Sunzi Suanjing on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 ''Sunzi Suanjing'' () was a mathematical
''Sunzi Suanjing'' () was a mathematical

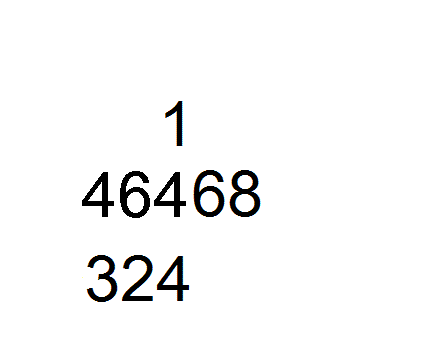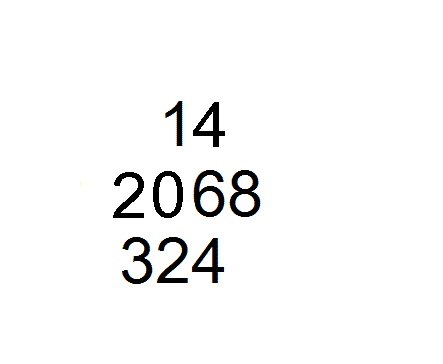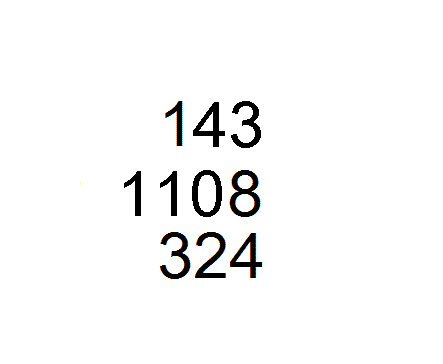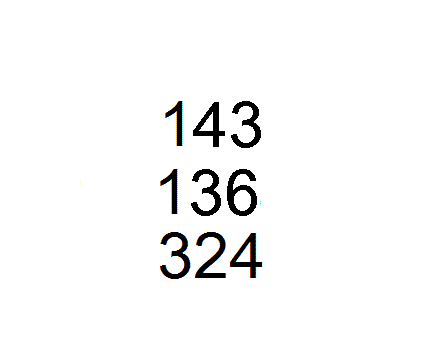
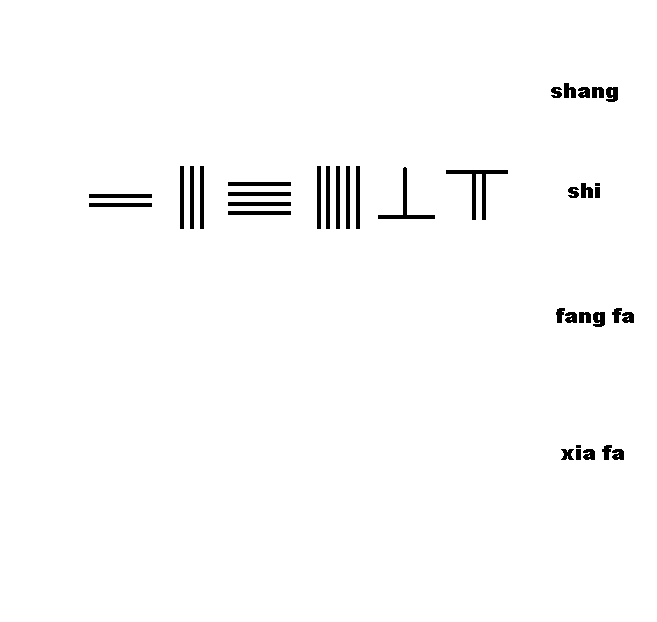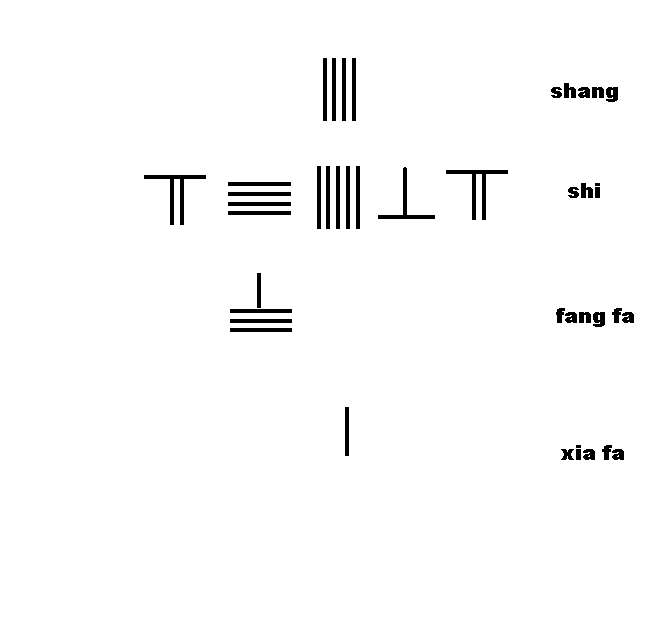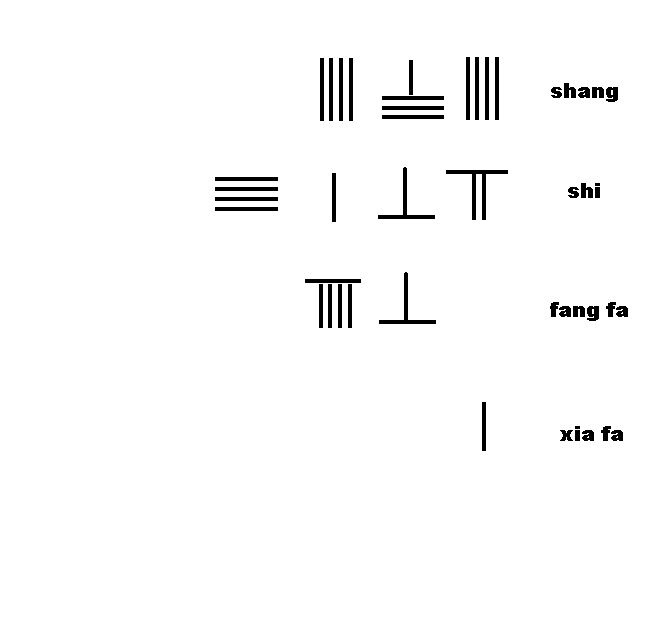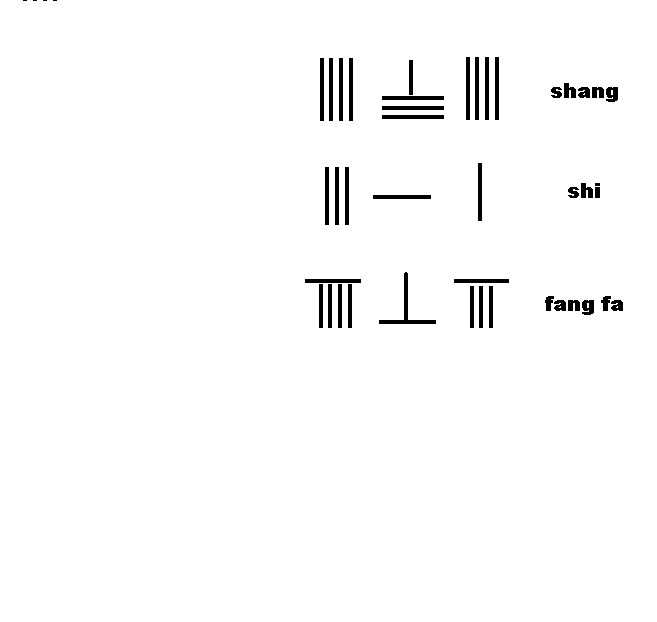
 The book is divided into three chapters.
The book is divided into three chapters.
Sun Zi at MacTutor
treatise
A treatise is a Formality, formal and systematic written discourse on some subject concerned with investigating or exposing the main principles of the subject and its conclusions."mwod:treatise, Treatise." Merriam-Webster Online Dictionary. Acc ...
written during 3rd to 5th centuries CE which was listed as one of the Ten Computational Canons during the Tang dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, c=唐朝), or the Tang Empire, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907, with an Wu Zhou, interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed ...
