Supreme Ultimate on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In
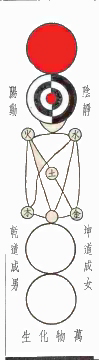 In the
In the
Chinese philosophy
Chinese philosophy (Simplified Chinese characters, simplified Chinese: 中国哲学; Traditional Chinese characters, traditional Chinese: 中國哲學) refers to the philosophical traditions that originated and developed within the historical ...
, ''taiji'' () is a cosmological
Cosmology () is a branch of physics and metaphysics dealing with the nature of the universe, the cosmos. The term ''cosmology'' was first used in English in 1656 in Thomas Blount's ''Glossographia'', with the meaning of "a speaking of the wo ...
state of the universe and its affairs on all levels—including the mutually reinforcing interactions between the two opposing forces of yin and yang
Originating in Chinese philosophy, yin and yang (, ), also yinyang or yin-yang, is the concept of opposite cosmic principles or forces that interact, interconnect, and perpetuate each other. Yin and yang can be thought of as complementary an ...
(a dualistic monism), as well as that among the Three Treasures, the four cardinal direction
The four cardinal directions or cardinal points are the four main compass directions: north (N), south (S), east (E), and west (W). The corresponding azimuths ( clockwise horizontal angle from north) are 0°, 90°, 180°, and 270°.
The ...
s, and the Five Elements—which together ultimately bring about the myriad things, each with their own nature. The concept of ''taiji'' has reappeared throughout the technological, religious, and philosophical history of the Sinosphere
The Sinosphere, also known as the Chinese cultural sphere, East Asian cultural sphere, or the Sinic world, encompasses multiple countries in East Asia and Southeast Asia that were historically heavily influenced by Chinese culture. The Sinosph ...
, finding concrete application in techniques developed in acupuncture
Acupuncture is a form of alternative medicine and a component of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) in which thin needles are inserted into the body. Acupuncture is a pseudoscience; the theories and practices of TCM are not based on scientif ...
and traditional Chinese medicine
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) is an alternative medicine, alternative medical practice drawn from traditional medicine in China. A large share of its claims are pseudoscientific, with the majority of treatments having no robust evidence ...
.
Etymology
''Taiji'' () is a compound of ''tai'' ( 'great', 'supreme') and ''ji'' ( 'pole', 'extremity'). Used together, ''taiji'' may be understood as 'source of the world'. Common English translations of ''taiji'' in the cosmological sense include "Supreme Ultimate", "Supreme Pole", and "Great Absolute".Core concept
Scholars Zhang and Ryden explain theontological
Ontology is the philosophical study of being. It is traditionally understood as the subdiscipline of metaphysics focused on the most general features of reality. As one of the most fundamental concepts, being encompasses all of reality and every ...
necessity of ''taiji'':
Any philosophy that asserts two elements such as the ''''Taiji'' is understood to be the highest conceivable principle from which existence flows. This is very similar to theyin-yang Originating in Chinese philosophy, yin and yang (, ), also yinyang or yin-yang, is the concept of opposite cosmic principles or forces that interact, interconnect, and perpetuate each other. Yin and yang can be thought of as complementary an ...'' of Chinese philosophy will also look for a term to reconcile the two, to ensure that both belong to the same sphere of discourse. The term 'supreme ultimate' performs this role in the philosophy of the ''Book of Changes The ''I Ching'' or ''Yijing'' ( ), usually translated ''Book of Changes'' or ''Classic of Changes'', is an ancient Chinese divination text that is among the oldest of the Chinese classics. The ''I Ching'' was originally a divination manual in ...''. In the Song dynasty it became a metaphysical term on a par with the Way.
Daoist
Taoism or Daoism (, ) is a diverse philosophical and religious tradition indigenous to China, emphasizing harmony with the Tao ( zh, p=dào, w=tao4). With a range of meaning in Chinese philosophy, translations of Tao include 'way', 'road', ' ...
idea "reversal is the movement of the Dao". The "supreme ultimate" creates yang and yin. Movement generates yang, and when its activity reaches its limit, it becomes tranquil. Through tranquility the supreme ultimate generates yin. When tranquility has reached its limit, there is a return to movement. Movement and tranquility, in alternation, each become the source of the other. The distinction between the yin and the yang is determined and their two forms stand revealed. By the transformations of the yang and the union of the yin, emerge the 4 directions and then the 5 phases ('' wuxing'') of wood, fire, earth, metal, and water.
