surge protector on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A surge protector, spike suppressor, surge suppressor, surge diverter, surge protection device (SPD), transient voltage suppressor (TVS) or transient voltage surge suppressor (TVSS) is an appliance or device intended to protect electrical devices in
A surge protector, spike suppressor, surge suppressor, surge diverter, surge protection device (SPD), transient voltage suppressor (TVS) or transient voltage surge suppressor (TVSS) is an appliance or device intended to protect electrical devices in
 A transient surge protector attempts to limit the
A transient surge protector attempts to limit the

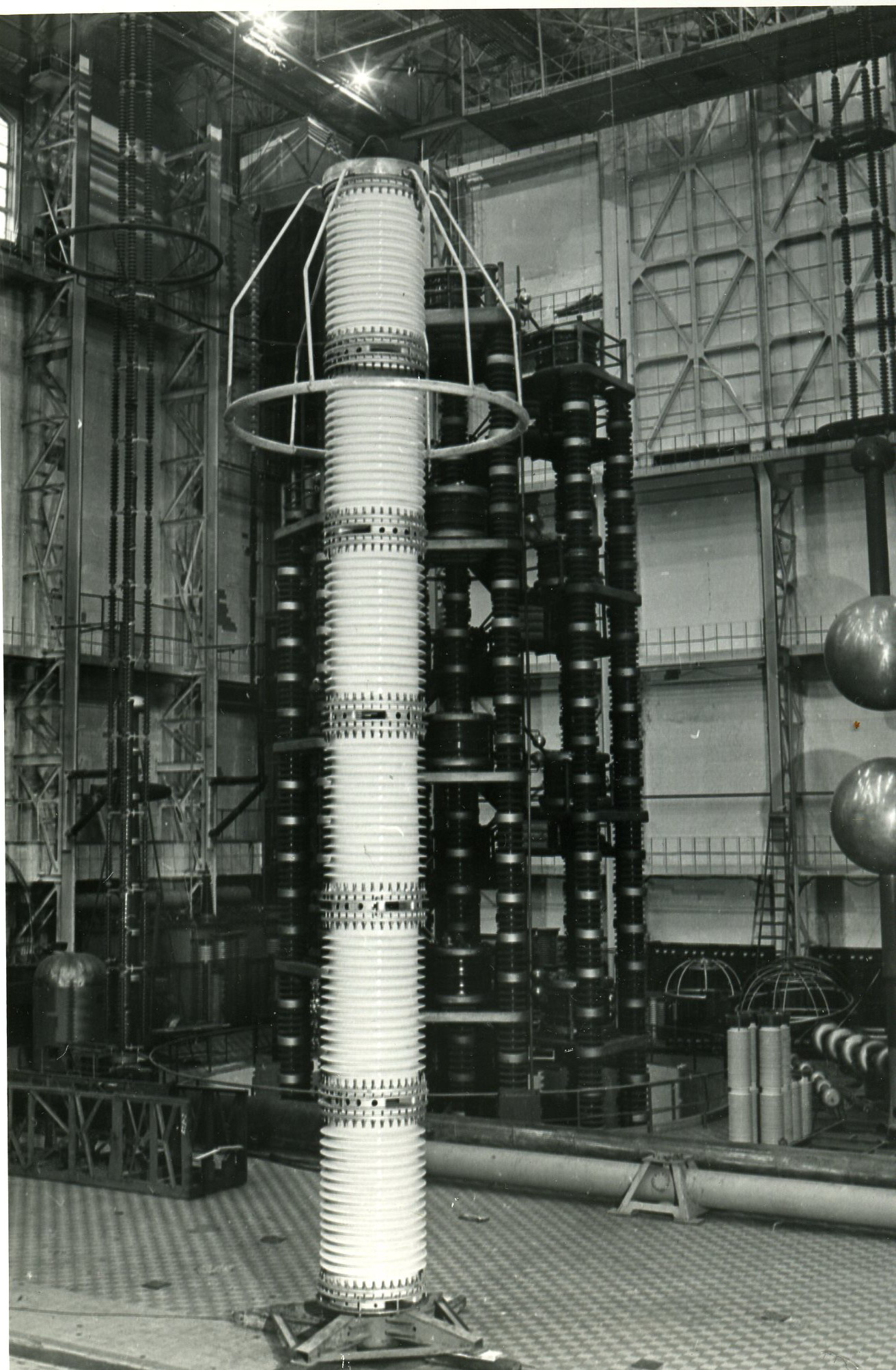 A surge arrester, surge protection device (SPD) or transient voltage surge suppressor (TVSS), is used to protect equipment in
A surge arrester, surge protection device (SPD) or transient voltage surge suppressor (TVSS), is used to protect equipment in
 These are some of the most prominently featured specifications which define a surge protector for AC mains, as well as for some data communications protection applications.
These are some of the most prominently featured specifications which define a surge protector for AC mains, as well as for some data communications protection applications.

 The Joule rating number defines how much energy a MOV-based surge protector can theoretically absorb in a single event, without failure. Better protectors exceed ratings of 1,000 joules and 40,000 amperes. Since the actual duration of a spike is only about 10 microseconds, the actual dissipated energy is low. Any more than that and the MOV will fuse, or sometimes short and melt, hopefully blowing a fuse, disconnecting itself from the circuit.
The MOV (or other shorting device) requires resistance in the supply line in order to limit the voltage. For large, low resistance power lines a higher joule rated MOV is required. Inside a house, with smaller wires that have more resistance, a smaller MOV is acceptable.
Every time an MOV shorts, its internal structure is changed and its threshold voltage reduced slightly. After many spikes the threshold voltage can reduce enough to be near the line voltage, i.e. 120 vac or 240 vac. At this point, the MOV will partially conduct and heat up and eventually fail, sometimes in a dramatic meltdown or even a fire. Most modern surge protectors have circuit breakers and temperature fuses to prevent serious consequences. Many also have an LED light to indicate if the MOVs are still functioning.
The joule rating is commonly quoted for comparing MOV-based surge protectors. An average surge (spike) is of short duration, lasting for nanoseconds to microseconds, and experimentally modeled surge energy can be less than 100 joules. Well-designed surge protectors consider the resistance of the lines that supply the power, the chance of lightning or other seriously energetic spike, and specify the MOVs accordingly. A little battery charger might include a MOV of only 1 watt, whereas a surge strip will have a 20 watt MOV or several of them in parallel. A house protector will have a large block-type MOV.
Some manufacturers commonly design higher joule-rated surge protectors by connecting multiple MOVs in parallel and this can produce a misleading rating. Since individual MOVs have slightly different voltage thresholds and non-linear responses when exposed to the same voltage curve, any given MOV might be more sensitive than others. This can cause one MOV in a group to conduct more (a phenomenon called current hogging), leading to possible overuse and eventual premature failure of that component. However the other MOVs in the group do help a little as they start to conduct as the voltage continues to rise as it does since a MOV does not have a sharp threshold. It may start to short at 270 volts but not reach full short until 450 or more volts. A second MOV might start at 290 volts and another at 320 volts so they all can help clamp the voltage, and at full current there is a series ballast effect that improves current sharing, but stating the actual joule rating as the sum of all the individual MOVs does not accurately reflect the total clamping ability. The first MOV may bear more of the burden and fail earlier.
One MOV manufacturer recommends using fewer but bigger MOVs (e.g. 60 mm vs 40 mm diameter) if they can fit in the device. It is further recommended that multiple smaller MOVs be matched and derated. In some cases, it may take four 40 mm MOVs to be equivalent to one 60 mm MOV.
A further problem is that if a single inline fuse is placed in series with a group of paralleled MOVs as a disconnect safety feature, it will open and disconnect all remaining working MOVs.
The ''effective'' surge energy absorption capacity of the entire system is dependent on the MOV matching so derating by 20% or more is usually required. This limitation can be managed by using carefully ''matched sets'' of MOVs, matched according to manufacturer's specification. See pp. 7–8, "Parallel Operation of Varistors".
According to industry testing standards, based on
The Joule rating number defines how much energy a MOV-based surge protector can theoretically absorb in a single event, without failure. Better protectors exceed ratings of 1,000 joules and 40,000 amperes. Since the actual duration of a spike is only about 10 microseconds, the actual dissipated energy is low. Any more than that and the MOV will fuse, or sometimes short and melt, hopefully blowing a fuse, disconnecting itself from the circuit.
The MOV (or other shorting device) requires resistance in the supply line in order to limit the voltage. For large, low resistance power lines a higher joule rated MOV is required. Inside a house, with smaller wires that have more resistance, a smaller MOV is acceptable.
