Author(s): J. Murray Barbour. Source: ''The American Mathematic ...
as the basis for a passage of music and constructs chords from its tones, in much the same way that a tonal composer may use a major
Major most commonly refers to:
* Major (rank), a military rank
* Academic major, an academic discipline to which an undergraduate student formally commits
* People named Major, including given names, surnames, nicknames
* Major and minor in musi ...
or minor scale
In Classical_music, Western classical music theory, the minor scale refers to three Scale (music), scale patterns – the natural minor scale (or Aeolian mode), the harmonic minor scale, and the melodic minor scale (ascending or descending).
...
's notes to build harmonies
In music, harmony is the concept of combining different sounds in order to create new, distinct musical ideas. Theories of harmony seek to describe or explain the effects created by distinct pitches or tones coinciding with one another; harm ...
, then the resulting chords may be synthetic chords and referred to as such.
Some synthetic chords may be analyzed as traditional chords, including the Prometheus chord, which may be analyzed as an altered dominant chord.
An example of a synthetic chord would be the repeated chord in the first act of Puccini
Giacomo Puccini (22 December 1858 29 November 1924) was an Italian composer known primarily for his operas. Regarded as the greatest and most successful proponent of Italian opera after Verdi, he was descended from a long line of composers, s ...
's ''Turandot
''Turandot'' ( ; see #Origin and pronunciation of the name, below) is an opera in three acts by Giacomo Puccini to a libretto in Italian by Giuseppe Adami and Renato Simoni. Puccini left the opera unfinished at the time of his death in 1924; it ...
'' at the beginning of the text passage ''"Non indugiare, se chiami appare..."''.
See also
* Synthetic modeReferences