''Taiji'' is often translated as "polar" (having polarity), revealing opposing features as in expanding/contracting, rising/falling, clockwise/anticlockwise. However, ''taiji'' has sometimes been thought of as a monistic
Monism attributes oneness or singleness () to a concept, such as to existence. Various kinds of monism can be distinguished:
* Priority monism states that all existing things go back to a source that is distinct from them; e.g., in Neoplatonis ...
concept similar to '' wuji'', as in the ''Wujitu'' diagram. ''Wuji'' literally translates as "without roof
A roof (: roofs or rooves) is the top covering of a building, including all materials and constructions necessary to support it on the walls of the building or on uprights, providing protection against rain, snow, sunlight, extremes of tempera ...
pole", but means 'without limit, polarity, or opposite'. ''Wuji'' is undifferentiated, timeless, absolute, infinite potential. In contrast, ''taiji'' describes movement and change wherein limits do arise. ''Taiji'' is often wrongly portrayed as conflictual, differentiated, and dualistic, but its core philosophy is harmonious, relative, and complementary natures.
Yin and yang
Originating in Chinese philosophy, yin and yang (, ), also yinyang or yin-yang, is the concept of opposite cosmic principles or forces that interact, interconnect, and perpetuate each other. Yin and yang can be thought of as complementary an ...
are reflections and originate from ''wuji'' to become ''taiji''.
In Chinese texts
''Zhuangzi''
The Daoist classic ''Zhuangzi Zhuangzi may refer to:
* ''Zhuangzi'' (book) (莊子), an ancient Chinese collection of anecdotes and fables, one of the foundational texts of Taoism
**Zhuang Zhou
Zhuang Zhou (), commonly known as Zhuangzi (; ; literally "Master Zhuang"; als ...
'' introduced the ''taiji'' concept. One of the "Inner Chapters" (ca. 3rd century BCE) contrasts the ''taiji'', here translated as 'zenith', with the ''liuji'' (; ), which is here translated as 'nadir
The nadir is the direction pointing directly ''below'' a particular location; that is, it is one of two vertical directions at a specified location, orthogonal to a horizontal flat surface.
The direction opposite of the nadir is the zenith.
Et ...
'.
The Way has attributes and evidence, but it has no action and no form. It may be transmitted but cannot be received. It may be apprehended but cannot be seen. From the root, from the stock, before there was heaven or earth, for all eternity truly has it existed. It inspirits demons and gods, gives birth to heaven and earth. It lies above the zenith but is not high; it lies beneath the nadir but is not deep. It is prior to heaven and earth, but is not ancient; it is senior to high antiquity, but it is not old.
''Huainanzi''
The 2nd century BCE ''Huainanzi
The ''Huainanzi'' is an ancient Chinese text made up of essays from scholarly debates held at the court of Liu An, Prince of Huainan, before 139 BCE. Compiled as a handbook for an enlightened sovereign and his court, the work attempts to defi ...
'' mentions a ''zhenren
''Zhenren'' ( zh, c=真人, p=zhēnrén, w=chen-jen, l=true/ upright/ genuine person or 'person of truth') is a Chinese term that first appeared in the '' Zhuangzi'' meaning "a Taoist spiritual master" in those writings, as in one who has mastered ...
'' ('true person; perfected person') and the ''taiji'' that transcends categories like yin and yang, exemplified with the ''fusui
Fusui County is a county in the southwest of Guangxi, China. It is the easternmost county-level division of the prefecture-level city of Chongzuo.
Geography
Fusui is located in southwestern Guangxi and in eastern Chongzuo City. It borders Qingxi ...
'' and '' fangzhu'' mirrors.
The ''fu-sui'' (burning mirror) gathers fire energy from the sun; the ''fang-chu'' (moon mirror) gathers dew from the moon. What are [contained] between Heaven and Earth, even an expert calculator cannot compute their number. Thus, though the hand can handle and examine extremely small things, it cannot lay hold of the brightness [of the sun and moon]. Were it within the grasp of one's hand (within one's power) to gather [things within] one category from the Supreme Ultimate (''t'ai-chi'' ) above, one could immediately produce both fire and water. This is because ''Yin'' and ''Yang'' share a common ''ch'i'' and move each other.
''I Ching''
''Taiji'' also appears in the ''Xici ''Xici'' or ''Xi Ci'' (''Great Commentary'', ) is one of the Ten Wings, a collection of Confucian books traditionally included in the ''I Ching'' written during the fifth century BC. Its origins are unknown, but it is suspected of being the produc ...
'', a commentary to the ''I Ching
The ''I Ching'' or ''Yijing'' ( ), usually translated ''Book of Changes'' or ''Classic of Changes'', is an ancient Chinese divination text that is among the oldest of the Chinese classics. The ''I Ching'' was originally a divination manual in ...
.'' It is traditionally attributed to Confucius
Confucius (; pinyin: ; ; ), born Kong Qiu (), was a Chinese philosopher of the Spring and Autumn period who is traditionally considered the paragon of Chinese sages. Much of the shared cultural heritage of the Sinosphere originates in the phil ...
but more likely dates to about the 3rd century BCE.