Every time an MOV shorts, its internal structure is changed and its threshold voltage reduced slightly. After many spikes the threshold voltage can reduce enough to be near the line voltage, i.e. 120 vac or 240 vac. At this point, the MOV will partially conduct and heat up and eventually fail, sometimes in a dramatic meltdown or even a fire. Most modern surge protectors have circuit breakers and temperature fuses to prevent serious consequences. Many also have an LED light to indicate if the MOVs are still functioning.
The joule rating is commonly quoted for comparing MOV-based surge protectors. An average surge (spike) is of short duration, lasting for nanoseconds to microseconds, and experimentally modeled surge energy can be less than 100 joules. Well-designed surge protectors consider the resistance of the lines that supply the power, the chance of lightning or other seriously energetic spike, and specify the MOVs accordingly. A little battery charger might include a MOV of only 1 watt, whereas a surge strip will have a 20 watt MOV or several of them in parallel. A house protector will have a large block-type MOV.
Some manufacturers commonly design higher joule-rated surge protectors by connecting multiple MOVs in parallel and this can produce a misleading rating. Since individual MOVs have slightly different voltage thresholds and non-linear responses when exposed to the same voltage curve, any given MOV might be more sensitive than others. This can cause one MOV in a group to conduct more (a phenomenon called current hogging), leading to possible overuse and eventual premature failure of that component. However the other MOVs in the group do help a little as they start to conduct as the voltage continues to rise as it does since a MOV does not have a sharp threshold. It may start to short at 270 volts but not reach full short until 450 or more volts. A second MOV might start at 290 volts and another at 320 volts so they all can help clamp the voltage, and at full current there is a series ballast effect that improves current sharing, but stating the actual joule rating as the sum of all the individual MOVs does not accurately reflect the total clamping ability. The first MOV may bear more of the burden and fail earlier.
One MOV manufacturer recommends using fewer but bigger MOVs (e.g. 60 mm vs 40 mm diameter) if they can fit in the device. It is further recommended that multiple smaller MOVs be matched and derated. In some cases, it may take four 40 mm MOVs to be equivalent to one 60 mm MOV.
A further problem is that if a single inline fuse is placed in series with a group of paralleled MOVs as a disconnect safety feature, it will open and disconnect all remaining working MOVs.
The ''effective'' surge energy absorption capacity of the entire system is dependent on the MOV matching so derating by 20% or more is usually required. This limitation can be managed by using carefully ''matched sets'' of MOVs, matched according to manufacturer's specification. See pp. 7–8, "Parallel Operation of Varistors".
According to industry testing standards, based on
 Surge protectors do not operate instantly; a slight delay exists, some few nanoseconds. With longer response time and depending on system impedance, the connected equipment may be exposed to some of the surge. However, surges typically are much slower and take around a few
Surge protectors do not operate instantly; a slight delay exists, some few nanoseconds. With longer response time and depending on system impedance, the connected equipment may be exposed to some of the surge. However, surges typically are much slower and take around a few
TR-NWT-001011
*
 A metal-oxide varistor (MOV) consists of a bulk
A metal-oxide varistor (MOV) consists of a bulk
See Figures 4 & 5 for Pulse Life Curves. Every time an MOV activates, its threshold voltage reduces slightly. After many spikes the threshold voltage can reduce enough to be near the protection voltage, either mains or data. At this point the MOV conducts more and more often, heats up and finally fails. In data circuits, the data channel becomes shorted and non-functional. In a power circuit, you may get a dramatic meltdown or even a fire if not protected by a fuse of some kind.. Modern surge strips and house protectors have circuit breakers and temperature fuses to prevent serious consequences. A thermal fuse disconnects the MOV when it gets too hot. Only the MOV is disconnected leaving the rest of the circuit working but without surge protection. Often there is an LED light to indicate if the MOVs are still functioning. Older surge strips had no thermal fuse and relied on a 10 or 15 amp circuit breaker which usually blew only after the MOVs had smoked, burned, popped, melted and permanently shorted. A failing MOV is a fire risk, which is a reason for the
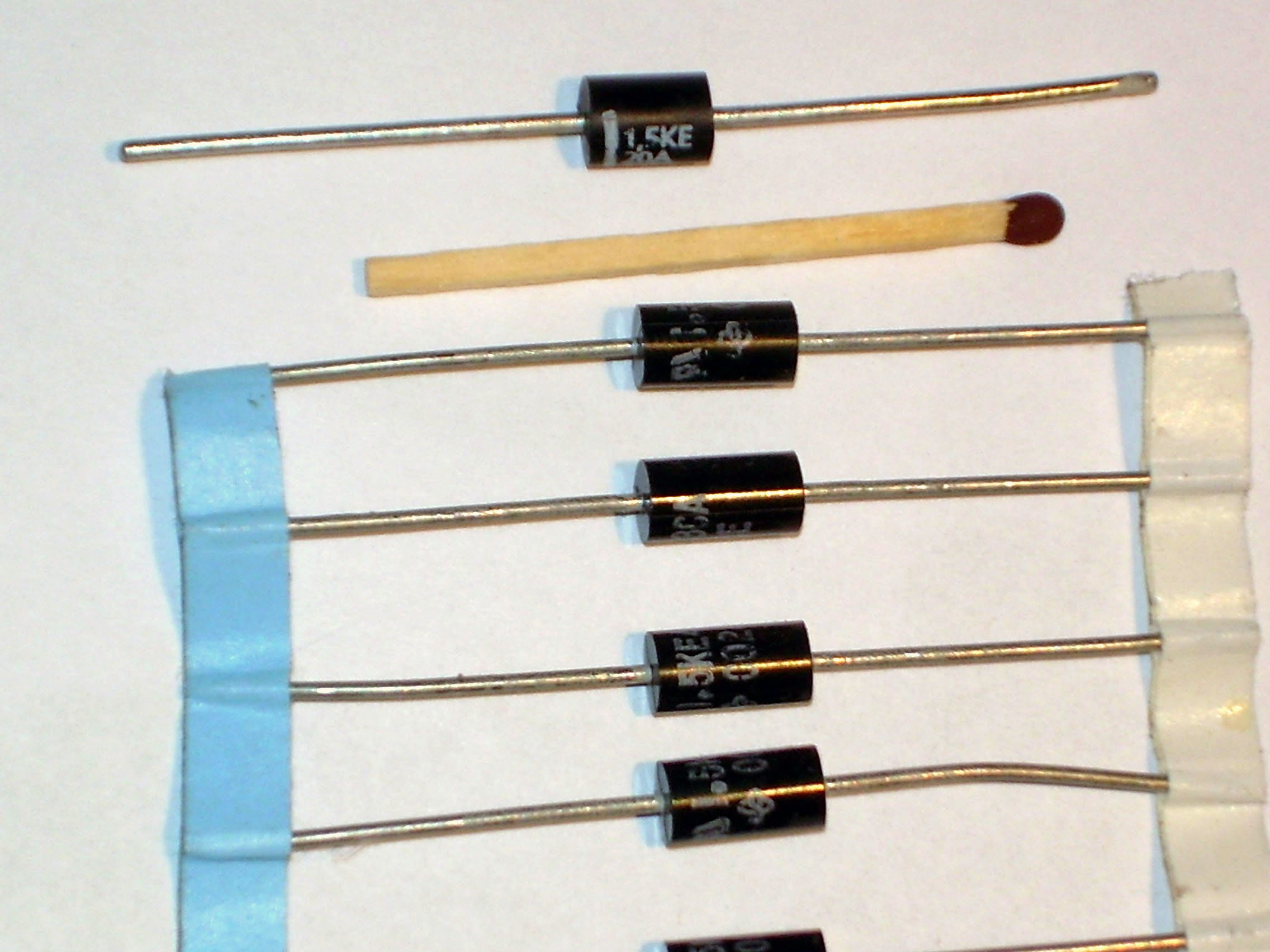 A transient-voltage-suppression diode (TVS diode) is a type of avalanche diode which can limit voltage spikes. These components provide the fastest limiting action of protective components (theoretically in picoseconds), but have a relatively low energy-absorbing capability. Voltages can be clamped to less than twice the normal operation voltage. If current impulses remain within the device ratings, life expectancy is exceptionally long. If component ratings are exceeded, the diode may fail as a permanent short circuit; protection may remain, but normal circuit operation is terminated in the case of low-power signal lines.
Due to their relatively limited current capacity, TVS diodes are often restricted to circuits with smaller current spikes. TVS diodes are also used where spikes occur significantly more often than once a year, since this type of component will not degrade when used within its ratings. A unique type of TVS diode (trade names Transzorb or Transil) contains reversed paired ''series'' avalanche diodes for bi-polar operation.