. The specific identity of its author Sunzi (lit. "Master Sun") is still unknown but he lived much later than his namesake Sun Tzu
Sun Tzu (; zh, t=孫子, s=孙子, first= t, p=Sūnzǐ) may have been a Chinese General, military general, strategist, philosopher, and writer who lived during the Eastern Zhou period (771–256 BC). Sun Tzu is traditionally credited as the au ...
, author of ''The Art of War
''The Art of War'' is an ancient Chinese military treatise dating from the late Spring and Autumn period (roughly 5th century BC). The work, which is attributed to the ancient Chinese military strategist Sun Tzu ("Master Sun"), is compos ...
''. From the textual evidence in the book, some scholars concluded that the work was completed during the Southern and Northern Dynasties. Besides describing arithmetic methods and investigating Diophantine equation ''Diophantine'' means pertaining to the ancient Greek mathematician Diophantus. A number of concepts bear this name:
*Diophantine approximation
In number theory, the study of Diophantine approximation deals with the approximation of real n ...
s, the treatise touches upon astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that studies celestial objects and the phenomena that occur in the cosmos. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and their overall evolution. Objects of interest includ ...
and attempts to develop a calendar
A calendar is a system of organizing days. This is done by giving names to periods of time, typically days, weeks, months and years. A calendar date, date is the designation of a single and specific day within such a system. A calendar is ...
.
Contents
Chapter 1
Chapter 1 discusses measurement units of length, weight and capacity, and the rules ofcounting rods
Counting rods (筭) are small bars, typically 3–14 cm (1" to 6") long, that were used by mathematicians for calculation in ancient East Asia. They are placed either horizontally or vertically to represent any integer or rational number.
...
. Although counting rods were in use in the Spring and Autumn period
The Spring and Autumn period () was a period in History of China, Chinese history corresponding roughly to the first half of the Eastern Zhou (256 BCE), characterized by the gradual erosion of royal power as local lords nominally subject t ...
and there were many ancient books on mathematics such as '' Book on Numbers and Computation'' and ''The Nine Chapters on the Mathematical Art
''The Nine Chapters on the Mathematical Art'' is a Chinese mathematics book, composed by several generations of scholars from the 10th–2nd century BCE, its latest stage being from the 1st century CE. This book is one of the earliest surviving ...
'', no detailed account of the rules was given. For the first time, ''The Mathematical Classic of Sun Zi'' provided a detail description of the rules of counting rods: "one must know the position of the counting rods, the units are vertical, the tens horizontal, the hundreds stand, the thousands prostrate", followed by the detailed layout and rules for manipulation of the counting rods in addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division with ample examples.
Chapter 2
Chapter 2 deals with operational rules for fractions with rod numerals: the reduction, addition, subtraction, and division of fractions, followed by mechanical algorithm for the extraction of square roots. Lam Lay Yong and An Tian Se, Fleeting Footsteps p65, ''World Scientific'',Chapter 3
Chapter 3 contains the earliest example of theChinese remainder theorem
In mathematics, the Chinese remainder theorem states that if one knows the remainders of the Euclidean division of an integer ''n'' by several integers, then one can determine uniquely the remainder of the division of ''n'' by the product of thes ...
, a key tool to understanding and resolving Diophantine equation ''Diophantine'' means pertaining to the ancient Greek mathematician Diophantus. A number of concepts bear this name:
*Diophantine approximation
In number theory, the study of Diophantine approximation deals with the approximation of real n ...
s.
Bibliography
Researchers have published a full English translation of the ''Sūnzĭ Suànjīng'': * ''Fleeting Footsteps; Tracing the Conception of Arithmetic and Algebra in Ancient China'', by Lam Lay Yong and Ang Tian Se, Part Two, pp 149–182. World Scientific Publishing Company; June 2004 The original Chinese text is available on Wikisource.External links
Sun Zi at MacTutor
References