Therefore there is in the Changes the Great Primal Beginning. This generates the two primary forces. The two primary forces generate the four images. The four images generate the eight trigrams. The eight trigrams determine good fortune and misfortune. Good fortune and misfortune create the great field of action.This sequence of
powers of two
A power of two is a number of the form where is an integer, that is, the result of exponentiation with number two as the base and integer as the exponent. In the fast-growing hierarchy, is exactly equal to f_1^n(1). In the Hardy hi ...
includes ''taiji'' → yin and yang
Originating in Chinese philosophy, yin and yang (, ), also yinyang or yin-yang, is the concept of opposite cosmic principles or forces that interact, interconnect, and perpetuate each other. Yin and yang can be thought of as complementary an ...
(two polarities) → ''Sixiang'' (Four Symbols
The Four Symbols are mythological creatures appearing among the Chinese constellations along the ecliptic, and viewed as the guardians of the four cardinal directions. These four creatures are also referred to by a variety of other names, in ...
) → ''Bagua
The ''bagua'' ( zh, c=八卦, p=bāguà, l=eight trigrams) is a set of symbols from China intended to illustrate the nature of reality as being composed of mutually opposing forces reinforcing one another. ''Bagua'' is a group of trigrams—co ...
'' (eight trigrams) → ''Hexagram
, can be seen as a compound polygon, compound composed of an upwards (blue here) and downwards (pink) facing equilateral triangle, with their intersection as a regular hexagon (in green).
A hexagram (Greek language, Greek) or sexagram (Latin l ...
.
The fundamental postulate is the "great primal beginning" of all that exists, ''t'ai chi'' – in its original meaning, the "ridgepole". Later Indian philosophers devoted much thought to this idea of a primal beginning. A still earlier beginning, ''wu chi'', was represented by the symbol of a circle. Under this conception, ''t'ai chi'' was represented by the circle divided into the light and the dark, yang and yin, . This symbol has also played a significant part in India and Europe. However, speculations of a Gnostic-dualistic character are foreign to the original thought of the ''I Ching''; what it posits is simply the ridgepole, the line. With this line, which in itself represents oneness, duality comes into the world, for the line at the same time posits an above and a below, a right and left, front and back – in a word, the world of the opposites.
Song dynasty
 In the
In the Neo-Confucianism
Neo-Confucianism (, often shortened to ''lǐxué'' 理學, literally "School of Principle") is a moral, ethical, and metaphysical Chinese philosophy influenced by Confucianism, which originated with Han Yu (768–824) and Li Ao (772–841) i ...
philosophy that developed during the Song dynasty
The Song dynasty ( ) was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 960 to 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song, who usurped the throne of the Later Zhou dynasty and went on to conquer the rest of the Fiv ...
, ''taiji'' was viewed "as a microcosm equivalent to the structure of the human body." The Song-era philosopher Zhou Dunyi
Zhou Dunyi (; 1017–1073) was a Chinese cosmologist, philosopher, and writer during the Song dynasty. He conceptualized the Neo-Confucianism, Neo-Confucian cosmology of the day, explaining the relationship between human conduct and universal ...
(1017–1073 CE) wrote the ''Taijitushuo'' (; "Explanation of the Diagram of the Supreme Ultimate"), which became the cornerstone of Neo-Confucianist cosmology. Zhou's brief text synthesized aspects of Chinese Buddhism
Chinese Buddhism or Han Buddhism ( zh, s=汉传佛教, t=漢傳佛教, first=t, poj=Hàn-thoân Hu̍t-kàu, j=Hon3 Cyun4 Fat6 Gaau3, p=Hànchuán Fójiào) is a Chinese form of Mahayana Buddhism. The Chinese Buddhist canonJiang Wu, "The Chin ...
and Daoism with the metaphysical discussions in the ''I Ching''. Zhou's opening lines are:
Non-polar ('' wuji'') and yet Supreme Polarity (''taiji'')! The Supreme Polarity in activity generates ''yang''; yet at the limit of activity it is still. In stillness it generates ''yin''; yet at the limit of stillness it is also active. Activity and stillness alternate; each is the basis of the other. In distinguishing ''yin'' and ''yang'', the Two Modes are thereby established. The alternation and combination of ''yang'' and ''yin'' generate water, fire, wood, metal, and earth. With these five [phases of] '' qi'' harmoniously arranged, the Four Seasons proceed through them. TheFive Phases ( zh, c=五行, p=wǔxíng), usually translated as Five Phases or Five Agents, is a fivefold conceptual scheme used in many traditional Chinese fields of study to explain a wide array of phenomena, including terrestrial and celestial rela ...are simply ''yin'' and ''yang''; ''yin'' and ''yang'' are simply the Supreme Polarity; the Supreme Polarity is fundamentally Non-polar. [Yet] in the generation of the Five Phases, each one has its nature.