TVS diodes are often used in high-speed but low-power circuits, such as occur in data communications. These devices can be paired in ''series'' with another diode to provide low capacitance as required in communication circuits.
A transient-voltage-suppression diode (TVS diode) is a type of avalanche diode which can limit voltage spikes. These components provide the fastest limiting action of protective components (theoretically in picoseconds), but have a relatively low energy-absorbing capability. Voltages can be clamped to less than twice the normal operation voltage. If current impulses remain within the device ratings, life expectancy is exceptionally long. If component ratings are exceeded, the diode may fail as a permanent short circuit; protection may remain, but normal circuit operation is terminated in the case of low-power signal lines.
Due to their relatively limited current capacity, TVS diodes are often restricted to circuits with smaller current spikes. TVS diodes are also used where spikes occur significantly more often than once a year, since this type of component will not degrade when used within its ratings. A unique type of TVS diode (trade names Transzorb or Transil) contains reversed paired ''series'' avalanche diodes for bi-polar operation.
TVS diodes are often used in high-speed but low-power circuits, such as occur in data communications. These devices can be paired in ''series'' with another diode to provide low capacitance as required in communication circuits.
 A Trisil is a type of thyristor surge protection device (TSPD), a specialized solid-state electronic device used in crowbar circuits to protect against overvoltage conditions. A SIDACtor is another
A Trisil is a type of thyristor surge protection device (TSPD), a specialized solid-state electronic device used in crowbar circuits to protect against overvoltage conditions. A SIDACtor is another
 A gas discharge tube (GDT) is a sealed glass-enclosed device containing a special gas mixture trapped between two electrodes, which conducts electric current after becoming
A gas discharge tube (GDT) is a sealed glass-enclosed device containing a special gas mixture trapped between two electrodes, which conducts electric current after becoming
 Used in RF signal transmission paths, this technology features a tuned quarter-wavelength short-circuit stub that allows it to pass a bandwidth of frequencies, but presents a short to any other signals, especially down towards DC. The passbands can be narrowband (about ±5% to ±10% bandwidth) or wideband (above ±25% to ±50% bandwidth). Quarter-wave coax surge arrestors have coaxial terminals, compatible with common coax cable connectors (especially N or 7-16 types). They provide the most rugged available protection for RF signals above ; at these frequencies they can perform much better than the gas discharge cells typically used in the universal/broadband coax surge arrestors. Quarter-wave arrestors are useful for
Used in RF signal transmission paths, this technology features a tuned quarter-wavelength short-circuit stub that allows it to pass a bandwidth of frequencies, but presents a short to any other signals, especially down towards DC. The passbands can be narrowband (about ±5% to ±10% bandwidth) or wideband (above ±25% to ±50% bandwidth). Quarter-wave coax surge arrestors have coaxial terminals, compatible with common coax cable connectors (especially N or 7-16 types). They provide the most rugged available protection for RF signals above ; at these frequencies they can perform much better than the gas discharge cells typically used in the universal/broadband coax surge arrestors. Quarter-wave arrestors are useful for
Surge Protection in Low-Voltage AC Power Circuits: An 8-part Anthology
A comprehensive compilation of papers and articles published 1963–2003, hosted by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), an agency of the US Commerce Department
NEMA Surge Protection Institute
Important Points About Surge Protectors
Surgege Protector Tech
Intro to TVS on AllAboutCircuits''Inductive Load Arc Suppression''
{{DEFAULTSORT:Surge Protector Consumer electronics Computer peripherals Electric power systems components Voltage stability
 A surge protector, spike suppressor, surge suppressor, surge diverter, surge protection device (SPD), transient voltage suppressor (TVS) or transient voltage surge suppressor (TVSS) is an appliance or device intended to protect electrical devices in
A surge protector, spike suppressor, surge suppressor, surge diverter, surge protection device (SPD), transient voltage suppressor (TVS) or transient voltage surge suppressor (TVSS) is an appliance or device intended to protect electrical devices in alternating current
Alternating current (AC) is an electric current that periodically reverses direction and changes its magnitude continuously with time, in contrast to direct current (DC), which flows only in one direction. Alternating current is the form in w ...
(AC) circuits from voltage spike
In electrical engineering, spikes are fast, short duration electrical transients in voltage (voltage spikes), current (current spikes), or transferred energy (energy spikes) in an electrical circuit.
Fast, short duration electrical transients ...
s with very short duration measured in microsecond
A microsecond is a unit of time in the International System of Units (SI) equal to one millionth (0.000001 or 10−6 or ) of a second. Its symbol is μs, sometimes simplified to us when Unicode is not available.
A microsecond is to one second, ...
s, which can arise from a variety of causes including lightning strikes in the vicinity.
A surge protector limits the voltage
Voltage, also known as (electrical) potential difference, electric pressure, or electric tension, is the difference in electric potential between two points. In a Electrostatics, static electric field, it corresponds to the Work (electrical), ...
supplied to the electrical devices to a certain threshold by short-circuiting current to ground or absorbing the spike when a transient occurs, thus avoiding damage to the devices connected to it.
Key specifications that characterize this device are the clamping voltage, or the transient voltage at which the device starts functioning, the Joule
The joule ( , or ; symbol: J) is the unit of energy in the International System of Units (SI). In terms of SI base units, one joule corresponds to one kilogram- metre squared per second squared One joule is equal to the amount of work d ...
rating, a measure of how much energy can be absorbed per surge, and the response time.
Definitions
The terms ''surge protection device'' (''SPD'') and ''transient voltage surge suppressor'' (''TVSS'') are used to describe electrical devices typically installed in power distribution panels, process control systems, communications systems, and other heavy-duty industrial systems, for the purpose of protecting against electrical surges and spikes, including those caused bylightning
Lightning is a natural phenomenon consisting of electrostatic discharges occurring through the atmosphere between two electrically charged regions. One or both regions are within the atmosphere, with the second region sometimes occurring on ...
. Scaled-down versions of these devices are sometimes installed in residential service entrance electrical panels to protect equipment in a household from similar hazards.
Voltage spikes
In an AC circuit, avoltage spike
In electrical engineering, spikes are fast, short duration electrical transients in voltage (voltage spikes), current (current spikes), or transferred energy (energy spikes) in an electrical circuit.
Fast, short duration electrical transients ...
is a transient event, typically lasting 1 to 30 microseconds, that may reach over 1,000 volts. Lightning that hits a power line can cause a spike of thousands of volts. A motor when switched off can generate a spike of 1,000 or more volts. Spikes can degrade wiring insulation and destroy electronic devices like light bulbs, battery chargers, modems, TVs, and other consumer electronics.
Spikes can also occur on telephone and data lines when AC main lines accidentally connect to them or lightning hits them, or if the telephone and data lines travel near lines with a spike and the voltage is induced.
A long-term overvoltage surge, lasting seconds, minutes, or hours, caused by power transformer failures such as a lost neutral or other power company error, are not protected by transient protectors. Long-term surges can destroy the protectors in an entire building or area. Even tens of milliseconds can be longer than a protector can handle. Long-term surges may or may not be handled by fuses and overvoltage relays.
Surge currents
A building's wiring addselectrical impedance
In electrical engineering, impedance is the opposition to alternating current presented by the combined effect of Electrical_resistance, resistance and Electrical_reactance, reactance in a electrical circuit, circuit.
Quantitatively, the impedan ...
that limits the surge current that reaches the loads when a voltage transient arrives at the service entrance (the point where the supply company's wiring enters a property). There is less surge current at longer wire distances and where more impedance is present between the service entrance and the load.
Category A loads are more than 60 feet of wire length from the service entrance to the load. Category A loads can be exposed to and surge currents. Category B loads are between 30 and 60 feet of wire length from the service entrance to the load. Category B loads can be exposed to and . Category C loads are less than 30 feet from the service entrance to the load. Category C loads can be exposed to and .
A coiled extension cord can be used to increase the wire length to more than 60 feet and increase the impedance between the service entrance and the load.
Protectors
 A transient surge protector attempts to limit the
A transient surge protector attempts to limit the voltage
Voltage, also known as (electrical) potential difference, electric pressure, or electric tension, is the difference in electric potential between two points. In a Electrostatics, static electric field, it corresponds to the Work (electrical), ...
supplied to an electric device by either blocking or shorting
In finance, being short in an asset means investing in such a way that the investor will profit if the market value of the asset falls. This is the opposite of the more common long position, where the investor will profit if the market value ...
current to reduce the voltage below a safe threshold. Blocking is done by using inductor
An inductor, also called a coil, choke, or reactor, is a Passivity (engineering), passive two-terminal electronic component, electrical component that stores energy in a magnetic field when an electric current flows through it. An inductor typic ...
s that inhibit a sudden change in current. Shorting is done by capacitor
In electrical engineering, a capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy by accumulating electric charges on two closely spaced surfaces that are insulated from each other. The capacitor was originally known as the condenser, a term st ...
s which inhibit a sudden change in voltage or by spark gap
A spark gap consists of an arrangement of two Conductor (material), conducting electrodes separated by a gap usually filled with a gas such as air, designed to allow an electric spark to pass between the conductors. When the potential differenc ...
s, discharge tube
A gas-filled tube, also commonly known as a discharge tube or formerly as a Plücker tube, is an arrangement of electrodes in a gas within an insulating, temperature-resistant envelope. Gas-filled tubes exploit phenomena related to electri ...
s, Zener effect
In electronics, the Zener effect (employed most notably in the appropriately named Zener diode) is a type of electrical breakdown, discovered by Clarence Zener, Clarence Melvin Zener. It occurs in a p-n junction#Reverse bias, reverse biased p-n di ...
semiconductors, and metal-oxide varistors (MOVs), all of which begin to conduct current once a certain voltage threshold is reached. Some surge protectors use multiple elements.
In the shorting method, the electrical lines are temporarily shorted together (as by a spark gap) or clamped to a target voltage (as by a MOV), resulting in a large current flow. The voltage spike is reduced as the shorting current flows through the resistance in the power lines. The spike's energy is dissipated in the power lines or the ground, or in the protector, converted to heat. Since a spike lasts only tens of microseconds, the temperature rise is minimal. However, if the spike is large enough or long enough, the protector can be destroyed and power lines damaged.
Surge protectors for homes can be in power strips used inside, or a device outside at the power panel. Sockets in a modern house use three wires: line, neutral and ground. Many protectors will connect between all three in pairs (line–neutral, line–ground and neutral–ground), because there are conditions, such as lightning, where both line and neutral have high voltage spikes that need to be shorted to ground.
Additionally, some consumer-grade protectors have ports for Ethernet
Ethernet ( ) is a family of wired computer networking technologies commonly used in local area networks (LAN), metropolitan area networks (MAN) and wide area networks (WAN). It was commercially introduced in 1980 and first standardized in 198 ...
, cable television
Cable television is a system of delivering television programming to consumers via radio frequency (RF) signals transmitted through coaxial cables, or in more recent systems, light pulses through fibre-optic cables. This contrasts with bro ...
and plain old telephone service
Plain old telephone service (POTS), or publicly offered telephone service, is basic Voice band, voice-grade telephone service. Historically, POTS has been delivered by Analog signal, analog signal transmission over copper loops, but the term also d ...
, and plugging them in allows the surge protector to shield them from external electrical damage.
The characteristic of a TVS requires that it respond to overvoltages faster than other common overvoltage protection components such as varistors or gas discharge tubes. This makes TVS devices or components useful for protection against very fast and often damaging voltage spike
In electrical engineering, spikes are fast, short duration electrical transients in voltage (voltage spikes), current (current spikes), or transferred energy (energy spikes) in an electrical circuit.
Fast, short duration electrical transients ...
s. These fast overvoltage spikes are present on all distribution networks and can be caused by either internal or external events, such as lightning
Lightning is a natural phenomenon consisting of electrostatic discharges occurring through the atmosphere between two electrically charged regions. One or both regions are within the atmosphere, with the second region sometimes occurring on ...
or motor arcing.
Applications of transient voltage suppression diodes are used for unidirectional or bidirectional electrostatic discharge
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) is a sudden and momentary flow of electric current between two differently-charged objects when brought close together or when the dielectric between them breaks down, often creating a visible electric spark, spark as ...
protection of transmission or data lines in electronic circuits. MOV-based TVSs are used to protect home electronics and distribution systems and may accommodate industrial-level power distribution disturbances, saving downtime and damage to equipment. The level of energy in a transient overvoltage can be equated to energy measured in joule
The joule ( , or ; symbol: J) is the unit of energy in the International System of Units (SI). In terms of SI base units, one joule corresponds to one kilogram- metre squared per second squared One joule is equal to the amount of work d ...
s or related to electric current
An electric current is a flow of charged particles, such as electrons or ions, moving through an electrical conductor or space. It is defined as the net rate of flow of electric charge through a surface. The moving particles are called charge c ...
when devices are rated for various applications. These bursts of overvoltage can be measured with specialized electronic meters that can show power disturbances of thousands of volts amplitude that last for a few microseconds or less.
It is possible for a MOV to overheat when exposed to overvoltage sufficient for the MOV to start conducting, but not enough to totally destroy it, or to blow a house fuse. If the overvoltage condition persists long enough to cause significant heating of the MOV, it can result in thermal damage to the device and potentially start a fire.
Comparison of transient suppressors
Domestic use
Many power strips have basic surge protection built in; these are typically clearly labeled as such. However, in countries without regulations, there are power strips labeled as "surge" or "spike" protectors that only have a capacitor, an RFI circuit, or nothing at all and do ''not'' provide surge protection.Industrial use

 A surge arrester, surge protection device (SPD) or transient voltage surge suppressor (TVSS), is used to protect equipment in
A surge arrester, surge protection device (SPD) or transient voltage surge suppressor (TVSS), is used to protect equipment in power transmission
Power transmission is the movement of energy from its place of generation to a location where it is applied to perform useful Mechanical work, work.
Power (physics), Power is defined formally as units of energy per unit time. In SI units:
:\text ...
and distribution Distribution may refer to:
Mathematics
*Distribution (mathematics), generalized functions used to formulate solutions of partial differential equations
*Probability distribution, the probability of a particular value or value range of a varia ...
systems. The energy criterion for various insulation materials can be compared by impulse ratio. A surge arrester should have a low impulse ratio so that a surge incident on the surge arrester may be bypassed to the ground instead of passing through the apparatus.
To protect a unit of equipment from transients occurring on an attached conductor, a surge arrester is connected to the conductor just before it enters the equipment. The surge arrester is also connected to ground and functions by routing energy from an over-voltage transient to ground if one occurs, while isolating the conductor from ground at normal operating voltages. This is usually achieved through use of a varistor, which has substantially different resistances at different voltages.
Surge arresters are not generally designed to protect against a direct lightning strike
A lightning strike or lightning bolt is a lightning event in which an electric discharge takes place between the atmosphere and the ground. Most originate in a cumulonimbus cloud and terminate on the ground, called cloud-to-ground (CG) lightning ...
to a conductor, but rather against electrical transients resulting from lightning strikes occurring in the vicinity of the conductor. Lightning striking the earth produces ground currents that can pass over buried conductors and induce a transient that propagates outward towards the ends of the conductor. The same kind of induction happens in overhead and above-ground conductors, which experience the passing energy of an atmospheric electromagnetic pulse
An electromagnetic pulse (EMP), also referred to as a transient electromagnetic disturbance (TED), is a brief burst of electromagnetic energy. The origin of an EMP can be natural or artificial, and can occur as an electromagnetic field, as an ...
caused by the lightning flash.
Surge arresters can only protect against induced transients characteristic of a lightning discharge's rapid rise-time, and will not protect against electrification caused by a direct strike to the conductor. Transients similar to lightning-induced, such as from a high voltage system's fault switching, may also be safely diverted to ground; however, continuous overcurrents are not protected against by these devices. The energy in a handled transient is substantially less than that of a lightning discharge; however, it is still of sufficient quantity to cause equipment damage and often requires protection.
Without very thick insulation, which is generally cost prohibitive, most conductors running more than approximately will experience lightning-induced transients at some time during use. Because the transient is usually initiated at some point between the two ends of the conductor, most applications install a surge arrester at each end just before the conductor lands in each piece of equipment to be protected. Each conductor must be protected, as each will have its own transient induced, and each SPD must provide a pathway to earth to safely divert the transient away from the protected component.
The one notable exception where they are not installed at both ends is in high-voltage distribution systems. In general, the induced voltage is not sufficient to do damage at the electric generation end of the lines; however, installation at the service entrance to a building is key to protecting downstream products that are not as robust.