In tai chi
The martial art tai chi draws heavily on Chinese philosophy, especially the concept of the ''taiji''. The Chinese name of tai chi, ''taijiquan'', literally translates as "taiji boxing" or "taiji fist". Early tai chi masters such asYang Luchan
Yang Luchan ( zh, c=杨露禅, w=Yang Lu-ch'an, p=Yáng Lùchán), also known as Yang Fukui (1799–1872), was an influential Chinese practitioner and teacher of the internal style tai chi martial art. He is known as the founder of Yang-styl ...
promoted the connection between their martial art and the concept of the ''taiji''. The twenty-fourth chapter of the "Forty Chapter" tai chi classic that Yang Banhou
Yang Banhou (Yang Pan-hou; 1837–1890) was an influential teacher of tai chi in Qing dynasty China, known for his bellicose temperament.
Biography
He was the eldest son of Yang Luchan to survive to adulthood. Like his father, he was retaine ...
gave to Wu Quanyou
Wu Quanyou ( zh, c=吴全佑, w=Wu Ch‘üan-yu; 1834–1902) was an influential teacher of the tai chi martial art in late Imperial China. His son is credited as the founder of the Wu-style tai chi. As he was of Manchu descent, and would hav ...
says the following about the connect between tai chi and spirituality:
If the essence of material substances lies in their phenomenological reality, then the presence of the ontological status of abstract objects shall become clear in the final culmination of the energy that is derived from oneness and the Real. How can man learn this truth? By truly seeking that which is the shadow of philosophy and the charge of all living substances, that of the nature of the divine.
See also
*''Bagua
The ''bagua'' ( zh, c=八卦, p=bāguà, l=eight trigrams) is a set of symbols from China intended to illustrate the nature of reality as being composed of mutually opposing forces reinforcing one another. ''Bagua'' is a group of trigrams—co ...
''
* National and regional symbols which contain the ''Taiji'' mark
** Flag of Mongolia
The national flag of Mongolia is a vertical triband with a red stripe at each side and a blue stripe in the middle, with the Mongolian Soyombo symbol centering on the leftmost stripe. The blue stripe represents the eternal blue sky, and the ...
** Flag of Tibet
The national flag of Tibet (), also unofficially known as the Snow Lion Flag, depicts a white snow-covered mountain, a yellow sun with red and blue rays emanating from it, two Tibetan snow lions, a multi-coloured jewel representing Buddhist va ...
** Taegeuk
''Taegeuk'' (, ) is a Sino-Korean vocabulary, Sino-Korean term meaning "supreme ultimate", although it can also be translated as "great polarity / duality / extremes". The term and its overall concept is derived from the Chinese ''Taiji (philos ...
– Sino-Korean pronunciation for ''Taiji''
*** Flag of South Korea
The national flag of South Korea, also known as the ''Taegeukgi'' (), consists of three components: a white rectangular background, a red and blue ''taegeuk'' in its center, accompanied by four black Bagua, trigrams, one in each corner. The p ...
*** Emblem of South Korea
The National Emblem of the Republic of Korea (), also officially referred as ''Naramunjang'' (, ), consists of the ''taegeuk'' symbol present on the flag of South Korea, South Korean national flag surrounded by five stylized petals and a ribbon ...
* ''Taijitu
In Chinese philosophy, a ''taijitu'' () is a Character (symbol), symbol or diagram () representing ''Taiji (philosophy), taiji'' () in both its monist (''Wuji (philosophy), wuji'') and its Dualism in cosmology, dualist (yin and yang) forms in a ...
''
* Tomoe
, commonly translated as "comma", is a comma-like swirl symbol used in Japanese (roughly equivalent to a heraldic badge or charge in European heraldry). It closely resembles the usual form of a .
The appears in many designs with various us ...
* Absolute (philosophy)
In philosophy (often specifically metaphysics), the absolute, in most common usage, is a perfect, self-sustainability, self-sufficient reality that depends upon nothing external to itself. In theology, the term is also used to designate the supre ...
* Ohr
Ohr (, plural: ''ʾoroṯ'') is a central Kabbalistic term in Jewish mysticism. The analogy to physical light describes divine emanations. Shefa "flow" ( ''šep̄aʿ'') and its derivative, hashpaʾa "influence" ( ''hašpāʿā''), are sometim ...
Notes
References
Citations
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{Taoism footer Concepts in Chinese philosophy Chinese culture Taoist cosmology Tai chi Neo-Confucianism Eastern esotericism