Types
*Low-voltage surge arrester: Apply in Low-voltage distribution system, exchange of electrical appliances protector, low-voltage distribution transformer windings *Distribution arrester: Apply in 3, 6 and 10 kV AC power distribution systems to protect distribution transformers, cables and power station equipment *The station type of common valve arrester: Used to protect the 3 ~ 220 kV transformer station equipment and communication systems *Magnetic blow valve station arrester: Used to protect the 35 ~ 500 kV communication systems, transformers and other equipment *Protection of rotating machine using magnetic blow valve arrester: Used to protect the AC generator and motor insulation *Line Magnetic blow valve arrester: Used to protect 330 kV and above communication systems and circuit equipment insulation *DC or blowing valve-type arrester: Use to protect the DC system's insulation of electrical equipment *Neutral protection arrester: Apply in motor or the transformer's neutral protection *Fiber-tube arrester: Apply in the power station's wires *Plug-in signal arrester: Used on twisted-pair transmission lines to protect communications and computer systems *High-frequency feeder arrester: Used to protect the microwave, mobile base stations, satellite receiver, etc. *Receptacle-type surge arrester: Use to Protect the terminal Electronic equipment *Signal arrester: Applies to modem, DDN line, fax, phone, process control signal circuit, etc. *Network arrester: Apply in servers, workstations, interfaces, etc. *Coaxial cable lightning arrester: Used on the coaxial cable to protect the wireless transmission and receiving systemImportant specifications
 These are some of the most prominently featured specifications which define a surge protector for AC mains, as well as for some data communications protection applications.
These are some of the most prominently featured specifications which define a surge protector for AC mains, as well as for some data communications protection applications.
Clamping voltage
Also known as the let-through voltage, this specifies what spike voltage will cause the protective components inside a surge protector to short or clamp. A lower clamping voltage indicates better protection, but can sometimes result in a shorter life expectancy for the overall protective system. The lowest three levels of protection defined in the UL rating are 330 V, 400 V and 500 V. The standard let-through voltage for 120 V AC devices is 330 volts.Underwriters Laboratories
The UL enterprise is a global private safety company headquartered in Northbrook, Illinois, composed of three organizations, UL Research Institutes, UL Standards & Engagement and UL Solutions.
Established in 1894, the UL enterprise was founded a ...
(UL), a global independent safety science company, defines how a protector may be used safely. UL 1449 became compliance mandatory in jurisdictions that adopted the NEC with the 3rd edition in September 2009 to increase safety compared to products conforming to the 2nd edition. A measured limiting voltage test, using six times higher current (and energy), defines a voltage protection rating (VPR). For a specific protector, this voltage may be higher compared to a Suppressed Voltage Ratings (SVR) in previous editions that measured let-through voltage with less current. Due to non-linear characteristics of protectors, let-through voltages defined by 2nd edition and 3rd edition testing are not comparable.
A protector may be larger to obtain a same let-through voltage during 3rd edition testing. Therefore, a 3rd edition or later protector should provide superior safety with increased life expectancy.
A protector with a higher let-through voltage, e.g. 400 V vs 330 V, will pass a higher voltage to the connected device. The design of the connected device determines whether this pass-through spike will cause damage. Motors and mechanical devices are usually not affected. Some (especially older) electronic parts, like chargers, LED or CFL bulbs and computerized appliances are sensitive and can be compromised and have their life reduced.
Joule rating

 The Joule rating number defines how much energy a MOV-based surge protector can theoretically absorb in a single event, without failure. Better protectors exceed ratings of 1,000 joules and 40,000 amperes. Since the actual duration of a spike is only about 10 microseconds, the actual dissipated energy is low. Any more than that and the MOV will fuse, or sometimes short and melt, hopefully blowing a fuse, disconnecting itself from the circuit.
The MOV (or other shorting device) requires resistance in the supply line in order to limit the voltage. For large, low resistance power lines a higher joule rated MOV is required. Inside a house, with smaller wires that have more resistance, a smaller MOV is acceptable.
Every time an MOV shorts, its internal structure is changed and its threshold voltage reduced slightly. After many spikes the threshold voltage can reduce enough to be near the line voltage, i.e. 120 vac or 240 vac. At this point, the MOV will partially conduct and heat up and eventually fail, sometimes in a dramatic meltdown or even a fire. Most modern surge protectors have circuit breakers and temperature fuses to prevent serious consequences. Many also have an LED light to indicate if the MOVs are still functioning.
The joule rating is commonly quoted for comparing MOV-based surge protectors. An average surge (spike) is of short duration, lasting for nanoseconds to microseconds, and experimentally modeled surge energy can be less than 100 joules. Well-designed surge protectors consider the resistance of the lines that supply the power, the chance of lightning or other seriously energetic spike, and specify the MOVs accordingly. A little battery charger might include a MOV of only 1 watt, whereas a surge strip will have a 20 watt MOV or several of them in parallel. A house protector will have a large block-type MOV.
Some manufacturers commonly design higher joule-rated surge protectors by connecting multiple MOVs in parallel and this can produce a misleading rating. Since individual MOVs have slightly different voltage thresholds and non-linear responses when exposed to the same voltage curve, any given MOV might be more sensitive than others. This can cause one MOV in a group to conduct more (a phenomenon called current hogging), leading to possible overuse and eventual premature failure of that component. However the other MOVs in the group do help a little as they start to conduct as the voltage continues to rise as it does since a MOV does not have a sharp threshold. It may start to short at 270 volts but not reach full short until 450 or more volts. A second MOV might start at 290 volts and another at 320 volts so they all can help clamp the voltage, and at full current there is a series ballast effect that improves current sharing, but stating the actual joule rating as the sum of all the individual MOVs does not accurately reflect the total clamping ability. The first MOV may bear more of the burden and fail earlier.
One MOV manufacturer recommends using fewer but bigger MOVs (e.g. 60 mm vs 40 mm diameter) if they can fit in the device. It is further recommended that multiple smaller MOVs be matched and derated. In some cases, it may take four 40 mm MOVs to be equivalent to one 60 mm MOV.
A further problem is that if a single inline fuse is placed in series with a group of paralleled MOVs as a disconnect safety feature, it will open and disconnect all remaining working MOVs.
The ''effective'' surge energy absorption capacity of the entire system is dependent on the MOV matching so derating by 20% or more is usually required. This limitation can be managed by using carefully ''matched sets'' of MOVs, matched according to manufacturer's specification. See pp. 7–8, "Parallel Operation of Varistors".
According to industry testing standards, based on
The Joule rating number defines how much energy a MOV-based surge protector can theoretically absorb in a single event, without failure. Better protectors exceed ratings of 1,000 joules and 40,000 amperes. Since the actual duration of a spike is only about 10 microseconds, the actual dissipated energy is low. Any more than that and the MOV will fuse, or sometimes short and melt, hopefully blowing a fuse, disconnecting itself from the circuit.
The MOV (or other shorting device) requires resistance in the supply line in order to limit the voltage. For large, low resistance power lines a higher joule rated MOV is required. Inside a house, with smaller wires that have more resistance, a smaller MOV is acceptable.
Every time an MOV shorts, its internal structure is changed and its threshold voltage reduced slightly. After many spikes the threshold voltage can reduce enough to be near the line voltage, i.e. 120 vac or 240 vac. At this point, the MOV will partially conduct and heat up and eventually fail, sometimes in a dramatic meltdown or even a fire. Most modern surge protectors have circuit breakers and temperature fuses to prevent serious consequences. Many also have an LED light to indicate if the MOVs are still functioning.
The joule rating is commonly quoted for comparing MOV-based surge protectors. An average surge (spike) is of short duration, lasting for nanoseconds to microseconds, and experimentally modeled surge energy can be less than 100 joules. Well-designed surge protectors consider the resistance of the lines that supply the power, the chance of lightning or other seriously energetic spike, and specify the MOVs accordingly. A little battery charger might include a MOV of only 1 watt, whereas a surge strip will have a 20 watt MOV or several of them in parallel. A house protector will have a large block-type MOV.
Some manufacturers commonly design higher joule-rated surge protectors by connecting multiple MOVs in parallel and this can produce a misleading rating. Since individual MOVs have slightly different voltage thresholds and non-linear responses when exposed to the same voltage curve, any given MOV might be more sensitive than others. This can cause one MOV in a group to conduct more (a phenomenon called current hogging), leading to possible overuse and eventual premature failure of that component. However the other MOVs in the group do help a little as they start to conduct as the voltage continues to rise as it does since a MOV does not have a sharp threshold. It may start to short at 270 volts but not reach full short until 450 or more volts. A second MOV might start at 290 volts and another at 320 volts so they all can help clamp the voltage, and at full current there is a series ballast effect that improves current sharing, but stating the actual joule rating as the sum of all the individual MOVs does not accurately reflect the total clamping ability. The first MOV may bear more of the burden and fail earlier.
One MOV manufacturer recommends using fewer but bigger MOVs (e.g. 60 mm vs 40 mm diameter) if they can fit in the device. It is further recommended that multiple smaller MOVs be matched and derated. In some cases, it may take four 40 mm MOVs to be equivalent to one 60 mm MOV.
A further problem is that if a single inline fuse is placed in series with a group of paralleled MOVs as a disconnect safety feature, it will open and disconnect all remaining working MOVs.
The ''effective'' surge energy absorption capacity of the entire system is dependent on the MOV matching so derating by 20% or more is usually required. This limitation can be managed by using carefully ''matched sets'' of MOVs, matched according to manufacturer's specification. See pp. 7–8, "Parallel Operation of Varistors".
According to industry testing standards, based on IEEE
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) is an American 501(c)(3) organization, 501(c)(3) public charity professional organization for electrical engineering, electronics engineering, and other related disciplines.
The IEEE ...
and ANSI
The American National Standards Institute (ANSI ) is a private nonprofit organization that oversees the development of voluntary consensus standards for products, services, processes, systems, and personnel in the United States. The organiz ...
assumptions, power line surges inside a building can be up to 6,000 volts and 3,000 amperes, and deliver up to 90 joules of energy, including surges from external sources not including lightning strikes.
The common assumptions regarding lightning specifically, based ANSI/IEEE C62.41 and UL 1449 (3rd ed.) at time of this writing, are that minimum lightning-based power line surges inside a building are typically 10,000 amperes or 10 kiloamperes (kA). This is based on 20 kA striking a power line, the imparted current then traveling equally in both directions on the power line with the resulting 10 kA traveling into the building or home. These assumptions are based on an average approximation for testing minimum standards. While 10 kA is typically good enough for minimum protection against lightning strikes, it is possible for a lightning strike to impart up to 200 kA to a power line with 100 kA traveling in each direction.
Lightning and other high-energy transient voltage surges can be suppressed with pole-mounted suppressors by the utility, or with an owner-supplied whole-house surge protector. A whole-house product is more expensive than simple single-outlet surge protectors and often needs professional installation on the incoming electrical power feed; however, they prevent power line spikes from entering the house. Damage from direct lightning strikes via other paths, such as telephone lines, must be controlled separately.
Response time
 Surge protectors do not operate instantly; a slight delay exists, some few nanoseconds. With longer response time and depending on system impedance, the connected equipment may be exposed to some of the surge. However, surges typically are much slower and take around a few
Surge protectors do not operate instantly; a slight delay exists, some few nanoseconds. With longer response time and depending on system impedance, the connected equipment may be exposed to some of the surge. However, surges typically are much slower and take around a few microsecond
A microsecond is a unit of time in the International System of Units (SI) equal to one millionth (0.000001 or 10−6 or ) of a second. Its symbol is μs, sometimes simplified to us when Unicode is not available.
A microsecond is to one second, ...
s to reach their peak voltage, and a surge protector with a nanosecond
A nanosecond (ns) is a unit of time in the International System of Units (SI) equal to one billionth of a second, that is, of a second, or seconds.
The term combines the SI prefix ''nano-'' indicating a 1 billionth submultiple of an SI unit (e ...
response time would kick in fast enough to suppress the most damaging portion of the spike.
Thus response time under standard testing is not a useful measure of a surge protector's ability when comparing MOV devices. All MOVs have response times measured in nanoseconds, while test waveforms usually used to design and calibrate surge protectors are all based on modeled waveforms of surges measured in microseconds. As a result, MOV-based protectors have no trouble producing impressive response-time specs.
Slower-responding technologies (notably, GDTs) may have difficulty protecting against fast spikes. Therefore, good designs incorporating slower but otherwise useful technologies usually combine them with faster-acting components, to provide more comprehensive protection.
Standards
Some frequently listed standards include: * IEC 61643-11 Low-voltage surge protective devices – Part 11: Surge protective devices connected to low-voltage power systems – Requirements and test methods (replaces IEC 61643-1) * IEC 61643-21 Low voltage surge protective devices – Part 21: Surge protective devices connected to telecommunications and signalling networks – Performance requirements and testing methods * IEC 61643-22 Low-voltage surge protective devices – Part 22: Surge protective devices connected to telecommunications and signalling networks – Selection and application principles * EN , 61643-21 and * Telcordia Technologies Technical ReferencTR-NWT-001011
*
ANSI
The American National Standards Institute (ANSI ) is a private nonprofit organization that oversees the development of voluntary consensus standards for products, services, processes, systems, and personnel in the United States. The organiz ...
/IEEE
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) is an American 501(c)(3) organization, 501(c)(3) public charity professional organization for electrical engineering, electronics engineering, and other related disciplines.
The IEEE ...
C62.xx
* Underwriters Laboratories
The UL enterprise is a global private safety company headquartered in Northbrook, Illinois, composed of three organizations, UL Research Institutes, UL Standards & Engagement and UL Solutions.
Established in 1894, the UL enterprise was founded a ...
(UL) 1449
* AS/NZS 1768
Each standard defines different protector characteristics, test vectors, or operational purpose.
The 3rd Edition of UL Standard 1449 for SPDs was a major rewrite of previous editions, and was also accepted as an ANSI standard for the first time. A subsequent revision in 2015 included the addition of low-voltage circuits for USB
Universal Serial Bus (USB) is an industry standard, developed by USB Implementers Forum (USB-IF), for digital data transmission and power delivery between many types of electronics. It specifies the architecture, in particular the physical ...
charging ports and associated batteries.
EN 62305 and ANSI/IEEE C62.xx define what spikes a protector might be expected to divert. EN 61643-11 and 61643-21 specify both the product's performance and safety requirements. In contrast, the IEC only writes standards and does not certify any particular product as meeting those standards. IEC Standards are used by members of the CB Scheme of international agreements to test and certify products for safety compliance.
None of those standards guarantee that a protector will provide proper protection in a given application. Each standard defines what a protector should do or might accomplish, based on standardized tests that may or may not correlate to conditions present in a particular real-world situation. A specialized engineering analysis may be needed to provide sufficient protection, especially in situations of high lightning
Lightning is a natural phenomenon consisting of electrostatic discharges occurring through the atmosphere between two electrically charged regions. One or both regions are within the atmosphere, with the second region sometimes occurring on ...
risk.
In addition, the following standards are not standards for standalone surge protectors, but are instead meant for testing surge immunity in electrical and electronic equipment as a whole. Thus, they're frequently used in the design and test of surge protection circuitry.
* IEC 61000-4-2 Electrostatic discharge immunity test
* IEC 61000-4-4 Electrical fast transient/burst immunity test
* IEC 61000-4-5 Surge immunity test
Primary components
Systems used to reduce or limit high-voltage surges can include one or more of the following types ofelectronic component
An electronic component is any basic discrete electronic device or physical entity part of an electronic system used to affect electrons or their associated fields. Electronic components are mostly industrial products, available in a singula ...
s. Some surge suppression systems use multiple technologies, since each method has its strong and weak points. Includes extensive comparison of design tradeoffs among various surge suppression technologies. Connection of MOVs and GDTs in series. The first six methods listed operate primarily by diverting unwanted surge energy away from the protected load, through a protective component connected in a ''parallel'' (or shunted) topology. The last two methods also block unwanted energy by using a protective component connected in ''series'' with the power feed to the protected load, and additionally may shunt the unwanted energy like the earlier systems.
Metal oxide varistor
 A metal-oxide varistor (MOV) consists of a bulk
A metal-oxide varistor (MOV) consists of a bulk semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity between that of a conductor and an insulator. Its conductivity can be modified by adding impurities (" doping") to its crystal structure. When two regions with different doping level ...
material (typically sintered
Sintering or frittage is the process of compacting and forming a solid mass of material by pressure or heat without melting it to the point of liquefaction. Sintering happens as part of a manufacturing process used with metals, ceramics, pla ...
granular zinc oxide
Zinc oxide is an inorganic compound with the Chemical formula, formula . It is a white powder which is insoluble in water. ZnO is used as an additive in numerous materials and products including cosmetics, Zinc metabolism, food supplements, rubbe ...
) that can conduct large currents when presented with a voltage above its rated voltage. MOVs typically limit voltages to about 3 to 4 times the normal circuit voltage by diverting surge current elsewhere than the protected load. MOVs may be connected in parallel to increase current capability and life expectancy, providing they are ''matched sets''.
MOVs have finite life expectancy and degrade when exposed to a few large transients, or many small transients.Walaszczyk, et al. 2001 "Does Size Really Matter? An Exploration of ... Paralleling Multiple Lower Energy Movs".See Figures 4 & 5 for Pulse Life Curves. Every time an MOV activates, its threshold voltage reduces slightly. After many spikes the threshold voltage can reduce enough to be near the protection voltage, either mains or data. At this point the MOV conducts more and more often, heats up and finally fails. In data circuits, the data channel becomes shorted and non-functional. In a power circuit, you may get a dramatic meltdown or even a fire if not protected by a fuse of some kind.. Modern surge strips and house protectors have circuit breakers and temperature fuses to prevent serious consequences. A thermal fuse disconnects the MOV when it gets too hot. Only the MOV is disconnected leaving the rest of the circuit working but without surge protection. Often there is an LED light to indicate if the MOVs are still functioning. Older surge strips had no thermal fuse and relied on a 10 or 15 amp circuit breaker which usually blew only after the MOVs had smoked, burned, popped, melted and permanently shorted. A failing MOV is a fire risk, which is a reason for the
National Fire Protection Association
The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) is a U.S.-based international nonprofit organization devoted to eliminating death, injury, property damage, and economic loss due to fire, electrical, and related hazards. , the NFPA claims to have 5 ...
's (NFPA's) UL1449 standard in 1986< and subsequent revisions in 1998, 2009 and 2015. NFPA's primary concern is protection from fire.
Therefore, all MOV-based protectors intended for long-term use should have an indicator that the protective components have failed, and this indication must be checked on a regular basis to ensure that protection is still functioning.
Because of their good price–performance ratio
In economics, engineering, business management and marketing the price–performance ratio is often written as cost–performance, cost–benefit or capability/price (C/P), refers to a product's ability to deliver performance, of any sort, for i ...
, MOVs are the most common protector component in low-cost basic AC power protectors.
Transient voltage suppression diode
 A transient-voltage-suppression diode (TVS diode) is a type of avalanche diode which can limit voltage spikes. These components provide the fastest limiting action of protective components (theoretically in picoseconds), but have a relatively low energy-absorbing capability. Voltages can be clamped to less than twice the normal operation voltage. If current impulses remain within the device ratings, life expectancy is exceptionally long. If component ratings are exceeded, the diode may fail as a permanent short circuit; protection may remain, but normal circuit operation is terminated in the case of low-power signal lines.
Due to their relatively limited current capacity, TVS diodes are often restricted to circuits with smaller current spikes. TVS diodes are also used where spikes occur significantly more often than once a year, since this type of component will not degrade when used within its ratings. A unique type of TVS diode (trade names Transzorb or Transil) contains reversed paired ''series'' avalanche diodes for bi-polar operation.
TVS diodes are often used in high-speed but low-power circuits, such as occur in data communications. These devices can be paired in ''series'' with another diode to provide low capacitance as required in communication circuits.
A transient-voltage-suppression diode (TVS diode) is a type of avalanche diode which can limit voltage spikes. These components provide the fastest limiting action of protective components (theoretically in picoseconds), but have a relatively low energy-absorbing capability. Voltages can be clamped to less than twice the normal operation voltage. If current impulses remain within the device ratings, life expectancy is exceptionally long. If component ratings are exceeded, the diode may fail as a permanent short circuit; protection may remain, but normal circuit operation is terminated in the case of low-power signal lines.
Due to their relatively limited current capacity, TVS diodes are often restricted to circuits with smaller current spikes. TVS diodes are also used where spikes occur significantly more often than once a year, since this type of component will not degrade when used within its ratings. A unique type of TVS diode (trade names Transzorb or Transil) contains reversed paired ''series'' avalanche diodes for bi-polar operation.
TVS diodes are often used in high-speed but low-power circuits, such as occur in data communications. These devices can be paired in ''series'' with another diode to provide low capacitance as required in communication circuits.
Thyristor surge protection device (TSPD)
 A Trisil is a type of thyristor surge protection device (TSPD), a specialized solid-state electronic device used in crowbar circuits to protect against overvoltage conditions. A SIDACtor is another
A Trisil is a type of thyristor surge protection device (TSPD), a specialized solid-state electronic device used in crowbar circuits to protect against overvoltage conditions. A SIDACtor is another thyristor
A thyristor (, from a combination of Greek language ''θύρα'', meaning "door" or "valve", and ''transistor'' ) is a solid-state semiconductor device which can be thought of as being a highly robust and switchable diode, allowing the passage ...
type device used for similar protective purposes.
These thyristor-family devices can be viewed as having characteristics much like a spark gap
A spark gap consists of an arrangement of two Conductor (material), conducting electrodes separated by a gap usually filled with a gas such as air, designed to allow an electric spark to pass between the conductors. When the potential differenc ...
or a GDT, but can operate much faster. They are related to TVS diodes, but can "break over" to a low clamping voltage analogous to an ionized and conducting spark gap. After triggering, the low clamping voltage allows large current surges while limiting heat dissipation in the device.
Gas discharge tube (GDT) spark gap
 A gas discharge tube (GDT) is a sealed glass-enclosed device containing a special gas mixture trapped between two electrodes, which conducts electric current after becoming
A gas discharge tube (GDT) is a sealed glass-enclosed device containing a special gas mixture trapped between two electrodes, which conducts electric current after becoming ionized
Ionization or ionisation is the process by which an atom or a molecule acquires a negative or positive charge by gaining or losing electrons, often in conjunction with other chemical changes. The resulting electrically charged atom or molecule i ...
by a high voltage spike. GDTs can conduct more current for their physical size than other components. Like MOVs, GDTs have a finite life expectancy, and can handle a few very large transients or a greater number of smaller transients. The typical failure mode occurs when the triggering voltage rises so high that the device becomes ineffective, although lightning surges can occasionally cause a dead short.
GDTs take a relatively long time to trigger (longer than a lightning
Lightning is a natural phenomenon consisting of electrostatic discharges occurring through the atmosphere between two electrically charged regions. One or both regions are within the atmosphere, with the second region sometimes occurring on ...
strike of 60 ns to 70 ns), permitting a higher voltage spike to pass through briefly before the GDT conducts significant current. It is not uncommon for a GDT to let through pulses of 500 V or more of 100 ns in duration.
In some cases, additional protective components are necessary to prevent damage to a protected load, caused by high-speed let-through voltage which occurs before the GDT begins to operate. The triggering voltages are typically 400–600 volts for gas tubes and those that are UL Standard 497 listed typically have high surge current ratings, 5,000 to 10,000 amperes (8x20 μs).
GDTs create an effective short circuit when triggered, so that if any electrical energy (spike, signal, or power) is present, the GDT will short. Once triggered, a GDT will continue conducting (called follow-on current), until all electric current sufficiently diminishes, and the gas discharge quenches. Unlike other shunt protector devices, a GDT once triggered will continue to conduct at a voltage ''less than'' the high voltage that initially ionized the gas; this behavior is called negative resistance.
Additional auxiliary circuitry may be needed in DC (and some AC) applications to suppress follow-on current, to prevent this from destroying the GDT after the initiating spike has dissipated. Some GDTs are designed to deliberately short out to a grounded terminal when overheated, thereby triggering an external fuse or circuit breaker.
Many GDTs are light-sensitive, in that exposure to light lowers their triggering voltage. Therefore, GDTs should be shielded from light exposure, or opaque versions that are insensitive to light should be used.
The CG2 SN series of surge arrestors, formerly produced by C P Clare, are advertised as being non-radioactive, and the datasheet for that series states that some members of the CG/CG2 series (75–470V) are inherently radioactive
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is conside ...
.
Due to their exceptionally low capacitance, GDTs are commonly used on high-frequency lines, such as those used in telecommunications equipment. Because of their high current-handling capability, GDTs can also be used to protect power lines, but the follow-on current problem must be controlled.
Selenium voltage suppressor
An "overvoltage clamping" bulk semiconductor similar to an MOV, though it does not clamp as well. However, it usually has a longer life than an MOV. It is used mostly in high-energy DC circuits, like the exciter field of analternator
An alternator (or synchronous generator) is an electrical generator that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy in the form of alternating current. For reasons of cost and simplicity, most alternators use a rotating magnetic field wit ...
. It can dissipate power continuously, and it retains its clamping characteristics throughout the surge event, if properly sized.
Carbon block spark gap overvoltage suppressor
Aspark gap
A spark gap consists of an arrangement of two Conductor (material), conducting electrodes separated by a gap usually filled with a gas such as air, designed to allow an electric spark to pass between the conductors. When the potential differenc ...
is one of the oldest protective electrical technologies still found in telephone circuits, having been developed in the nineteenth century. A carbon rod electrode is held with an insulator at a specific distance from a second electrode. The gap dimension determines the voltage at which a spark will jump between the two parts and short to ground. The typical spacing for telephone applications in North America is (0.003 inches). Carbon block suppressors are similar to gas arrestors (GDTs); but as the two electrodes are exposed to the air, their behavior is affected by the surrounding atmosphere, especially higher humidity
Humidity is the concentration of water vapor present in the air. Water vapor, the gaseous state of water, is generally invisible to the human eye. Humidity indicates the likelihood for precipitation (meteorology), precipitation, dew, or fog t ...
. Since their operation produces an open spark, these devices should ''never'' be installed where an explosive atmosphere may develop.
Inductors, line reactors, chokes, capacitors
Inductors, line reactors, chokes, and capacitors are used to limit fault currents and can reduce or prevent overvoltage events. In applications that limit fault currents, inductors are more commonly known as electrical line reactors or a choke. Line reactors can prevent overvoltage trips, increase the reliability and life of solid state devices, and reduce nuisance trips.Marshalling cabinet panels with surge protectors
Metal marshalling cabinet panels can allow surge protection device (SPD) failures to be contained remotely from digital devices and electrical controllers. Direct flashes of lightning and lightning surge on secondary systems can cause catastrophic failures of SPDs. Catastrophic failures of SPDs can release fireballs of metal fragments and clouds of conductive carbon soot. Marshalling panels keep such hazards from reaching the digital and control devices that are mounted in the remote main control panels. Marshalling cabinet panels are used for digital system panels (fire alarm, security access control, computer clean power, etc.). Wiring and cables to be protected include both the power supply and any wiring (signaling circuit, initiating device circuit, shields, etc.), which extend beyond the building by underground, overhead or other means, such as walkways, bridges, etc. In addition, it should include the wiring of devices located in high places such as attics, roof levels of parking lots, parking lights, etc. After passing through the SPDs in the marshalling cabinets, the wiring can pass through conduits into other remote, nearly adjacent, cabinets that contain the input & output connections to for digital system panels (fire alarm, security access control, computer clean power,programmable logic controller
A programmable logic controller (PLC) or programmable controller is an industrial computer that has been ruggedized and adapted for the control of manufacturing processes, such as assembly lines, machines, robotic devices, or any activity that ...
s (PLCs), etc.
Quarter-wave coaxial surge arrestor
 Used in RF signal transmission paths, this technology features a tuned quarter-wavelength short-circuit stub that allows it to pass a bandwidth of frequencies, but presents a short to any other signals, especially down towards DC. The passbands can be narrowband (about ±5% to ±10% bandwidth) or wideband (above ±25% to ±50% bandwidth). Quarter-wave coax surge arrestors have coaxial terminals, compatible with common coax cable connectors (especially N or 7-16 types). They provide the most rugged available protection for RF signals above ; at these frequencies they can perform much better than the gas discharge cells typically used in the universal/broadband coax surge arrestors. Quarter-wave arrestors are useful for
Used in RF signal transmission paths, this technology features a tuned quarter-wavelength short-circuit stub that allows it to pass a bandwidth of frequencies, but presents a short to any other signals, especially down towards DC. The passbands can be narrowband (about ±5% to ±10% bandwidth) or wideband (above ±25% to ±50% bandwidth). Quarter-wave coax surge arrestors have coaxial terminals, compatible with common coax cable connectors (especially N or 7-16 types). They provide the most rugged available protection for RF signals above ; at these frequencies they can perform much better than the gas discharge cells typically used in the universal/broadband coax surge arrestors. Quarter-wave arrestors are useful for telecommunications
Telecommunication, often used in its plural form or abbreviated as telecom, is the transmission of information over a distance using electronic means, typically through cables, radio waves, or other communication technologies. These means of ...
applications, such as Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi () is a family of wireless network protocols based on the IEEE 802.11 family of standards, which are commonly used for Wireless LAN, local area networking of devices and Internet access, allowing nearby digital devices to exchange data by ...
at 2.4 or but less useful for TV/ CATV frequencies. Since a quarter-wave arrestor shorts out the line for low frequencies, it is not compatible with systems which send DC power for a LNB up the coaxial downlink.
Series mode (SM) surge suppressors
These devices are not rated injoule
The joule ( , or ; symbol: J) is the unit of energy in the International System of Units (SI). In terms of SI base units, one joule corresponds to one kilogram- metre squared per second squared One joule is equal to the amount of work d ...
s because they operate differently from the above listed suppressors, and they do not depend on materials that inherently wear out during repeated surges. SM suppressors are primarily used to control transient voltage surges on electrical power feeds to protected devices. They are essentially heavy-duty low-pass filter
A low-pass filter is a filter that passes signals with a frequency lower than a selected cutoff frequency and attenuates signals with frequencies higher than the cutoff frequency. The exact frequency response of the filter depends on the filt ...
s connected so that they allow 50 or 60 Hz line voltages through to the load, while blocking and diverting higher frequencies. This type of suppressor differs from others by using banks of inductor
An inductor, also called a coil, choke, or reactor, is a Passivity (engineering), passive two-terminal electronic component, electrical component that stores energy in a magnetic field when an electric current flows through it. An inductor typic ...
s, capacitor
In electrical engineering, a capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy by accumulating electric charges on two closely spaced surfaces that are insulated from each other. The capacitor was originally known as the condenser, a term st ...
s and resistor
A resistor is a passive two-terminal electronic component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element. In electronic circuits, resistors are used to reduce current flow, adjust signal levels, to divide voltages, bias active e ...
s that suppress voltage surges and inrush current to the neutral wire
In electrical engineering, ground (or earth) and neutral are circuit conductors used in alternating current (AC) electrical systems. The neutral conductor carries alternating current (in tandem with one or more ''phase '' conductors) during ...
, whereas other designs shunt to the ground wire. Surges are not diverted but actually suppressed. The inductors slow the energy. Since the inductor in series with the circuit path slows the current spike, the peak surge energy is spread out in the time domain
In mathematics and signal processing, the time domain is a representation of how a signal, function, or data set varies with time. It is used for the analysis of mathematical functions, physical signals or time series of economic or environmental ...
and harmlessly absorbed and slowly released from a capacitor bank.
Experimental results show that most surge energies occur at under 100 joules, so exceeding the SM design parameters is unlikely. SM suppressors do not present a fire risk should the absorbed energy exceed design limits of the dielectric
In electromagnetism, a dielectric (or dielectric medium) is an Insulator (electricity), electrical insulator that can be Polarisability, polarised by an applied electric field. When a dielectric material is placed in an electric field, electric ...
material of the components because the surge energy is also limited via arc-over to ground during lightning
Lightning is a natural phenomenon consisting of electrostatic discharges occurring through the atmosphere between two electrically charged regions. One or both regions are within the atmosphere, with the second region sometimes occurring on ...
strikes, leaving a surge remnant that often does not exceed a theoretical maximum (such as 6000 V at 3000 A with a modeled shape of 8 × 20 microsecond waveform specified by IEEE/ANSI C62.41). Because SMs work on both the current rise and the voltage rise, they can safely operate in the worst surge environments.
SM suppression focuses its protective philosophy on a ''power supply input'', but offers nothing to protect against surges appearing between the input of an SM device and ''data lines'', such as antennae, telephone or LAN connections, or multiple such devices cascaded and linked to the primary devices. This is because they do not divert surge energy to the ground line. Data transmission requires the ground line to be clean in order to be used as a reference point. In this design philosophy, such events are already protected against by the SM device before the power supply. NIST reports that "Sending them urgesdown the drain of a grounding conductor only makes them reappear within a microsecond about 200 meters away on some other conductor." So having protection on a data transmission line is only required if surges are diverted to the ground line.
SM devices tend to be bulkier and heavier than devices using other surge suppression technologies. The initial costs of SM filters are higher, typically and up, but a long service life can be expected if they are used properly. In-field installation costs can be higher, since SM devices are installed in ''series
Series may refer to:
People with the name
* Caroline Series (born 1951), English mathematician, daughter of George Series
* George Series (1920–1995), English physicist
Arts, entertainment, and media
Music
* Series, the ordered sets used i ...
'' with the power feed, requiring the feed to be cut and reconnected.
See also
* Lightning arrester *Lightning rod
A lightning rod or lightning conductor (British English) is a metal rod mounted on a structure and intended to protect the structure from a lightning strike. If lightning hits the structure, it is most likely to strike the rod and be conducted ...
Notes
References
External links
Surge Protection in Low-Voltage AC Power Circuits: An 8-part Anthology
A comprehensive compilation of papers and articles published 1963–2003, hosted by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), an agency of the US Commerce Department
NEMA Surge Protection Institute
Important Points About Surge Protectors
Surgege Protector Tech
Intro to TVS on AllAboutCircuits
{{DEFAULTSORT:Surge Protector Consumer electronics Computer peripherals Electric power systems components Voltage stability